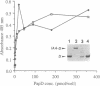
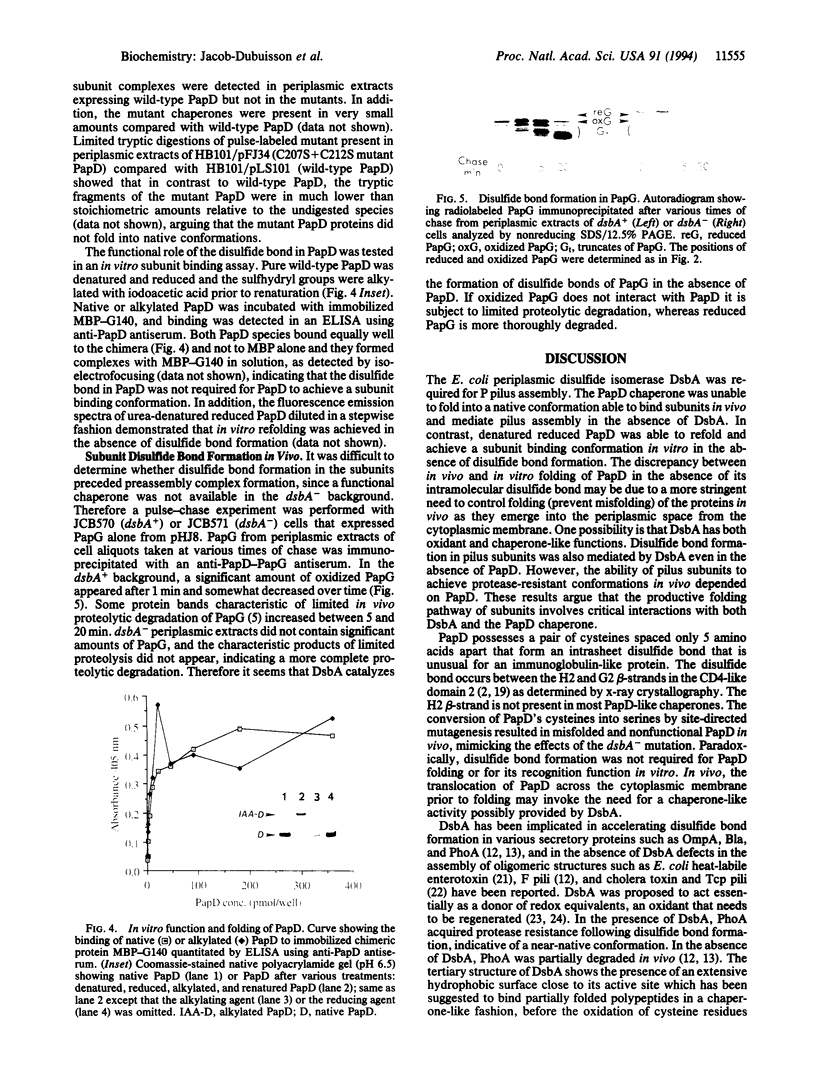
Abstract
Adhesive P pili of uropathogenic Escherichia coli were not assembled by a strain that lacks the periplasmic disulfide isomerase DsbA. This defect was mostly attributed to the immunoglobulin-like pilus chaperone PapD, which possesses an unusual intrasheet disulfide bond between the last two beta-strands of its CD4-like carboxyl-terminal domain. The DsbA-dependent formation of this disulfide bond was critical for PapD's proper folding in vivo. Interestingly, the absence of the disulfide bond did not prevent PapD from folding in vitro or from forming a complex with the pilus adhesin in vitro. We suggest that DsbA maintains nascently translocated PapD in a folding-competent conformation prior to catalyzing disulfide bond formation, acting both as an oxidant and in a chaperone-like fashion. Disulfide bond formation in pilus subunits was also mediated by DsbA even in the absence of PapD. However, the ability of pilus subunits to achieve native-like conformations in vivo depended on PapD. These results suggest that a productive folding pathway for subunits requires sequential interactions with DsbA and the PapD chaperone.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama Y., Kamitani S., Kusukawa N., Ito K. In vitro catalysis of oxidative folding of disulfide-bonded proteins by the Escherichia coli dsbA (ppfA) gene product. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22440–22445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Beckwith J. The bonds that tie: catalyzed disulfide bond formation. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):769–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90455-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Lee J. O., Jander G., Martin N., Belin D., Beckwith J. A pathway for disulfide bond formation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1038–1042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., McGovern K., Beckwith J. Identification of a protein required for disulfide bond formation in vivo. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):581–589. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier D. N., Bankaitis V. A., Weiss J. B., Bassford P. J., Jr The antifolding activity of SecB promotes the export of the E. coli maltose-binding protein. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90389-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman A. I., Prinz W. A., Belin D., Beckwith J. Mutations that allow disulfide bond formation in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. Science. 1993 Dec 10;262(5140):1744–1747. doi: 10.1126/science.8259521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dill K. A., Fiebig K. M., Chan H. S. Cooperativity in protein-folding kinetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1942–1946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson K. W., Jacob-Dubuisson F., Striker R. T., Hultgren S. J. Outer-membrane PapC molecular usher discriminately recognizes periplasmic chaperone-pilus subunit complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3670–3674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Protein folding in the cell. Nature. 1992 Jan 2;355(6355):33–45. doi: 10.1038/355033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong M., Makowski L. Helical structure of P pili from Escherichia coli. Evidence from X-ray fiber diffraction and scanning transmission electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1992 Dec 5;228(3):735–742. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90860-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Experimental support for the "hydrophobic zipper" hypothesis. Science. 1994 Jan 28;263(5146):536–536. doi: 10.1126/science.8290964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A., Bränden C. I. Crystal structure of chaperone protein PapD reveals an immunoglobulin fold. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):248–251. doi: 10.1038/342248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren A., Kuehn M. J., Brändén C. I., Hultgren S. J. Conserved immunoglobulin-like features in a family of periplasmic pilus chaperones in bacteria. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1617–1622. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05207.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultgren S. J., Abraham S., Caparon M., Falk P., St Geme J. W., 3rd, Normark S. Pilus and nonpilus bacterial adhesins: assembly and function in cell recognition. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):887–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90269-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob-Dubuisson F., Heuser J., Dodson K., Normark S., Hultgren S. Initiation of assembly and association of the structural elements of a bacterial pilus depend on two specialized tip proteins. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):837–847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05724.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob-Dubuisson F., Striker R., Hultgren S. J. Chaperone-assisted self-assembly of pili independent of cellular energy. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 29;269(17):12447–12455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. H., Pinkner J. S., Nicholes A. V., Slonim L. N., Abraham S. N., Hultgren S. J. FimC is a periplasmic PapD-like chaperone that directs assembly of type 1 pili in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8397–8401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamitani S., Akiyama Y., Ito K. Identification and characterization of an Escherichia coli gene required for the formation of correctly folded alkaline phosphatase, a periplasmic enzyme. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):57–62. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05027.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn M. J., Heuser J., Normark S., Hultgren S. J. P pili in uropathogenic E. coli are composite fibres with distinct fibrillar adhesive tips. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):252–255. doi: 10.1038/356252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn M. J., Normark S., Hultgren S. J. Immunoglobulin-like PapD chaperone caps and uncaps interactive surfaces of nascently translocated pilus subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10586–10590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn M. J., Ogg D. J., Kihlberg J., Slonim L. N., Flemmer K., Bergfors T., Hultgren S. J. Structural basis of pilus subunit recognition by the PapD chaperone. Science. 1993 Nov 19;262(5137):1234–1241. doi: 10.1126/science.7901913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaMantia M. L., Lennarz W. J. The essential function of yeast protein disulfide isomerase does not reside in its isomerase activity. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):899–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90469-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg F., Tennent J. M., Hultgren S. J., Lund B., Normark S. PapD, a periplasmic transport protein in P-pilus biogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6052–6058. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6052-6058.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Bardwell J. C., Kuriyan J. Crystal structure of the DsbA protein required for disulphide bond formation in vivo. Nature. 1993 Sep 30;365(6445):464–468. doi: 10.1038/365464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Missiakas D., Georgopoulos C., Raina S. The Escherichia coli dsbC (xprA) gene encodes a periplasmic protein involved in disulfide bond formation. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 15;13(8):2013–2020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06471.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigam S. K., Goldberg A. L., Ho S., Rohde M. F., Bush K. T., Sherman MYu A set of endoplasmic reticulum proteins possessing properties of molecular chaperones includes Ca(2+)-binding proteins and members of the thioredoxin superfamily. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1744–1749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsu M., Omura F., Yoshimori T., Kikuchi M. Protein disulfide isomerase associates with misfolded human lysozyme in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6874–6877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peek J. A., Taylor R. K. Characterization of a periplasmic thiol:disulfide interchange protein required for the functional maturation of secreted virulence factors of Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):6210–6214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.6210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puig A., Gilbert H. F. Protein disulfide isomerase exhibits chaperone and anti-chaperone activity in the oxidative refolding of lysozyme. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7764–7771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Model P. The role of thioredoxin in filamentous phage assembly. Construction, isolation, and characterization of mutant thioredoxins. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):14997–15005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons B. L., Rathman P., Malij C. R., Oudega B., de Graaf F. K. The penultimate tyrosine residue of the K99 fibrillar subunit is essential for stability of the protein and its interaction with the periplasmic carrier protein. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jan 15;55(1-2):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90177-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slonim L. N., Pinkner J. S., Brändén C. I., Hultgren S. J. Interactive surface in the PapD chaperone cleft is conserved in pilus chaperone superfamily and essential in subunit recognition and assembly. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4747–4756. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Webb H., Hirst T. R. A homologue of the Escherichia coli DsbA protein involved in disulphide bond formation is required for enterotoxin biogenesis in Vibrio cholerae. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jul;6(14):1949–1958. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01368.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]