Abstract
A cell free system that supports replication-dependent chromatin assembly has been used to determine the mechanism of histone deposition during DNA replication. CAF-I, a human cell nuclear factor, promotes chromatin assembly on replicating SV40 DNA in the presence of a crude cytosol replication extract. Biochemical fractionation of the cytosol extract has allowed separation of the chromatin assembly reaction into two steps. During the first step, CAF-I targets the deposition of newly synthesized histones H3 and H4 to the replicating DNA. This reaction is dependent upon and coupled with DNA replication, and utilizes the newly synthesized forms of histones H3 and H4, which unlike bulk histone found in chromatin, do not bind to DNA by themselves. The H3/H4-replicated DNA complex is a stable intermediate which exhibits a micrococcal nuclease resistant structure and can be isolated by sucrose gradient sedimentation. In the second step, this replicated precursor is converted to mature chromatin by the addition of histones H2A and H2B in a reaction that can occur after DNA replication. The requirement for CAF-I in at least the first step of the reaction suggests a level of cellular control for this fundamental process.
Full text
PDF


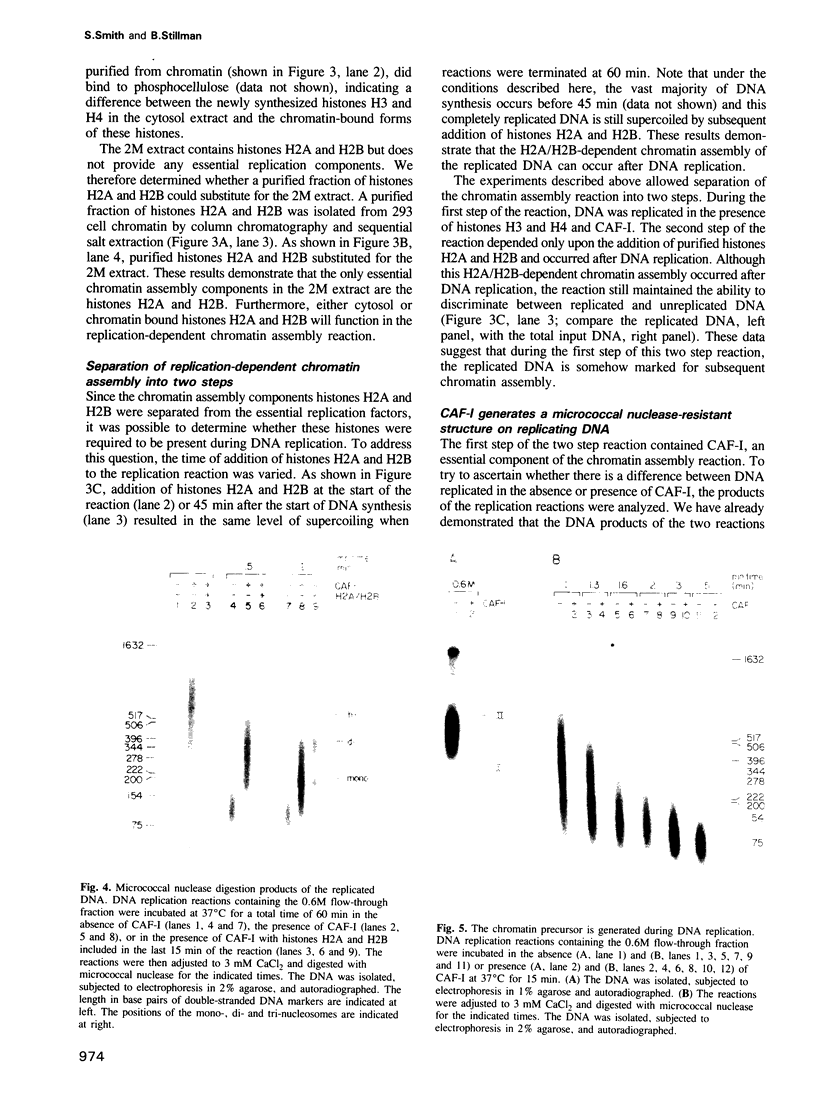
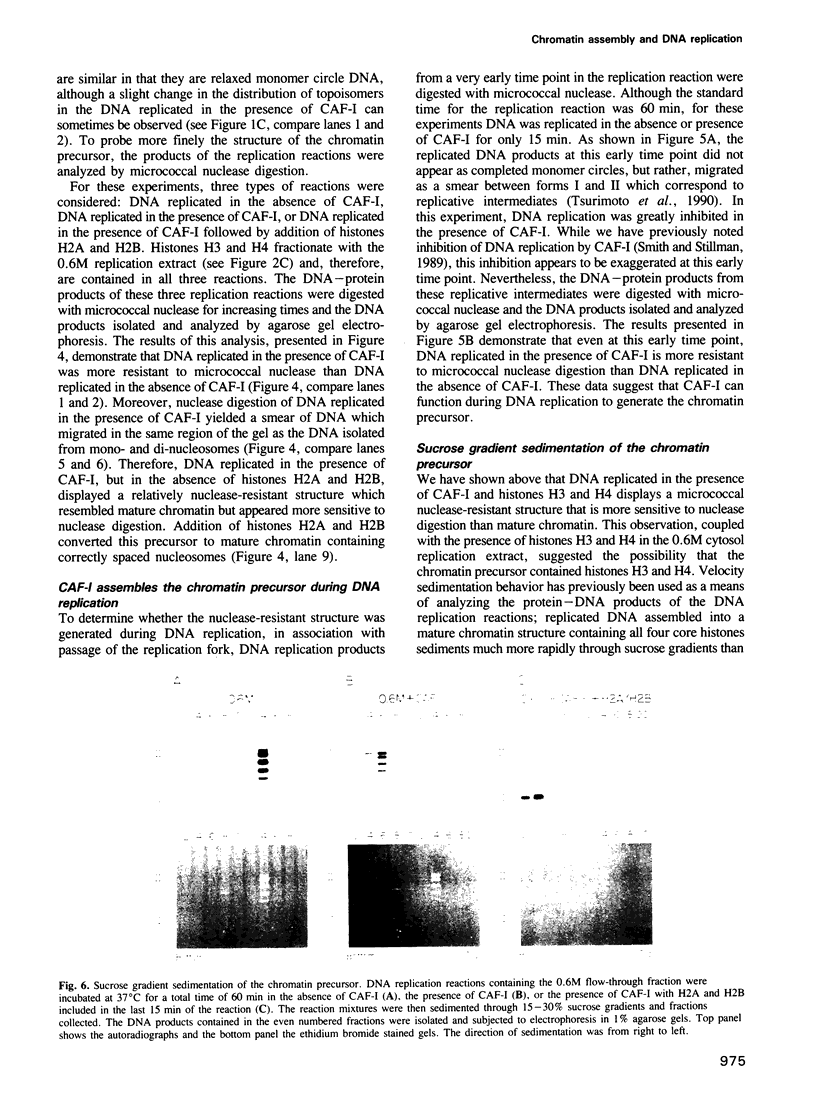





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfageme C. R., Zweidler A., Mahowald A., Cohen L. H. Histones of Drosophila embryos. Electrophoretic isolation and structural studies. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 25;249(12):3729–3736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almouzni G., Clark D. J., Méchali M., Wolffe A. P. Chromatin assembly on replicating DNA in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5767–5774. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Wu R. S., Panusz H. T., Muneses C. Kinetics of accumulation and depletion of soluble newly synthesized histone in the reciprocal regulation of histone and DNA synthesis. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6542–6550. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crémisi C., Chestier A., Yaniv M. Assembly of SV40 and polyoma minichromosomes during replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):409–416. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crémisi C., Chestier A., Yaniv M. Preferential association of newly synthesized histones with replicating SV40 DNA. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):947–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90159-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crémisi C., Yaniv M. Sequential assembly of newly synthesized histones on replicating SV40 DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Feb 27;92(4):1117–1123. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90402-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusick M. E., Herman T. M., DePamphilis M. L., Wassarman P. M. Structure of chromatin at deoxyribonucleic acid replication forks: prenucleosomal deoxyribonucleic acid is rapidly excised from replicating simian virus 40 chromosomes by micrococcal nuclease. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 10;20(23):6648–6658. doi: 10.1021/bi00526a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusick M. E., Lee K. S., DePamphilis M. L., Wassarman P. M. Structure of chromatin at deoxyribonucleic acid replication forks: nuclease hypersensitivity results from both prenucleosomal deoxyribonucleic acid and an immature chromatin structure. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 2;22(16):3873–3884. doi: 10.1021/bi00285a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth S. M., Black S. J., Laskey R. A. Two complexes that contain histones are required for nucleosome assembly in vitro: role of nucleoplasmin and N1 in Xenopus egg extracts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1009–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90587-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth S. M., Dingwall C. Chromatin assembly in vitro and in vivo. Bioessays. 