Abstract
Hepatocytes are critical for the maintenance of liver homeostasis, but its involvement in hepatic fibrogenesis remains elusive. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α (HNF1α) is a liver-enriched transcription factor that plays a key role in hepatocyte function. Our previous study revealed a significant inhibitory effect of HNF1α on hepatocellular carcinoma. In this study, we report that the expression of HNF1α is significantly repressed in both human and rat fibrotic liver. Knockdown of HNF1α in the liver significantly aggravates hepatic fibrogenesis in either dimethylnitrosamine (DMN) or bile duct ligation (BDL) model in rats. In contrast, forced expression of HNF1α markedly alleviates hepatic fibrosis. HNF1α regulates the transcriptional expression of SH2 domain-containing phosphatase-1 (SHP-1) via directly binding to SHP-1 promoter in hepatocytes. Inhibition of SHP-1 expression abrogates the anti-fibrotic effect of HNF1α in DMN-treated rats. Moreover, HNF1α repression in primary hepatocytes leads to the activation of NF-κB and JAK/STAT pathways and initiates an inflammatory feedback circuit consisting of HNF1α, SHP-1, STAT3, p65, miR-21 and miR-146a, which sustains the deregulation of HNF1α in hepatocytes. More interestingly, a coordinated crosstalk between hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) participates in this positive feedback circuit and facilitates the progression of hepatocellular damage. Our findings demonstrate that impaired hepatocytes play an active role in hepatic fibrogenesis. Early intervention of HNF1α-regulated inflammatory feedback loop in hepatocytes may have beneficial effects in the treatment of chronic liver diseases.
Keywords: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α, liver fibrosis, SH2 domain-containing phosphatase-1, microRNA, feedback, crosstalk
Introduction
Chronic liver injury from a wide variety of etiologies is associated with progressive hepatic fibrosis that is characterized by excess production and deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) in the liver. The fibrosis eventually leads to the loss of liver function and disruption of liver structure. It is well accepted that the activation of resident hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) into fibroblast-like cells is a hallmark of hepatic fibrogenesis1,2. Activated HSCs are the major producers of fibrotic extracellular matrix (ECM), and have been considered as an attractive target for anti-fibrotic therapy3,4. However, no effective treatment for hepatic fibrosis is currently available in clinical practice.
Functional integrity of hepatocytes, the main cell type in the liver, is critical for the maintenance of liver homeostasis5,6. It is well known that progression of liver fibrosis is associated with considerable hepatocyte injuries in all animal models7. Several studies have indicated that apoptotic hepatocytes may present as a major inflammatory stimulus for HSC activation8,9,10. Hepatocyte apoptosis induced by hepatocyte-specific deletion of TAK1, Mcl-1 or Bcl-xL triggers fibrogenesis in mouse model11,12,13. Nevertheless, the role of damaged hepatocytes in hepatic fibrogenesis remains largely unknown. Furthermore, the relationship between hepatocyte injury and HSC activation is still not clear.
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1α (HNF1α), a POU homeodomain family transcription factor, plays a key role in many aspects of hepatocyte functions, including carbohydrate synthesis and storage, lipid metabolism, detoxification, and synthesis of serum proteins14,15,16. HNF1α knockout mice (HNF1α−/−) have drastically enlarged liver and develop progressive liver damage leading to the degeneration of hepatocytes17,18. Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) revealed that SNPs in HNF1α locus influence levels of liver enzymes in plasma19. HNF1α also regulates the expression of cytokine-induced C-reactive protein (CRP) by direct binding to CRP promoter20. These findings suggest that HNF1α plays a major role in inflammatory response in liver diseases. Our recent study revealed that forced expression of HNF1α impedes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) xenograft in mice by inducing the differentiation of hepatoma cells into hepatocytes21. However, the role of HNF1α in hepatic fibrogenesis remains to be clarified.
SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SHP-1, also known as Ptpn6) is expressed mainly in hematopoietic and epithelial cells22,23 and widely accepted as a negative regulator of inflammation24. SHP-1 inhibits intracellular signal transduction by dephosphorylation of transmembrane receptors, including cytokine receptors and growth factor receptors25,26. SHP-1 also binds and dephosphorylates the activated signaling molecules such as ERKs, JNKs, STATs, JAK2 and NF-κB27. Recent studies demonstrated that hepatocyte-specific Shp1 knockout mice (Ptpn6H-KO) are protected from hepatic insulin resistance and develop hepatic steatosis when subsisting on a high-fat diet (HFD)28,29. However, the role of SHP-1 in liver fibrosis is not reported yet.
In this study, we clarify the role of HNF1α in hepatic fibrogenesis and elucidate a crosstalk between hepatocytes and HSCs through an inflammatory feedback circuit consisting of HNF1α, SHP-1, STAT3, p65, miR-21 and miR-146a.
Results
HNF1α is suppressed in rat and human fibrotic liver
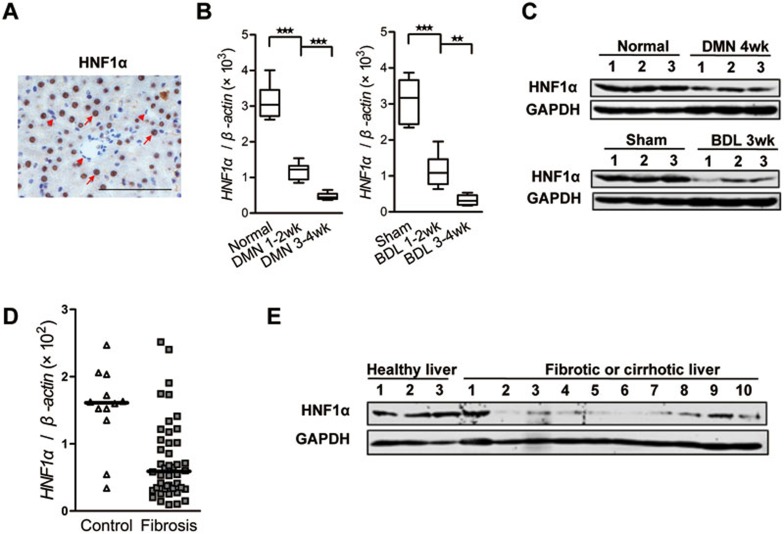
It is known that HNF1α is a liver-enriched transcription factor. HNF1α regulates the transcription of genes essential for the hepatocytic cell lineage and has been used as a marker for mature hepatocytes15,30. Our result showed that endogenous HNF1α was present in the nucleus of hepatocytes and was not observed in the nucleus of non-parenchymal cells in rat livers (Figure 1A). Interestingly, the mRNA levels of HNF1α were gradually reduced in rat hepatocytes upon the progression of hepatic fibrosis induced by either dimethylnitrosamine (DMN) or bile duct ligation (BDL) (Figure 1B and Supplementary information, Figure S1). The protein levels of HNF1α were also decreased in rat fibrotic livers (Figure 1C). Similar phenomenon was observed in the liver from patients with fibrosis or cirrhosis (Figure 1D and 1E).
Figure 1.
HNF1α is repressed in fibrotic liver. (A) Immunohistochemical staining of HNF1α in normal rat liver. HNF1α is detected exclusively in the nuclei of hepatocytes (arrow). No obvious staining is observed in non-parenchymal cells (arrow head). Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) mRNA level of HNF1α was assessed by real-time PCR in the livers treated with dimethylnitrosamine (DMN, left) or bile duct ligation (BDL, right) (n = 6 in each group). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 by Mann-Whitney U test. (C) HNF1α protein level in the liver of 3 individual rats after DMN injection (top) or BDL operation (bottom) was detected. (D) A scatter dot plot showing HNF1α expression levels in 12 human control and 44 fibrotic samples as assessed by RT-PCR analysis. Data (median) are normalized to β-actin, and P value was computed by Mann-Whitney U test (P = 0.0008). (E) Western blot analysis of HNF1α in the livers from 3 healthy control individuals and 10 patients with either fibrosis or cirrhosis.
