Abstract
Background
The Arabian Peninsula is home to a unique fauna that has assembled and evolved throughout the course of major geophysical events, including the separation of the Arabian Plate from Africa and subsequent collision with Eurasia. Opportunities for faunal exchanges with particular continents occurred in temporally distinct periods, and the presence of African, Western Eurasian, and South Asian derived taxa on the Arabian Peninsula signifies the complexity of these historical biogeographic events. The six true toad species (family Bufonidae) endemic to the Arabian Peninsula present a considerable taxonomic and biogeographic challenge because they are part of a global bufonid radiation, including several genera surrounding the Arabian Peninsula, and difficult to discriminate morphologically. As they could be derived from African, Western Eurasian, or South Asian toad groups, elucidating their evolutionary relationships has important implications for historical biogeography. Here, we analyze a global molecular data set of 243 bufonid lineages, with an emphasis on new sampling from the Horn of Africa, Western Eurasia, South Asia, and the Arabian Peninsula, to reconstruct the evolutionary relationships of the Arabian species. We produce a robust time-calibrated phylogeny to infer the biogeographic history of this group on and around the Arabian Peninsula.
Results
Our phylogenetic analyses indicate two of the endemic Arabian toad species, “Bufo” tihamicus and “Bufo” arabicus, evolved independently within the African genus Amietophrynus. We confirm the Arabian species Duttaphrynus dhufarensis is of South Asian origin, but do not find evidence for the Asian genus Duttaphrynus being present in the Horn of Africa, discrediting a previously proposed Asian bufonid dispersal event to Africa. We also do not find evidence of the African genus Amietophrynus occurring in South Asia, suggesting that unlike many other vertebrate taxa, toads have not used the Arabian Peninsula as a stepping-stone for trans-continental dispersal. Our divergence dating estimates strongly suggest the formation of the Red Sea drove simultaneous divergences between two of the Arabian species (A. tihamicus comb. nov. and A. arabicus comb. nov.) and their closest mainland African relatives in the Early Miocene. We estimate the divergence of D. dhufarensis with its closest South Asian relatives occurred in the mid to Late Miocene, suggesting the temporary or permanent land connections between the Arabian plate and Eurasia facilitated dispersal of this lineage to the Arabian Peninsula.
Conclusions
The Arabian bufonid assemblage, despite being comparatively depauperate with respect to surrounding continents, exemplifies the faunal pattern of the Arabian Peninsula, namely being a complex admixture of African, Western Eurasian, and South Asian elements. The historical biogeographic patterns exhibited by Arabian toads and their allies are concordant with studies of other vertebrate taxa, building support for the role of major geological events in driving simultaneous vicariance and dispersal events around the Arabian Peninsula. Although many taxa or groups exhibiting disjunct Afro-Arabian distributions appear to have dispersed more recently from the Horn of Africa via a southern land bridge or overwater dispersal, both Amietophrynus tihamicus and A. arabicus likely represent true African relicts resulting from vicariance associated with the Red Sea formation, a pattern that so far is rare among the vertebrate species investigated.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12862-015-0417-y) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Arabian Peninsula, Historical biogeography, Amphibians, Toads, Red Sea
Background
The Arabian Peninsula possesses a unique assemblage of plant and animal species that result from the dynamic geologic history and shifting climate of this region. The flora and fauna range from localized temperate endemics occurring in the disjunct extensions of the Horn of Africa Hotspot and the Eastern Afromontane Hotspot [1, 2] in the southwest regions (Fig. 1), to more broadly distributed arid-adapted clades occurring throughout much of the Arabian Peninsula [3–13]. Many large-scale biogeographic patterns for Arabian taxa have been profoundly shaped by the complex tectonic history of the Arabian Peninsula [14–22]. The tectonic activity ultimately responsible for the separation of the Arabian Plate from Africa began approximately 30 Ma, and rifting of the southern Red Sea occurred in the early Miocene (27 Ma), and a connection to the Neotethys Sea and was completed by 23 Ma [23, 24]. The formation of the Red Sea represented a major vicariance event for taxa with formerly continuous Afro-Arabian distributions. The isolated Arabian plate collided with the Anatolian plate approximately 18–16 Ma, forming the temporary Gomphotherium bridge [25, 26]. A more permanent land bridge was established after the Arabian plate collided with Eurasia approximately 15 Ma [24], which allowed regular faunal exchanges between North Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, and Eurasia. These land bridges also created opportunities for trans-continental dispersals using the Arabian Peninsula as a stepping-stone. Sea levels dropped throughout the Red Sea around 10 Ma, providing evidence for the closing of the Strait of Bab el Mandeb and establishment of a southern land bridge between Africa and Arabia [24]. Pliocene marine sediment deposits formed around 5.3 Ma, indicating this land bridge was subsequently lost, and although cyclical Pleistocene land bridges related to glacial cycles have been proposed [27], more recent evidence does not support their existence [28]. Conversely, there is evidence the Persian Gulf was reduced to a series of freshwater lakes [29] or completely waterless [30] during the late Pleistocene, providing a connection between the Arabian Peninsula and Southwest Asia. Plio-Pleistocene climate change is hypothesized to have driven speciation in the southwest montane regions of the Arabian Peninsula [3, 11], and is linked to aridification in the Neogene [31, 32]. This may explain additional biogeographic patterns, but on a much more localized scale.
Fig. 1.
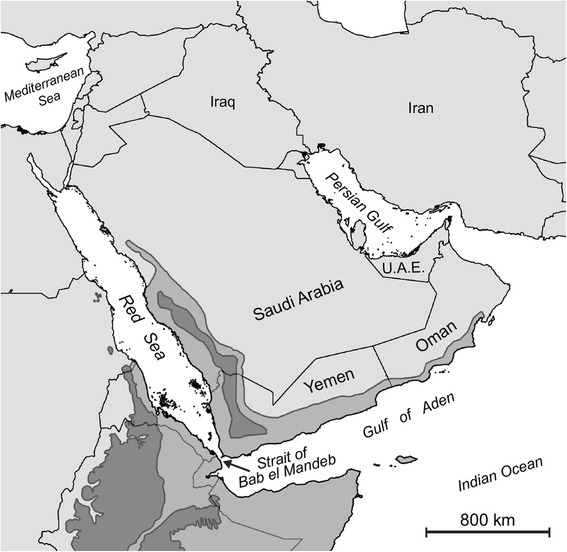
The Arabian Peninsula. A map of the Arabian Peninsula showing disjunct extensions of the Horn of Africa Hotspot (medium grey) and the Eastern Afromontane Hotspot (dark grey), along with pertinent seas and country borders. Shape files for hotspots were obtained through the “Biodiversity Hotspots” package produced by Conservation International (2011).
The geologic activity associated with the Arabian Peninsula altered the historical connectivity of this landmass to surrounding continents, and as a result opportunities for faunal exchanges with particular continents occurred in temporally distinct periods. For example, taxa exhibiting disjunct Afro-Arabian distributions either exhibit early Miocene divergences associated with vicariance resulting from the Red Sea formation (30–23 Ma), or dispersed more recently from the Horn of Africa via a southern landbridge or overwater dispersal (10–5.3 Ma or 5.3 Ma to present, respectively) (reviewed in [18]). If the phylogenetic placement of an Arabian focal group is recovered, predictions can be made concerning the timing of speciation and tested in a temporally explicit phylogenetic framework to infer historical biogeographic patterns. The limited phylogenetic studies focusing on or including Arabian species have demonstrated concordant divergence timings for taxa with similar biogeographic origins [16–20], however these biogeographic patterns remain largely understudied for most Arabian taxa.
Although overall levels of endemism among vertebrate groups across the Arabian Peninsula are moderate, Arabian amphibians exhibit a high degree of endemism [15, 33]. Of the nine described Arabian anuran species, six of these species are true toads belonging to the family Bufonidae, a clade that contains close to 600 described species and which exhibits a nearly worldwide distribution [34]. The dispersal ability of toads is limited by their reliance on freshwater habitat for breeding and their intolerance to saltwater, making them an interesting system for investigating historical biogeography in this region. Several broad-scale phylogenetic studies of bufonids have revealed the existence of largely discrete continental clades [35–39] that are now accepted as distinct genera or subgenera [34, 40]. Three such genera are currently distributed in geographic regions directly surrounding the Arabian Peninsula, including Amietophrynus (Africa), Bufotes (Northern Eurasia and North Africa), and Duttaphrynus (Southwest and South Asia), allowing the possibility of multiple biogeographic origins for the Arabian species.
Due to a lack of molecular sampling, the assignment of the Arabian bufonid species to genera, and therefore biogeographic origin, has long been problematic. One Arabian toad species, Bufotes cf. variabilis, is attributable to the Western Eurasian Bufotes viridis species complex on the basis of morphology [33, 41]. However, the affinities of the other Arabian toads are unresolved in part due to the similar morphology among the many species of toads occurring in regions surrounding the Arabian Peninsula. Based on molecular evidence the Arabian endemic Duttaphrynus dhufarensis was recently determined to be of Asian origin, with its closest relatives occurring on the Indian subcontinent [37], although several taxa occurring across Southwest Asia were not included in the analysis. This discovery, and the assignment of D. dodsoni (a species distributed throughout the Horn of Africa) to the genus [37, 40], implies the Arabian Peninsula has acted as a stepping-stone for Asian-derived bufonid species to colonize mainland Africa. This scenario remains to be tested in a phylogenetic framework, but has important biogeographic implications. Other than B. cf. variabilis and D. dhufarensis, the remaining Arabian toads could not be allocated to genera, and remain in a non-taxon Bufo that is currently polyphyletic and is denoted as “Bufo”. These species include “Bufo” arabicus, “Bufo” tihamicus, “Bufo” hadramautinus, and “Bufo” scorteccii. Both “Bufo” arabicus and D. dhufarensis possess the largest geographic distribution of the Arabian toads, whereas “Bufo” tihamicus is only distributed along the coastal Red Sea region. Although “Bufo” tihamicus is thought to be a close relative of the Sahelian distributed African taxon “Bufo” pentoni, the latter species is also currently not assigned to a genus, and therefore the phylogenetic relationships of this complex remains convoluted. The species “Bufo” hadramautinus and scorteccii are restricted to one or two localities, and their validity has been questioned as they may represent isolated phenotypically variable populations of the wider ranging “Bufo” arabicus and D. dhufarensis, respectively [33]. As a result of these hypotheses “Bufo” scorteccii has been tentatively assigned to the genus Duttaphrynus [40], although this taxonomic assignment is certainly premature, and some authors have regarded “Bufo” hadramautinus as a synonym of “Bufo” arabicus [42].