1988 Aug-Sep;9(2-3):44–49. doi: 10.1002/bies.950090203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotedar R., Roberts J. M. Multistep pathway for replication-dependent nucleosome assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6459–6463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Weintraub H. Propagation of globin DNAase I-hypersensitive sites in absence of factors required for induction: a possible mechanism for determination. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss C., Gutierrez C., Burhans W. C., DePamphilis M. L., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Nucleosome assembly in mammalian cell extracts before and after DNA replication. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2911–2922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand C. E., Walters R. A. Rapid assembly of newly synthesized DNA into chromatin subunits prior to joining to small DNA replication intermediates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Nov 8;73(1):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90510-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V., Chalkley R. A new method for the isolation of replicative chromatin: selective deposition of histone on both new and old DNA. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):121–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90277-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V., Chalkley R. A reevaluation of new histone deposition on replicating chromatin. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5095–5103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V., Chalkley R. Histone synthesis and deposition in the G1 and S phases of hepatoma tissue culture cells. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 19;24(24):6921–6930. doi: 10.1021/bi00345a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V. Deposition of newly synthesized histones: hybrid nucleosomes are not tandemly arranged on daughter DNA strands. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):2109–2120. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V. Deposition of newly synthesized histones: new histones H2A and H2B do not deposit in the same nucleosome with new histones H3 and H4. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 21;26(8):2315–2325. doi: 10.1021/bi00382a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V., Shires A., Tanphaichitr N., Chalkley R. Modifications to histones immediately after synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 25;104(2):471–483. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Franke W. W. Soluble acidic complexes containing histones H3 and H4 in nuclei of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):799–809. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Seiter A., Zentgraf H. Nucleosome assembly in vitro: separate histone transfer and synergistic interaction of native histone complexes purified from nuclei of Xenopus laevis oocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1309–1318. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Fanning E., Otto B., Knippers R. Maturation of newly replicated chromatin of simian virus 40 and its host cell. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 5;136(4):359–374. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90395-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E. Expression of simian virus 40 T antigen in insect cells using a baculovirus expression vector. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):72–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy A., Jakob K. M. Nascent DNA in nucleosome like structures from chromatin. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Miller K. G. Eukaryotic DNA topoisomerases: two forms of type I DNA topoisomerases from HeLa cell nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3487–3491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Miller O. L., Jr Electron microscopic analysis of chromatin replication in the cellular blastoderm Drosophila melanogaster embryo. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):795–804. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90278-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Carrillo A., Wangh L. J., Allfrey V. G. Processing of newly synthesized histone molecules. Science. 