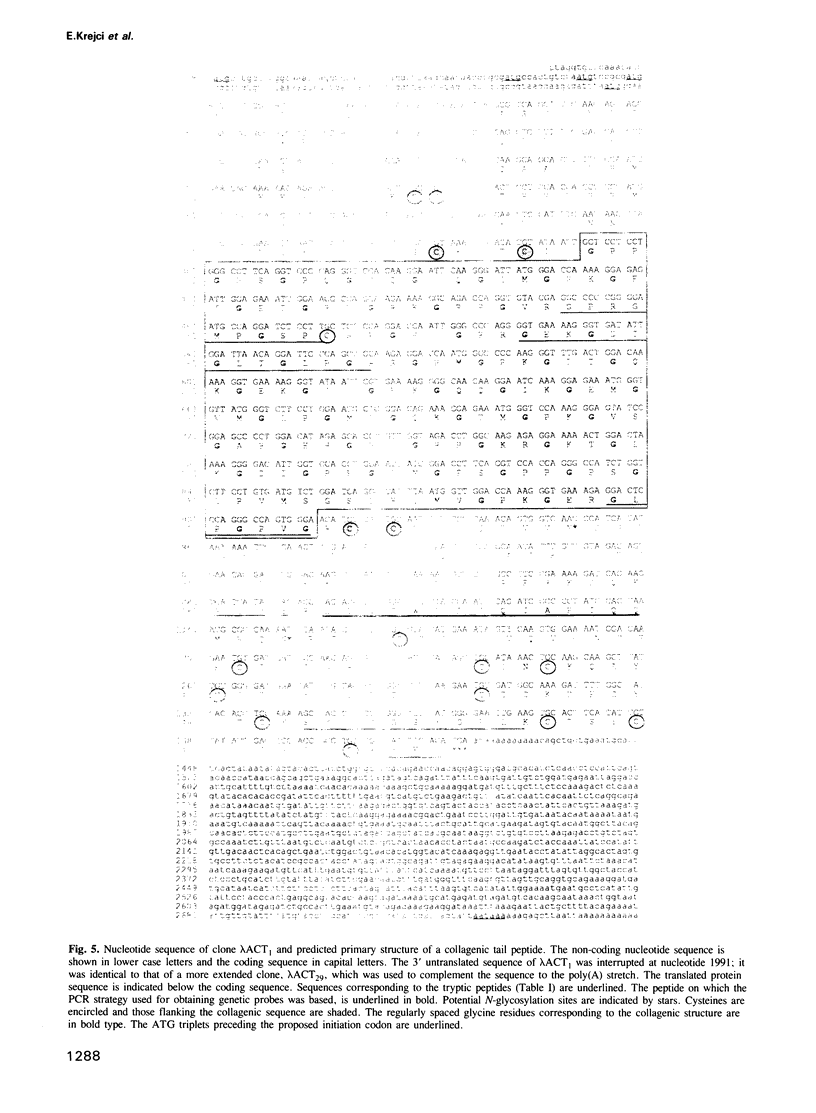
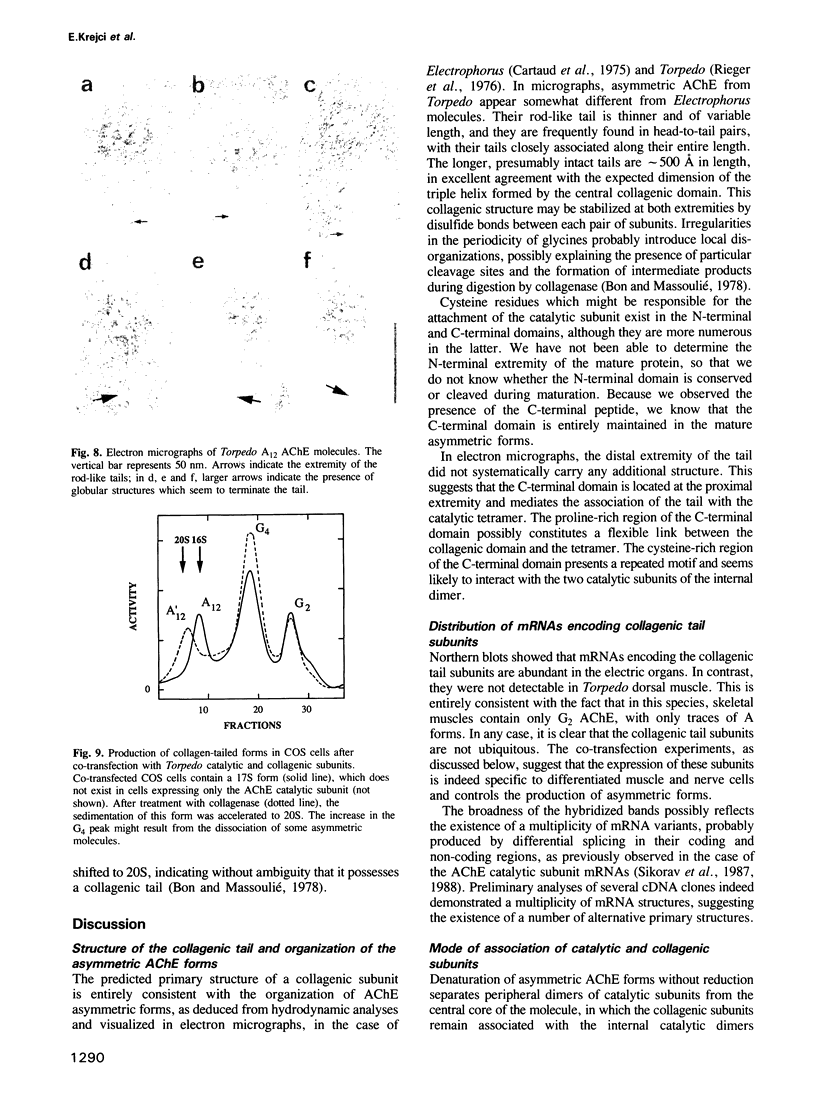
Abstract
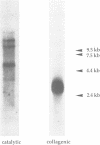
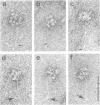
The asymmetric forms of cholinesterases are synthesized only in differentiated muscular and neural cells of vertebrates. These complex oligomers are characterized by the presence of a collagen-like tail, associated with one, two or three tetramers of catalytic subunits. The collagenic tail is responsible for ionic interactions, explaining the insertion of these molecules in extracellular basal lamina, e.g. at neuromuscular endplates. We report the cloning of a collagenic subunit from Torpedo marmorata acetylcholinesterase (AChE). The predicted primary structure contains a putative signal peptide, a proline-rich domain, a collagenic domain, and a C-terminal domain composed of proline-rich and cysteine-rich regions. Several variants are generated by alternative splicing. Apart from the collagenic domain, the AChE tail subunit does not present any homology with previously known proteins. We show that co-expression of catalytic AChE subunits and collagenic subunits results in the production of asymmetric, collagen-tailed AChE forms in transfected COS cells. Thus, the assembly of these complex forms does not depend on a specific cellular processing, but rather on the expression of the collagenic subunits.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anglister L., Silman I. Molecular structure of elongated forms of electric eel acetylcholinesterase. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 5;125(3):293–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90404-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauw G., De Loose M., Inzé D., Van Montagu M., Vandekerckhove J. Alterations in the phenotype of plant cells studied by NH(2)-terminal amino acid-sequence analysis of proteins electroblotted from two-dimensional gel-separated total extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4806–4810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellon B. Apple Macintosh programs for nucleic and protein sequence analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1837–1846. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bon S., Cartaud J., Massoulié J. The dependence of acetylcholinesterase aggregation at low ionic strength upon a polyanionic component. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bon S., Chang J. Y., Strosberg A. D. Identical N-terminal peptide sequences of asymmetric forms and of low-salt-soluble and detergent-soluble amphiphilic dimers of Torpedo acetylcholinesterase. Comparison with bovine acetylcholinesterase. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):206–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bon S., Massoulié J. Collagen-tailed and hydrophobic components of acetylcholinesterase in Torpedo marmorata electric organ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4464–4468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bon S., Massoulié J. Collagenase sensitivity and aggregation properties of Electrophorus acetylcholinesterase. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):89–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bon S., Massoulié J. Molecular forms of Electrophorus acetylcholinesterase the catalytic subunits: fragmentation, intra- and inter-subunit disulfide bonds. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 1;71(2):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80949-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bon S., Méflah K., Musset F., Grassi J., Massoulié J. An immunoglobulin M monoclonal antibody, recognizing a subset of acetylcholinesterase molecules from electric organs of Electrophorus and Torpedo, belongs to the HNK-1 anti-carbohydrate family. J Neurochem. 