The evolution of Arabian bufonids and their close relatives remains a challenging biogeographic and taxonomic problem, and it is unknown if the unassigned Arabian toads are derived from African, Southwest Asian, or Western Eurasian lineages, or are the result of in-situ diversification on the Peninsula. In addition, the biogeographic patterns of the genus Duttaphrynus have not been investigated yet have important implications concerning whether amphibians successfully colonized the Horn of Africa using the Arabian Peninsula as a stepping-stone. A similar problem persists for “Bufo” tihamicus and pentoni, which could be derived from African, Southwest Asian, or Western Eurasian clades, each of which has implies different biogeographic scenarios for explaining the current geographic distributions of these two species.
Through several years of fieldwork, TJP obtained key samples of Arabian taxa (including “Bufo” arabicus, “Bufo” tihamicus, D. dhufarensis) as well as many biogeographically important species surrounding the Arabian Peninsula (including “Bufo” pentoni and D. dodsoni), finally allowing an assessment of their evolutionary relationships using a molecular phylogenetic framework. We seek to untangle the various biogeographic scenarios resulting in the evolution of the Arabian bufonids and their close relatives. We aim to identify the closest relatives of “Bufo” tihamicus and “Bufo” arabicus to determine if they are derived from African, Western Eurasian, or South Asian lineages. If they are African in origin, we predict they will have diverged from their closest mainland relatives either 1) following the formation of the Red Sea (23 Ma), or 2) as a result of dispersal across a southern Afro-Arabian land bridge (10–5.3 Ma). Alternatively, if they are Western Eurasian or South Asian in origin, we predict they will have colonized the Arabian Peninsula following establishment of Eurasian land bridge connections (18–15 Ma). We also seek to test the stepping-stone colonization of the Horn of Africa by the genus Duttaphrynus, and predict a sister-taxon relationship between D. dodsoni and D. dhufarensis, with a divergence time following permanent Eurasian land bridge connections (15 Ma). We use newly generated multi-locus molecular data and a comprehensive data set of published bufonid sequences to reconstruct phylogenetic relationships to identify the origins of the Arabian taxa. We use these molecular data to estimate divergence times to identify key biogeographic events that could have led to the formation of these lineages. We examine our results in the context of prior studies that have investigated historical biogeographic patterns in other Arabian taxa, and highlight areas requiring further study.
Results
Phylogenetic relationships
The overall phylogenetic relationships within the family Bufonidae are concordant across analyses and are presented in Figs. 2-4 (full length figure available in Additional file 1). We find strong support for the monophyly of the Bufonidae, and relationships among the basal genera (Melanophryniscus, Dendrophryniscus, Osornophryne, Atelopus, Amazophrynella, Nannophryne, Peltophryne) are well resolved and consistent with previous studies [35–39]. Our phylogenetic analyses place Anaxyrus as the sister clade to Incilius with high support, and together these two genera are moderately supported as being sister to the genus Rhinella (Figs. 2, 3). Beyond this grouping, the relationships among the other derived genera (Rhaebo, Didynamipus, Poyntonophrynus, Nimbaphrynoides, Vandijkophrynus, Capensibufo, Mertensophryne, Amietophrynus, Wolterstorffina, Werneria, Nectophryne, Barbarophryne, Schismaderma, Churamiti, Nectophrynoides, Pedobistes, Adenomus, Xanthophryne, Duttaphrynus, Bufotes, Epidalea, Strauchbufo, Sabahphrynus, Bufo, Leptophryne, Ingerophrynus, Ghatophryne, Phrynoidis, Pelophryne, Ansonia) are largely unresolved (Figs. 3, 4). Genera sampled for more than one lineage are supported as monophyletic, with the exception of Pedobistes (as found by Van Bocxlaer et al. [38]). This is true for the speciose genera surrounding the Arabian Peninsula, including Amietophrynus, Bufotes, and Duttaphrynus, which are all recovered as independent monophyletic groups with strong support (Figs. 3, 4). In this global bufonid species data set with an emphasis on sampling surrounding the Arabian Peninsula, our analyses consistently place the Arabian toad species within particular genera.
Fig. 2.
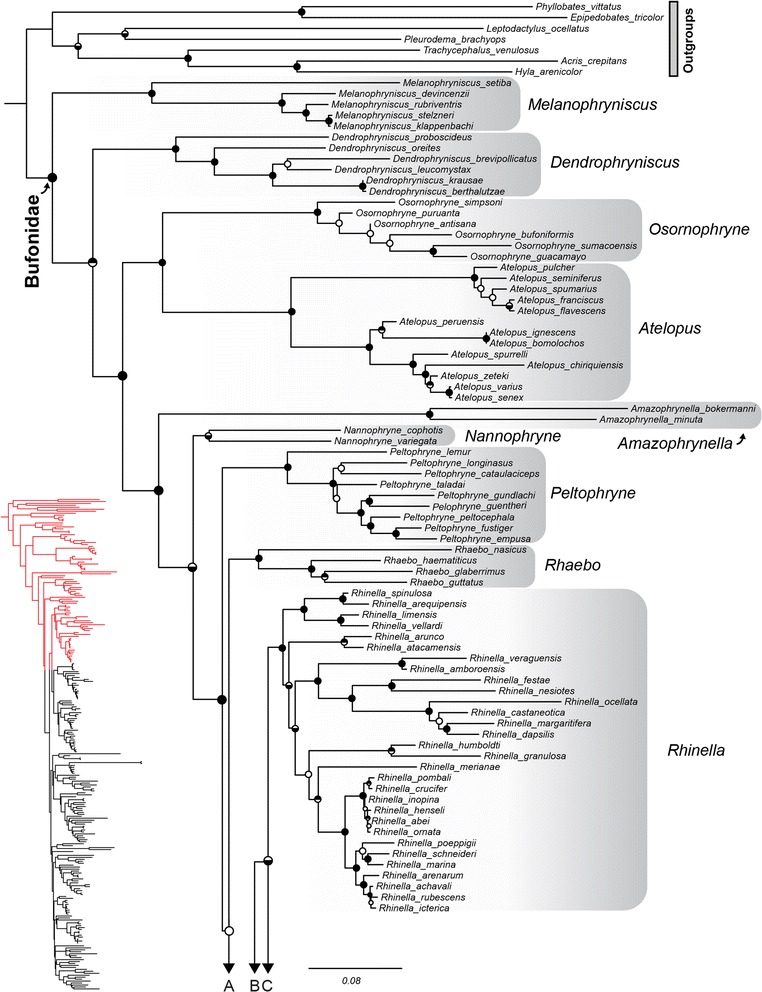
Phylogenetic relationships of global bufonids, part one. The maximum likelihood tree of the Bufonidae, based on 13 loci and 243 taxa. Filled circles on nodes represent high support (Bayesian posterior probabilities [BPP] > 0.95 and maximum likelihood bootstrap scores [MLBS] > 70%); circles with top half fill: MLBS > 70% and BPP < 0.95; circles with bottom half fill: MLBS < 70% and BPP > 0.95; open circles represent support values less than given threshold for both analysis types. Branch lengths are proportional to substitutions/site, indicated by scale bar below, and genera are outlined in grey shading. Letters below correspond to connections to Fig 3. The portion of the phylogeny represented is highlighted in red on the full topology.
Fig. 4.
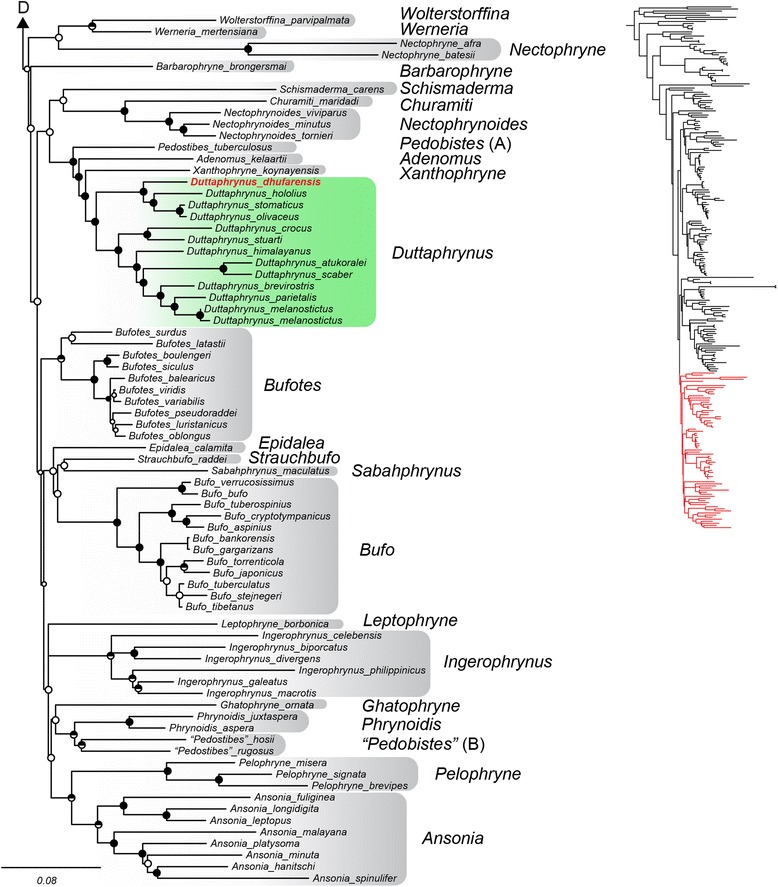
Phylogenetic relationships of global bufonids, part three. The maximum likelihood tree of the Bufonidae, based on 13 loci and 243 taxa. Filled circles on nodes represent high support (BPP > 0.95 and MLBS > 70%); circles with top half fill: MLBS > 70% and BPP < 0.95; circles with bottom half fill: MLBS < 70% and BPP > 0.95; open circles represent support values less than given threshold for both analysis types. Branch lengths are proportional to substitutions/site, indicated by scale bar below. Genera are outlined in grey shading, genera containing Arabian taxa are colored and Arabian species are denoted by red bold text. Letters above correspond to connections to Fig. 3. The portion of the phylogeny represented is highlighted in red on the full topology.