Down-regulation of HNF1α exacerbates hepatic fibrogenesis
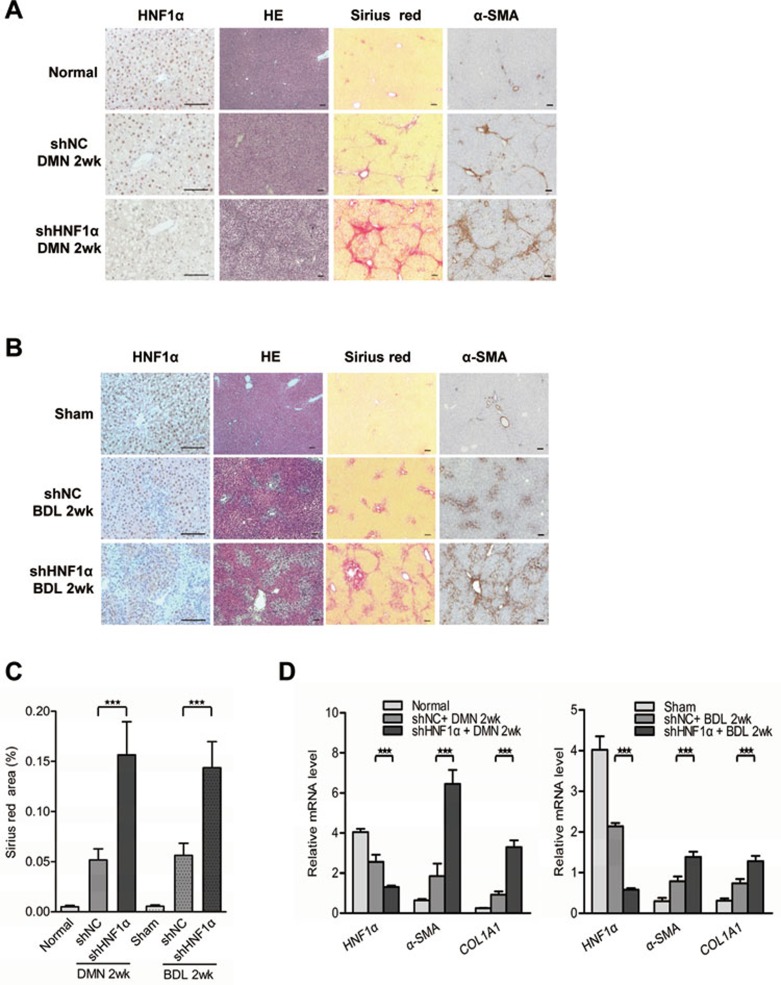
We then explored the effect of HNF1α reduction on hepatic fibrogenesis by repressing HNF1α expression with adenovirus carrying small hairpin RNA against HNF1α (AdshHNF1) prior to DMN treatment or BDL operation (Supplementary information, Figure S2A and S2B). A single injection of AdshHNF1α significantly decreased HNF1α expression in the livers of both models (Figure 2A and 2B). Sirius red staining indicated that the livers treated with AdshHNF1α had excessive ECM deposition and a continuous meshwork of connective tissue infiltrating the hepatic parenchyma two weeks after DMN injection, while the livers treated with control virus only had small amount of ECM deposition (Figure 2A). Similarly, AdshHNF1α treatment also led to more ECM deposition in the fibrotic livers induced by BDL (Figure 2B). Compared with AdshNC controls, HNF1α knockdown increased the ECM area by 202% and 156% in the DMN and BDL fibrotic model, respectively (P < 0.01, Figure 2C). In addition, the expression of fibrotic marker, α-SMA, was up-regulated by HNF1α knockdown, indicating that the activation of HSC was enhanced (Figure 2A and 2B). Real-time PCR showed that the mRNA levels of α-SMA and COL1A1 were also increased in fibrotic livers upon AdshHNF1α treatment (Figure 2D). Moreover, hydroxyproline content was much higher in the AdshHNF1α-treated group than in AdshNC group in DMN model (251.0 ± 23.1 μg/mg vs 163.2 ± 13.2 μg/mg, P < 0.01) and BDL model (242.8 ± 12.9 μg/mg vs 167.3 ± 12.9 μg/mg, P < 0.01). In addition, the expression of profibrotic and proinflammatory cytokines, including TGFβ1, TNFα and IL-6, was also increased in hepatic cells in AdshHNF1α-treated fibrotic livers over the control in both models (Supplementary information, Figure S3).
Figure 2.
Repression of HNF1α aggravates hepatic fibrogenesis in both DMN and BDL models. (A, B) Adenovirus carrying shRNA against HNF1α (shHNF1α) or negative control (shNC) was injected into rats prior to DMN administration (A) and BDL treatment (B), and 2 weeks later the expression of HNF1α and α-SMA in the fibrotic livers was analyzed by immunohistochemistry. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) and Sirius red staining were used to examine pathological alterations and collagen deposition. (C) Semi-quantitative analysis of Sirius red staining in the fibrotic livers from AdshHNF1α or AdshNC-treated rats (n = 10 rats in each group). (D) mRNA levels of HNF1α, α-SMA and COL1A1 in the livers were detected by real-time PCR Scale bar, 100 μm. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
It has been reported that adenovirus induces strong immune responses in animals, which may influence liver fibrogenesis31. We therefore knocked down HNF1α in rats using a lentivirus carrying shHNF1α, and again we observed that HNF1α knockdown worsened liver fibrosis induced by DMN injection (Supplementary information, Figure S4A). The data confirms that down-regulation of HNF1α exacerbates hepatic fibrogenesis (Supplementary information, Figure S4).
Overexpression of HNF1α ameliorates hepatic fibrosis
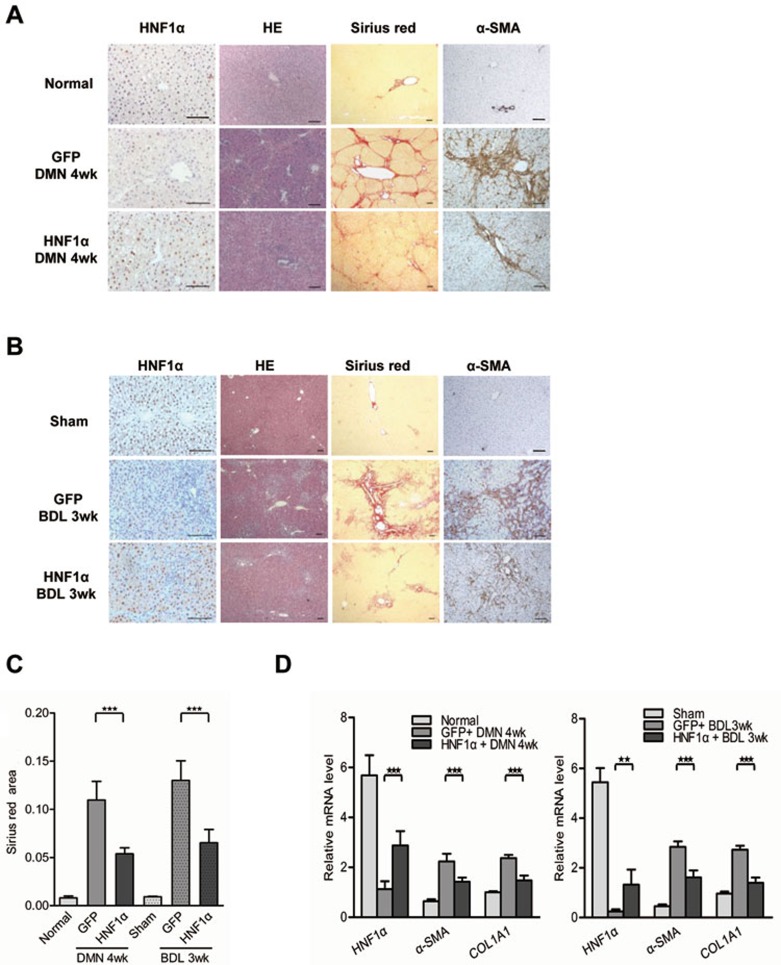
We next tested if HNF1α overexpression could mitigate hepatic fibrosis in rats. A single injection of AdHNF1α (Supplementary information, Figure S2C and S2D) significantly restored the level of HNF1α in the nucleus of hepatocytes in fibrotic livers (Figure 3A and 3B). AdHNF1α injection reduced the ECM area by 50.9% and 49.8% in the DMN and BDL fibrotic model, respectively, in comparison to the AdGFP controls (P < 0.01, Figure 3C). The mRNA levels of α-SMA and COL1A1 were also reduced in fibrotic livers upon AdHNF1α treatment (Figure 3D). The level of hydroxyproline in livers treated with AdHNF1α was significantly lower than treated with AdGFP control in both DMN model (163.0 ± 17.4 g/mg vs 259.3 ± 23.7 μg/mg, P < 0.01) and BDL model (191.8 ± 10.8 μg/mg vs 252.5 ± 12.2 μg/mg, P < 0.01). Consistently, AdHNF1α treatment resulted in a significant reduction of inflammatory cytokines in the livers from both fibrotic models in comparison to the AdGFP control (Supplementary information, Figure S5). Similarly, up-regulation of HNF1α using lentivirus infection also ameliorated hepatic fibrosis induced with DMN (Supplementary information, Figure S6).
Figure 3.
