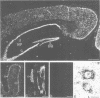
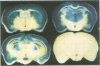
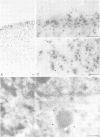
Abstract
The accumulation of beta-amyloid protein in specific brain regions is a central pathological feature of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The 4 kd beta-amyloid protein derives from a larger amyloid precursor protein (APP) by as yet unknown mechanisms. In the absence of a laboratory animal model of AD, transgenic mice expressing various APP gene products may provide new insights into the relationship between APP and beta-amyloid formation and the pathogenesis of AD. beta-amyloid accumulation in AD brain may result from interactions between APP and other molecules. Such interactions are likely to be developmentally regulated and tissue-specific. A transgenic mouse model of AD, therefore, would aim for APP transgene expression that mimics the endogenous APP gene. As an initial step in developing an animal model, we have identified a 4.5 kb DNA fragment from the 5' end of the human APP gene, which mediates neuron-specific gene expression in the CNS of transgenic mice, using E. coli lacZ as a reporter gene. Detectable levels of transgene expression are found in most neurons but not in glial and vascular endothelial cells. The expression pattern of this reporter gene closely resembles the distribution of endogenous APP mRNA in both the human and mouse CNS.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
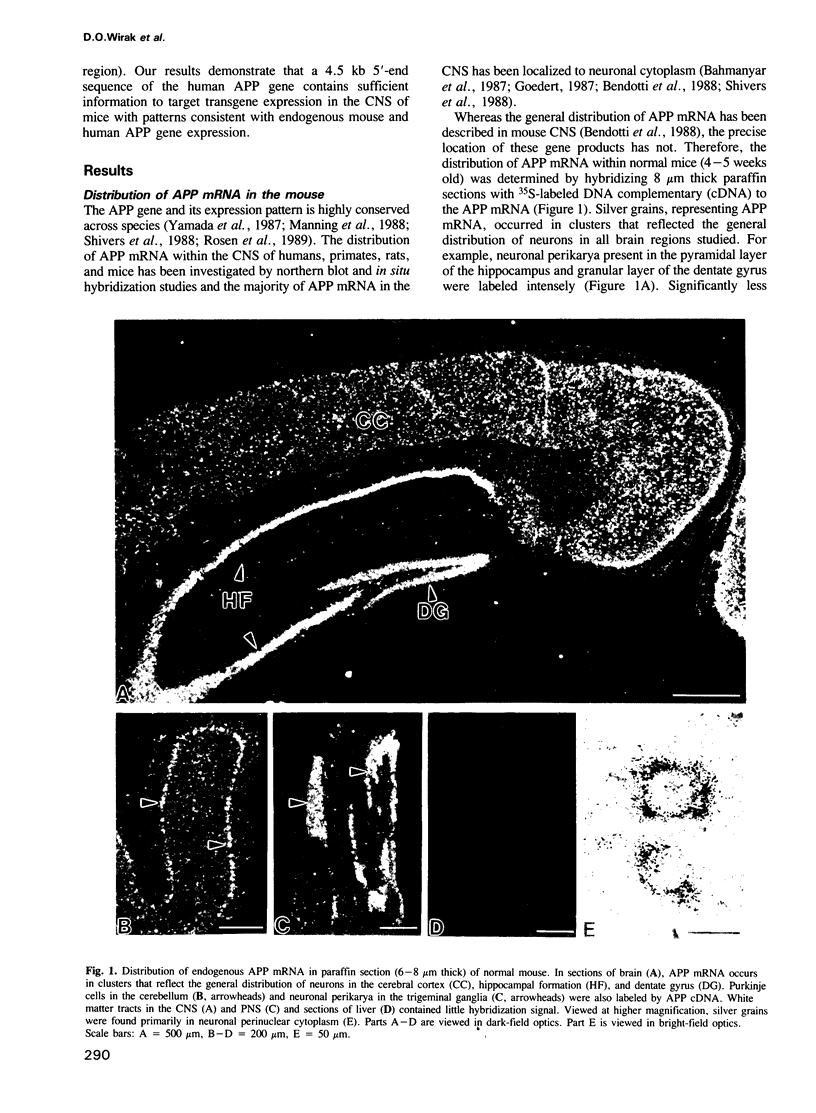
- Bahmanyar S., Higgins G. A., Goldgaber D., Lewis D. A., Morrison J. H., Wilson M. C., Shankar S. K., Gajdusek D. C. Localization of amyloid beta protein messenger RNA in brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Jul 3;237(4810):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3299701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendotti C., Forloni G. L., Morgan R. A., O'Hara B. F., Oster-Granite M. L., Reeves R. H., Gearhart J. D., Coyle J. T. Neuroanatomical localization and quantification of amyloid precursor protein mRNA by in situ hybridization in the brains of normal, aneuploid, and lesioned mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3628–3632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Allen J. M., Behringer R. R., Gelinas R. E., Palmiter R. D. Introns increase transcriptional efficiency in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):836–840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L., Herman S. A., Martínez-Salas E., Chalifour L. E., Wirak D. O., Cupo D. Y., Miranda M. Microinjecting DNA into mouse ova to study DNA replication and gene expression and to produce transgenic animals. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):662–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly R. J., Rasool C. G., Bartus R., Vitek S., Blume A. J., Vitek M. Multiple forms of beta-amyloid peptide precursor RNAs in a single cell type. Neurobiol Aging. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(4):333–338. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(88)80078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F. S., Keim P. S., Beattie E. C., Blacher R. W., Culwell A. R., Oltersdorf T., McClure D., Ward P. J. Cleavage of amyloid beta peptide during constitutive processing of its precursor. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1122–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.2111583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. Homeo boxes in the study of development. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1245–1252. doi: 10.1126/science.2884726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goedert M. Neuronal localization of amyloid beta protein precursor mRNA in normal human brain and in Alzheimer's disease. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3627–3632. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde T. E., Estus S., Usiak M., Younkin L. H., Younkin S. G. Expression of beta amyloid protein precursor mRNAs: recognition of a novel alternatively spliced form and quantitation in Alzheimer's disease using PCR. