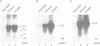Abstract
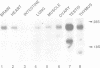
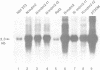
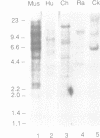
We have carried out an analysis of amplified DNA sequences present in a tumorigenic mouse cell line, designated 3T3DM, to determine if the presence of cellular transforming activity is correlated with the elevated expression of any of the amplified genes. These studies utilized a selection protocol that allowed for DNA sequence amplification after the introduction of each gene into non-transformed recipient cells. Cell lines obtained from this selection protocol were assayed for tumorigenicity in nude mice. The results provided evidence that a gene, mdm2, that is amplified more than 50-fold in the 3T3DM cell line, induces tumorigenicity when experimentally overexpressed in NIH3T3 cells and in Rat2 cells. Analysis of the predicted amino acid composition of the mdm2 product(s) revealed features similar to those that have been shown to be functionally significant in certain DNA binding proteins/transcriptional activators. These include two potential metal binding motifs and a negatively charged domain rich in acidic amino acid residues. Overall, the data support the conclusion that mdm2 represents an evolutionarily conserved gene with tumorigenic potential and a predicted role in mechanisms of cellular growth control.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Schwab M. Oncogene amplification in tumor cells. Adv Cancer Res. 1986;47:235–281. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahilly-Snyder L., Yang-Feng T., Francke U., George D. L. Molecular analysis and chromosomal mapping of amplified genes isolated from a transformed mouse 3T3 cell line. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 May;13(3):235–244. doi: 10.1007/BF01535205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Filby G., Greco S., Lau Y. F., Kan Y. W. Cosmid vectors for high efficiency DNA-mediated transformation and gene amplification in mammalian cells: studies with the human growth hormone gene. Gene. 1986;46(2-3):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90412-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Protein import into the cell nucleus. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:367–390. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. L., Powers V. E. Cloning of DNA from double minutes of Y1 mouse adrenocortical tumor cells: evidence for gene amplification. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90507-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin J. L., Milbrandt J. D., Heintz N. H., Azizkhan J. C. DNA sequence amplification in mammalian cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;90:31–82. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelekar A., Cole M. D. Tumorigenicity of fibroblast lines expressing the adenovirus E1a, cellular p53, or normal c-myc genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):7–14. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp B. E., Pearson R. B. Protein kinase recognition sequence motifs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Sep;15(9):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90073-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. P., Slate D. L., Gravel R., Ruddle F. H. Biological detection of specific mRNA molecules by microinjection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4503–4506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured animal cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Amler L. C. Amplification of cellular oncogenes: a predictor of clinical outcome in human cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1990 Jan;1(3):181–193. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigler P. B. Transcriptional activation. Acid blobs and negative noodles. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):210–212. doi: 10.1038/333210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh L., Jones K. W. The use of heparin as a simple cost-effective means of controlling background in nucleic acid hybridization procedures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5627–5638. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small M. B., Hay N., Schwab M., Bishop J. M. Neoplastic transformation by the human gene N-myc. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1638–1645. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder L. C., Trusko S. P., Freeman N., Eshleman J. R., Fakharzadeh S. S., George D. L. A gene amplified in a transformed mouse cell line undergoes complex transcriptional processing and encodes a nuclear protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):17150–17158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Gene amplification. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:447–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Lewis K. A., Ruiz J. C., Rothenberg B., Zhao J., Evans G. A. Cosmid vectors for rapid genomic walking, restriction mapping, and gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2160–2164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]