HNF1α overexpression attenuates hepatic fibrosis. (A, B) A single dose of adenovirus carrying human HNF1α gene (HNF1α) or control virus (GFP) was injected into rats after DMN injection (A) or BDL operation (B). The fibrotic livers were analyzed at 4 weeks after DMN treatment or 3 weeks after BDL. The expression of HNF1α and α-SMA was assessed by immunohistochemistry. HE and Sirius red staining were used to examine pathological alterations and collagen deposition. (C) Semi-quantitative analysis of Sirius red staining in the fibrotic livers from AdHNF1α or AdGFP-treated rats (n = 6 rats in each group). (D) mRNA levels of HNF1α, α-SMA and COL1A1 in the livers were detected by real-time PCR. Scale bars, 100 μm. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
The anti-fibrotic effect of HNF1α mainly depends on the transcriptional activation of SHP-1
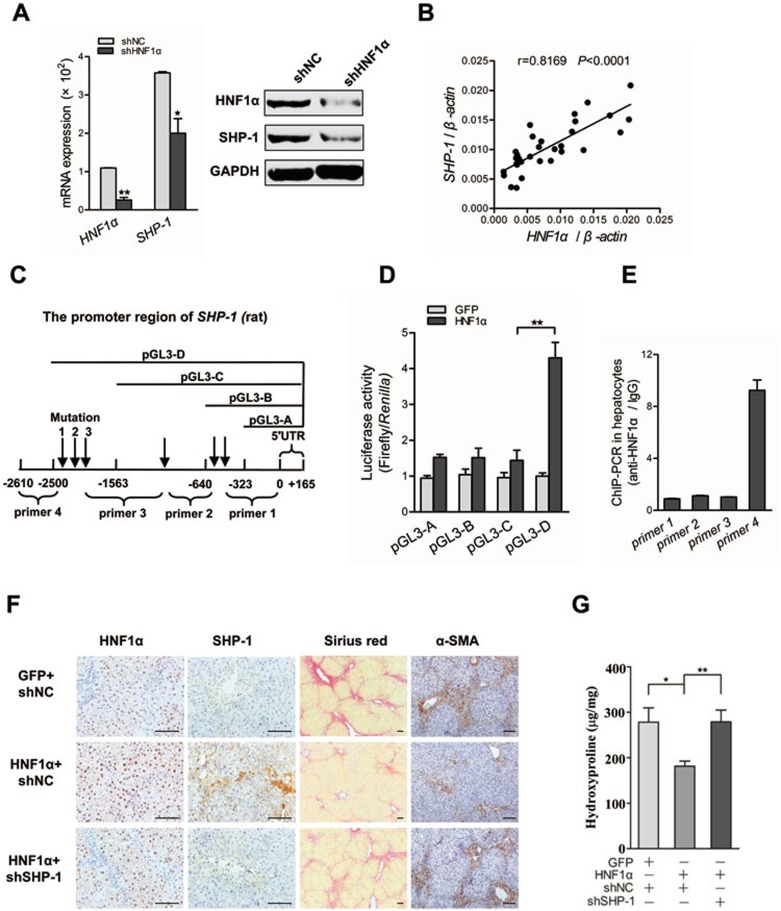
It is known that inflammation contributes to hepatic fibrosis in various types of acute and chronic liver diseases. Many tyrosine phosphatases have been reported to be involved in regulation of inflammatory response32,33,34,35. By searching a high quality transcription factor binding profile database, JASPAR36, six tyrosine phosphatase genes containing putative binding sites of HNF1α in their promoter region were selected as potential targets of HNF1α (Supplementary information, Table S1). Interestingly, HNF1α suppression by siRNA in primary rat hepatocytes markedly decreased the SHP-1 level (Figure 4A), but did not significantly affect the expression of other five phosphatases (data not shown). We also found significant positive correlations between the mRNA levels of HNF1α and SHP-1 in the liver from patients with cirrhosis (fibrosis) (Figure 4B, r = 0.8169, P < 0.0001), the rat fibrotic livers from DMN model (Supplementary information, Figure S7A, r = 0.7909, P = 0.0037) and the rat livers treated with AdshHNF1α or AdHNF1α in DMN model (Supplementary information, Figure S7B).
Figure 4.
Anti-fibrotic effect of HNF1α depends on the transcriptional activation of SHP-1. (A) Transcript level of HNF1α and SHP-1 in primary rat hepatocytes treated with AdshHNF1α or AdshNC. (B) Correlation between the mRNA levels of HNF1α and SHP-1 in human liver tissues. Each data point represents an individual sample, and the correlation coefficient (r) is shown. (C) A schematic representation of the promoter region of SHP-1, the potential cis-acting elements for HNF1α (arrow), mutation sites and the fragment amplified in ChIP-PCR. (D) The nested deletion analysis shows the transactivation effect of HNF1α on rat SHP-1 promoter. (E) HNF1α occupancy at the SHP-1 loci detected by ChIP-PCR in freshly isolated hepatocytes. (F) Suppression of SHP-1 reverses the anti-fibrotic effect of HNF1α. AdshSHP-1 or AdshNC was simultaneously delivered with AdHNF1α into DMN-treated rats. Collagen deposition and the expression of HNF1α, SHP-1 and α-SMA were detected in the livers. (G) Hydroxyproline content was assayed in the fibrotic livers (n = 9 rats in each group). Scale bars, 100 μm. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
To further determine the transactivation effect of HNF1α on SHP-1, a series of luciferase reporter plasmids containing nested deletions of SHP-1 promoter were transfected into HeLa cells infected with AdHNF1α (Figure 4C). This approach identified a potential HNF1α-binding region at -1563 nt to -2500 nt relative to the transcription start site in SHP-1 promoter (Figure 4D). Mutation experiment demonstrated that two cis-acting elements in SHP-1 promoter were required for the induction of SHP-1 transcription by HNF1α (Supplementary information, Figure S7D). Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay confirmed the direct binding of HNF1 to SHP-1 promoter in freshly isolated hepatocytes (Figure 4E). Overall, these data suggest that the expression of SHP-1 is transcriptionally regulated by HNF1α in hepatocytes.
To validate the functional role of SHP-1 in anti-fibrotic effect of HNF1α in vivo, we simultaneously delivered AdshSHP-1 and AdHNF1α into DMN-treated rats (Supplementary information, Figure S2E). SHP-1 knockdown decreased the magnitude of HNF1α-induced reduction of collagen deposition and HSC activation (Figure 4F). The hydroxyproline level was significantly higher in the AdSHP-1+AdHNF1α group (278.9 ± 25.8 μg/mg) than in the AdshNC+AdHNF1α group (181.6 ± 10.8 μg/mg, P = 0.0059, Figure 4G).
An inflammatory feedback circuit consisting of HNF1α, SHP-1, p65, STAT3, miR-21 and miR-146a aggravates hepatocellular impairment
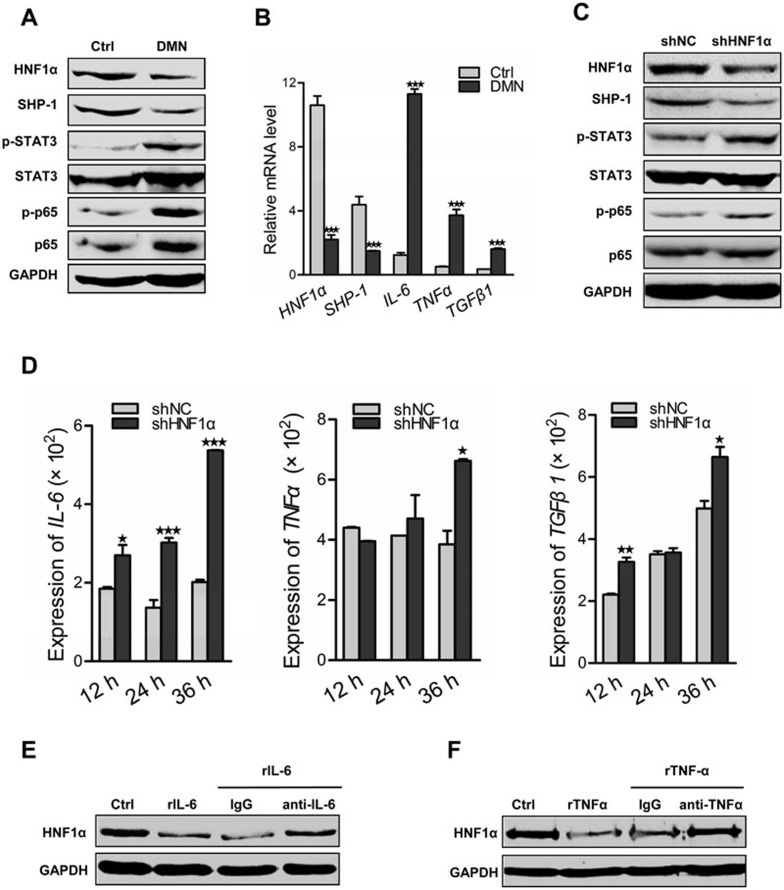
It is widely believed that SHP-1 negatively regulates inflammatory signal. Herein, we found that overexpression of HNF1α inhibited the activation of p65 (RelA), STAT3 and ERK in the fibrotic liver, which was reversed by SHP-1 suppression (Supplementary information, Figure S8). We then addressed the effect of HNF1α in inflammation signaling in hepatocytes. The expression of HNF1α and SHP-1 was significantly decreased in primary hepatocytes isolated from the DMN-treated rats, whereas JAK/STAT and NF-κB signaling pathways were activated (Figure 5A). Interestingly, the expression levels of representative proinflammatory and profibrotic cytokine, including IL-6, TNFα and TGFβ1, were significantly increased in these damaged hepatocytes (Figure 5B). Moreover, HNF1α knockdown in primary rat hepatocytes also led to the phosphorylation of STAT3 and p65 (RelA) (Figure 5C) and the increased expression of IL-6, TNFα and TGFβ1 (Figure 5D). A previous study has demonstrated the inhibitory effect of IL-6 on HNF1α expression in HBV-infected hepatocytes37. Consistently, we also found that IL-6 stimulation reduced the level of HNF1α in normal hepatocytes (Figure 5E). Similarly, TNFα treatment decreased HNF1α expression in hepatocytes (Figure 5F). These data imply that an inflammatory feedback mechanism may sustain the deregulation of HNF1α in the impaired hepatocytes.
