Abstract
The new thiazolyl peptide antibiotic GE2270 A, isolated from Planobispora rosea strain ATCC 53773, is shown to inhibit bacterial protein biosynthesis in vitro by affecting specifically the GTP-bound form of elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu). The 'off' rate of EF-Tu.GTP is slowed down 400-fold, locking GTP on EF-Tu, whereas EF-Tu.GDP is unaffected. Therefore, on the EF-Tu.guanine nucleotide interaction, GE2270 A mimicks the effect of aa-tRNA. In line with this, the binding of aa-tRNA to EF-Tu.GTP is hindered by the antibiotic, as shown by the absence of a stable ternary complex and the inhibition of the enzymatic binding of aa-tRNA to the ribosome. This blocks the elongation cycle. GE2270 A does not essentially modify the intrinsic GTPase activity of EF-Tu, but impairs the stimulation by ribosomes of this reaction. The negative effect of GE2270 A on the EF-Tu.GTP interaction with aa-tRNA bears similarities with that of the structurally unrelated pulvomycin, whereas marked differences were found by comparing the effects of these two antibiotics on EF-Tu.GDP. This work emphasizes the varieties of the transitional conformations which tune the EF-Tu interaction with GTP and GDP.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai K., Kawakita M., Kaziro Y. Studies on the polypeptide elongation factors from E. coli. V. Properties of various complexes containing EF-Tu and EF-Ts. J Biochem. 1974 Aug;76(2):293–306. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch L., Kraal B., Van der Meide P. H., Duisterwinkel F. J., Van Noort J. M. The elongation factor EF-Tu and its two encoding genes. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;30:91–126. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60684-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Properties of the elongation factors from Escherichia coli. Exchange of elongation factor G during elongation of polypeptide chain. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 1;32(3):463–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02629.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cundliffe E., Thompson J. Concerning the mode of action of micrococcin upon bacterial protein synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(1):47–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
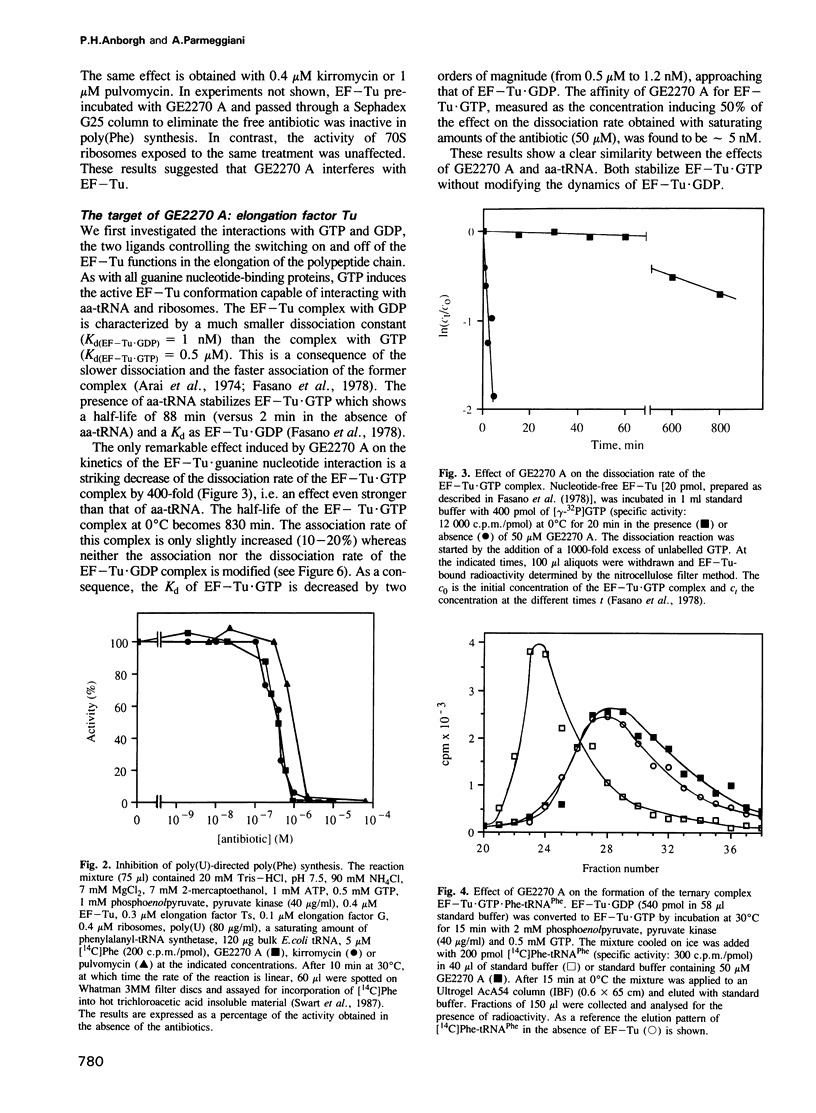
- Fasano O., Bruns W., Crechet J. B., Sander G., Parmeggiani A. Modification of elongation-factor-Tu . guanine-nucleotide interaction by kirromycin. A comparison with the effect of aminoacyl-tRNA and elongation factor Ts. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 1;89(2):557–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12560.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