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):253–267. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90100-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goring D. R., Rossant J., Clapoff S., Breitman M. L., Tsui L. C. In situ detection of beta-galactosidase in lenses of transgenic mice with a gamma-crystallin/lacZ gene. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):456–458. doi: 10.1126/science.3099390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Wilson F. D., Lang G., Kioussis D. Human CD2 3'-flanking sequences confer high-level, T cell-specific, position-independent gene expression in transgenic mice. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):979–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90631-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland P. W., Hogan B. L. Expression of homeo box genes during mouse development: a review. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):773–782. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joachim C. L., Morris J. H., Selkoe D. J. Diffuse senile plaques occur commonly in the cerebellum in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1989 Aug;135(2):309–319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman R. Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 1986 Apr 10;314(15):964–973. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198604103141506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitaguchi N., Takahashi Y., Tokushima Y., Shiojiri S., Ito H. Novel precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid protein shows protease inhibitory activity. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):530–532. doi: 10.1038/331530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
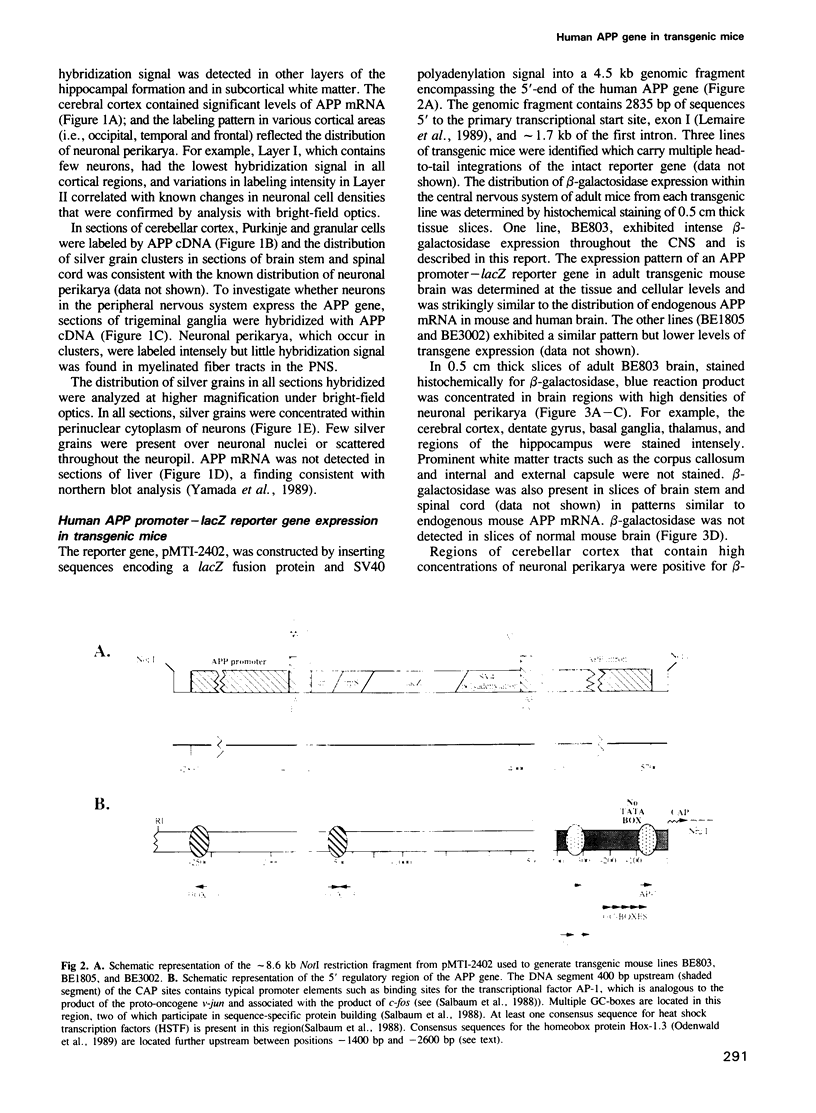
- La Fauci G., Lahiri D. K., Salton S. R., Robakis N. K. Characterization of the 5'-end region and the first two exons of the beta-protein precursor gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 28;159(1):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92437-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Haslinger A., Karin M., Tjian R. Activation of transcription by two factors that bind promoter and enhancer sequences of the human metallothionein gene and SV40. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):368–372. doi: 10.1038/325368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire H. G., Salbaum J. M., Multhaup G., Kang J., Bayney R. M., Unterbeck A., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The PreA4(695) precursor protein of Alzheimer's disease A4 amyloid is encoded by 16 exons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):517–522. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Esiri M. M. The site of the earliest lesions of Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 24;318(12):789–790. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803243181218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning R. W., Reid C. M., Lampe R. A., Davis L. G. Identification in rodents and other species of an mRNA homologous to the human beta-amyloid precursor. Brain Res. 1988 Jun;427(3):293–297. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(88)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Hill B., Beyreuther K. Molecular biology of Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:287–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odenwald W. F., Garbern J., Arnheiter H., Tournier-Lasserve E., Lazzarini R. A. The Hox-1.3 homeo box protein is a sequence-specific DNA-binding phosphoprotein. Genes Dev. 1989 Feb;3(2):158–172. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.2.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oltersdorf T., Fritz L. C., Schenk D. B., Lieberburg I., Johnson-Wood K. L., Beattie E. C., Ward P. J., Blacher R. W., Dovey H. F., Sinha S. The secreted form of the Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein with the Kunitz domain is protease nexin-II. