Abstract
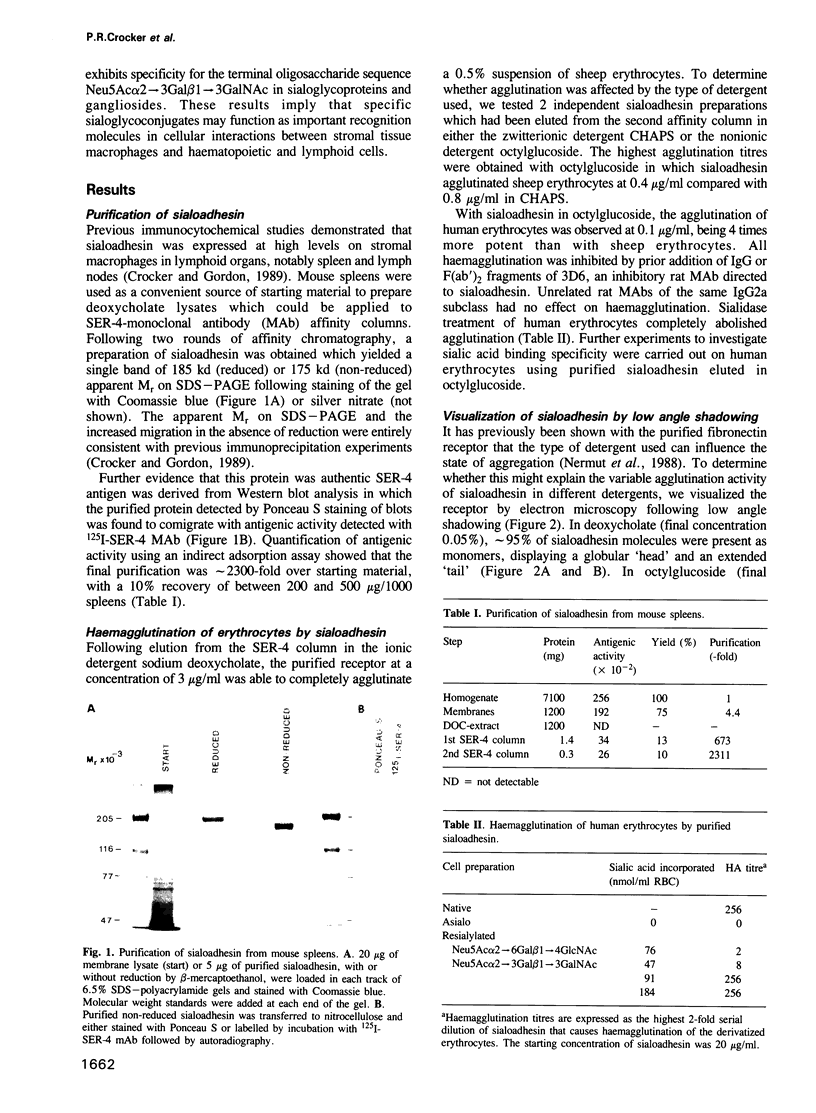
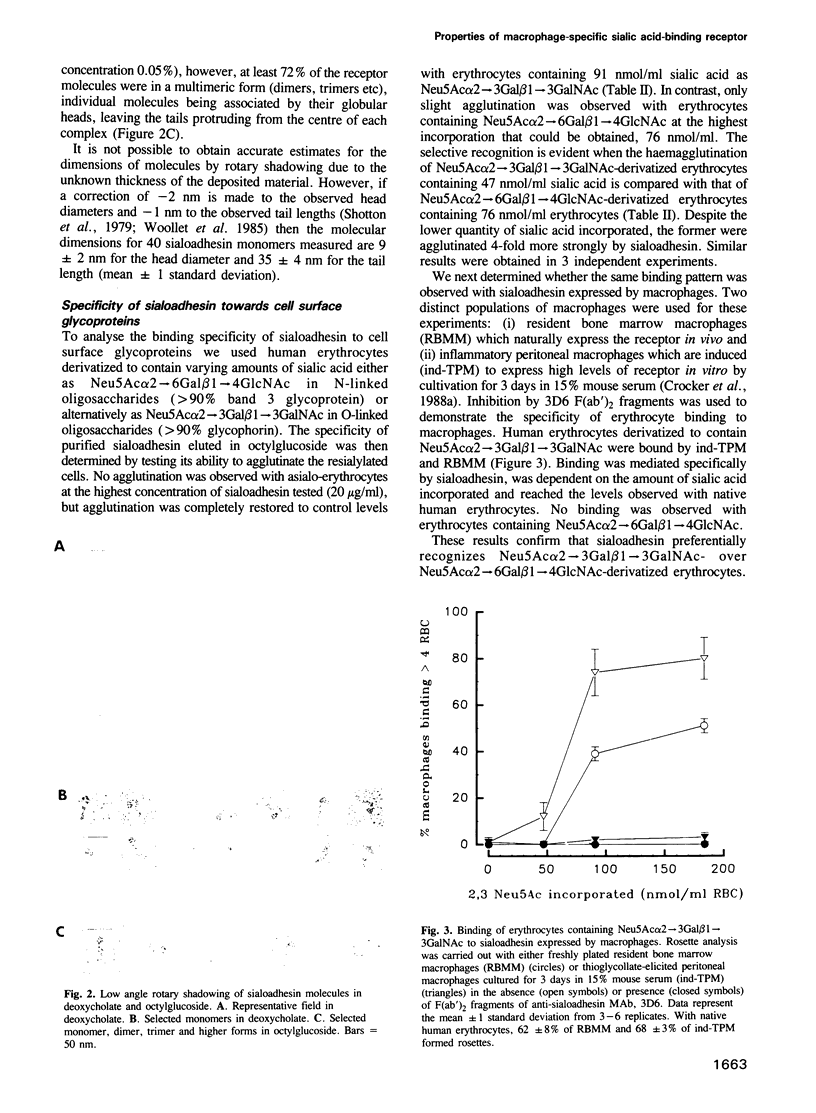
Macrophage subpopulations in the mouse express a lectin-like receptor, sialoadhesin (originally named sheep erythrocyte receptor, SER), which selectively recognizes sialoglycoconjugates and is likely to be involved in cellular interactions of stromal macrophages in haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. In this report we describe the purification and ligand specificity of sialoadhesin isolated from mouse spleen. Purified sialoadhesin, a glycoprotein of 185 kd apparent Mr, agglutinated sheep or human erythrocytes at nanomolar concentrations in a sialic acid-dependent manner. Low angle shadowing and electron microscopy showed that sialoadhesin consisted of a globular head region of approximately 9 nm and an extended tail of approximately 35 nm. To investigate the specificity for sialic acid, we studied the interaction of sialoadhesin with derivatized human erythrocytes, glycoproteins, and glycolipids. In conclusion, sialoadhesin specifically recognizes the oligosaccharide sequence Neu5Ac alpha 2----3Gal beta 1----3GalNAc in either sialoglycoproteins or gangliosides. These findings imply that specific sialoglycoconjugates carrying this structure may be involved in cellular interactions between stromal macrophages and subpopulations of haematopoietic cells and lymphocytes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed H., Gabius H. J. Purification and properties of a Ca2+-independent sialic acid-binding lectin from human placenta with preferential affinity to O-acetylsialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18673–18678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anstee D. J., Mawby W. J., Tanner M. J. Abnormal blood-group-Ss-active sialoglycoproteins in the membrane of Miltenberger class III, IV and V human erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1979 Nov 1;183(2):193–203. doi: 10.1042/bj1830193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Stengelin S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Seed B. Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1: an inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1160–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2466335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlos T. M., Harlan J. M. Membrane proteins involved in phagocyte adherence to endothelium. Immunol Rev. 1990 Apr;114:5–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1990.tb00559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson S. R., Sasaki H., Fukuda M. Structural variations of O-linked oligosaccharides present in leukosialin isolated from erythroid, myeloid, and T-lymphoid cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12787–12795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., Higa H. H., Paulson J. C. Different cell-surface receptor determinants of antigenically similar influenza virus hemagglutinins. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8357–8363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K. F. Ganglioside-modulated protein phosphorylation in muscle. Activation of phosphorylase b kinase by gangliosides. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18632–18637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly D. T., Townsend R. R., Kawaguchi K., Bell W. R., Lee Y. C. Binding and endocytosis of cluster glycosides by rabbit hepatocytes. Evidence for a short-circuit pathway that does not lead to degradation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):939–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corfield A. P., Higa H., Paulson J. C., Schauer R. The specificity of viral and bacterial sialidases for alpha(2-3)- and alpha(2-6)-linked sialic acids in glycoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 28;744(2):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corral L., Singer M. S., Macher B. A., Rosen S. D. Requirement for sialic acid on neutrophils in a GMP-140 (PADGEM) mediated adhesive interaction with activated platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1349–1356. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91598-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker P. R., Gordon S. Mouse macrophage hemagglutinin (sheep erythrocyte receptor) with specificity for sialylated glycoconjugates characterized by a monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1333–1346. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker P. R., Gordon S. Properties and distribution of a lectin-like hemagglutinin differentially expressed by murine stromal tissue macrophages. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1862–1875. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker P. R., Hill M., Gordon S. Regulation of a murine macrophage haemagglutinin (sheep erythrocyte receptor) by a species-restricted serum factor. Immunology. 1988 Dec;65(4):515–522. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker P. R., Werb Z., Gordon S., Bainton D. F. Ultrastructural localization of a macrophage-restricted sialic acid binding hemagglutinin, SER, in macrophage-hematopoietic cell clusters. Blood. 1990 Sep 15;76(6):1131–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois C., Manuguerra J. C., Hauttecoeur B., Maze J. Monoclonal antibody A2B5, which detects cell surface antigens, binds to ganglioside GT3 (II3 (NeuAc)3LacCer) and to its 9-O-acetylated derivative. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2797–2803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournet B., Montreuil J., Strecker G., Dorland L., Haverkamp J., Vliegenthart F. G., Binette J. P., Schmid K. Determination of the primary structures of 16 asialo-carbohydrate units derived from human plasma alpha 1-acid glycoprotein by 360-MHZ 1H NMR spectroscopy and permethylation analysis. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5206–5214. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda M., Carlsson S. R., Klock J. C., Dell A. Structures of O-linked oligosaccharides isolated from normal granulocytes, chronic myelogenous leukemia cells, and acute myelogenous leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12796–12806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furthmayr H., Marchesi V. T. Glycophorins: isolation, orientation, and localization of specific domains. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:268–280. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geoffroy J. S., Rosen S. D. Demonstration that a lectin-like receptor (gp90MEL) directly mediates adhesion of lymphocytes to high endothelial venules of lymph nodes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2463–2469. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. Blot analyses of glycoconjugates: enzyme-hydrazide--a novel reagent for the detection of aldehydes. Anal Biochem. 1985 Apr;146(1):59–63. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90395-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkamp J., van Halbeek H., Dorland L., Vliegenthart J. F., Pfeil R., Schauer R. High-resolution 1H-NMR spectroscopy of free and glycosidically linked O-acetylated sialic acids. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Feb;122(2):305–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai Y., True D. D., Singer M. S., Rosen S. D. Direct demonstration of the lectin activity of gp90MEL, a lymphocyte homing receptor. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1225–1232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. I., Cook R. G., McEver R. P. Cloning of GMP-140, a granule membrane protein of platelets and endothelium: sequence similarity to proteins involved in cell adhesion and inflammation. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1033–1044. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90636-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen N., Barclay A. N., Willis A. C., Williams A. F. The sequence of rat leukosialin (W3/13 antigen) reveals a molecule with O-linked glycosylation of one third of its extracellular amino acids. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4029–4034. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02747.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen E., Palabrica T., Sajer S., Gilbert G. E., Wagner D. D., Furie B. C., Furie B. PADGEM-dependent adhesion of platelets to monocytes and neutrophils is mediated by a lineage-specific carbohydrate, LNF III (CD15). Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):467–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90443-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky L. A., Singer M. S., Yednock T. A., Dowbenko D., Fennie C., Rodriguez H., Nguyen T., Stachel S., Rosen S. D. Cloning of a lymphocyte homing receptor reveals a lectin domain. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):1045–1055. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90637-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H., Kelm S., Yoshino T., Schauer R. Carbohydrate specificity of the galactose-recognizing receptor of rat peritoneal macrophages. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 Aug;369(8):705–714. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1988.369.2.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe J. B., Stoolman L. M., Nair R. P., Larsen R. D., Berhend T. L., Marks R. M. ELAM-1--dependent cell adhesion to vascular endothelium determined by a transfected human fucosyltransferase cDNA. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):475–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90444-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnani J. L., Smith D. F., Ginsburg V. Detection of gangliosides that bind cholera toxin: direct binding of 125I-labeled toxin to thin-layer chromatograms. Anal Biochem. 1980 Dec;109(2):399–402. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90667-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Tsuji S. Bioactive ganglioside-mediated carbohydrate recognition in coupling with ecto-protein phosphorylation. Ciba Found Symp. 1989;145:119-30, discussion 130-4. doi: 10.1002/9780470513828.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nermut M. V., Green N. M., Eason P., Yamada S. S., Yamada K. M. Electron microscopy and structural model of human fibronectin receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4093–4099. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03303.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda S., Sato M., Toyoshima S., Osawa T. Purification and characterization of a lectin-like molecule specific for galactose/N-acetyl-galactosamine from tumoricidal macrophages. J Biochem. 1988 Oct;104(4):600–605. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L. Leukocyte adhesion to endothelium in inflammation. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):3–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90230-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallant A., Eskenazi A., Mattei M. G., Fournier R. E., Carlsson S. R., Fukuda M., Frelinger J. G. Characterization of cDNAs encoding human leukosialin and localization of the leukosialin gene to chromosome 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1328–1332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Rogers G. N., Korhonen T., Dahr W., Finne J. Identification of the O-linked sialyloligosaccharides of glycophorin A as the erythrocyte receptors for S-fimbriated Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):37–42. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.37-42.