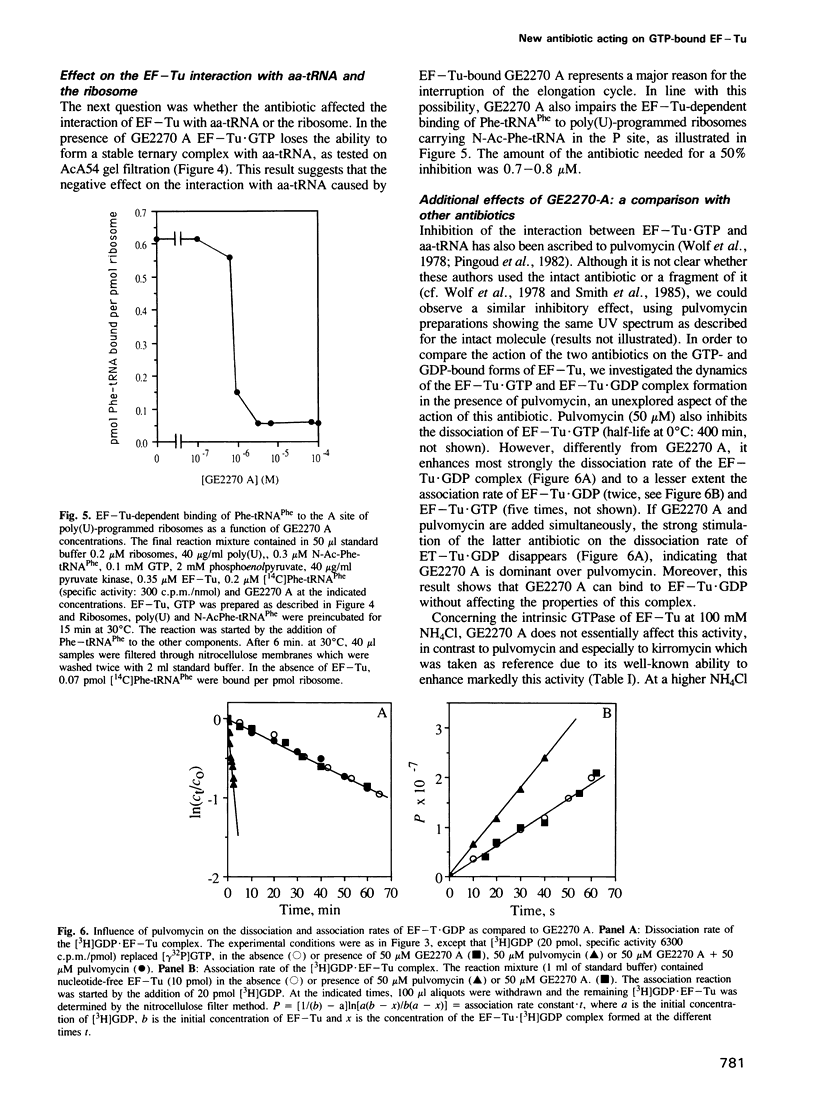
- Kaziro Y. The role of guanosine 5'-triphosphate in polypeptide chain elongation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 21;505(1):95–127. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(78)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otaka T., Kaji A. Micrococcin: acceptor-site-specific inhibitor of protein synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 16;50(1):101–106. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parlato G., Guesnet J., Crechet J. B., Parmeggiani A. The GTPase activity of elongation factor Tu and the 3'-terminal end of aminoacyl-tRNA. FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 23;125(2):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80733-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmeggiani A., Sander G. Properties and regulation of the GTPase activities of elongation factors Tu and G, and of initiation factor 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Mar 27;35(3):129–158. doi: 10.1007/BF02357085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmeggiani A., Swart G. W. Mechanism of action of kirromycin-like antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:557–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmeggiani A., Swart G. W., Mortensen K. K., Jensen M., Clark B. F., Dente L., Cortese R. Properties of a genetically engineered G domain of elongation factor Tu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3141–3145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pingoud A., Block W., Urbanke C., Wolf H. The antibiotics kirromycin and pulvomycin bind to different sites on the elongation factor Tu from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):261–265. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spedding G., Cundliffe E. Identification of the altered ribosomal component responsible for resistance to micrococcin in mutants of Bacillus megaterium. Eur J Biochem. 1984 May 2;140(3):453–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swart G. W., Parmeggiani A., Kraal B., Bosch L. Effects of the mutation glycine-222----aspartic acid on the functions of elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 7;26(7):2047–2054. doi: 10.1021/bi00381a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Assmann D., Fischer E. Pulvomycin, an inhibitor of protein biosynthesis preventing ternary complex formation between elongation factor Tu, GTP, and aminoacyl-tRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5324–5328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Kirromycin, an inhibitor of protein biosynthesis that acts on elongation factor Tu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]