Fig. 3.
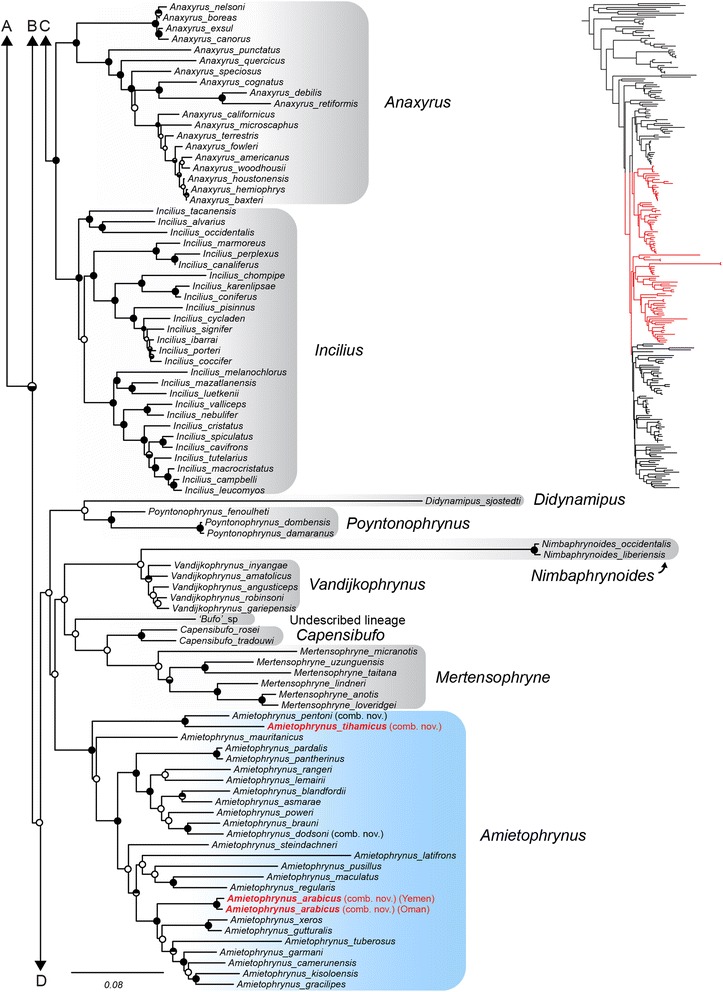
Phylogenetic relationships of global bufonids, part two. The maximum likelihood tree of the Bufonidae, based on 13 loci and 243 taxa. Filled circles on nodes represent high support (BPP > 0.95 and MLBS > 70%); circles with top half fill: MLBS > 70% and BPP < 0.95; circles with bottom half fill: MLBS < 70% and BPP > 0.95; open circles represent support values less than given threshold for both analysis types. Branch lengths are proportional to substitutions/site, indicated by scale bar below. Genera are outlined in grey shading, genera containing Arabian taxa are colored and Arabian species are denoted by red bold text. Letters above correspond to connections to Fig. 2, and below to Fig. 4. The portion of the phylogeny represented is highlighted in red on the full topology.
The Arabian species “Bufo” tihamicus is strongly supported as the sister taxon of the African Sahelian distributed “Bufo” pentoni, and together these two lineages are recovered as sister to all other species of Amietophrynus (Figs. 3, 5). Our analyses recover “Bufo” arabicus as the sister taxon to a grouping of two clades. One clade consists of the more arid-adapted species A. xeros and A. gutturalis, and the other consists of A. tuberosus, A. garmani, A. camerunensis, A. kisolensis, and A. gracilipes. The resolution of the relationship between “Bufo” arabicus and these two clades is not strongly supported, with some results placing “Bufo” arabicus as sister to A. xeros and A. gutturalis, and others placing “Bufo” arabicus as sister to both clades (as in Fig. 3). Our results confirm the findings of Van Bocxlaer et al. [37] in recovering the Arabian species Duttaphrynus dhufarensis within the Asian genus Duttaphrynus. Our improved sampling from Iran and Pakistan places D. dhufarensis as sister to a clade consisting of D. hololius, D. stomaticus and D. olivaceus with strong support (Figs. 4, 6). Duttaphrynus dodsoni, which is distributed across the Horn of Africa, is not recovered as a member of the genus Duttaphrynus, but rather is found deeply nested in the genus Amietophrynus and is a close relative of the East African species Amietophrynus brauni (Figs. 3, 5).
Fig. 5.
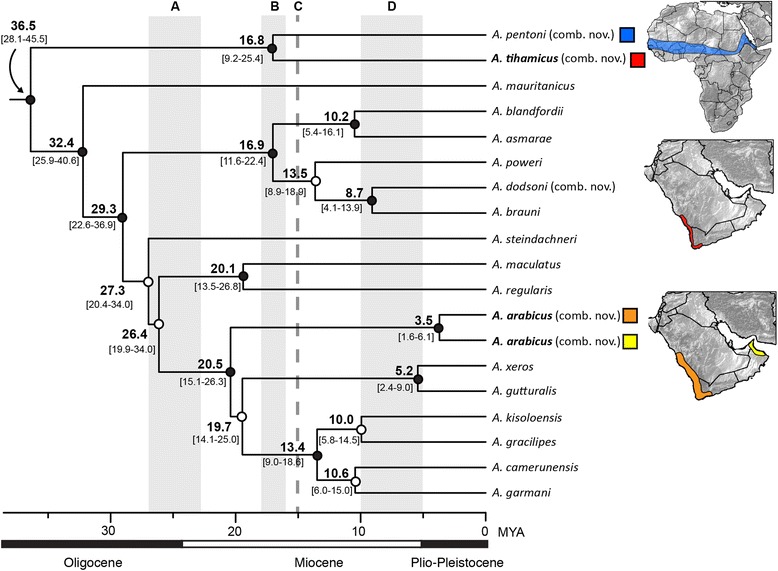
Divergence timings of the genus Amietophrynus. Bayesian maximum clade credibility chronogram of the genus Amietophrynus inferred in BEAST (Analysis 2) with median divergence times and associated 95 % highest posterior distributions of dates in brackets. Timings of relevant geologic events are illustrated: A – Red Sea formation (27–23 Ma); B – Gomphotherium bridge (18–16 Ma); C – permanent Eurasian landbridge (15 Ma); D – southern Afro-Arabian landbridge (10–5.3 Ma). Ranges of Arabian species and, if relevant, corresponding sister taxon are illustrated. Filled circles on nodes represent Bayesian posterior probabilities > 0.95, open circles represent support values < 0.95.
Fig. 6.
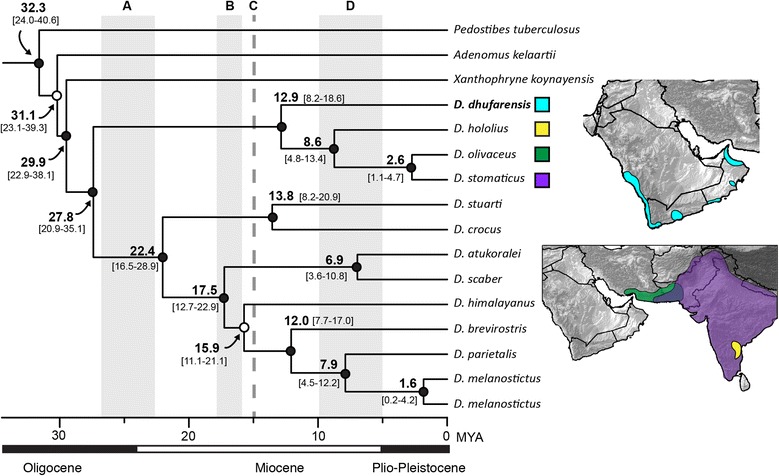
Divergence timings of the genus Duttaphrynus. Bayesian maximum clade credibility chronogram of the genus Duttaphrynus inferred in BEAST (Analysis 2) with median divergence times and associated 95 % highest posterior distributions of dates in brackets. Timings of relevant geologic events are illustrated: A – Red Sea formation (27–23 Ma); B - Gomphotherium bridge (18–16 Ma); C – permanent Eurasian landbridge (15 Ma); D – southern Afro-Arabian landbridge (10–5.3 Ma). Ranges of Arabian species and, if relevant, corresponding sister taxon are illustrated. Filled circles on nodes represent Bayesian posterior probabilities > 0.95, open circles represent support values < 0.95.
In addition to elucidating the relationships of Arabian bufonids, our phylogenetic analyses revealed a unique bufonid lineage restricted to the Horn of Africa, designated as “Bufo” sp. (Fig. 3, “Undescribed lineage”). The placement of this lineage is not well resolved and it does not appear to be a member of any currently described African genus (Figs. 2-4). Maximum likelihood and Bayesian consensus trees show this new genus is most closely related to a clade of African genera (Capensibufo, Mertensophryne, Vandijkophrynus, and Nimbaphrynoides) but this relationship is not strongly supported (Fig. 3). An additional extensive comparison with over 500 unpublished 16S sequences of mainly African bufonids also failed to resolve the placement of this taxon with any described genus (H.C. Liedtke, pers. comm.), and additional taxonomic work is therefore required for this unique lineage.
Divergence dating estimates
The three divergence dating analyses (A1, A2, A3) produced largely congruent phylogenetic topologies (Additional file 5). Divergence dating estimates varied little between analyses, though the 95 % highest posterior density regions are slightly broader in analyses A1 and A3 than those in A2 (Table 1, Additional file 6). All dating analyses suggest a mid-Cretaceous origin of the family Bufonidae, with median estimates ranging between 93.5–100.3 Ma ([A1: 94.9 Ma, 95 % HPD 64.6–129.8]; [A2: 93.5, 73.0–114.0 Ma]; [A3: 100.3, 70.1–133.1 Ma]. These dates are consistent with Pramuk et al. [36], who also recover a mid-Cretaceous origin of the family with an estimate of 88.2 Ma (78.3–98.8 Ma), but are approximately 20–25 million years older than dates recovered by Van Bocxlaer et al. [38] for the group (67.9 Ma, 95 % HPD 52.7–92.7]. Similar to both Pramuk et al. [36] and Van Bocxlaer et al. [38], we find the origin and diversification of most derived (eg. formerly Bufo) bufonid genera occurred in a window of approximately 10 million years. Our estimates place this rapid diversification in the Eocene, as found by Pramuk et al. [36], though Van Bocxlaer et al. [38] date this radiation to the Oligocene.
