Abstract
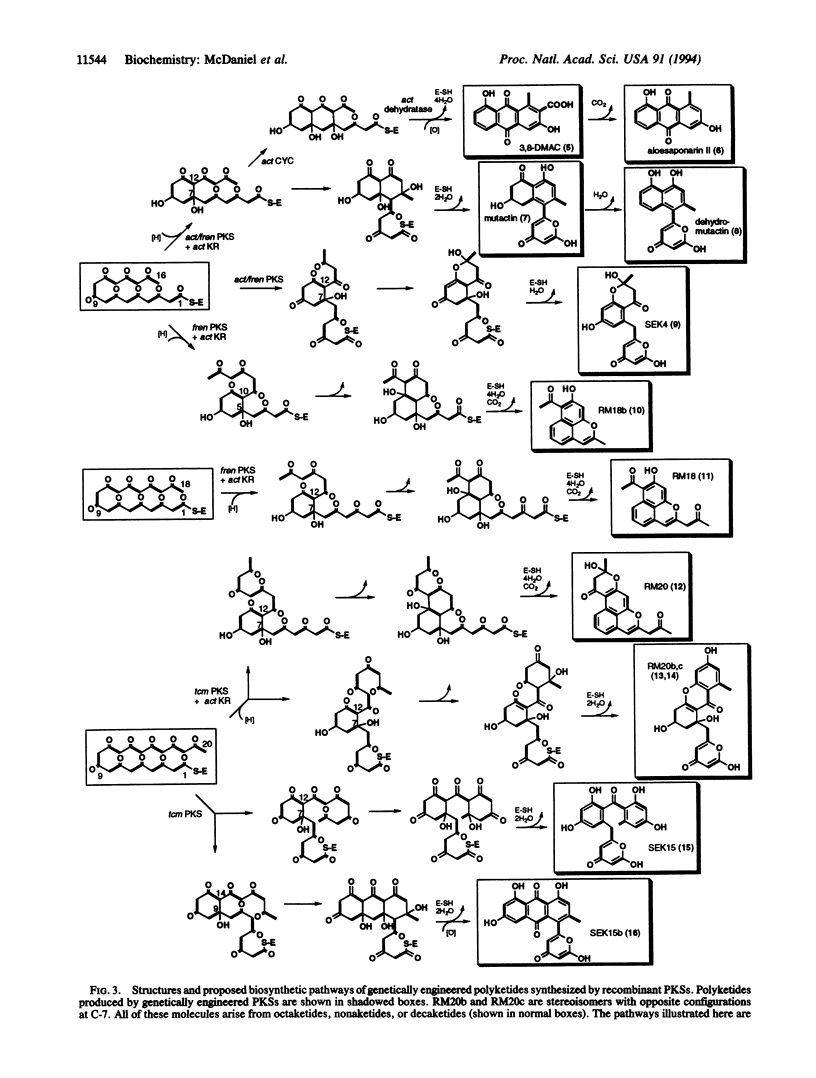
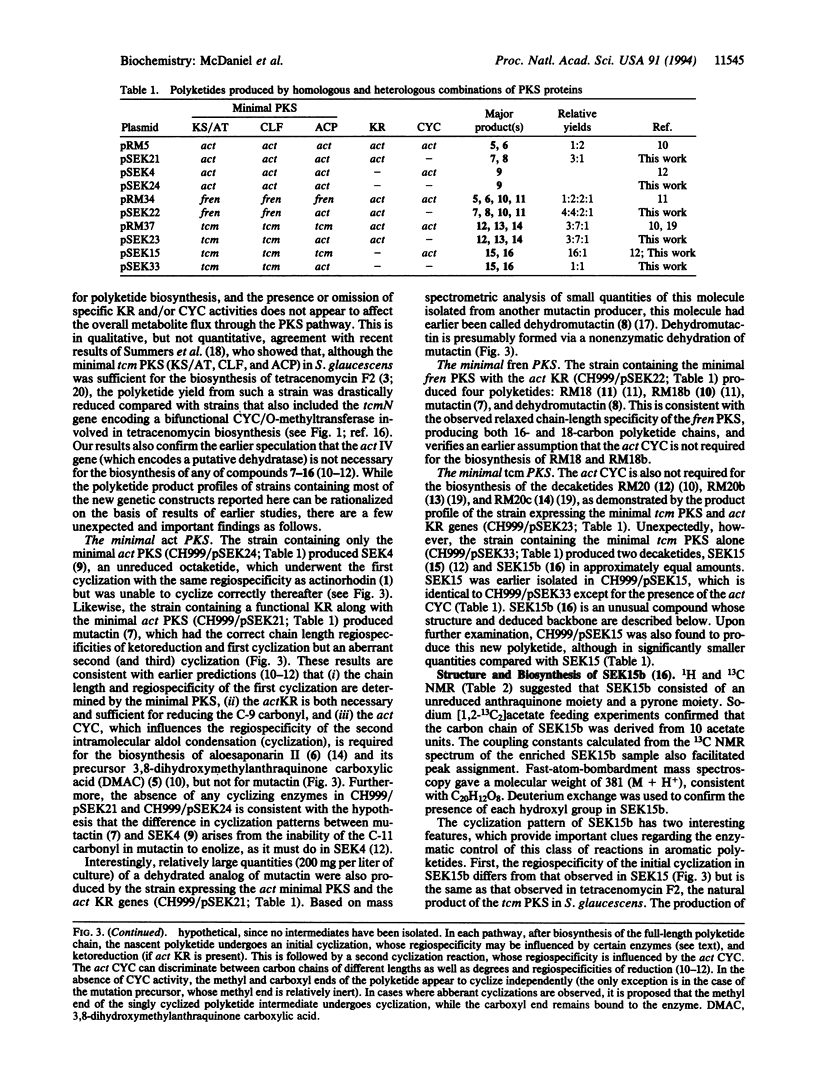
To identify the minimum set of polyketide synthase (PKS) components required for in vivo biosynthesis of aromatic polyketides, combinations of genes encoding subunits of three different aromatic PKSs--act from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) (an actinorhodin producer), fren from Streptomyces roseofulvus (a frenolicin and nanaomycin producer), and tcm from Streptomyces glaucescens (a tetracenomycin producer)--were expressed in a recently developed Streptomyces host-vector system. The "minimal" components (ketosynthase/putative acyltransferase, chain length-determining factor, and acyl carrier protein) were produced with and without a functional polyketide ketoreductase and/or cyclase, and the polyketide products of these recombinant strains were structurally characterized. Several previously identified polyketides were isolated in addition to two previously unidentified polyketides, dehydromutactin and SEK 15b, described here. The results proved that the act cyclase is not required for the biosynthesis of several aberrantly cyclized products that have been previously reported. They are also consistent with earlier conclusions that the minimal PKS controls chain length as well as the regiospecificity of the first cyclization and that it can do so in the absence of both a ketoreductase and a cyclase. However, the ability of the minimal tcm PKS to synthesize two different singly cyclized intermediates suggests that it is unable to accurately control the course of this reaction by itself. In the presence of a downstream enzyme, the flux through one branch of the cyclization pathway increases relative to the other. We propose that these alternative specificities may be due to the ability of downstream enzymes to associate with the minimal PKS and to selectively inhibit a particular branch of the cyclization pathway.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartel P. L., Zhu C. B., Lampel J. S., Dosch D. C., Connors N. C., Strohl W. R., Beale J. M., Jr, Floss H. G. Biosynthesis of anthraquinones by interspecies cloning of actinorhodin biosynthesis genes in streptomycetes: clarification of actinorhodin gene functions. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4816–4826. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4816-4826.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb M. J., Biró S., Motamedi H., Collins J. F., Hutchinson C. R. Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of the Streptomyces glaucescens tcmI genes provides key information about the enzymology of polyketide antibiotic biosynthesis. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2727–2736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08414.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes J., Haydock S. F., Roberts G. A., Bevitt D. J., Leadlay P. F. An unusually large multifunctional polypeptide in the erythromycin-producing polyketide synthase of Saccharopolyspora erythraea. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):176–178. doi: 10.1038/348176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donadio S., Staver M. J., McAlpine J. B., Swanson S. J., Katz L. Modular organization of genes required for complex polyketide biosynthesis. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):675–679. doi: 10.1126/science.2024119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Moreno M. A., Martínez E., Boto L., Hopwood D. A., Malpartida F. Nucleotide sequence and deduced functions of a set of cotranscribed genes of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) including the polyketide synthase for the antibiotic actinorhodin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19278–19290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu H., McDaniel R., Hopwood D. A., Khosla C. Engineered biosynthesis of novel polyketides: stereochemical course of two reactions catalyzed by a polyketide synthase. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 9;33(31):9321–9326. doi: 10.1021/bi00197a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz L., Donadio S. Polyketide synthesis: prospects for hybrid antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1993;47:875–912. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.47.100193.004303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosla C., Ebert-Khosla S., Hopwood D. A. Targeted gene replacements in a Streptomyces polyketide synthase gene cluster: role for the acyl carrier protein. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(21):3237–3249. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01778.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosla C., McDaniel R., Ebert-Khosla S., Torres R., Sherman D. H., Bibb M. J., Hopwood D. A. Genetic construction and functional analysis of hybrid polyketide synthases containing heterologous acyl carrier proteins. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(8):2197–2204. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.8.2197-2204.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNeil D. J. Characterization of a unique methyl-specific restriction system in Streptomyces avermitilis. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5607–5612. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5607-5612.