Abstract
A large family of C2H2 (Krüppel-like) zinc finger protein genes is maternally transcribed in Xenopus oocytes; many of the corresponding mRNAs are actively translated post-fertilization, before the onset of zygotic activation of transcription. With the aim of asking if any of these stored mRNAs have a function in Xenopus development, we made use of antisense oligonucleotide mediated, targeted RNA destruction. Injected oocytes lose the entire pool of C2H2 zinc finger protein encoding mRNAs. They are indistinguishable from control oocytes in their abilities to mature in vitro and to be fertilized in vitro. Embryos generated from such oocytes develop normally until tadpole stage. These findings do not rule out the possibility that C2H2 zinc finger protein genes are involved in developmental control in Xenopus. However, they do suggest that the biological function for at least some of the early expressed zinc finger proteins in Xenopus differs in important aspects from the way Krüppel or other DNA binding factors act as developmental regulators in Drosophila.
Full text
PDF
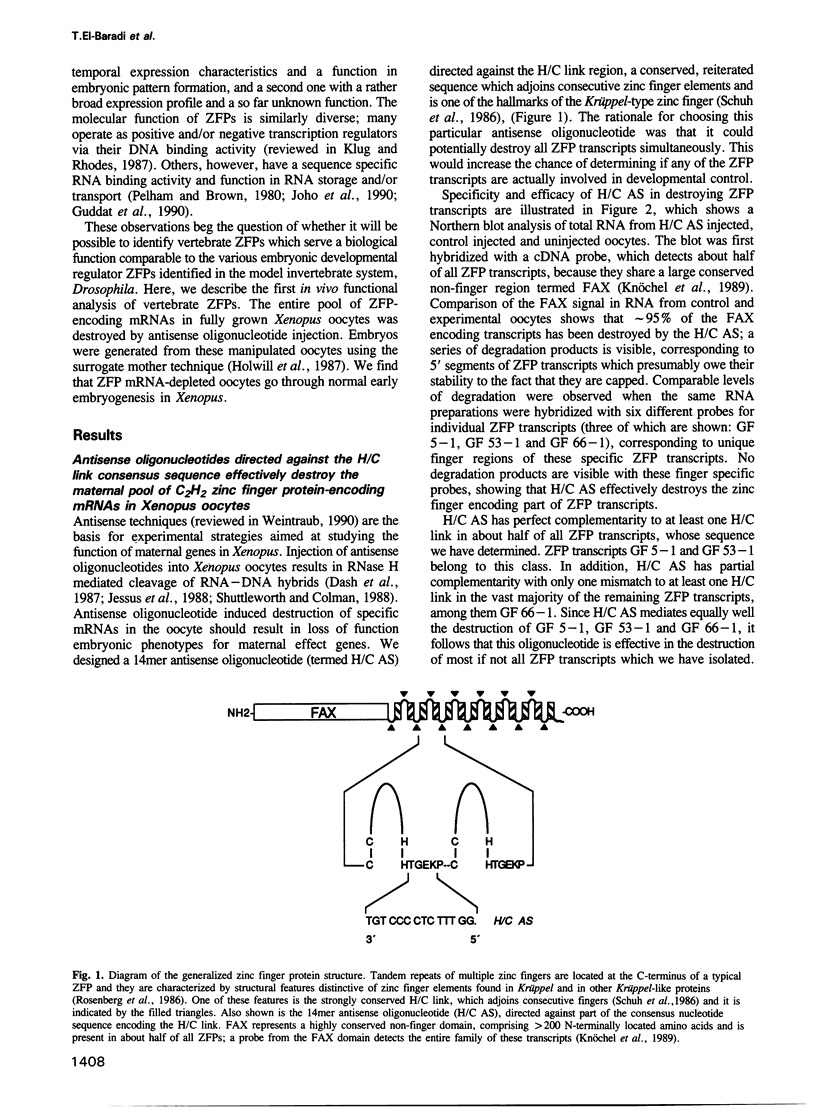
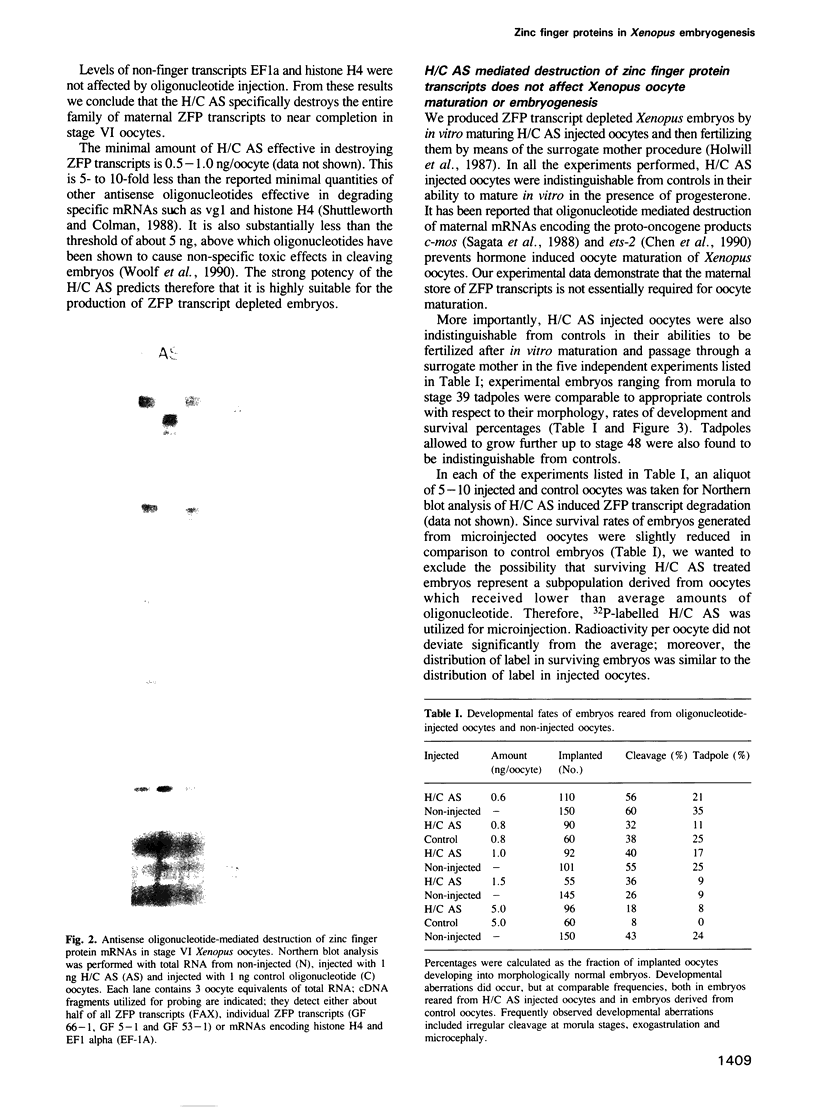




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bellefroid E. J., Lecocq P. J., Benhida A., Poncelet D. A., Belayew A., Martial J. A. The human genome contains hundreds of genes coding for finger proteins of the Krüppel type. DNA. 1989 Jul-Aug;8(6):377–387. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulay J. L., Dennefeld C., Alberga A. The Drosophila developmental gene snail encodes a protein with nucleic acid binding fingers. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):395–398. doi: 10.1038/330395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Lemaire P., Revelant O., Bravo R., Charnay P. Characterization of a mouse multigene family that encodes zinc finger structures. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1319–1326. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Q., Burdett L. A., Seth A. K., Lautenberger J. A., Papas T. S. Requirement of ets-2 expression for Xenopus oocyte maturation. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1416–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.2255913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Deutsch U., Gruss P. A multigene family encoding several "finger" structures is present and differentially active in mammalian genomes. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):771–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Dietrich S., Balling R., Guenet J. L., Gruss P. Structure, expression and chromosomal localization of Zfp-1, a murine zinc finger protein gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10427–10438. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Dressler G., Breier G., Deutsch U., Gruss P. The primary structure of the murine multifinger gene mKr2 and its specific expression in developing and adult neurons. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1345–1353. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Rohdewohld H., Gruss P. Specific and ubiquitous expression of different Zn finger protein genes in the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):9995–10011. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.9995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter D. E., Swaykus E. A., Beran-Koehn M. A., Goldberg D., Wieschaus E., Schedl P. Molecular analysis of odd-skipped, a zinc finger encoding segmentation gene with a novel pair-rule expression pattern. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3795–3804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunliffe V., Koopman P., McLaren A., Trowsdale J. A mouse zinc finger gene which is transiently expressed during spermatogenesis. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):197–205. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08096.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dash P., Lotan I., Knapp M., Kandel E. R., Goelet P. Selective elimination of mRNAs in vivo: complementary oligodeoxynucleotides promote RNA degradation by an RNase H-like activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7896–7900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler G. R., Gruss P. Do multigene families regulate vertebrate development? Trends Genet. 1988 Aug;4(8):214–219. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(88)80003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M. B., Dworkin-Rastl E. Functions of maternal mRNA in early development. Mol Reprod Dev. 1990 Jul;26(3):261–297. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080260310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. Homeotic genes, the homeo box, and the genetic control of development. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:243–251. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guddat U., Bakken A. H., Pieler T. Protein-mediated nuclear export of RNA: 5S rRNA containing small RNPs in xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):619–628. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90665-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B. Methods for nuclear transplantation in amphibia. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;16:125–139. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman L. E., Wormington W. M. Translational inactivation of ribosomal protein mRNAs during Xenopus oocyte maturation. Genes Dev. 1988 May;2(5):598–605. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.5.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hülskamp M., Pfeifle C., Tautz D. A morphogenetic gradient of hunchback protein organizes the expression of the gap genes Krüppel and knirps in the early Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):577–580. doi: 10.1038/346577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessus C., Cazenave C., Ozon R., Hélène C. Specific inhibition of endogenous beta-tubulin synthesis in Xenopus oocytes by anti-messenger oligodeoxynucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):2225–2233. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.2225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho K. E., Darby M. K., Crawford E. T., Brown D. D. A finger protein structurally similar to TFIIIA that binds exclusively to 5S RNA in Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90809-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Balling R., Gruss P. Variations of cervical vertebrae after expression of a Hox-1.1 transgene in mice. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90810-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knöchel W., Pöting A., Köster M., el Baradi T., Nietfeld W., Bouwmeester T., Pieler T. Evolutionary conserved modules associated with zinc fingers in Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6097–6100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Varnum S. M., Wormington W. M., Melton D. A. The mRNA encoding elongation factor 1-alpha (EF-1 alpha) is a major transcript at the midblastula transition in Xenopus. Dev Biol. 1989 May;133(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90300-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köster M., Pieler T., Pöting A., Knöchel W. The finger motif defines a multigene family represented in the maternal mRNA of Xenopus laevis oocytes. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1735–1741. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03002.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mardon G., Page D. C. The sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome encodes a protein with a highly acidic domain and 13 zinc fingers. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):765–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90680-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muriel W. J., Cole J., Lehmann A. R. Molecular analysis of ouabain-resistant mutants of the mouse lymphoma cell line L5178Y. Mutagenesis. 1987 Sep;2(5):383–389. doi: 10.1093/mutage/2.5.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nietfeld W., el-Baradi T., Mentzel H., Pieler T., Köster M., Pöting A., Knöchel W. Second-order repeats in Xenopus laevis finger proteins. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 20;208(4):639–659. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nüsslein-Volhard C., Frohnhöfer H. G., Lehmann R. Determination of anteroposterior polarity in Drosophila. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1675–1681. doi: 10.1126/science.3686007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orenic T. V., Slusarski D. C., Kroll K. L., Holmgren R. A. Cloning and characterization of the segment polarity gene cubitus interruptus Dominant of Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):1053–1067. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pankratz M. J., Seifert E., Gerwin N., Billi B., Nauber U., Jäckle H. Gradients of Krüppel and knirps gene products direct pair-rule gene stripe patterning in the posterior region of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90811-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passananti C., Felsani A., Caruso M., Amati P. Mouse genes coding for "zinc-finger"-containing proteins: characterization and expression in differentiated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9417–9421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payre F., Yanicostas C., Vincent A. Serendipity delta, a Drosophila zinc finger protein present in embryonic nuclei at the onset of zygotic gene transcription. Dev Biol. 1989 Dec;136(2):469–480. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90272-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierandrei-Amaldi P., Campioni N., Beccari E., Bozzoni I., Amaldi F. Expression of ribosomal-protein genes in Xenopus laevis development. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):163–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. D., Smith L. D. Differential capacity for translation and lack of competition between mRNAs that segregate to free and membrane-bound polysomes. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90372-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz i Altaba A., Melton D. A. Involvement of the Xenopus homeobox gene Xhox3 in pattern formation along the anterior-posterior axis. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90969-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagata N., Oskarsson M., Copeland T., Brumbaugh J., Vande Woude G. F. Function of c-mos proto-oncogene product in meiotic maturation in Xenopus oocytes. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):519–525. doi: 10.1038/335519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent M. G., Bennett M. F. Identification in Xenopus of a structural homologue of the Drosophila gene snail. Development. 1990 Aug;109(4):967–973. doi: 10.1242/dev.109.4.967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh R., Aicher W., Gaul U., Côté S., Preiss A., Maier D., Seifert E., Nauber U., Schröder C., Kemler R. A conserved family of nuclear proteins containing structural elements of the finger protein encoded by Krüppel, a Drosophila segmentation gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90817-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth J., Colman A. Antisense oligonucleotide-directed cleavage of mRNA in Xenopus oocytes and eggs. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):427–434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02830.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. C., Dworkin M. B., Dworkin-Rastl E. Destruction of a translationally controlled mRNA in Xenopus oocytes delays progesterone-induced maturation. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1296–1306. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Colot H. V., Rosbash M. Sequence and structure of the serendipity locus of Drosophila melanogaster. A densely transcribed region including a blastoderm-specific gene. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):149–166. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90265-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Kejzlarovà-Lepesant J., Segalat L., Yanicostas C., Lepesant J. A. sry h-1, a new Drosophila melanogaster multifingered protein gene showing maternal and zygotic expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4459–4468. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Misulovin Z. Long-term growth and differentiation of Xenopus oocytes in a defined medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5534–5538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bhatt S., Chavrier P., Bravo R., Charnay P. Segment-specific expression of a zinc-finger gene in the developing nervous system of the mouse. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):461–464. doi: 10.1038/337461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf T. M., Jennings C. G., Rebagliati M., Melton D. A. The stability, toxicity and effectiveness of unmodified and phosphorothioate antisense oligodeoxynucleotides in Xenopus oocytes and embryos. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1763–1769. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. V., Cho K. W., Hardwicke J., Collins R. H., De Robertis E. M. Interference with function of a homeobox gene in Xenopus embryos produces malformations of the anterior spinal cord. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90871-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. V., Cho K. W., Oliver G., De Robertis E. M. Vertebrate homeodomain proteins: families of region-specific transcription factors. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90043-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