Table 1.
Key results of divergence dating analyses
| Dating analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Node label | A1 | A2 | A3 |
| Root age | 124.8 [84.1–177.1] | 121.5 [89.3–160.3] | 128.0 [85.7–182.1] |
| Bufonidae | 94.9 [64.6–129.8] | 93.5 [73.0–114.0] | 100.3 [70.1–133.1] |
| Origin Amietophrynus | 37.6 [25.6–51.5] | 36.5 [28.1–45.5] | 37.2 [27.1–50.4] |
| TMRCA A. arabicus | 21.2 [14.2–29.2] | 20.5 [15.1–26.3] | 20.7 [14.8–29.2] |
| TMRCA A. tihamicus | 17.9 [9.0–26.6] | 16.8 [9.3–25.4] | 17.0 [9.3–25.9] |
| Origin Duttaphrynus | 29.3 [19.3–40.5] | 27.8 [20.9–35.1] | 29.2 [20.4–40.0] |
| TMRCA D. dhufarensis | 13.5 [7.9–20.9] | 12.9 [8.2–18.6] | 13.5 [8.4–20.1] |
For relevant nodes, median age and 95 % highest posterior density region are given (Ma). Analysis 1 (A1): inclusion of four internal calibrations with lognormal calibration prior for age of the Bufonidae; Analysis 2 (A2): inclusion of four internal calibrations with normal calibration prior for age of the Bufonidae; Analysis 3 (A3): inclusion of four internal calibrations with exponential calibration prior for age of the Bufonidae.
Based on our data, diversification of the genus Amietophrynus began around the Eocene-Oligocene boundary ([A1: 37.6, 25.6–51.5 Ma]; [A2: 36.5, 28.1–45.5 Ma]; [A3: 37.2, 27.1–50.4 Ma]) whereas comparatively diversification began more recently in Duttaphrynus during the mid-Oligocene ([A1: 29.3, 19.3–40.5 Ma]; [A2: 27.8, 20.9–35.1 Ma]; [A3: 29.2, 20.4–40.0 Ma]) (Table 1). The divergences of the Arabian species (“Bufo” tihamicus and arabicus, D. dhufarensis) are estimated to have occurred during the Miocene. An Early Miocene divergence is estimated between “Bufo” tihamicus and “Bufo” pentoni ([A1: 17.9, 9.0–26.6 Ma]; [A2: 16.8, 9.2–25.4 Ma]; [A3: 17.0, 9.3–25.9 Ma]) as well as the split between “Bufo” arabicus and its sister clade ([A1: 21.2, 14.2–29.2 Ma]; [A2: 20.5, 15.1–26.3 Ma]; [A3: 20.7, 14.8–29.2 Ma]) (Fig. 5, Table 1). Within “Bufo” arabicus, the allopatric populations occurring in Yemen and Oman are supported as genetically distinct and are estimated to have diverged in the Pliocene ([A1: 4.0, 1.5–6.7 Ma]; [A2: 3.5, 1.6–6.1 Ma]; [A3: 3.5, 1.5–7.3 Ma]) (Fig. 5). The divergence estimates for the split between Duttaphrynus dhufarensis and the clade consisting of D. hololius, D. stomaticus and D. olivaceus occur in the mid-Miocene, with median estimates ranging from 12.9–13.5 Ma ([A1: 13.5, 7.9–20.9 Ma]; [A2: 12.9, 8.2–18.6 Ma]; [A3: 13.5, 8.4–20.1 Ma]) (Fig. 6). These dates are slightly older than those recovered by Van Bocxlaer et al. [37], who estimate this divergence at 8.5 Ma (95 % HPD 5.9–12.3). Previously untested, the divergence event between closely related D. stomaticus and D. olivaceus is estimated to have occurred in the late Pliocene ([A1: 3.0, 1.0–5.1 Ma]; [A2: 2.6, 1.1–4.7 Ma]; [A3: 2.7, 1.0–5.2 Ma]; Fig. 5).
Discussion
Evolutionary relationships of Arabian bufonids
The relationships among Arabian toad species have long been problematic, owing in part to the generalized morphology of these species and of lineages in surrounding regions [33, 45]. The molecular delimitation of at least three speciose toad genera differentially distributed around the Arabian Peninsula (Amietophrynus, Bufotes, Duttaphrynus) further highlighted the possibility of several alternative biogeographic origins for the Arabian species [35]. Prior to our study, the Arabian bufonid species assemblage was recognized as having both Western Eurasian and Asian elements (Bufotes cf. variabilis [33, 41], Duttaphrynus dhufarensis [37]), and here we identify a previously unrecognized, though not unexpected, African component. We find strong support for a sister relationship between “Bufo” pentoni and “Bufo” tihamicus, which together form a monophyletic assemblage with all other species in the African genus Amietophrynus (Figs. 3, 5). The Arabian lineage “Bufo” arabicus is also recovered in this clade (Figs. 3, 5), and our results do not support a close relationship between these Arabian lineages. Rather, these species have independent evolutionary origins in the genus.
We recover the Arabian species Duttaphrynus dhufarensis as part of a largely South Asian clade, represented by other species in the genus Duttaphrynus (Figs. 4, 6), consistent with Van Bocxlaer et al. [37]. In their study, Van Bocxlaer et al. [37] recover D. dhufarensis as sister to a clade containing D. stomaticus and D. hololius. They report D. hololius as widespread on the Indian subcontinent, with D. stomaticus being restricted to the Western Ghats [37:Fig. 2]. The true distributions of these species are actually converse, though their interpretation of the biogeographic results is sound. Regardless, both species were sampled from India, and together with the other species included in their analyses the westernmost sampling for the genus was limited to India. This left a vast sampling gap across Pakistan and Iran, a region that contains many widespread species in the genus Duttaphrynus and Bufotes. Our sampling includes six species from this region (Bufotes oblongus, B. pseudoraddei, B. surdus, B. variabilis, D. olivaceus, and D. stomaticus) and includes geographically relevant localities adjacent to the Gulf of Oman and Persian Gulf in Iran and Pakistan. With this biogeographically improved sampling, we find D. dhufarensis is the sister taxon to a clade containing D. hololius, D. olivaceus and D. stomaticus. We find D. stomaticus exhibits a distribution throughout Pakistan and India, and the D. olivaceus is distributed largely throughout Iran and into Pakistan (Figs. 4, 6).
With our broad species sampling of Duttaphrynus, Bufotes, and Amietophrynus, our analyses do not recover Duttaphrynus dodsoni as monophyletic with other members of the genus. Instead, this species is strongly supported as nested within the African distributed genus Amietophrynus as sister taxon to the East African species Amietophrynus brauni (Figs. 3, 5). We discuss the biogeographic implications of this discovery and the overall historical biogeography of the Arabian toad species below.
Historical biogeography of Arabian toads
Our phylogenetic analyses have resolved the origins of several biogeographically interesting toad lineages distributed throughout the Horn of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, and Southwest Asia, and here we interpret major divergence events in the context of the geological history of this region.
The species “Bufo” arabicus and “Bufo” tihamicus are both estimated to have diverged from their closest African relatives in the Early Miocene, approximately 20.5–21.2 Ma (95 % HPD range: 14.2–29.2 Ma) and 16.8–17.9 Ma (95 % HPD range: 9.0–26.6 Ma), respectively (Fig. 5, Table 1). These timings are remarkably concordant considering these two lineages have evolved independently within the genus. The age estimates are quite ancient and rule out dispersal across a southern Afro-Arabian landbridge (10–5.3 Ma) and overwater dispersal (5.3 Ma to present), but are consistent with the separation of the Arabian Plate from mainland Africa as a result of the Red Sea formation during the Oligocene-Miocene boundary (27–23 Ma) (Fig. 5) [24, 25]. The landbridge spanning the Strait of Bab el Mandeb, which created a dispersal route between Arabian Peninsula and the Horn of Africa, was not established until 10–5.3 Ma. Many of the African-derived terrestrial vertebrate taxa present in the southwestern Arabian Peninsula arrived by dispersing from the Horn of Africa beginning in the late Miocene via a southern land bridge or overwater dispersal events [17, 18, 20, 22] rather than originating as a result of the initial separation of the Arabian plate from Africa. This classifies the Arabian toad species “Bufo” arabicus and “Bufo” tihamicus as true African relicts, a pattern that has only been demonstrated for one other taxon, the viper species Echis coloratus, which also diverged in the Early Miocene [17].
The Asian derived species Duttaphrynus dhufarensis is estimated to have diverged in the mid-Miocene, 12.9–13.5 Ma (95 % HPD range: 7.9–20.9 Ma) (Fig. 6, Table 1). The temporary connections between the Arabian plate and Eurasia established 18–16 Ma are thought to have allowed the first faunal exchanges between these distinct biogeographic regions, with a permanent Eurasian connection being established ~15 Ma [24–26]. The divergence estimates for D. dhufarensis are congruent with the temporal range of these events, and the establishment of land bridges likely served as dispersal routes for this lineage to colonize the Arabian Peninsula.
Following a stepping stone model of dispersal, if the genus Duttaphrynus occurred on mainland Africa, the temporal origins of these lineages would be expected to be younger than the age of D. dhufarensis (13 Ma; 7.9–20.9 Ma). However, with the discovery of the phylogenetic placement of Duttaphrynus dodsoni in the genus Amietophrynus, we find no support for the genus occurring on the Horn of Africa, indicating South Asian-derived bufonid lineages did not successfully complete trans-continental dispersals across the Arabian Peninsula. Additionally, based on our extensive sampling of the Horn of Africa, Arabian Peninsula, and South Asia, we find no evidence for the stepping-stone model of dispersal across the Arabian Peninsula for any African (Amietophrynus) or Asian (Duttaphrynus) bufonid species (Figs. 2-6), as no species of Amietophrynus are found in Iran or Pakistan. This is somewhat unexpected because this model has been invoked to explain ancient Asiatic-African dispersals in multiple groups of ranoid frogs [43]. Additionally, there is evidence suggesting the Persian Gulf region was greatly reduced or dry in the Pleistocene [29, 30]. The apparent lack of dispersals of toad lineages across the Persian Gulf region during this time period is surprising, as population exchanges of the viper species Echis carinatus likely occurred through this route [17].