1987 Dec;49(6):1720–1731. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb02429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartaud J., Rieger F., Bon S., Massoulie J. Fine structure of electric ell acetylcholinesterase. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 25;88(1):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90959-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaboriaud C., Bissery V., Benchetrit T., Mornon J. P. Hydrophobic cluster analysis: an efficient new way to compare and analyse amino acid sequences. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80439-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gennari K., Brunner J., Brodbeck U. Tetrameric detergent-soluble acetylcholinesterase from human caudate nucleus: subunit composition and number of active sites. J Neurochem. 1987 Jul;49(1):12–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb03386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibney G., MacPhee-Quigley K., Thompson B., Vedvick T., Low M. G., Taylor S. S., Taylor P. Divergence in primary structure between the molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1140–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III in DNA sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:156–165. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inestrosa N. C., Roberts W. L., Marshall T. L., Rosenberry T. L. Acetylcholinesterase from bovine caudate nucleus is attached to membranes by a novel subunit distinct from those of acetylcholinesterases in other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4441–4444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. L., Heinemann S., Taylor P. Structural characterization of the asymmetric (17 + 13) S forms of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo. I. Analysis of subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12282–12291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. L., Taylor P. Structural characterization of the asymmetric (17 + 13) S species of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo. II. Component peptides obtained by selective proteolysis and disulfide bond reduction. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12292–12301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemesle-Varloot L., Henrissat B., Gaboriaud C., Bissery V., Morgat A., Mornon J. P. Hydrophobic cluster analysis: procedures to derive structural and functional information from 2-D-representation of protein sequences. Biochimie. 1990 Aug;72(8):555–574. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockridge O., Bartels C. F., Vaughan T. A., Wong C. K., Norton S. E., Johnson L. L. Complete amino acid sequence of human serum cholinesterase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):549–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee-Quigley K., Taylor P., Taylor S. Primary structures of the catalytic subunits from two molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase. A comparison of NH2-terminal and active center sequences. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12185–12189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maulet Y., Camp S., Gibney G., Rachinsky T. L., Ekström T. J., Taylor P. Single gene encodes glycophospholipid-anchored and asymmetric acetylcholinesterase forms: alternative coding exons contain inverted repeat sequences. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90103-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McTiernan C., Adkins S., Chatonnet A., Vaughan T. A., Bartels C. F., Kott M., Rosenberry T. L., La Du B. N., Lockridge O. Brain cDNA clone for human cholinesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musset F., Frobert Y., Grassi J., Vigny M., Boulla G., Bon S., Massoulié J. Monoclonal antibodies against acetylcholinesterase from electric organs of Electrophorus and Torpedo. Biochimie. 1987 Feb;69(2):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90247-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prody C. A., Zevin-Sonkin D., Gnatt A., Goldberg O., Soreq H. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones coding for cholinesterase from fetal human tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3555–3559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieger F., Bon S., Massoulié J., Cartauld J., Picard B., Benda P. Torpedo marmorata acetylcholinesterase; a comparison with the Electrophorus electricus enzyme. Molecular forms, subunits, electron microscopy, immunological relationship. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep 15;68(2):513–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry T. L., Richardson J. M. Structure of 18S and 14S acetylcholinesterase. Identification of collagen-like subunits that are linked by disulfide bonds to catalytic subunits. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 9;16(16):3550–3558. doi: 10.1021/bi00635a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotundo R. L. Asymmetric acetylcholinesterase is assembled in the Golgi apparatus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):479–483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schowalter D. B., Sommer S. S. The generation of radiolabeled DNA and RNA probes with polymerase chain reaction. Anal Biochem. 1989 Feb 15;177(1):90–94. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher M., Camp S., Maulet Y., Newton M., MacPhee-Quigley K., Taylor S. S., Friedmann T., Taylor P. Primary structure of Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase deduced from its cDNA sequence. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):407–409. doi: 10.1038/319407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Aruffo A. Molecular cloning of the CD2 antigen, the T-cell erythrocyte receptor, by a rapid immunoselection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3365–3369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorav J. L., Duval N., Anselmet A., Bon S., Krejci E., Legay C., Osterlund M., Reimund B., Massoulié J. Complex alternative splicing of acetylcholinesterase transcripts in Torpedo electric organ; primary structure of the precursor of the glycolipid-anchored dimeric form. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):2983–2993. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03161.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorav J. L., Krejci E., Massoulié J. cDNA sequences of Torpedo marmorata acetylcholinesterase: primary structure of the precursor of a catalytic subunit; existence of multiple 5'-untranslated regions. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1865–1873. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsim K. W., Randall W. R., Barnard E. A. An asymmetric form of muscle acetylcholinesterase contains three subunit types and two enzymic activities in one molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1262–1266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallette F. M., Marsh D. J., Muller F., Massoulié J., Marçot B., Viel C. Comparative affinity chromatography of acetylcholinesterases from five vertebrate species. J Chromatogr. 1983 Mar 4;257(2):285–296. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)88184-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]