1975 Oct 10;190(4210):117–128. doi: 10.1126/science.1166303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapp M., Worcel A. Purification and mechanism of action of a nucleosome assembly factor from Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9357–9365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schomburg U., Grosse F. Purification and characterization of DNA topoisomerase II from calf thymus associated with polypeptides of 175 and 150 kDa. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 3;160(3):451–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seale R. L. Assembly of DNA and protein during replication in HeLa cells. Nature. 1975 May 15;255(5505):247–249. doi: 10.1038/255247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seale R. L. Nucleosomes associated with newly replicated DNA have an altered conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2717–2721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman M. M., Garon C. F., Salzman N. P. The relationship of SV40 replicating chromosomes to two forms of the non-replicating SV40. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Aug;5(8):2877–2893. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.8.2877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senshu T., Fukuda M., Ohashi M. Preferential association of newly synthesized H3 and H4 histones with newly replicated DNA. J Biochem. 1978 Oct;84(4):985–988. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura A., Tremethick D., Worcel A. Characterization of the repressed 5S DNA minichromosomes assembled in vitro with a high-speed supernatant of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4257–4269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Lane D. P. An immunoaffinity purification procedure for SV40 large T antigen. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):88–100. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. H., Felsenfeld G. A new procedure for purifying histone pairs H2A + H2B and H3 + H4 from chromatin using hydroxylapatite. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):689–696. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Stillman B. Purification and characterization of CAF-I, a human cell factor required for chromatin assembly during DNA replication in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. W., Gluzman Y. Replication and supercoiling of simian virus 40 DNA in cell extracts from human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2051–2060. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Chromatin assembly during SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication in vitro. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:197–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svaren J., Chalkley R. The structure and assembly of active chromatin. Trends Genet. 1990 Feb;6(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90074-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Melendy T., Stillman B. Sequential initiation of lagging and leading strand synthesis by two different polymerase complexes at the SV40 DNA replication origin. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):534–539. doi: 10.1038/346534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Purification of a cellular replication factor, RF-C, that is required for coordinated synthesis of leading and lagging strands during simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):609–619. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Assembly of an active chromatin structure during replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 10;7(3):781–792. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.3.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Han S., Wong M. L. Assembly of newly replicated chromatin. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):969–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90280-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker K., Worcel A. The histone H3/H4.N1 complex supplemented with histone H2A-H2B dimers and DNA topoisomerase I forms nucleosomes on circular DNA under physiological conditions. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14487–14496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]