Taxonomic implications
Based on our sampling strategy and the phylogenetic placement of key species, we recommend several taxonomic changes. The species “Bufo” tihamicus and “Bufo” pentoni form a monophyletic group with all other Amietophrynus, and although they represent the most basal divergence in the group we recommend assignment to the genus, and recognize Amietophrynus tihamicus comb. nov. and Amietophrynus pentoni comb. nov. The assignment of these two species can be further tested through karyotyping, as the 20-chromosome condition is considered apomorphic for this group [44, 45]. If an alternative chromosome condition is discovered in these two species, additional insight into chromosome evolution among bufonids will be gained and their generic assignment can be reconsidered. The Arabian species “Bufo” arabicus can be confidently assigned to the genus Amietophrynus, as Amietophrynus arabicus comb. nov., and Duttaphrynus dodsoni is also transferred to the genus as Amietophrynus dodsoni comb. nov.
The origins of several Arabian bufonids have been investigated, however several lineages require further investigation. The Arabian population of Bufotes cf. variabilis warrants further study to determine its distinctiveness with respect to B. variabilis sensu stricto. This population shares a similar distribution with Hyla felixarabica, a recently described Arabian species that was previously thought to be an isolate of a wider ranging Western Eurasian species complex (Hyla arborea) [15]. Additionally, the relationships of “Bufo” hadramautinus and “Bufo” scorteccii remain speculative. Although “Bufo” hadramautinus is morphologically similar to Amietophrynus arabicus [33], “Bufo” scorteccii is morphologically intermediate between A. arabicus and D. dhufarensis [33]. On this basis, “Bufo” hadramautinus can be tentatively recognized as Amietophrynus hadramautinus comb. nov., but “Bufo” scorteccii remains problematic and should remain unassigned until further study. Although inconvenient, there are major biogeographic implications associated with assignment to particular genera, and this action would circumvent such issues. When population-level sampling becomes available, additional phylogenetic work can clarify if these two geographically restricted lineages are: 1) intraspecific populations of one of the widespread Arabian bufonid species, 2) distinct lineages derived independently from surrounding continental faunas, or 3) distinct lineages resulting from in-situ speciation of an Arabian species, and further taxonomic assessments can be made.
Conclusions
The Arabian Peninsula is home to a unique fauna that has assembled and evolved throughout the course of major geophysical events. The Arabian species assemblage represents an admixture of African, Western Eurasian, and South Asian elements, and this pattern is exemplified even in the relatively depauperate Arabian bufonids. In addition to having South Asian and Western Eurasian lineages, we have identified two lineages independently derived from continental Africa. Our dating estimates strongly suggest Amietophrynus arabicus and A. tihamicus did not colonize the Arabian Peninsula through overwater dispersal or a southern land bridge from the Horn of Africa, rather the formation of the Red Sea likely drove simultaneous divergences in these species. In this sense, they represent true African relicts in their current distribution on the Arabian Peninsula. More importantly, across all dating analyses the relative timing of divergence for these species is considerably older than that for the South Asian derived Duttaphrynus dhufarensis. These results conform to predictions based on geological events that species dispersing to the Arabian Peninsula across Eurasian land bridges should be younger in origin than true African relicts. Our investigation has revealed the stepping-stone hypothesis for trans-continental Afro-Asian bufonid dispersals is not accurate, and we find no evidence for Amietophrynus or Duttaphrynus species distributed outside of their main continental range and the Arabian Peninsula. Further studies of the remaining Arabian amphibian species can test if these biogeographic scenarios hold true for not only bufonids but also other anuran families. These amphibian studies and comparative studies of other terrestrial vertebrates can provide a clearer picture of the diversification of the unique faunal assemblage present on the Arabian Peninsula.
Methods
Taxon sampling
Due to the uncertainty of the phylogenetic placement of Arabian bufonid taxa, we sampled broadly across the family Bufonidae with an emphasis on regions directly surrounding the Arabian Peninsula (Table 2). We generated new multi-locus sequence data for 114 bufonid samples from 21 recognized species distributed across the Horn of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, and Southwest Asia (Table 2, Additional file 2).
Table 2.
New sampling of taxa included for this study
| Species | Museum no. | Latitude | Longitude | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amietophrynus arabicus* | CAS 250888 | 25.2651 | 56.3068 | Oman |
| CAS 250889 | 25.2651 | 56.3068 | Oman | |
| CAS 250890 | 25.2651 | 56.3068 | Oman | |
| CAS 250907 | 25.387 | 56.2649 | Oman | |
| CAS 250908 | 25.387 | 56.2649 | Oman | |
| CAS 251024 | 22.6052 | 59.0886 | Oman | |
| CAS 251026 | 22.6052 | 59.0886 | Oman | |
| CAS 251027 | 22.6052 | 59.0886 | Oman | |
| CAS 251126 | 20.6888 | 58.2949 | Oman | |
| CAS 251127 | 20.6888 | 58.2949 | Oman | |
| CAS 251130 | 20.6888 | 58.2949 | Oman | |
| CAS 251147 | 23.0548 | 57.4679 | Oman | |
| CAS 251148 | 23.0548 | 57.4679 | Oman | |
| CAS 251149 | 23.0548 | 57.4679 | Oman | |
| CAS 251166 | 23.0713 | 57.6042 | Oman | |
| CAS 251167 | 23.0713 | 57.6042 | Oman | |
| MVZ 236403 | 15.3443 | 44.217 | Yemen | |
| MVZ 236407 | 15.4693 | 44.2618 | Yemen | |
| MVZ 236866 | 24.2633 | 56.1633 | Oman | |
| MVZ 241304 | 23.0525 | 57.4691 | Oman | |
| MVZ 241305 | 23.0525 | 57.4691 | Oman | |
| MVZ 241306 | 23.0713 | 57.6043 | Oman | |
| MVZ 241307 | 23.0713 | 57.6043 | Oman | |
| Amietophrynus asmarae | MVZ 257839 | Ethiopia | ||
| MVZ 257840 | Ethiopia | |||
| MVZ 257843 | Ethiopia | |||
| MVZ 257844 | Ethiopia | |||
| MVZ 257847 | Ethiopia | |||
| MVZ 257848 | Ethiopia | |||
| MVZ 257849 | Ethiopia | |||
| MVZ 257850 | Ethiopia | |||
| MVZ 257852 | Ethiopia | |||
| Amietophrynus blandfordii | MVZ 241309 | 9.9493 | 43.2193 | Somalia |
| MVZ 241313 | 9.9698 | 43.4325 | Somalia | |
| MVZ 241314 | 9.9698 | 43.4325 | Somalia | |
| MVZ 241316 | 9.9698 | 43.4325 | Somalia | |
| MVZ 241317 | 9.9698 | 43.4325 | Somalia | |
| MVZ 241318 | 9.9698 | 43.4325 | Somalia | |
| MVZ 242725 | 11.0261 | 49.193 | Somalia | |
| Amietophrynus dodsoni* | MVZ 241310 | 9.9493 | 43.2193 | Somalia |
| MVZ 241312 | 9.9493 | 43.2193 | Somalia | |
| Amietophrynus garmani | MVZ 257841 | Ethiopia | ||
| MVZ 257846 | Ethiopia | |||
| Amietophrynus mauritanicus | MVZ 235679 | 36.9641 | 8.8822 | Tunisia |
| Amietophrynus pentoni* | MVZ 235732 | 16.5796 | −15.8735 | Mauritania |
| MVZ 249297 | 9.24191 | −1.84415 | Ghana | |
| MVZ 249298 | 9.24191 | −1.84415 | Ghana | |
| Amietophrynus regularis | MVZ 235735 | 16.5165 | −15.8135 | Mauritania |
| MVZ 238858 | 13.5036 | 2.1135 | Niger | |
| MVZ 238859 | 13.5036 | 2.1135 | Niger | |
| MVZ 249302 | 9.259 | −1.8541 | Ghana | |
| Amietophrynus steindachneri | MVZ 234101 | −3.1999 | 40.0077 | Kenya |
| MVZ 234102 | −3.1999 | 40.0077 | Kenya | |
| Amietophrynus tihamicus* | MVZ 236409 | 14.8238 | 43.1273 | Yemen |
| MVZ 236413 | 14.8238 | 43.1273 | Yemen | |
| Amietophrynus xeros | MVZ 235737 | 16.5165 | −15.8135 | Mauritania |
| MVZ 238867 | 17.3868 | 7.9563 | Niger | |
| MVZ 238868 | 17.3868 | 7.9563 | Niger | |
| “Bufo” sp. | MVZ 242731 | 11.2493 | 49.2678 | Somalia |
| MVZ 242732 | 11.2493 | 49.2678 | Somalia | |
| MVZ 242733 | 11.2493 | 49.2678 | Somalia | |
| MVZ 242776 | 11.0261 | 49.193 | Somalia | |
| Bufotes oblongus | MVZ 241548 | 36.2797 | 60.548 | Iran |
| MVZ 245904 | 32.8198 | 59.2171 | Iran | |
| MVZ 245905 | 32.8198 | 59.2171 | Iran | |
| MVZ 245906 | 32.8198 | 59.2171 | Iran | |
| MVZ 245910 | 33.631 | 57.1616 | Iran | |
| MVZ 245911 | 33.631 | 57.1616 | Iran | |
| MVZ 245912 | 33.631 | 57.1616 | Iran | |
| MVZ 245917 | 35.9666 | 56.0684 | Iran | |
| MVZ 248374 | 36.2688 | 60.5357 | Iran | |
| MVZ 248376 | 37.7194 | 55.9001 | Iran | |
| MVZ 249177 | 37.7332 | 55.9006 | Iran | |
| MVZ 249178 | 37.7332 | 55.9006 | Iran | |
| Bufotes pseudoraddei | MVZ 241550 | 36.5 | 74.8666 | Pakistan |
| MVZ 241551 | 36.5 | 74.8666 | Pakistan | |
| MVZ 241552 | 36.5 | 74.8666 | Pakistan | |
| MVZ 241553 | 35.8833 | 71.7833 | Pakistan | |
| MVZ 241554 | 36.0663 | 72.5166 | Pakistan | |
| MVZ 248375 | 36.5 | 74.87 | Pakistan | |
| Bufotes surdus | MVZ 234217 | 29.4441 | 60.5136 | Iran |
| MVZ 234218 | 29.4441 | 60.5136 | Iran | |
| MVZ 234219 | 29.4441 | 60.5136 | Iran | |
| MVZ 234238 | 27.8763 | 60.0955 | Iran | |