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. C., Rogers G. N. Resialylated erythrocytes for assessment of the specificity of sialyloligosaccharide binding proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1987;138:162–168. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)38013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulson J. C., Weinstein J., de Souza-e-Silva U. Identification of a Gal beta 1 goes to 3GlcNAc alpha 2 goes to 3 sialyltransferase in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4034–4037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. L., Nudelman E., Gaeta F. C., Perez M., Singhal A. K., Hakomori S., Paulson J. C. ELAM-1 mediates cell adhesion by recognition of a carbohydrate ligand, sialyl-Lex. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1130–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.1701274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piller F., Piller V., Fox R. I., Fukuda M. Human T-lymphocyte activation is associated with changes in O-glycan biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):15146–15150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett T. J., Brossmer R., Rose U., Paulson J. C. Recognition of monovalent sialosides by influenza virus H3 hemagglutinin. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):502–506. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90026-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett T. J., Paulson J. C. Basis for the potent inhibition of influenza virus infection by equine and guinea pig alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 15;264(17):9850–9858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravindranath M. H., Higa H. H., Cooper E. L., Paulson J. C. Purification and characterization of an O-acetylsialic acid-specific lectin from a marine crab Cancer antennarius. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8850–8856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter G., Kelm S., Schauer R. Chemistry and biology of cell surface glycoconjugates. Acta Histochem Suppl. 1988;36:51–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedl M., Forster O., Rumpold H., Bernheimer H. A ganglioside-dependent cellular binding mechanism in rat macrophages. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1205–1210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers G. N., Paulson J. C. Receptor determinants of human and animal influenza virus isolates: differences in receptor specificity of the H3 hemagglutinin based on species of origin. Virology. 1983 Jun;127(2):361–373. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen S. D., Chi S. I., True D. D., Singer M. S., Yednock T. A. Intravenously injected sialidase inactivates attachment sites for lymphocytes on high endothelial venules. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 15;142(6):1895–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen S. D., Singer M. S., Yednock T. A., Stoolman L. M. Involvement of sialic acid on endothelial cells in organ-specific lymphocyte recirculation. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):1005–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.4001928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVENNERHOLM L. Quantitative estimation of sialic acids. II. A colorimetric resorcinol-hydrochloric acid method. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jun;24(3):604–611. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90254-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. E., Rearick J. I., Paulson J. C., Hill R. L. Purification to homogeneity of a beta-galactoside alpha2 leads to 3 sialyltransferase and partial purification of an alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminide alpha2 leads to 6 sialyltransferase from porcine submaxillary glands. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4434–4442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sariola H., Aufderheide E., Bernhard H., Henke-Fahle S., Dippold W., Ekblom P. Antibodies to cell surface ganglioside GD3 perturb inductive epithelial-mesenchymal interactions. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90556-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauter N. K., Bednarski M. D., Wurzburg B. A., Hanson J. E., Whitesides G. M., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Hemagglutinins from two influenza virus variants bind to sialic acid derivatives with millimolar dissociation constants: a 500-MHz proton nuclear magnetic resonance study. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 17;28(21):8388–8396. doi: 10.1021/bi00447a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer R. Analysis of sialic acids. Methods Enzymol. 1987;138:132–161. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)38012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon N., Lis H. Lectins as cell recognition molecules. Science. 1989 Oct 13;246(4927):227–234. doi: 10.1126/science.2552581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shier W. T., Lin Y., DeVries A. L. Structure of the carbohydrate of antifreeze glycoproteins from an antartic fish. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jun 15;54(2):135–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80060-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotton D. M., Burke B. E., Branton D. The molecular structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. Biophysical and electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jun 25;131(2):303–329. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speert D. P., Wright S. D., Silverstein S. C., Mah B. Functional characterization of macrophage receptors for in vitro phagocytosis of unopsonized Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):872–879. doi: 10.1172/JCI113692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Nagao Y., Kato H., Matsumoto M., Nerome K., Nakajima K., Nobusawa E. Human influenza A virus hemagglutinin distinguishes sialyloligosaccharides in membrane-associated gangliosides as its receptor which mediates the adsorption and fusion processes of virus infection. Specificity for oligosaccharides and sialic acids and the sequence to which sialic acid is attached. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):17057–17061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner M. J. Erythrocyte membrane structure and function. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;94:3–23. doi: 10.1002/9780470715444.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz G., Aruffo A., Kolanus W., Bevilacqua M., Seed B. Recognition by ELAM-1 of the sialyl-Lex determinant on myeloid and tumor cells. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1132–1135. doi: 10.1126/science.1701275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein J., de Souza-e-Silva U., Paulson J. C. Sialylation of glycoprotein oligosaccharides N-linked to asparagine. Enzymatic characterization of a Gal beta 1 to 3(4)GlcNAc alpha 2 to 3 sialyltransferase and a Gal beta 1 to 4GlcNAc alpha 2 to 6 sialyltransferase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13845–13853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong R. C., Remold-O'Donnell E., Vercelli D., Sancho J., Terhorst C., Rosen F., Geha R., Chatila T. Signal transduction via leukocyte antigen CD43 (sialophorin). Feedback regulation by protein kinase C. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1455–1460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woollett G. R., Williams A. F., Shotton D. M. Visualisation by low-angle shadowing of the leucocyte-common antigen. A major cell surface glycoprotein of lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2827–2830. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]