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDaniel R., Ebert-Khosla S., Hopwood D. A., Khosla C. Engineered biosynthesis of novel polyketides. Science. 1993 Dec 3;262(5139):1546–1550. doi: 10.1126/science.8248802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen B., Hutchinson C. R. Enzymatic synthesis of a bacterial polyketide from acetyl and malonyl coenzyme A. Science. 1993 Dec 3;262(5139):1535–1540. doi: 10.1126/science.8248801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen B., Nakayama H., Hutchinson C. R. Isolation and structural elucidation of tetracenomycin F2 and tetracenomycin F1: early intermediates in the biosynthesis of tetracenomycin C in Streptomyces glaucescens. J Nat Prod. 1993 Aug;56(8):1288–1293. doi: 10.1021/np50098a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman D. H., Kim E. S., Bibb M. J., Hopwood D. A. Functional replacement of genes for individual polyketide synthase components in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) by heterologous genes from a different polyketide pathway. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(19):6184–6190. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.19.6184-6190.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman D. H., Malpartida F., Bibb M. J., Kieser H. M., Bibb M. J., Hopwood D. A. Structure and deduced function of the granaticin-producing polyketide synthase gene cluster of Streptomyces violaceoruber Tü22. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2717–2725. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. G., Wendt-Pienkowski E., Motamedi H., Hutchinson C. R. Nucleotide sequence of the tcmII-tcmIV region of the tetracenomycin C biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces glaucescens and evidence that the tcmN gene encodes a multifunctional cyclase-dehydratase-O-methyl transferase. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):1810–1820. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.1810-1820.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. G., Wendt-Pienkowski E., Motamedi H., Hutchinson C. R. The tcmVI region of the tetracenomycin C biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces glaucescens encodes the tetracenomycin F1 monooxygenase, tetracenomycin F2 cyclase, and, most likely, a second cyclase. J Bacteriol. 1993 Dec;175(23):7571–7580. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.23.7571-7580.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakil S. J. Fatty acid synthase, a proficient multifunctional enzyme. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4523–4530. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