| MVZ 234239 | 28.6066 | 61.0771 | Iran | |
| MVZ 234240 | 28.6066 | 61.0771 | Iran | |
| Bufotes variabilis | MVZ 234222 | 32.9395 | 48.2558 | Iran |
| MVZ 234223 | 32.9395 | 48.2558 | Iran | |
| MVZ 234241 | 31.2133 | 49.2173 | Iran | |
| MVZ 234242 | 31.2133 | 49.2173 | Iran | |
| MVZ 238503 | 29.615 | 52.5386 | Iran | |
| Duttaphrynus dhufarensis | MVZ 241308 | 26.1503 | 56.1606 | Oman |
| MVZ 242729 | 23.0655 | 57.4701 | Oman | |
| MVZ 242774 | 17.1001 | 54.284 | Oman | |
| MVZ 242775 | 23.0655 | 57.4701 | Oman | |
| Duttaphrynus himalayanus | MVZ 241543 | 28.598 | 83.6469 | Himalayas |
| MVZ 241544 | 28.598 | 83.6469 | Himalayas | |
| Duttaphrynus melanostictus | MVZ 226298 | 21.4536 | 105.6436 | Vietnam |
| MVZ 239140 | −3.957 | 122.5315 | Indonesia | |
| Duttaphrynus olivaceus | MVZ 234225 | 27.2035 | 60.6785 | Iran |
| MVZ 234226 | 27.1853 | 60.5895 | Iran | |
| MVZ 234227 | 27.1853 | 60.5895 | Iran | |
| MVZ 234228 | 27.1853 | 60.5895 | Iran | |
| MVZ 234235 | 25.2563 | 60.8326 | Iran | |
| MVZ 234236 | 25.2563 | 60.8326 | Iran | |
| MVZ 234237 | 25.2703 | 60.7553 | Iran | |
| Duttaphrynus stomaticus | MVZ 237424 | 34.4366 | 70.4483 | Afghanistan |
| MVZ 248377 | 25.7768 | 66.6256 | Pakistan | |
| MVZ 248378 | 25.7768 | 66.6256 | Pakistan | |
| MVZ 248379 | 25.7768 | 66.6256 | Pakistan | |
| MVZ 248380 | 24.3516 | 70.7573 | Pakistan | |
| MVZ 248382 | 24.3516 | 70.7573 | Pakistan | |
| MVZ 248383 | 24.3516 | 70.7573 | Pakistan | |
| Duttaphrynus stuarti | CAS 242587 | 27.7746 | 98.3354 | China |
Museum numbers in bold represent samples included in the dating analyses. Complete information about gene sampling is included in Additional file 2. Asterisks indicate new name combinations for species.
DNA extraction and amplification
Whole genomic DNA was extracted from liver samples using a high-salt DNA extraction [46]. We obtained a combination of sequence data from two mitochondrial markers, NADH dehydrogenase subunit 2 (ND2) and 16S ribosomal RNA (16S), and partial exonic sequence from the nuclear markers Recombination activating gene 1 (RAG1). The three loci (ND2, 16S, and RAG1) were amplified using the primer pairs 16SA and 16SB [47] for the 16S rRNA partial gene fragment, MET F1 L4437 and TRP R3 [48] for the ND2 partial gene fragment, and the primer pairs MartF1 and AmpR1 [49] were used to amplify RAG1.
Polymerase chain reactions (PCRs) were carried out in 12.5 μl volumes consisting of: 1.25 μl Roche 10x (500 mM Tris/HCl, 100 mM KCl, 50 mM (NH4)2 SO4, 20 mM MgCl2, pH = 8.3), 0.75 μl 25 mM MgCl2, 0.75 μl 2 mM DNTPs, 0.25 μl 10.0 μM forward primer, 0.25 μl 10.0 μM reverse primer, 8.40 μl H2O, 0.10 μl Taq, and 0.75 μl DNA. Amplification of both ND2 and 16S involved initial denaturation at 94 °C for 4 min, followed by 35 cycles of 95 °C for 60 s, 51 °C for 60 s, 72 °C for 90 s, and a final extension at 72 °C for 7 min. The amplification of RAG1 followed the extended touchdown gradient reported by [41], and involved initial denaturation at 95 °C for 4 min, followed by a first program of 15 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 60 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 90 s (decreasing annealing temperature by −1 °C per cycle), then a second program consisting of 20 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 45 °C for 30 s, and 72 °C for 60 s, with a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min.
The PCR amplifications were visualized on an agarose gel and cleaned using ExoSAP-IT (USB). Gene products were sequenced using BigDye v3.1 on an ABI3730 (Applied Biosystems). Newly generated sequences were edited using Geneious Pro [50]. All newly generated sequences are deposited in GenBank (Accession numbers: KT031406–KT031518 [16S]; KT031519–KT031601 [ND2]; KT031602–KT031708 [RAG-1]).
GenBank sampling
To provide the most updated bufonid phylogeny for placing our focal taxa, we included GenBank data of representatives of all available unique bufonids (234 species, 39 genera) and several outgroups (seven species) (Additional file 2). The resulting data matrix is largely based on the alignment produced by Pyron and Wiens [39] for their comprehensive analysis of amphibian sequence data (Dryad repository doi:10.5061/dryad.vd0m7). Their matrix was composed of 12 loci: nine nuclear genes consisting of C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), histone 3a (H3A), sodium–calcium exchanger (NCX1), pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC), recombination-activating gene 1 (RAG1), rhodopsin (RHOD), seventh-in-absentia (SIA), solute-carrier family 8 (SLC8A3), and tyrosinase (TYR); and three mtDNA loci including cytochrome b (cyt-b), and the large and small sub-units of the mitochondrial ribosome genes (12S/16S; without tRNAs). We conducted GenBank searches for additional taxa not included in this data matrix, and we added sequence data for NADH dehydrogenase subunit 2 (ND2), which has been sequenced for many bufonid taxa. The final data matrix containing both GenBank and newly generated sequence data consists of 243 bufonid lineages and 7 outgroup species. The taxonomy of the family Bufonidae has been under revision, and names of several genera have been changed to reflect evolutionary relationships [34, 35]. Species names were updated accordingly and are here presented using the newest taxonomy from AmphibiaWeb [34] and the Amphibian Species of the World v6.0 [35]. GenBank numbers for all sequence data included are given in Additional file 2.
Sequence alignment
All protein-coding genes were aligned using MUSCLE [51], and subsequently translated to ensure conservation of reading frame. The 12S and 16S sequences were initially aligned using Clustal Omega [52], manually adjusted by eye, and poorly aligned regions were trimmed from the alignment. Trimmed sequences were then realigned using Clustal Omega, with some slight manual adjustments. The final concatenated alignment consists of 13 loci, 250 taxa, and 10,492 base pairs. The matrix is composed of the following data: 12S, 215 sequences (85 %, 1,011 bp); 16S, 236 sequences (93 %, 1,223 bp); cyt-b, 91 sequences (36 %, 1,122 bp); ND2, 78 sequences (30 %, 1,035 bp); CXCR4, 114 sequences (45 %, 732 bp); H3A, 38 sequences (15 %, 328 bp); NCX1, 60 sequences (23 %, 1,275 bp); POMC, 69 sequences (27 %, 550 bp); RAG1, 101 sequences (40 %, 840 bp); RHOD, 38 sequences (15 %, 315 bp); SIA, 40 sequences (16 %, 397 bp); SLC8A3, 14 sequences (5 %, 1,132 bp); and TYR, 12 sequences (4 %, 532 bp). The mean sequence length is 3,185 bp, and the range in length across taxa is 375 to 7,886 bp. The proportion of missing data across the matrix is approximately 70 %. The full alignment is provided in Additional file 3.
Phylogenetic analyses
We used PartitionFinder to simultaneously determine our best partitioning strategy and models for each partition subset [53]. The greedy search algorithm was employed, and model selection was conducted using the Bayesian information criterion (BIC). Due to the large size and complexity of the molecular data set, we did not allow for partitioning of genes by codon position. The best partitioning scheme of the full data set includes four gene partitions: 12S and 16S: GTR + G + I; ND2 and cyt-b: GTR + G + I; RHOD, SIA, TYR: HKY + G; and CXCR4, H3A, NCX1, POMC, RAG1, and SLC8A3: GTR + G + I. We conducted Bayesian analyses using MrBayes v3.2 [54, 55], and parallel runs utilizing four MCMC chains were allowed to run for 2×107 million generations, with sampling every 1000 generations. Runs were assessed using Tracer v1.6 [56] to ensure key parameters had reached stationarity (ESS values >150). The first 25 % of the total number of generations were discarded as burn-in and a maximum clade credibility tree was calculated from the remaining trees (30,000) using TreeAnnotator v1.8.1 [57]. We performed maximum likelihood analyses of the partitioned data set using GARLI v2.0 [58]. Using default parameters in the ML search algorithm, 10 replicate searches for the best point estimate topology were conducted, and the tree with the best likelihood was selected as a guide tree for the bootstrap analyses. The Garli Web Service [59], functioning on the Lattice Project grid system [60], was used to execute 1000 nonparametric bootstrap replicates asynchronously in parallel using the default stopping criteria. A maximum clade credibility tree was generated from the 1000 replicates using TreeAnnotator v1.8.1 [57].
Divergence dating analyses
To infer the timing of lineage divergences of sampled Arabian amphibian taxa, we carried out dating analyses in BEAST v1.8.1 [57]. We included four internal calibration points, following recommendations of [36, 37]:
-
(A)
A minimum age of 20 million years (Myr) for the split between North- and Central America based on the fossil Bufo praevis [61]. This was enforced using a lognormal distribution with real space mean of 10, log(stdev) of 1, offset of 19, and initial value of 21, creating the following credibility interval: 5 % = 20.1, 95 % = 50.4.
