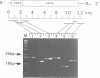
Abstract
Hypovirulent strain EP713 of the chestnut blight fungus Cryphonectria (Endothia) parasitica harbors a family of viral encoded double-stranded (ds) RNAs thought to be responsible for the hypovirulence phenotype. These include L-dsRNA, described in the accompanying paper (Shapira et al., 1991); several prominent species in the estimated size range of 8 to 10 kb, referred to here as M-dsRNAs; and several smaller species designated S-dsRNAs which range in size from approximately 0.6 to 1.7 kb. The characterization of the M- and S-dsRNA species is the subject of this report. Results from polymerase chain reaction mapping and molecular hybridization analysis indicate that the M- and S-dsRNA species are internally deleted forms of L-dsRNA. Three different S-dsRNA species were cloned and sequenced. Each species contained a single deletion breakpoint and retained either 149, 155 or 156 bp of the terminus corresponding to the 5'-end of the coding strand and 440, 447 or 449 bp of the other terminus. Two of the S-dsRNA species contained, within the boundaries of the breakpoint, additional sequence information consisting of 42 bp or 95 bp that appeared to be unrelated to the L-dsRNA sequence. These results demonstrate that defective RNAs contribute significantly to the complexity of dsRNA populations found in hypovirulent strains of C. parasitica and provide a first approximation of the location of cis-acting signals involved in their replication.
Full text
PDF