Figure 5.
HNF1α suppression aggravates hepatocellular inflammation. (A) Western blot analysis of HNF1α, SHP-1 and phosphorylation of STAT3 and p65 in the lysates of hepatocytes isolated from rats with DMN treatment for 2 weeks. (B) mRNA levels of HNF1α, SHP-1, IL-6, TNFα and TGFβ1 in hepatocytes from rats with DMN treatment for 2 weeks vs the control rats. (C) Representative western blot of HNF1α, SHP-1, p65 and STAT3 in hepatocytes treated with AdshHNF1α or AdshNC. (D) Transcript levels of IL-6, TNFα and TGFβ1 in hepatocytes treated with AdshHNF1α or AdshNC for 12-36 h. (E, F) Protein level of HNF1α in the hepatocytes stimulated by recombinant IL-6 (rIL-6, 50 ng/ml, E) or recombinant TNFα (rTNFα, 20 ng/ml, F). Rabbit antibody against IL-6 (anti-IL-6) or against TNFα (anti-TNFα) was simultaneously added into medium to block the effect of IL-6 or TNFα, respectively. Normal rabbit IgG was used as control. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
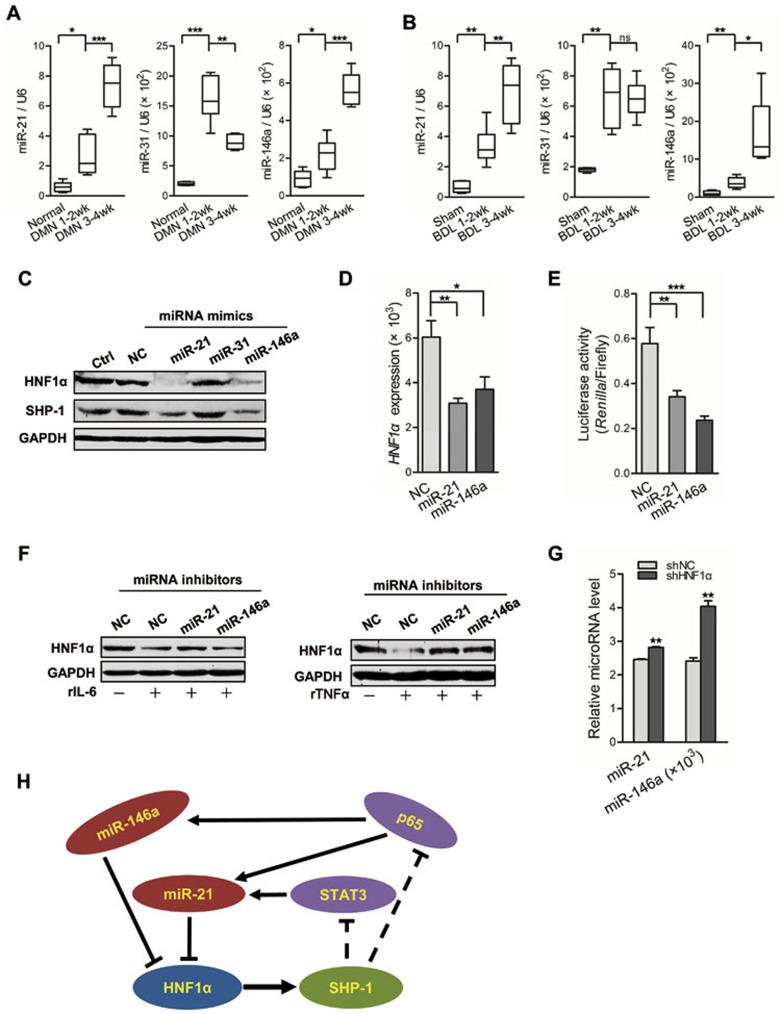
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are important post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression38. To delineate the mechanism by which HNF1α is repressed in hepatocytes, we searched the microRNA.org website for miRNA candidates that may directly regulate HNF1α expression. Sequence complementarity analysis revealed that HNF1α is a potential target of miR-21, miR-31 and miR-146a (Supplementary information, Figure S9A), all of which have been proven to be involved in inflammatory signaling pathways39,40,41. We found that these miRNAs were elevated in DMN- or BDL-induced fibrotic liver in rat (Figure 6A and 6B). Western blot showed that both HNF1α and SHP-1 in hepatocytes were notably repressed by the mimics of miR-21 and miR-146a, whereas miR-31 minic had no significant effect (Figure 6C). The mRNA level of HNF1α was also decreased by the mimic of miR-21 or miR-146a (Figure 6D). Luciferase assay showed that the mimic of miR-21 or miR-146a markedly decreased HNF1α 3′UTR reporter activity in HEK293T cells (Figure 6E). Together, these results demonstrate that both miR-21 and miR-146a can directly suppress HNF1α expression in hepatocytes.
Figure 6.
An HNF1α-regulated inflammatory circuit mediates hepatocellular impairment. (A, B) Real-time PCR analysis of miR-21, miR-31 and miR-146a in liver tissues from rats with DMN injection (n = 6 in each group) (A) and BDL treatment (n = 6 in each group) (B). (C) Western blot analysis of HNF1α and SHP-1 in hepatocytes transfected with indicated miRNA mimics for 72 h. (D) mRNA level of HNF1α in hepatocytes transfected with miRNA mimics for 48 h. (E) The effect of miR-21 and miR-146a mimics on luciferase activity of HNF1α 3′ UTR in HEK293T cells. (F) Western blot analysis of HNF1α in hepatocytes transfected with miRNA inhibitors and treated with IL-6 (rIL-6, left) or TNFα (rTNFα, right) for 48 h. (G) Levels of miR-21 and miR-146a in hepatocytes treated with AdshHNF1α or AdshNC. (H) A schematic model of the proposed HNF1α feedback circuit in hepatocellular damage. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
Previous study has indicated that NF-κB activation up-regulates the expression of miR-21 and miR-146a, while miR-21 also is transactivated by STAT342,43. Here, we also found that IL-6 increased the level of miR-21 but not miR-146a in hepatocytes. Inhibition of STAT3 with siRNA reversed the up-regulation of miR-21 expression by IL-6 (Supplementary information, Figure S9B), but did not alter the level of miR-146a. Similarly, suppressing p65 attenuated the up-regulation of both miR-21 and miR-146a induced by TNFα (Supplementary information, Figure S9C). Moreover, miR-21 inhibitor attenuated the reduction of HNF1α by IL-6 treatment. Likewise, inhibitors of both miR-21 and miR-146a apparently abrogated the suppression of HNF1α by TNFα stimulation in hepatocytes (Figure 6F). Furthermore, HNF1α knockdown in hepatocytes resulted in the increased expression of both miR-21 and miR-146a (Figure 6G). Based on these findings, we conclude that an intrinsic inflammatory feedback loop, consisting of HNF1α, SHP-1, STAT3, p65, miR-21 and miR-146a, can aggravate the hepatocellular impairment (Figure 6H).