-
(B)
A minimum age of 18 Mya for the stem origin of toads belonging to the Bufotes viridis complex [62, 63]. This was enforced using a lognormal distribution with real space mean of 10, log(stdev) of 1, offset of 17, and initial value of 19, creating the following credibility interval: 5 % = 18.1, 95 % = 48.4.
-
(C)
A minimum age of 11 Myr for the origin of the Rhinella marina group (sensu [64]) based on a fossil from the Middle Miocene [65]. This was enforced using a lognormal distribution with real space mean of 10, log(stdev) of 1, offset of 10, and initial value of 12, creating the following credibility interval: 5 % = 11.1, 95 % = 41.4.
-
(D)
A minimum age of 9.6 Myr for the origin of toads belonging to the Bufo bufo group based on the appearance of a Bufo bufo fossil from the Miocene of Europe [62]. This was enforced using a lognormal distribution with real space mean of 10, log(stdev) of 1, offset of 8, and initial value of 9, creating the following credibility interval: 5 % = 9.1, 95 % = 39.4.
In addition, we used a minimal constraint on the family Bufonidae for the oldest known bufonid fossils recovered from Paleocene deposits in both Brazil and France [66–68]. This was enforced using three different approaches: 1) a lognormal distribution with a real space mean of 15, log(stdev) of 1, offset of 55, and initial value of 65, producing a credibility interval of (5 % = 56.1, 95 % = 102.1); 2) a normal distribution with a mean of 80, a standard deviation of 14, and initial value of 65, creating a credibility interval of (5 % = 56.9, 95 % = 103); and 3) an exponential distribution with a mean of 20, offset of 57, and initial value of 60, producing a credibility interval of (5 % = 58.0, 95 % = 116.9).
Dating analyses were initially run using the full molecular data set of 13 loci and 253 taxa; analyses behaved very poorly and failed to converge even after several hundred million generations. Therefore, the data set was reduced to include only the most well sampled genes: 12S, 16S, ND2, CXCR4, and RAG1. Data were grouped into three partitions: 1) 12S and 16S, 2) ND2, and 3) CXCR4 and RAG1. Inclusion of taxa in the reduced data set required partial sequences for at least two of these three partitions. The final alignment for all subsequent dating analyses included 132 taxa, 5 loci, and 4,840 bp. The average sequence length was 3,051 bp, with a range of 811 to 4,640 bp, and the alignment contained 37 % missing data.
Dating analyses were run for 2×107 generations with sampling every 2000 generations. For all analyses, we used the Yule model of speciation as our tree prior, applied an uncorrelated relaxed lognormal clock, and unlinked clock and substitution models. The partitioning scheme and substitution models are as follows: 12S and 16S: GTR + G + I; ND2: GTR + G + I; CXCR4 and RAG1: GTR + G + I. Runs were assessed using Tracer v1.6 [56] to examine convergence. A burn-in of 25 % was discarded and maximum clade credibility trees were created from a total of 7,500 trees for each analysis.
To explore the effects of calibration choices, we ran multiple analyses with different combinations of calibrations enforced. Fixing the age of the Bufonidae, we explored every permutation of the internal calibrations resulting in 14 sets of analyses (Additional file 4). These 14 analyses revealed that various combinations of calibrations had little overall effect on dating results throughout the tree (Additional file 4). We therefore focused on exploring the effects of the shape of the calibration prior for the age of the Bufonidae in our final dating analyses. This produced three analyses: (A1) all four internal calibrations with a lognormal prior for the Bufonidae, (A2) all four internal calibrations with a normal distribution prior for the Bufonidae, and (A3) all four internal calibrations with an exponential prior for the Bufonidae. Input xml files of these analyses and resulting consensus trees are available from the Dryad Digital Repository: http://dx.doi.org/10.5061/dryad.bc578 [69].
Acknowledgments
T.J.P. thanks Ali Al Kiyumi, Ministry of Environment and Climate Affairs issued Oman for collecting and export permits, the American Institute for Yemeni Studies for facilitating fieldwork in Yemen, Abdurahman A. Osman, Director of the Puntland Development Research Center for arranging fieldwork in Puntland State, Somalia, Suleiman Ahmed Gulaid, President of Amoud University, Borama, Somaliland for facilitating fieldwork in Somaliland. Partial funding for T.J.P’s fieldwork was provided by a grant from the George Lindsay Field Research Fund of the California Academy of Sciences. Molecular work was funded in part by the Museum of Vertebrate Zoology of the University of California, Berkeley. D.M.P. was funded by teaching assistantships awarded by the Integrative Biology Department of the University of California, Berkeley. We thank J.A. McGuire, D.C. Blackburn, R.C.K. Bowie, S.M. Rovito, S. Hykin, P. Skipwith, and R. von May for comments on a prior version of a combined manuscript, R.C. Bell for comments on this manuscript, and H.C. Liedtke for comparisons of unpublished bufonid molecular data. We thank Václav Gvoždík, Ines Van Bocxlaer, and one anonymous reviewer for helpful comments on the first submission and resubmission of this manuscript.
Additional files
Phylogeny of the Bufonidae. A complete full-length version of Fig. 2.
Taxon Sampling. Voucher, locality information, and gene sampling of new specimens, and GenBank numbers of published data.
Final Alignment. Full nexus alignment of 13 loci and 250 taxa, and relevant data partitions.
Internal Calibration Dating Results. Dating estimates for nodes of interest under all permutations of the four internal calibrations.
Labeled Chronogram. The chronogram resulting from dating analysis A1 (lognormal prior on Bufonidae) with calibrated nodes highlighted and all nodes numbered.
Dating Comparisons Across Chronogram Nodes. A supporting table with all numbered node age estimates and intervals.
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
DMP and TJP conceived of the study. TJC conducted all fieldwork and funded all molecular work. DMP performed all lab work and analyses. DMP wrote the manuscript with contributions from TJP, and both authors approved of the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Daniel M. Portik, Email: daniel.portik@berkeley.edu
Theodore J. Papenfuss, Email: asiaherp@berkeley.edu
References
- 1.Mittermeier RA, Myers N, Gil PR, Mittermeier CG. Hotspots: Earth's Biologically Richest and Most Endangered Terrestrial Ecoregions. Monterrey: Cemex, Conservation International and Agrupacion Sierra Madre; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG, da Fonseca GAB, Kent J. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature. 2000;403:853–858. doi: 10.1038/35002501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fisher M, Membery DA. Climate. In: Ghazanfar SA, Fisher M, editors. Vegetation of the Arabian Peninsula. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1998. pp. 5–38. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gasperetti J. Snakes of Arabia. In: Büttiker W, Krupp F, editors. Fauna of Saudi Arabia, Vol. 9. Basle: Pro Entomologia, Natural History Museum; 1988. pp. 169–450. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Guba I, Glennie K. Geology and geomorphology. In: Ghazanfar SA, Fisher M, editors. Vegetation of the Arabian Peninsula. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1998. pp. 39–62. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Joger U. An interpretation of reptile zoogeography in Arabia, with special reference to Arabian herpetofaunal relations with Africa. In: Krupp F, Schneider W, Kinzelbach, editors. Proceedings of the Symposium on the Fauna and Zoogeography of the Middle East. Göttingen: R. Hubert & Co; 1987. pp. 257–271. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kürschner H. Biogeography and introduction to vegetation. In: Ghazanfar SA, Fisher M, editors. Vegetation of the Arabian Peninsula. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1998. pp. 63–98. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mallon DP. Global hotspots in the Arabian Peninsula. Zool Middle East. 2011;54(Supplementum 3):13–20. doi: 10.1080/09397140.2011.10648896. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Meister J, Hubaishan MA, Kilian N, Oberprieler C. Chloroplast DNA variation in the shrub Justicia areysiana (Acanthaceae) endemic to the monsoon affected coastal mountains of the southern Arabian Peninsula. Bot J Linn Soc. 2005;148:437–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8339.2005.00421.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Meister J, Hubaishan MA, Kilian N, Oberprieler C. Temporal and spatial diversification of the shrub Justicia areysiana Deflers (Acanthaceae) endemic to the monsoon affected coastal mountains of the southern Arabian Peninsula. Plant Systs Evol. 2006;262:153–171. doi: 10.1007/s00606-006-0459-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Miller AG, Cope TA. Flora of the Arabian Peninsula and Socotra. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vesey-Fitzgerald DF. Vegetation of the Red Sea coast south of Jedda, Saudi Arabia. J Ecol. 1955;43:477–489. doi: 10.2307/2257008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Vesey-Fitzgerald DF. The vegetation of central and eastern Arabia. J Ecol. 1957;45:779–798. doi: 10.2307/2256957. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Amer SAM, Kumazawa Y. Mitochondrial DNA sequences of the Afro-Arabian spiny-tailed lizards (genus Uromastyx; family Agamidae): phylogenetic analyses and evolution of gene arrangements. Biol J Linn Soc. 2005;85:247–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8312.2005.00485.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gvoždík V, Moravec J, Klüsch C, Kotlík P. Phylogeography of the Middle Eastern tree frogs (Hyla, Hylidae, Amphibia) as inferred from nuclear and mitochondrial DNA variation, with a description of a new species. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2010;55:1146–1166. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2010.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Metallinou M, Arnold NE, Crochet PA, Geniez P, Brito JC, Lymberakis P, El Din SB, Sindaco R, Robinson M, Carranza S. Conquering the Sahara and Arabian deserts: Systematics and biogeography of Stenodactylus geckos (Reptilia: Gekkonidae) BMC Evol Biol. 2012;12:258. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-12-258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pook CE, Joger U, Stümpel N, Wüster W. When continents collide: phylogeny, historical biogeography and systematics of the medically important viper genus Echis (Squamata: Serpentes: Viperidae) Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2009;53:792–807. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2009.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Portik DM, Papenfuss TJ. Monitors cross the Red Sea: the biogeographic history of Varanus yemenensis. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2012;62:561–565. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2011.09.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Šmíd J, Carranza S, Kratochvíl L, Gvoždík V, Nasher AK, Moravec J. Out of Arabia: A complex biogeographic history of multiple vicariance and dispersal events in the Gecko genus Hemidactylus (Reptilia: Gekkonidae) PLoS ONE. 2013;8(5) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wong RA, Fong JJ, Papenfuss TJ. Phylogeography of the African helmeted terrapin, Pelomedusa subrufa: genetic structure, dispersal, and human introduction. Proc Calif Acad Sci. 2010;61:575–585. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yu X-Q, Maki M, Drew BT, Paton AJ, Li H-W, Zhao J-L, Conran JG, Li J. Phylogeny and historical biogeography of Isodon (Lamiaceae): Rapid radiation in south-west China and Miocene overland dispersal into Africa. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2014;77:183–194. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2014.04.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zinner D, Groeneveld LF, Keller C, Roos C. Mitochondrial phylogeography of baboons (Papio spp.) – indication for introgressive hybridization? BMC Evol Biol. 2009;9:1–15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-9-83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bohannon RG. Tectonic configuration of the western Arabian continental margin, southern Red Sea. Tectonics. 1986;5:477–499. doi: 10.1029/TC005i004p00477. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bosworth W, Huchon P, McClay K. The Red Sea and Gulf of Aden Basins. J Afr Earth Sci. 2005;43:334–378. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2005.07.020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rögl F. Paleogeographic considerations for Meditteranean and Paratethys seaways (Oligocene to Miocene) Ann Naturhist Mus Wien. 1998;99A:279–310. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rögl F. Mediterranean and Paratethys. Facts and hypotheses of an Oligocene to Miocene paleogeography (short overview) Geol Carpath. 1999;50:339–349. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rohling EJ, Fenton M, Jorissen FJ, Bertrand P, Ganssen G, Caulet JP. Magnitudes of sea-level lowstands of the past 500,000 years. Nature. 1998;394:162–165. doi: 10.1038/28134. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fernandes CA, Rohling EJ, Siddall M. Absence of post-Miocene Red Sea land bridges: biogeographic implications. J Biogeogr. 2006;33:961–966. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2699.2006.01478.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lambeck K. Shoreline reconstructions for the Persian Gulf since the last glacial maximum. Earth Planet Sc Lett. 1996;142:43–57. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(96)00069-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Uchupi E, Swift SA, Ross DA. Late Quaternary stratigraphy, Paleoclimate and neotectonism of the Persian (Arabian) Gulf region. Mar Geol. 1999;160:1–23. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00011-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.deMenocal PB. Plio-Pleistocene African Climate. Science. 1995;270:53–59. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5233.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.deMenocal PB. African climate change and faunal evolution during the Pliocene-Pleistocene. Earth Planet Sc Lett. 2004;220:3–24. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00003-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Balletto E, Cherchi MA, Gasperetti J. Amphibians of the Arabian Peninsula. In: Büttiker W, Krupp F, editors. Fauna of Saudi Arabia, vol. 7. Basle: Pro Entomologia, Natural History Museum; 1985. pp. 318–392. [Google Scholar]
- 34.AmphibiaWeb. Information on amphibian biology and conservation. AmphibiaWeb. Berkeley, California; 2014. [http://amphibiaweb.org]
- 35.Frost DR, Grant T, Faivovich J, Bain RH, Haas A, Haddad CFB, Channing A, Wilkinson M, Donnellan SC, Raxworthy CJ, Campbell JA, Blotto BL, Moler P, Drewes RC, Nussbaum RA, Lynch JD, Green DM, Wheeler WC. The amphibian tree of life. B Am Mus Nat Hist. 2006;297:1–370. doi: 10.1206/0003-0090(2006)297[0001:TATOL]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pramuk JB, Robertson T, Sites JW, Noonan BP. Around the world in 10 million years: biogeography of the nearly cosmopolitan true toads (Anura: Bufonidae) Global Ecol Biogeogr. 2008;17:72–83. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Van Bocxlaer I, Biju SD, Loader SP, Bossuyt F. Toad radiation reveals into-India dispersal as a source of endemism in the Western Ghats-Sri Lanka biodiversity hotspot. BMC Evol Biol. 2009;9:131. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-9-131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Van Bocxlaer I, Loader SP, Roelants K, Biju SD, Menegon M, Bossuyt F. Gradual adaptation toward a range-expansion phenotype initiated the global radiation of toads. Science. 2010;327:679–682. doi: 10.1126/science.1181707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pyron RA, Wiens JJ. A large-scale phylogeny of Amphibia including over 2800 species, and a revised classification of extant frogs, salamanders, and caecilians. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2011;61:543–583. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2011.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Frost DR. Amphibian Species of the World: an Online Reference. Version 6.0. New York: American Museum of Natural History; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Stöck M, Moritz C, Hickerson M, Frynta D, Dujsebayeva T, Eremchenko V, Macey RJ, Papenfuss TJ, Wake DB. Evolution of mitochondrial relationships and biogeography of Palearctic green toads (Bufo viridis subgroup) with insights in their genomic plasticity. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2006;41:663–689. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2006.05.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schätti B, Desvoignes A. The herpetofauna of southern Yemen and the Socotran Archipelago. Instrumenta Biodiversitatis. 1999;4:1–178. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kosuch J, Vences M, Dubois A, Ohler A, Böhme W. Mitochondrial DNA evidence for an Oriental origin of Tiger Frogs, genus Hoplobatrachus. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2001;21:398–407. doi: 10.1006/mpev.2001.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cunningham M, Cherry MI. Molecular systematics of African 20-chromosome toads (Anura: Bufonidae) Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2004;32:671–685. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2004.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bogart JP. Chromosome number difference in the amphibian genus Bufo: the Bufo regularis species group. Evolution. 1968;22:42–45. doi: 10.2307/2406648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Aljanabi S, Martinez I. Universal and rapid salt-extraction of high quality genomic DNA for PCR-based techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:4692–4693. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.22.4692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Palumbi S, Martin A, Romano S, McMillan WO, Stice L, Grabowski G. The Simple Fool’s Guide to PCR. Version 2. Honolulu: University of Hawaii; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Macey RJ, Larson A, Ananjeva NB, Fang Z, Papenfuss TJ. Two novel gene orders and the role of light-strand replication in rearrangement of the vertebrate mitochondrial genome. Mol Biol Evol. 1997;14:91–104. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a025706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hoegg S, Vences M, Brinkmann H, Meyer A. Phylogeny and comparative substitution rates of frogs inferred from sequences of three nuclear genes. Mol Biol Evol. 2004;21:1188–1200. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Drummond AJ, Ashton B, Buxton S, Cheung M, Cooper A, Duran C, et al. Geneious v5.4. 2011. [http://www.geneious.com]
- 51.Edgar RC. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucl Acids Res. 2004;32:1792–1797. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen DG, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, Li W, Lopez R, McWilliam H, Remmert M, Söding J, Thompson JD, Higgins D. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol. 2011;7:Article 539. doi: 10.1038/msb.2011.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lanfear R, Calcott B, Ho SYW, Guindon S. PartitionFinder: combined selection of partitioning schemes and substitution models for phylogenetic analyses. Mol Biol Evol. 2012;29:1695–1701. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mss020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics. 2001;17:754–755. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/17.8.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:1572–1574. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Rambaut A, Drummond AJ. Tracer v1.5.0 and higher. 2009. [http://beast.bio.ed.ac.uk]
- 57.Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Xie D, Rambaut A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol Biol Evol. 2012;29:1969–1973. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mss075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zwickl DJ. Genetic algorithm approaches for the phylogenetic analysis of large biological sequence datasets under the maximum likelihood criterion. PhD thesis. Austin: The University of Texas at Austin; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Bazinet AL, Cummings MP. 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing Workshops and Phd Forum. 2011. Computing the Tree of Life — Leveraging the power of desktop and service grids (IPDPSW) pp. 1896–1902. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Bazinet AL, Cummings MP. The Lattice Project: a grid research and production environment combining multiple grid computing models. In: Weber MHW, editor. Distributed & Grid Computing - Science Made Transparent for Everyone. Principles, Applications and Supporting Communities. Marburg: Rechenkraft.net; 2008. pp. 2–13. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Tihen JA. Anuran remains from the Miocene of Florida, with the description of a new species of Bufo. Copeia. 1951;3:230–235. doi: 10.2307/1439102. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Rage J-C, Rocek Z. Evolution of anuran assemblages in the Tertiary and Quaternary of Europe, in the context of palaeoclimate and palaeogeography. Amphibia-Reptilia. 2003;24:133–167. doi: 10.1163/156853803322390408. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Böhme M. The Miocene climatic optimum: Evidence from ectothermic vertebrates of Central Europe. Palaeogeogr Palaeocl. 2003;195:389–401. doi: 10.1016/S0031-0182(03)00367-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Maciel NM, Collevatti RG, Colli GR, Schwartz EF. Late Miocene diversification and phylogenetic relationships of the huge toads in the Rhinella marina (Linnaeus, 1758) species group (Anura: Bufonidae) Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2010;57:787–797. doi: 10.1016/j.ympev.2010.08.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sanchíz B. Salientia. In: Wellnhofer P, editor. Handbuch der paläoherpetologie Volume Part 4. Munich: Verlag Dr. Friedrich Pfeil; 1998. pp. 1–275. [Google Scholar]
- 66.Estes R, Reig OA. The early fossil record of frogs: A review of the evidence. In: Vial JL, editor. Evolutionary Biology of the Anurans. Columbia: University of Missouri Press; 1973. pp. 11–63. [Google Scholar]
- 67.Estes R, Báez AM. Herpetofaunas of North and South America during the Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic: Evidence for interchange? In: Stehli FG, Webb SD, editors. The Great American Biotic Interchange. New York: Springer Science and Business Media LLC; 1985. pp. 139–197. [Google Scholar]
- 68.Rage J-L. Oldest Bufonidae (Amphibia, Anura) from the Old World: A bufonid from the Paleocene of France. J Vertebr Paleontol. 2003;23:462–463. doi: 10.1671/0272-4634(2003)023[0462:OBAAFT]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Portik, DM, Papenfuss TJ (2015): Dating analysis files and consensus trees for the Bufonidae. Dryad Digital Repository. http://dx.doi.org/10.5061/dryad.bc578