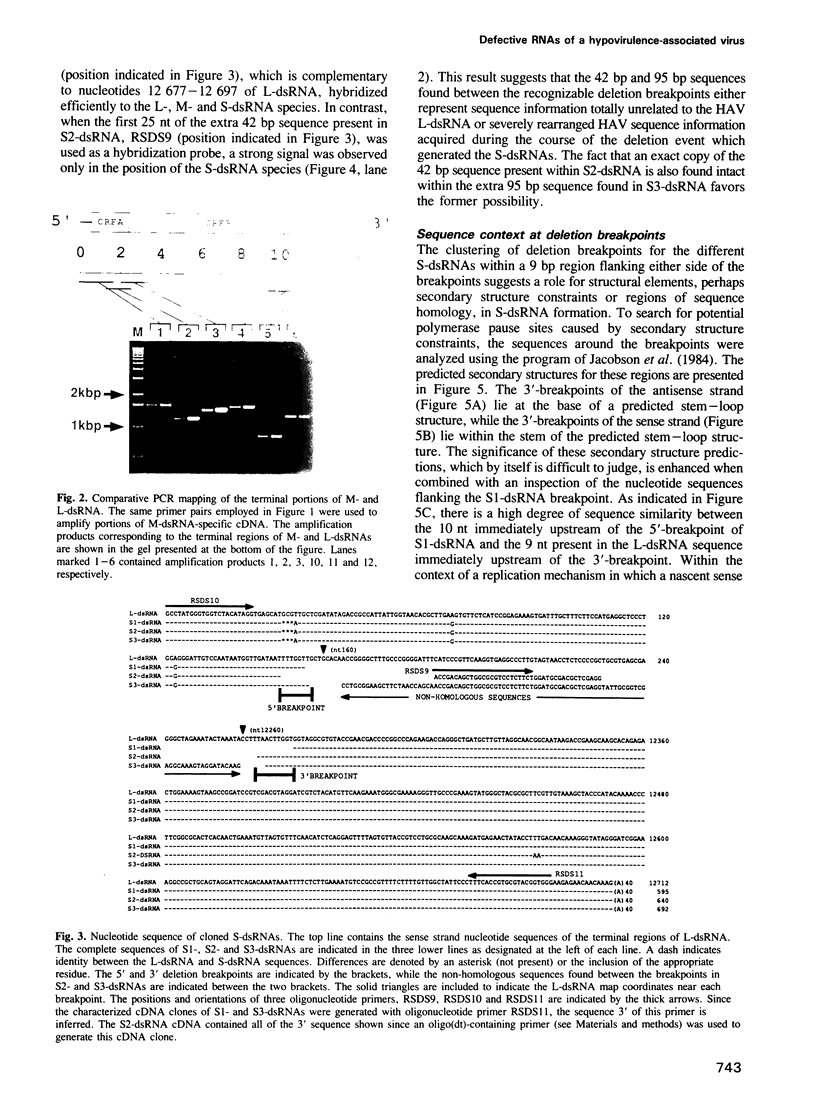

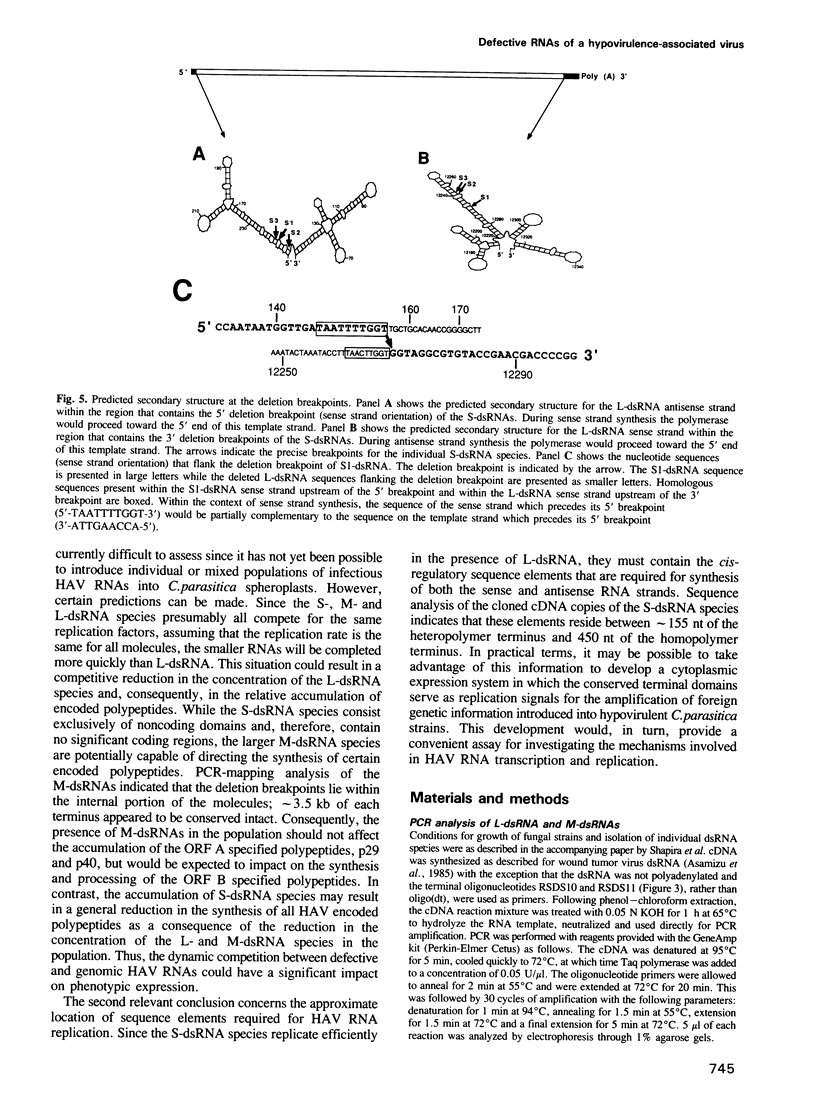

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostakis S. L. Biological control of chestnut blight. Science. 1982 Jan 29;215(4532):466–471. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4532.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anzola J. V., Xu Z. K., Asamizu T., Nuss D. L. Segment-specific inverted repeats found adjacent to conserved terminal sequences in wound tumor virus genome and defective interfering RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8301–8305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asamizu T., Summers D., Motika M. B., Anzola J. V., Nuss D. L. Molecular cloning and characterization of the genome of wound tumor virus: a tumor-inducing plant reovirus. Virology. 1985 Jul 30;144(2):398–409. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillman B. I., Carrington J. C., Morris T. J. A defective interfering RNA that contains a mosaic of a plant virus genome. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90638-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiremath S., L'Hostis B., Ghabrial S. A., Rhoads R. E. Terminal structure of hypovirulence-associated dsRNAs in the chestnut blight fungus Endothia parasitica. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9877–9896. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. J., Villarreal L. P. Persistent noncytocidal vesicular stomatitis virus infections mediated by defective T particles that suppress virion transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A. B., Good L., Simonetti J., Zuker M. Some simple computational methods to improve the folding of large RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):45–52. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatchikian D., Orlich M., Rott R. Increased viral pathogenicity after insertion of a 28S ribosomal RNA sequence into the haemagglutinin gene of an influenza virus. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):156–157. doi: 10.1038/340156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Weiss B. G., Tsiang M., Huang H., Schlesinger S. Deletion mapping of Sindbis virus DI RNAs derived from cDNAs defines the sequences essential for replication and packaging. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90492-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayak D. P., Chambers T. M., Akkina R. K. Defective-interfering (DI) RNAs of influenza viruses: origin, structure, expression, and interference. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;114:103–151. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70227-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae B. P., Hillman B. I., Tartaglia J., Nuss D. L. Characterization of double-stranded RNA genetic elements associated with biological control of chestnut blight: organization of terminal domains and identification of gene products. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):657–663. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Re G. G., Kingsbury D. W. Nucleotide sequences that affect replicative and transcriptional efficiencies of Sendai virus deletion mutants. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):578–582. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.578-582.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira R., Choi G. H., Nuss D. L. Virus-like genetic organization and expression strategy for a double-stranded RNA genetic element associated with biological control of chestnut blight. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):731–739. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglia J., Paul C. P., Fulbright D. W., Nuss D. L. Structural properties of double-stranded RNAs associated with biological control of chestnut blight fungus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9109–9113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]