HNF1α modulates the crosstalk between hepatocytes and HSCs
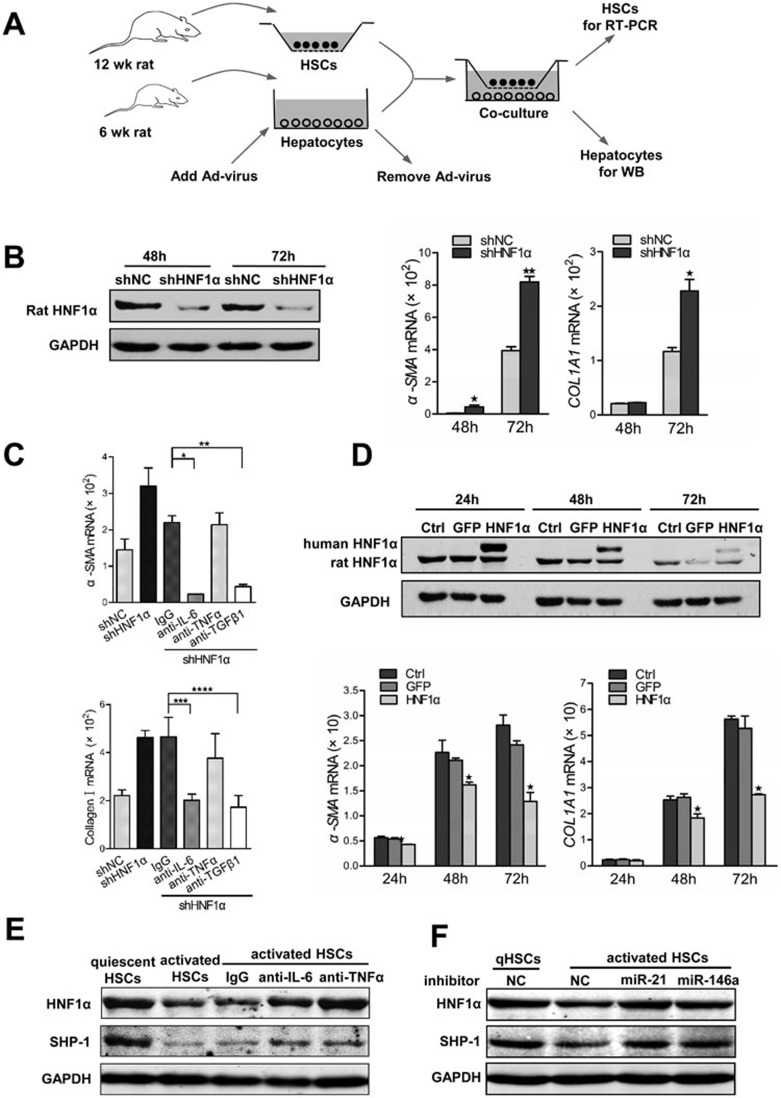
It is well known that the activation of HSCs is a central event in hepatic fibrogenesis3. The elevated expression of inflammatory cytokines in the impaired hepatocytes after DMN treatment (Figure 5B) or upon HNF1α suppression (Figure 5D) led us to investigate the potential effect of HNF1α expression in hepatocytes on the activation of HSCs. Previous studies have demonstrated the progressive activation of HSCs cultured on standard tissue culture plastic in vitro, and that this spontaneous activation of HSCs can be exploited to study cellular events similar to those occurring in liver injury44. Thus we co-cultured the primary HSCs with primary hepatocytes with HNF1α knockdown or overexpression (Figure 7A). Notably, HNF1α knockdown in hepatocytes led to higher expression of α-SMA and COL1A1 in HSCs (Figure 7B). In addition, IL-6 or TGFβ1 antibody blocked the effect of HNF1α knockdown in hepatocytes on HSC activation (Figure 7C). Consistently, co-transfection siHNF1α with siIL-6, siTgfb1 in hepatocytes reversed the effect of HNF1α knockdown in hepatocytes on HSC activation (Supplementary information, Figure S10A). In contrast, restoration of HNF1α in cultured hepatocytes significantly inhibited the expression of α-SMA and COL1A1 in HSCs (Figure 7D). These observations indicate that HNF1α suppression in hepatocytes can promote the activation of HSCs.
Figure 7.
Crosstalk between HSCs and hepatocytes in vitro. (A) A schematic representation of co-culture experiments with primary HSCs and hepatocytes isolated from rats. (B) Suppression of HNF1α in hepatocytes enhances the activation of HSCs. Endogenous HNF1α level in primary rat hepatocytes pretreated with AdshHNF1α or AdshNC was detected by western blot (left). mRNA levels of α-SMA and COL1A1 in HSCs were assessed by RT-PCR (right). (C) mRNA level of α-SMA and COL1A1 in HSCs co-cultured with AdshHNF1α- or AdshNC-treated hepatocytes. Antibody against IL-6, TNFα or TGFβ1 was added into the co-culture to block the corresponding cytokine. (D) Hepatocytes overexpressing HNF1α attenuates the activation of HSCs. Expression of exogenous human HNF1α and endogenous rat HNF1α in hepatocytes treated with AdHNF1α or AdGFP analyzed by western blot is shown in the top panel; mRNA levels of α-SMA and COL1A1 in HSCs are shown in the bottom panels. (E) Western blot analysis of HNF1α and SHP-1 in hepatocytes co-cultured with quiescent or activated HSCs for 48 h. Antibodies against TNFα, IL-6 and control IgG were used to block the cytokines in co-culture. (F) Expression of HNF1α and SHP-1 in hepatocytes transfected with miRNA inhibitors and then co-cultured with quiescent or activated HSCs for 48 h.
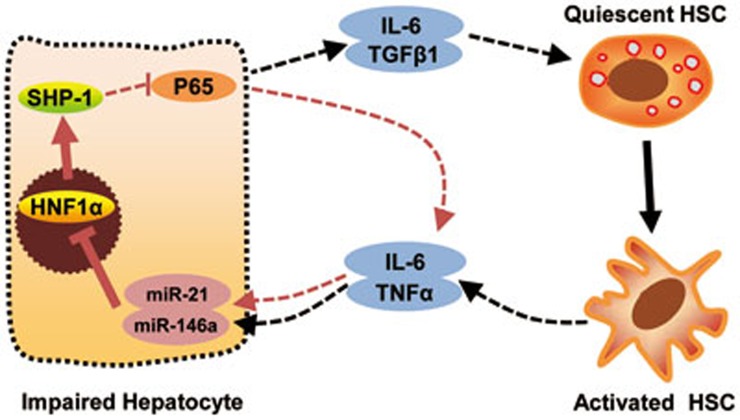
Activated HSCs produce several inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6 and TNFα44. We then asked whether activated HSCs affect the expression of HNF1α in hepatocytes. By co-culturing the primary hepatocytes with HSCs, we found that activated HSCs, but not quiescent HSCs, suppressed HNF1α expression in hepatocytes, and this suppression could be attenuated by neutralizing antibody to IL-6 or TNFα (Figure 7E). Knockdown of IL-6 or TNFα in activated HSCs also increased HNF1α expression in hepatocytes (Supplementary information, Figure S10B), suggesting that IL-6 and TNFα released from activated HSCs may inhibit HNF1α expression in hepatocytes. Moreover, transfection of hepatocytes with the inhibitor of miR-21 or miR-146a also abrogated the reduction of HNF1α induced by activated HSCs (Figure 7F). All together, these findings demonstrate that a microRNA-HNF1α-inflammatory circuit mediates the crosstalk between hepatocytes and HSCs, and drives the progression of hepatocellular damage and HSC activation (Figure 8).
Figure 8.
An HNF1α-mediated feedback circuit modulates the crosstalk between HSCs and hepatocytes. A schematic presentation of the proposed autocrine regulation and crosstalk between HSCs and hepatocytes. An intrinsic inflammatory feedback loop could aggravate the hepatocellular impairment. Inhibition of HNF1α in hepatocytes by miR-21 and miR-146a leads to an increase of IL-6 and TGFβ1 production, which causes the activation of HSCs. On the other hand, activated HSCs secrete IL-6 and TNFα, which further suppress the expression of HNF1α and SHP-1 in hepatocytes.
Discussion
In this study we provide several lines of evidence that implicate HNF1α in hepatic fibrogenesis. First, the abundant expression of HNF1α in hepatocytes gradually declines during the progression of fibrosis in both animal models and human chronic liver diseases. Second, inhibiting HNF1α exacerbates hepatic fibrogenesis in two independent rat models. Third, HNF1α overexpression attenuates ECM deposition in fibrotic liver in rats. We have previously shown a therapeutic effect of HNF1α on HCC21. Since the vast majority of HCC occurs in fibrotic or cirrhotic liver, the dual effect of HNF1α on HCC and fibrosis would be highly applicable in clinical practice. Our previous study demonstrated that up-regulation of HNF4α can potentially inhibit hepatic fibrosis45. The similar effect of HNF1α on fibrosis provides another support to our previous postulation that modulation of lineage-determining transcription factors such as HNF1α and HNF4α present a promising approach for the treatment of chronic liver diseases46.
Although the phosphatase SHP-1 is primarily detected in hematopoietic cells, it is also expressed in the liver, and its expression is suppressed in HCC tissues47. Previous study has demonstrated that SHP-1 regulates glucose homeostasis by modulating insulin signaling and insulin clearance in the liver48. A recent study revealed that hepatocyte-specific deletion of SHP-1 promotes hepatic lipid accretion in mice28. Additionally, Tai et al. have reported that SHP-1 is a major target of Sorafenib, the first clinically approved drug for HCC with additional therapeutic effect on hepatic fibrosis49. These studies suggest that SHP-1 plays an important role in liver homeostasis. In this study, we show that HNF1α transcriptionally activates SHP-1 expression via directly binding to SHP-1 promoter. Knockdown of SHP-1 significantly reverses the inhibitory effects of HNF1α on fibrosis as well as JAK/STAT and NF-κB signal pathways in fibrotic livers. These findings indicate that the suppression of inflammatory pathways by SHP-1 contributes significantly to the anti-fibrotic effect of HNF1α.