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):144–147. doi: 10.1038/341144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmert M. R., Podlisny M. B., Witker D. S., Oltersdorf T., Younkin L. H., Selkoe D. J., Younkin S. G. The beta-amyloid protein precursor of Alzheimer disease has soluble derivatives found in human brain and cerebrospinal fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6338–6342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gonzalez-DeWhitt P., Schilling J., Miller J., Hsu D., Greenberg B., Davis K., Wallace W., Lieberburg I., Fuller F. A new A4 amyloid mRNA contains a domain homologous to serine proteinase inhibitors. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):525–527. doi: 10.1038/331525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. L., Koo E. H., Unterbeck A. Cellular and molecular biology of Alzheimer's disease. Bioessays. 1989 Feb-Mar;10(2-3):69–74. doi: 10.1002/bies.950100208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. L. New perspectives on Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:489–512. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robakis N. K., Wisniewski H. M., Jenkins E. C., Devine-Gage E. A., Houck G. E., Yao X. L., Ramakrishna N., Wolfe G., Silverman W. P., Brown W. T. Chromosome 21q21 sublocalisation of gene encoding beta-amyloid peptide in cerebral vessels and neuritic (senile) plaques of people with Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):384–385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91754-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen D. R., Martin-Morris L., Luo L. Q., White K. A Drosophila gene encoding a protein resembling the human beta-amyloid protein precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2478–2482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salbaum J. M., Weidemann A., Lemaire H. G., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. The promoter of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 precursor gene. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2807–2813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03136.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F. Use of a recombinant retrovirus to study post-implantation cell lineage in mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J. Biochemistry of altered brain proteins in Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:463–490. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivers B. D., Hilbich C., Multhaup G., Salbaum M., Beyreuther K., Seeburg P. H. Alzheimer's disease amyloidogenic glycoprotein: expression pattern in rat brain suggests a role in cell contact. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1365–1370. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisodia S. S., Koo E. H., Beyreuther K., Unterbeck A., Price D. L. Evidence that beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer's disease is not derived by normal processing. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):492–495. doi: 10.1126/science.1691865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George-Hyslop P. H., Tanzi R. E., Polinsky R. J., Haines J. L., Nee L., Watkins P. C., Myers R. H., Feldman R. G., Pollen D., Drachman D. The genetic defect causing familial Alzheimer's disease maps on chromosome 21. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):885–890. doi: 10.1126/science.2880399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George-Hyslop P. H., Tanzi R. E., Polinsky R. J., Neve R. L., Pollen D., Drachman D., Growdon J., Cupples L. A., Nee L., Myers R. H. Absence of duplication of chromosome 21 genes in familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):664–666. doi: 10.1126/science.2890206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagliavini F., Giaccone G., Frangione B., Bugiani O. Preamyloid deposits in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease and nondemented individuals. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Nov 11;93(2-3):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. Application of cryoultramicrotomy to immunocytochemistry. J Microsc. 