Abstract
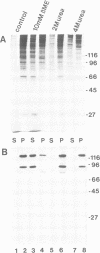
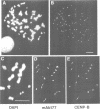
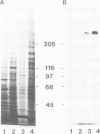
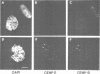
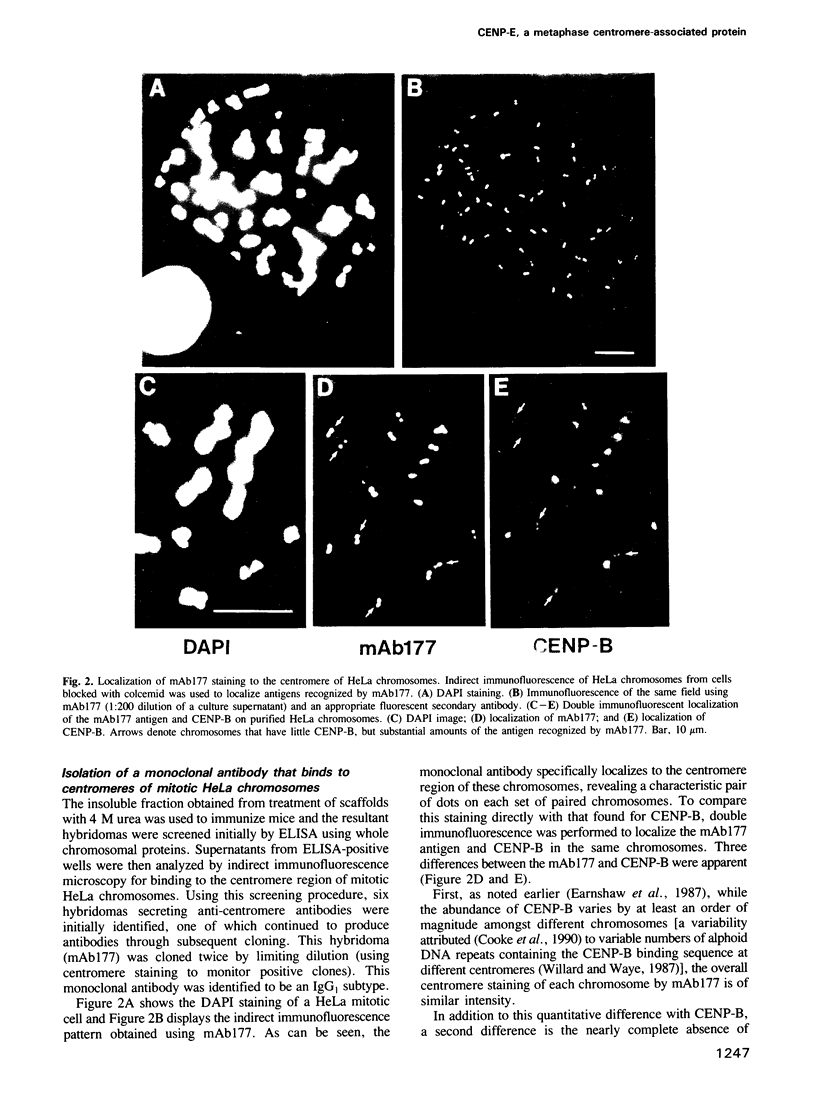
We have identified a novel human centromere-associated protein by preparing monoclonal antibodies against a fraction of HeLa chromosome scaffold proteins enriched for centromere/kinetochore components. One monoclonal antibody (mAb177) specifically stains the centromere region of mitotic human chromosomes and binds to a novel, approximately 250-300 kd chromosome scaffold associated protein named CENP-E. In cells progressing through different parts of the cell cycle, the localization of CENP-E differed markedly from that observed for the previously identified centromere proteins CENP-A, CENP-B, CENP-C and CENP-D. In contrast to these antigens, no mAb177 staining is detected during interphase, and staining first appears at the centromere region of chromosomes during prometaphase. This association with chromosomes remains throughout metaphase but is redistributed to the midplate at or just after the onset of anaphase. By telophase, the staining is localized exclusively to the midbody. Microinjection of the mAb177 into metaphase cells blocks or significantly delays progression into anaphase, although the morphology of the spindle and the configuration of the metaphase chromosomes appear normal in these metaphase arrested cells. This demonstrates that CENP-E function is required for the transition from metaphase to anaphase.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner S., Pepper D., Berns M. W., Tan E., Brinkley B. R. Kinetochore structure, duplication, and distribution in mammalian cells: analysis by human autoantibodies from scleroderma patients. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):95–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkley B. R. Toward a structural and molecular definition of the kinetochore. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1990;16(2):104–109. doi: 10.1002/cm.970160204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke C. A., Bernat R. L., Earnshaw W. C. CENP-B: a major human centromere protein located beneath the kinetochore. J Cell Biol. 1990 May;110(5):1475–1488. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke C. A., Heck M. M., Earnshaw W. C. The inner centromere protein (INCENP) antigens: movement from inner centromere to midbody during mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2053–2067. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis F. M., Tsao T. Y., Fowler S. K., Rao P. N. Monoclonal antibodies to mitotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2926–2930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Laemmli U. K. Architecture of metaphase chromosomes and chromosome scaffolds. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):84–93. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Rothfield N. Identification of a family of human centromere proteins using autoimmune sera from patients with scleroderma. Chromosoma. 1985;91(3-4):313–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00328227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Sullivan K. F., Machlin P. S., Cooke C. A., Kaiser D. A., Pollard T. D., Rothfield N. F., Cleveland D. W. Molecular cloning of cDNA for CENP-B, the major human centromere autoantigen. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):817–829. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W., Bordwell B., Marino C., Rothfield N. Three human chromosomal autoantigens are recognized by sera from patients with anti-centromere antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):426–430. doi: 10.1172/JCI112320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Euteneuer U., McIntosh J. R. Structural polarity of kinetochore microtubules in PtK1 cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):338–345. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbsky G. J., Sammak P. J., Borisy G. G. Chromosomes move poleward in anaphase along stationary microtubules that coordinately disassemble from their kinetochore ends. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;104(1):9–18. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingwell B., Rattner J. B. Mammalian kinetochore/centromere composition: a 50 kDa antigen is present in the mammalian kinetochore/centromere. Chromosoma. 1987;95(6):403–407. doi: 10.1007/BF00333991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Mitchison T. J., Kirschner M. W. Polewards chromosome movement driven by microtubule depolymerization in vitro. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):499–504. doi: 10.1038/331499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. D., Laemmli U. K. Higher order metaphase chromosome structure: evidence for metalloprotein interactions. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):171–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masumoto H., Masukata H., Muro Y., Nozaki N., Okazaki T. A human centromere antigen (CENP-B) interacts with a short specific sequence in alphoid DNA, a human centromeric satellite. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):1963–1973. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison T. J., Kirschner M. W. Properties of the kinetochore in vitro. II. Microtubule capture and ATP-dependent translocation. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):766–777. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroi Y., Peebles C., Fritzler M. J., Steigerwald J., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to centromere (kinetochore) in scleroderma sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1627–1631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Dominoes and clocks: the union of two views of the cell cycle. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):614–621. doi: 10.1126/science.2683077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas R. B. The motor for poleward chromosome movement in anaphase is in or near the kinetochore. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2245–2255. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. K., Margolis R. L. Kinetochore components recognized by human autoantibodies are present on mononucleosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):173–186. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. K., O'Day K., Wener M. H., Andrews B. S., Margolis R. L. A 17-kD centromere protein (CENP-A) copurifies with nucleosome core particles and with histones. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):805–815. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pankov R., Lemieux M., Hancock R. An antigen located in the kinetochore region in metaphase and on polar microtubule ends in the midbody region in anaphase, characterised using a monoclonal antibody. Chromosoma. 1990 Apr;99(2):95–101. doi: 10.1007/BF01735324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfarr C. M., Coue M., Grissom P. M., Hays T. S., Porter M. E., McIntosh J. R. Cytoplasmic dynein is localized to kinetochores during mitosis. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):263–265. doi: 10.1038/345263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluta A. F., Cooke C. A., Earnshaw W. C. Structure of the human centromere at metaphase. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 May;15(5):181–185. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport R. Cytokinesis in animal cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1971;31:169–213. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder C. L., Alexander S. P. Kinetochores are transported poleward along a single astral microtubule during chromosome attachment to the spindle in newt lung cells. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):81–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder C. L. The formation, structure, and composition of the mammalian kinetochore and kinetochore fiber. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;79:1–58. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61672-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steuer E. R., Wordeman L., Schroer T. A., Sheetz M. P. Localization of cytoplasmic dynein to mitotic spindles and kinetochores. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):266–268. doi: 10.1038/345266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]