Both Kupffer cells and HSCs play important roles in the production of inflammatory cytokines in hepatic inflammation upon injury50. Hepatocytes express several types of receptors for inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNFα, suggesting that hepatocytes are potential effectors of cytokines51. Our experiments show that HNF1α suppression in hepatocyte promotes the phosphorylation of STAT3 and p65, which leads to the elevation of IL-6 and TNFα. Increased levels of both cytokines cause further inhibition of HNF1α in hepatocytes. These results suggest that hepatocytes are an additional source of inflammatory cytokines and hepatocellular damage can be sustained in an autocrine manner via IL-6 and TNFα. MicroRNAs are crucial regulators in a variety of diseases including cancer and fibrosis52. It is well established that miR-21 is directly activated by both STAT3 and NF-κB42,43. The induction of miR-146a by LPS is NF-κB-dependent in immune cells43. Consistently, miR-21 and miR-146a are up-regulated by inflammatory cytokines in hepatocytes. The repression of HNF1α in hepatocytes by IL-6 or TNF-α is mediated by miR-21 and miR-146a. Taken together, these findings posit HNF1α as a guardian of hepatocytes protecting the cells from hepatocellular damage. Down-regulation of HNF1α initiates a feedback circuit consisting of HNF1α, SHP-1, STAT3, p65, miR-21 and miR-146a, and this feedback loop perpetuates hepatic fibrogenesis.
The crosstalk between Kupffer cells and HSCs has been reported to mediate the progression of hepatic fibrosis53,52,54. However, the role of hepatocytes in liver fibrogenesis is relatively less investigated in the past decades. It has been reported that the apoptotic hepatocytes can drive the activation of HSCs11,12,13. A recent study revealed that overexpression of c-Myc in hepatocytes has the potential to prime resident HSCs for activation, proliferation and myofibroblast differentiation55. However, the role of impaired hepatocytes in the activation of HSCs in chronic liver injury remains elusive. Moreover, the role of HSCs in liver regeneration and the underlying mechanisms are also far from clear. Several studies have suggested that activated HSCs can stimulate hepatocyte regeneration56,57. However, a study by Ebrahimkhani et al. demonstrated a negative regulation of hepatocyte regeneration by HSCs through 5-HT2B signaling58. Here we show a crosstalk between hepatocytes and fibrogenic HSCs mediated by cytokines. HNF1α knockdown in hepatocytes triggers the activation of HSCs. As no apparent apoptosis was observed in hepatocytes in AdshHNF1α-treated rats (data not shown), the activation of HSC cannot be attributed to hepatocyte apoptosis. Furthermore, the suppression of HNF1α in hepatocytes by activated HSCs suggests that hepatocellular damage is induced not only in an autocrine manner but also in a paracrine manner. Considering the complex interaction among various cell types in the liver, we do not exclude the role of other hepatic cells such as Kupffer cells in the activation of HSCs. Cytokines other than IL-6, TNFα and TGFβ1 may also participate in the crosstalk between hepatocytes and HSCs.
Current treatments of hepatic fibrosis mainly target the HSCs. Our previous study indicates that down-regulation of HNF4α promotes the hepatic fibrogenesis and up-regulation of HNF4α ameliorates hepatic fibrosis via blocking EMT of hepatic cells in rats45. The current data demonstrate that reduction of HNF1α enhances the development of hepatic fibrosis and restoration of HNF1α significantly attenuates hepatic fibrosis in rats. Given that hepatocyte injury is a ubiquitous event for chronic liver injury7, we propose that restoration of hepatocytes function, particularly the activities of HNF1α or HNF4α, may represent a more effective strategy in the treatment of hepatic fibrosis.
In conclusion, the present investigation elucidates a novel molecular and cellular mechanism that is responsible for hepatocyte impairment and hepatic fibrogenesis. These findings highlight the biological significance of HNF1α and hepatocytes in hepatic fibrogenesis and inspire novel strategies in the treatment of chronic liver diseases. Considering the close correlation between fibrosis and HCC, the role of HNF1α and SHP-1 in hepatocellular carcinogenesis merits exploration.
Materials and Methods
Human tissue samples
Liver tissues were obtained from the liver tissue bank of the Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai. The healthy control (n = 12) was normal liver or liver with angeioma or liparomphalus. Fibrotic liver (n = 18) was from patients with hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects. The study protocol was approved by the Scientific Investigation Board of Second Military Medical University.
Real-time PCR
RNA purified from liver tissues, hepatocytes and HSCs in different treatments was reverse transcribed and then subjected to SYBR Green-based real-time PCR analysis. mRNA expression was normalized against β-actin. MicroRNA expression levels were quantified as previously described59. microRNA transcript was normalized against U6. At least three independent experiments were carried out for each condition. Primer sequences can be found in Supplementary information, Table S2.
Virus
Recombinant adenoviruses AdHNF1α and AdGFP were previously established in our lab21. Adenoviral vector containing shRNA targeting HNF1α (AdshHNF1α) or SHP-1 (AdshSHP-1) and the control adenovirus (AdshNC) were constructed as previously described60.
To generate lentivirus for knockdown or overexpression of HNF1α, lentiviral vectors (pmiRZIP-shHNF1α or pCDH-CMV-HNF1α) were cotransfected into subconfluent HEK 293T cells with packaging plasmid psPAX2 (Addgene) and envelope plasmid pMD2.G (Addgene) using FuGENE 6 transfection reagent (Promaga). The medium containing lentivirus was collected 48 h later. Lentiviral particles were concentrated as previously described and stored in cryovials at −80 °C until use61.
Animals and treatment
Male Sprague Dawley rats (6 weeks of age, approximately 200 g, from Shanghai Experimental Center of Chinese Academy of Sciences) were used to establish two separate models of hepatic fibrosis by repeated injection of DMN (10 mg/kg, three injections per week for 2-4 weeks) or bile duct ligation (BDL). To observe the effect of HNF1α inhibition on hepatic fibrosis, a single dose of 4 × 109 pfu AdshNC or AdshHNF1α was injected via tail vein 2 days prior to the first DMN injection or BDL and the animals were sacrificed 2 weeks later (Supplementary information, Figure S2A and S2B). To perform HNF1α knockdown with lentivirus, a single dose of 1 × 108 TU lenti-shNC or lenti-shHNF1α was injected via tail vein 5 days prior to the first DMN injection (Supplementary information, Figure S4A). To evaluate the potential therapeutic efficacy of HNF1α, a single dose of 4 × 109 pfu adenovirus was delivered via tail vein 3 days after BDL or 2 weeks after the first DMN injection (Supplementary information, Figure S2C and S2D). To perform HNF1α overexpression with lentivirus, a single dose of 1 × 108 TU lenti-Ctrl or lenti-HNF1α was injected via tail vein 1 week after the first DMN injection (Supplementary information, Figure S6A). Simultaneous administration of AdHNF1α and AdshSHP-1 to DMN-induced rats was performed to investigate the role of SHP-1 in the anti-fibrotic effect of HNF1α (Supplementary information, Figure S2E). All animal experiments were in accordance with the National Institute of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, and were approved by the Scientific Investigation Board of Second Military Medical University.
Histology and immunohistological analysis
Sirius red was used to stain for collagen. Immunohistochemistry was performed on paraffin-embedded liver sections. Antibodies against HNF1α (ab96777, Abcam), α-SMA (BM0002, Boster, Wuhan, China), SHP-1 (ab2020, Abcam), p-Erk1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204, 4370, Cell Signaling), p-p65 (sc-101752, Santa Cruz) and p-STAT3 (Ser727, 9134, Cell Signaling) were used for immunohistochemistry. Sections were stained with ImmunoCruz™ goat ABC Staining (Sc-2023, Santa Cruz) or EnVision Detection Rabbit/Mouse Kit (GK500710, GeneTech, Shanghai, China) and counterstained with hematoxylin. Areas of positive stained sites were measured using image analyses software Image-Pro Plus 6.0 (Media Cybernetics). Percentage of positive area in corresponding field of liver tissue was calculated to show the intensity of collagen deposition or protein expression.
Measurement of hepatic hydroxyproline content
Total hepatic hydroxyproline level was determined in the liver hydrolysates. One hundred mg of wet liver samples was subjected to acid hydrolysis to determine the amount of hydroxyproline using a commercial kit from Jiancheng (A030-2, Jiancheng, Nanjing, China).
Cell isolation and treatment
Primary hepatocytes and HSCs were prepared from male Sprague Dawley rats and cultured as previously described62,63. Hepatocytes were infected with adenoviral vectors at multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10. siRNA, miRNA mimics, miRNA inhibitors and their negative controls (NC or NC inhibitors) were synthesized by GenePharma (Shanghai GenePharma Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) and transfected into hepatocytes, HSCs or HEK293T cells with lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. siRNA sequences are listed in Supplementary information, Table S3.