1986 Aug;143(Pt 2):139–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1986.tb02772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapp B. D., Andrews S. B., Cootauco C., Quarles R. The myelin-associated glycoprotein is enriched in multivesicular bodies and periaxonal membranes of actively myelinating oligodendrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2417–2426. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapp B. D., Andrews S. B., Wong A., O'Connell M., Griffin J. W. Co-localization of the myelin-associated glycoprotein and the microfilament components, F-actin and spectrin, in Schwann cells of myelinated nerve fibres. J Neurocytol. 1989 Feb;18(1):47–60. doi: 10.1007/BF01188423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapp B. D., Hauer P., Lemke G. Axonal regulation of myelin protein mRNA levels in actively myelinating Schwann cells. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3515–3521. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03515.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapp B. D., Moench T., Pulley M., Barbosa E., Tennekoon G., Griffin J. Spatial segregation of mRNA encoding myelin-specific proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7773–7777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Broeckhoven C., Genthe A. M., Vandenberghe A., Horsthemke B., Backhovens H., Raeymaekers P., Van Hul W., Wehnert A., Gheuens J., Cras P. Failure of familial Alzheimer's disease to segregate with the A4-amyloid gene in several European families. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):153–155. doi: 10.1038/329153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nostrand W. E., Wagner S. L., Suzuki M., Choi B. H., Farrow J. S., Geddes J. W., Cotman C. W., Cunningham D. D. Protease nexin-II, a potent antichymotrypsin, shows identity to amyloid beta-protein precursor. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):546–549. doi: 10.1038/341546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitek M. P., Rasool C. G., de Sauvage F., Vitek S. M., Bartus R. T., Beer B., Ashton R. A., Macq A. F., Maloteaux J. M., Blume A. J. Absence of mutation in the beta-amyloid cDNAs cloned from the brains of three patients with sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 1988 Sep;464(2):121–131. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(88)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidemann A., König G., Bunke D., Fischer P., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Identification, biogenesis, and localization of precursors of Alzheimer's disease A4 amyloid protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirak D. O., Chalifour L. E., Wassarman P. M., Muller W. J., Hassell J. A., DePamphilis M. L. Sequence-dependent DNA replication in preimplantation mouse embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2924–2935. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wilson S., Walker B., Dawid I., Paisley T., Zimarino V., Ueda H. Purification and properties of Drosophila heat shock activator protein. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1247–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.3685975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Sasaki H., Dohura K., Goto I., Sakaki Y. Structure and expression of the alternatively-spliced forms of mRNA for the mouse homolog of Alzheimer's disease amyloid beta protein precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 15;158(3):906–912. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92808-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Sasaki H., Furuya H., Miyata T., Goto I., Sakaki Y. Complementary DNA for the mouse homolog of the human amyloid beta protein precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):665–671. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90419-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Hirai S., Morimatsu M., Shoji M., Ihara Y. A variety of cerebral amyloid deposits in the brains of the Alzheimer-type dementia demonstrated by beta protein immunostaining. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(6):541–549. doi: 10.1007/BF00689591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]