Western blot assay
Cells were lysed in RIPA buffer (P0013B, Beyotime, Suzhou, China). Proteins were separated on a 10% polyacrylamide gel and transferred to a methanol-activated NC membrane (HAHY00010, Millipore). The membrane was blocked in PBS-T containing 5% milk for 2 h prior to incubation with a primary antibody overnight at 4 °C. After 2 h incubation with donkey-anti-mouse or donkey-anti-rabbit secondary antibody (IRDye 700 or IRDye 800, respectively), signals were examined and photographed using an Odyssey infrared imaging system (LI-COR) at a wavelength of 700 or 800 nm. The primary antibodies used included HNF1α (sc-10791, Santa Cruz), SHP-1 (sc-33162, Santa Cruz; 610125, BD biosciences), p-STAT3 (Ser727, 9134, Cell Signaling), STAT3 (4904, Cell Signaling), p-p65 (Ser536, 3033, Cell Signaling), p65 (3987, Cell Signaling), and GAPDH (BSAP0063, Bioworld). At least three independent experiments were carried out for each condition.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
Chromatin fragments derived from untreated hepatocytes were immunoprecipitated using 10 μg antibody against HNF1α (sc-6548, Santa Cruz). DNA extraction was performed using QIAGEN Purification Kit. Real-time PCR analysis was carried out for HNF1α binding sites in SHP-1 promoter. At least three independent experiments were carried out for each condition. The primers used are shown in Supplementary information, Table S4.
Reporter constructs and luciferase assay SHP-1 promoter construct
To test the transcriptional activity of HNF1α on SHP-1 promoter, rat SHP-1 fragments of −2500, −1563, −640 and −323/+165 were amplified by PCR from genomic DNA isolated from hepatocytes. The amplified fragments were cloned in the pGL3-Enhancer vector (E1771, Promega) at KpnI and XhoI. To test the HNF1α binding sites in the SHP-1 promoter region, SHP-1 promoter fragment (−3100/−1951) was inserted into pGL3-Promoter vector (E1761, Promega). Mutation was created using QuikChange® Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (200518, Stratagene). Primers for vector construction are listed in Supplementary information, Table S5. HeLa cells pre-infected with adenovirus for 24 h were co-transfected with SHP-1 promoter vectors together with the control pRL-CMV vector (E2261, Promega). Luciferase activity was measured by Dual-Glo® Luciferase Assay System (E2920, Promega) 48 h post transfection. At least three independent experiments were carried out for each construct.
HNF1α 3′UTR construct
HNF1α 3′UTR was amplified by PCR from rat hepatocyte cDNA and cloned into psiCHECK™-2 vector (C8021, Promega) at XhoI and NotI. The primers included: forward 5′-CCGCTCGAGGGATGGCTCTGAGGTGTCTC-3′ and reverse 5′-ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCCAAACCCGTGGCTTTACACT-3′. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with psiCHECK-HNF1α 3′UTR or control vector and microRNA mimics. Luciferase activity was measured 24 h post transfection. At least three independent transfection experiments were carried out for each condition.
Co-culture of HSCs and hepatocytes
To examine the effects of HNF1α knockdown in hepatocytes on HSCs, primary hepatocytes (48 h after isolation) were infected with AdshHNF1α or AdshNC at a MOI of 10 for 12 h. After thorough rinsing with PBS, the hepatocytes were co-cultured with primary HSCs for 24 h in the upper-chamber of 0.4 μm trans-well plates (3450, Corning). Antibodies against IL-6 (ab6672, Abcam), TNFα (ab66579, Abcam), TGFβ1 (sc-146, Santa Cruz) or control IgG (rabbit) was simultaneously added into the medium to neutralize the cytokine. Total RNA of HSCs and protein lysate of hepatocytes were harvested 48-72 h later. To examine the effects of hepatocytes with restored HNF1α on HSCs, primary hepatocytes from normal rats were infected with AdHNF1α or AdGFP at a MOI of 10 for 12 h, rinsed with PBS and then co-cultured with primary HSCs in trans-well plates. Total RNA of HSCs and protein lysate of hepatocytes were extracted 24-72 h later.
To determine the effect of HSCs on hepatocytes, HSCs were isolated from rats. Primary HSCs cultured for 7 d were used as activated HSCs and freshly isolated HSCs were used within 2 d as quiescent HSCs. The activated HSCs or quiescent HSCs were co-cultured with primary hepatocytes in trans-well plates. Antibodies or miRNA inhibitors were simultaneously added to the culture to block the effect of the cytokines or miRNAs. Protein lysates of hepatocytes were extracted 48 h later. At least three independent experiments were carried out for each condition.
Statistical analysis
Results are presented as mean ± sem. Two-sided independent Student's t test was performed to analyze gene and miRNA expression levels, hydroxyproline content, luciferase activity and histology data. Data on location parameter (median) were analyzed using Mann-Whitney methods.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Zhao-Hui Wei (TigerMed Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) for assistance on statistical analysis. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81470871; Key Program, 81230011; Creative Research Groups, 30921006) and Shanghai Science and Technology Committee for the Key Projects (13JC1407400).
Footnotes
(Supplementary information is linked to the online version of the paper on the Cell Research website.)
Supplementary Information
Expression of HNF1α in rat fibrotic liver.
Schematic representations for the induction of fibrotic models and treatment in rats.
HNF1α repression increases the expression of profibrotic and proinflammatory cytokines in hepatic fibrosis.
Downregulation of HNF1α increases the hepatic fibrogenesis in rats.
HNF1α overexpression attenuated hepatic fibrosis induced by DMN or BDL in rats.
Upregulation of HNF1α reduces the hepatic fibrogenesis in rats.
The SHP-1 was transcriptional regulated by HNF1α.
The anti-fibrotic effect of HNF1α mainly depends on the transcriptional activation of SHP-1.
HNF1α is downregulated by inflammation associating miRNAs.
The crosstalk between hepatocytes and HSCs is mediated by cytokines.
Predicted binding sites of HNF1α on the promoter of six phosphatases genes (rat) by JASPAR database
References
- Bataller R, Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:209–218. doi: 10.1172/JCI24282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuppan D, Afdhal NH. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet. 2008;371:838–851. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60383-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1655–1669. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Gea V, Friedman SL. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2011;6:425–456. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman SL. Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7:425–436. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2010.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malato Y, Naqvi S, Schurmann N, et al. Fate tracing of mature hepatocytes in mouse liver homeostasis and regeneration. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:4850–4860. doi: 10.1172/JCI59261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luedde T, Kaplowitz N, Schwabe RF. Cell death and cell death responses in liver disease: mechanisms and clinical relevance. Gastroenterology. 2014;147:765–783. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.07.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeschke H, Gujral JS, Bajt ML. Apoptosis and necrosis in liver disease. Liver Int. 2004;24:85–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2004.0906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan SS, Jiang JX, Wu J, et al. Phagocytosis of apoptotic bodies by hepatic stellate cells induces NADPH oxidase and is associated with liver fibrosis in vivo. Hepatology. 2006;43:435–443. doi: 10.1002/hep.21093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeschke H. Inflammation in response to hepatocellular apoptosis. Hepatology. 2002;35:964–966. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.0350964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inokuchi S, Aoyama T, Miura K, et al. Disruption of TAK1 in hepatocytes causes hepatic injury, inflammation, fibrosis, and carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:844–849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909781107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vick B, Weber A, Urbanik T, et al. Knockout of myeloid cell leukemia-1 induces liver damage and increases apoptosis susceptibility of murine hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2009;49:627–636. doi: 10.1002/hep.22664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takehara T, Tatsumi T, Suzuki T, et al. Hepatocyte specific disruption of Bcl-xL leads to continuous hepatocyte apoptosis and liver fibrotic responses. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1189–1197. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.07.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odom DT, Zizlsperger N, Gordon DB, et al. Control of pancreas and liver gene expression by HNF transcription factors. Science. 2004;303:1378–1381. doi: 10.1126/science.1089769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa RH, Kalinichenko VV, Holterman AX, Wang X. Transcription factors in liver development, differentiation, and regeneration. Hepatology. 2003;38:1331–1347. doi: 10.1016/j.hep.2003.09.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih DQ, Bussen M, Sehayek E, et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha is an essential regulator of bile acid and plasma cholesterol metabolism. Nat Genet. 2001;27:375–382. doi: 10.1038/86871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontoglio M, Barra J, Hadchouel M, et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 inactivation results in hepatic dysfunction, phenylketonuria, and renal Fanconi syndrome. Cell. 1996;84:575–585. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81033-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee YH, Sauer B, Gonzalez FJ. Laron dwarfism and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in the Hnf-1alpha knockout mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18:3059–3068. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.5.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers JC, Zhang W, Sehmi J, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies loci influencing concentrations of liver enzymes in plasma. Nat Genet. 2011;43:1131–1138. doi: 10.1038/ng.970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armendariz AD, Krauss RM. Hepatic nuclear factor 1-α: inflammation, genetics, and atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2009;20:106–111. doi: 10.1097/mol.0b013e3283295ee9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng X, Lin Y, Yin C, et al. Recombinant adenovirus carrying the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha gene inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma xenograft growth in mice. Hepatology. 2011;54:2036–2047. doi: 10.1002/hep.24647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paling NR, Welham MJ. Tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 acts at different stages of development to regulate hematopoiesis. Blood. 2005;105:4290–4297. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-08-3271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsui FW, Martin A, Wang J, Tsui HW. Investigations into the regulation and function of the SH2 domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase, SHP-1. Immunol Res. 2006;35:127–136. doi: 10.1385/IR:35:1:127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An H, Hou J, Zhou J, et al. Phosphatase SHP-1 promotes TLR- and RIG-I-activated production of type I interferon by inhibiting the kinase IRAK1. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:542–550. doi: 10.1038/ni.1604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharitonenkov A, Chen Z, Sures I, et al. A family of proteins that inhibit signalling through tyrosine kinase receptors. Nature. 1997;386:181–186. doi: 10.1038/386181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timms JF, Carlberg K, Gu H, et al. Identification of major binding proteins and substrates for the SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 in macrophages. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18:3838–3850. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.7.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong ZZ, Maiese K. The Src homology 2 domain tyrosine phosphatases SHP-1 and SHP-2: diversified control of cell growth, inflammation, and injury. Histol Histopathol. 2007;22:1251–1267. doi: 10.14670/hh-22.1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu E, Forest MP, Schwab M, et al. Hepatocyte-specific Ptpn6 deletion promotes hepatic lipid accretion, but reduces NAFLD in diet-induced obesity: Potential role of PPARgamma. Hepatology. 2014;59:1803–1815. doi: 10.1002/hep.26957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu E, Charbonneau A, Rolland Y, et al. Hepatocyte-specific Ptpn6 deletion protects from obesity-linked hepatic insulin resistance. Diabetes. 2012;61:1949–1958. doi: 10.2337/db11-1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y, Wong PP, Sjeklocha L, Steer CJ, Sahin MB. Mature hepatocytes exhibit unexpected plasticity by direct dedifferentiation into liver progenitor cells in culture. Hepatology. 2012;55:563–574. doi: 10.1002/hep.24712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. Immune response following intraocular delivery of recombinant viral vectors. Gene Ther. 2003;10:977–82. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3302030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanger K, Zong Y, Maggs L R, et al. Robust cellular reprogramming occurs spontaneously during liver regeneration. Genes Dev. 2013;27:719–724. doi: 10.1101/gad.207803.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang P, Liu X, Li Y, et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase with proline-glutamine-serine-threonine-rich motifs negatively regulates TLR-triggered innate responses by selectively inhibiting IkappaB kinase beta/NF-kappaB activation. J Immunol. 2013;190:1685–1694. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsumoto TR, Kudo M, Chen C, et al. The phosphatase CD148 promotes airway hyperresponsiveness through SRC family kinases. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:2037–2048. doi: 10.1172/JCI66397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalinger MR, Lang S, Weber A, et al. Loss of protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor type 22 regulates interferon-gamma-induced signaling in human monocytes. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:978–988. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.01.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryne JC, Valen E, Tang MH, et al. JASPAR, the open access database of transcription factor-binding profiles: new content and tools in the 2008 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:D102–106. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosel M, Quasdorff M, Wiegmann K, et al. Not interferon, but interleukin-6 controls early gene expression in hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 2009;50:1773–1782. doi: 10.1002/hep.23226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui M, Martello G, Piccolo S. MicroRNA control of signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:252–263. doi: 10.1038/nrm2868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nahid MA, Satoh M, Chan EK. MicroRNA in TLR signaling and endotoxin tolerance. Cell Mol Immunol. 2011;8:388–403. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2011.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moschos SA, Williams AE, Perry MM, et al. Expression profiling in vivo demonstrates rapid changes in lung microRNA levels following lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation but not in the anti-inflammatory action of glucocorticoids. BMC Genomics. 2007;8:240. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez Y, Wang C, Manes TD, Pober JS. Cutting edge: TNF-induced microRNAs regulate TNF-induced expression of E-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on human endothelial cells: feedback control of inflammation. J Immunol. 2010;184:21–25. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohanbash G, Okada H. MicroRNAs and STAT interplay. Semin Cancer Biol. 2012;22:70–75. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2011.12.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma X, Becker Buscaglia LE, Barker JR, Li Y. MicroRNAs in NF-kappaB signaling. J Mol Cell Biol. 2011;3:159–166. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjr007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman SL. Hepatic stellate cells: protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol Rev. 2008;88:125–172. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00013.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue HY, Yin C, Hou JL, et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha attenuates hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gut. 2010;59:236–246. doi: 10.1136/gut.2008.174904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ning BF, Ding J, Yin C, et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha suppresses the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2010;70:7640–7651. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Gorden A, et al. Ubiquitous activation of Ras and Jak/Stat pathways in human HCC. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1117–1128. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois MJ, Bergeron S, Kim HJ, et al. The SHP-1 protein tyrosine phosphatase negatively modulates glucose homeostasis. Nat Med. 2006;12:549–556. doi: 10.1038/nm1397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai WT, Shiau CW, Chen PJ, et al. Discovery of novel Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase 1 agonists from sorafenib for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2014;59:190–201. doi: 10.1002/hep.26640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan J.P. The role of intestinal endotoxin in liver injury: a long and evolving history. Hepatology. 2010;52:1829–1835. doi: 10.1002/hep.23917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacke F, Luedde T, Trautwein C. Inflammatory pathways in liver homeostasis and liver injury. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2009;36:4–12. doi: 10.1007/s12016-008-8091-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noetel A, Kwiecinski M, Elfimova N, Huang J, Odenthal M. microRNA are central players in anti- and profibrotic gene regulation during liver fibrosis. Front Physiol. 2012;3:49. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2012.00049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paik YH, Schwabe RF, Bataller R, Russo MP, Jobin C, Brenner DA. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory signaling by bacterial lipopolysaccharide in human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology. 2003;37:1043–1055. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2003.50182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki E, De Minicis S, Osterreicher CH, et al. TLR4 enhances TGF-beta signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med. 2007;13:1324–1332. doi: 10.1038/nm1663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevzorova YA, Hu W, Cubero FJ, et al. Overexpression of c-myc in hepatocytes promotes activation of hepatic stellate cells and facilitates the onset of liver fibrosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1832:1765–1775. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabuchi A, Mullaney I, Sheard PW, et al. Role of hepatic stellate cell/hepatocyte interaction and activation of hepatic stellate cells in the early phase of liver regeneration in the rat. J Hepatol. 2004;40:910–916. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2004.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passino MA, Adams RA, Sikorski SL, Akassoglou K. Regulation of hepatic stellate cell differentiation by the neurotrophin receptor p75NTR. Science. 2007;315:1853–1856. doi: 10.1126/science.1137603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimkhani MR, Oakley F, et al. Stimulating healthy tissue regeneration by targeting the 5-HT(2)B receptor in chronic liver disease. Nat Med. 2011;17:1668–1673. doi: 10.1038/nm.2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi R, Chiang VL. Facile means for quantifying microRNA expression by real-time PCR. Biotechniques. 2005;39:519–525. doi: 10.2144/000112010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong W, Shen WF, Ning BF, et al. Inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 by adenovirus mediated small interfering RNA attenuates hepatic fibrosis in rats. Hepatology. 2009;50:1524–1536. doi: 10.1002/hep.23189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B, Xia HQ, Cleghorn G, Gobe G, West M, Wei MQ. A highly efficient and consistent method for harvesting large volumes of high-titre lentiviral vectors. Gene Ther. 2001;8:1745–1751. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3301587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papeleu P, Vanhaecke T, Henkens T, et al. Isolation of rat hepatocytes. Methods Mol Biol. 2006;320:229–237. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-998-2:229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiskirchen R, Gressner AM. Isolation and culture of hepatic stellate cells. Methods Mol Med. 2005;117:99–113. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-940-0:099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Expression of HNF1α in rat fibrotic liver.
Schematic representations for the induction of fibrotic models and treatment in rats.
HNF1α repression increases the expression of profibrotic and proinflammatory cytokines in hepatic fibrosis.
Downregulation of HNF1α increases the hepatic fibrogenesis in rats.
HNF1α overexpression attenuated hepatic fibrosis induced by DMN or BDL in rats.
Upregulation of HNF1α reduces the hepatic fibrogenesis in rats.
The SHP-1 was transcriptional regulated by HNF1α.
The anti-fibrotic effect of HNF1α mainly depends on the transcriptional activation of SHP-1.
HNF1α is downregulated by inflammation associating miRNAs.
The crosstalk between hepatocytes and HSCs is mediated by cytokines.
Predicted binding sites of HNF1α on the promoter of six phosphatases genes (rat) by JASPAR database