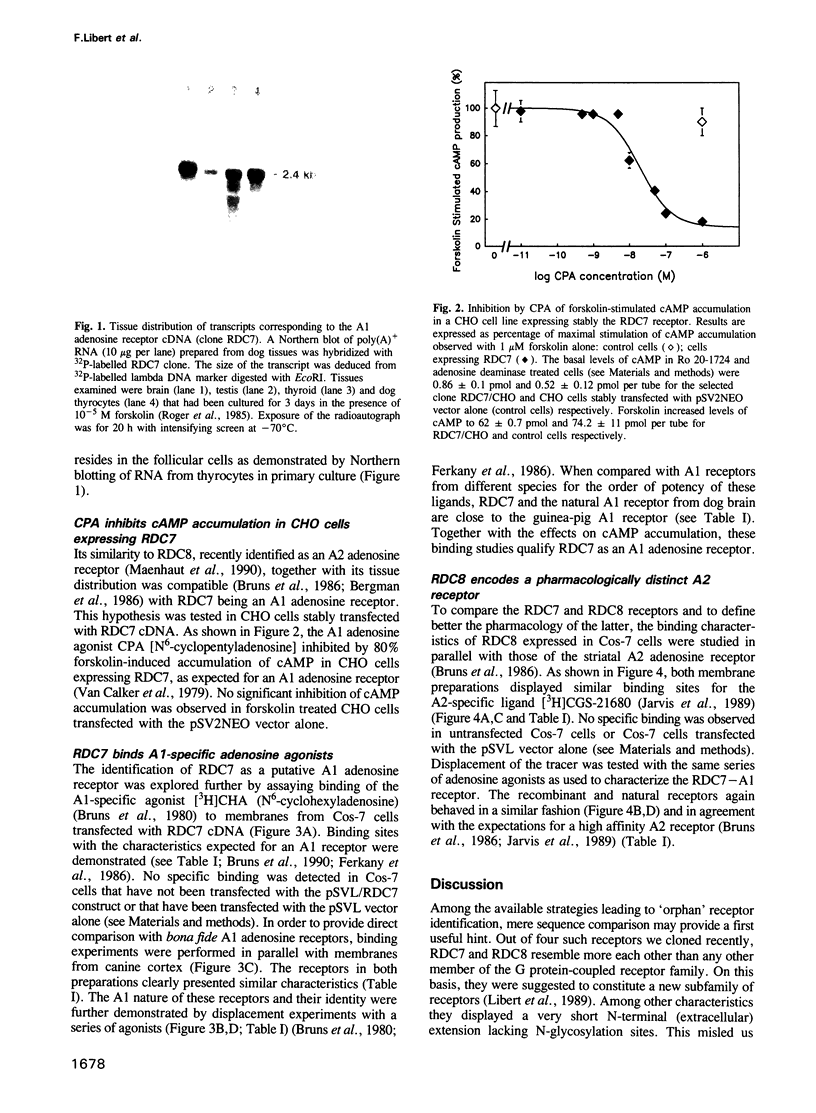
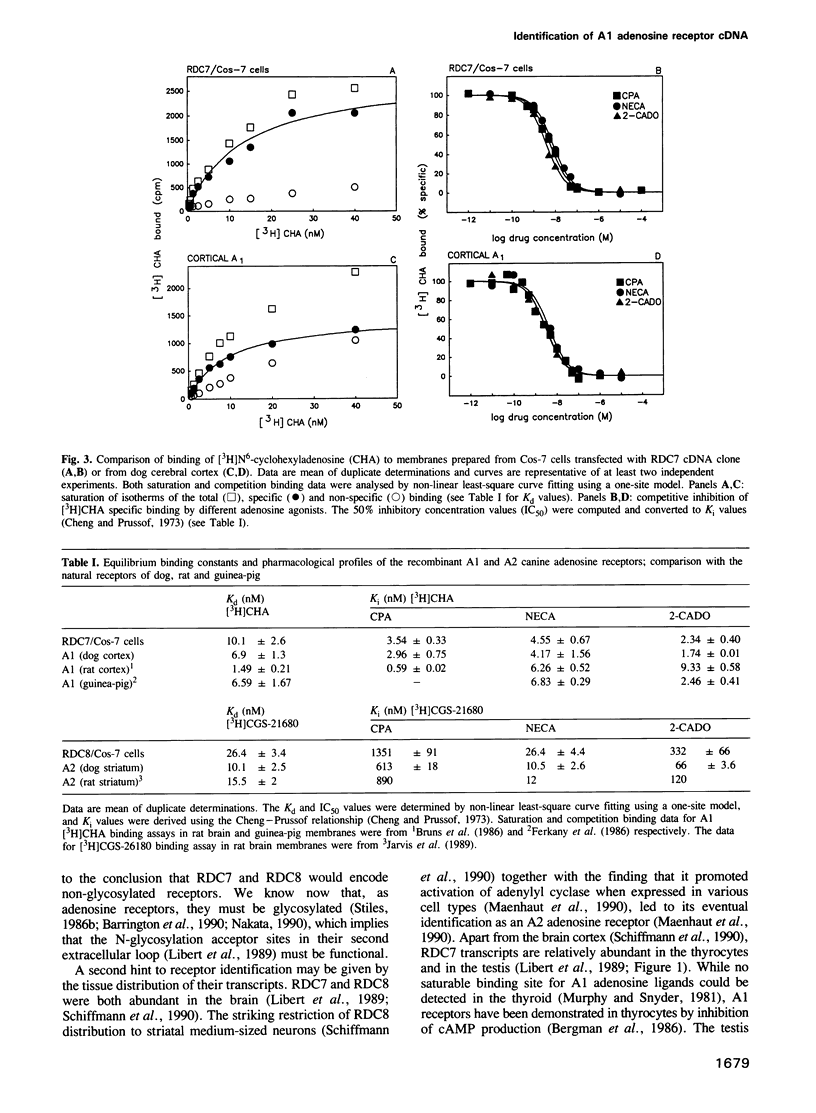
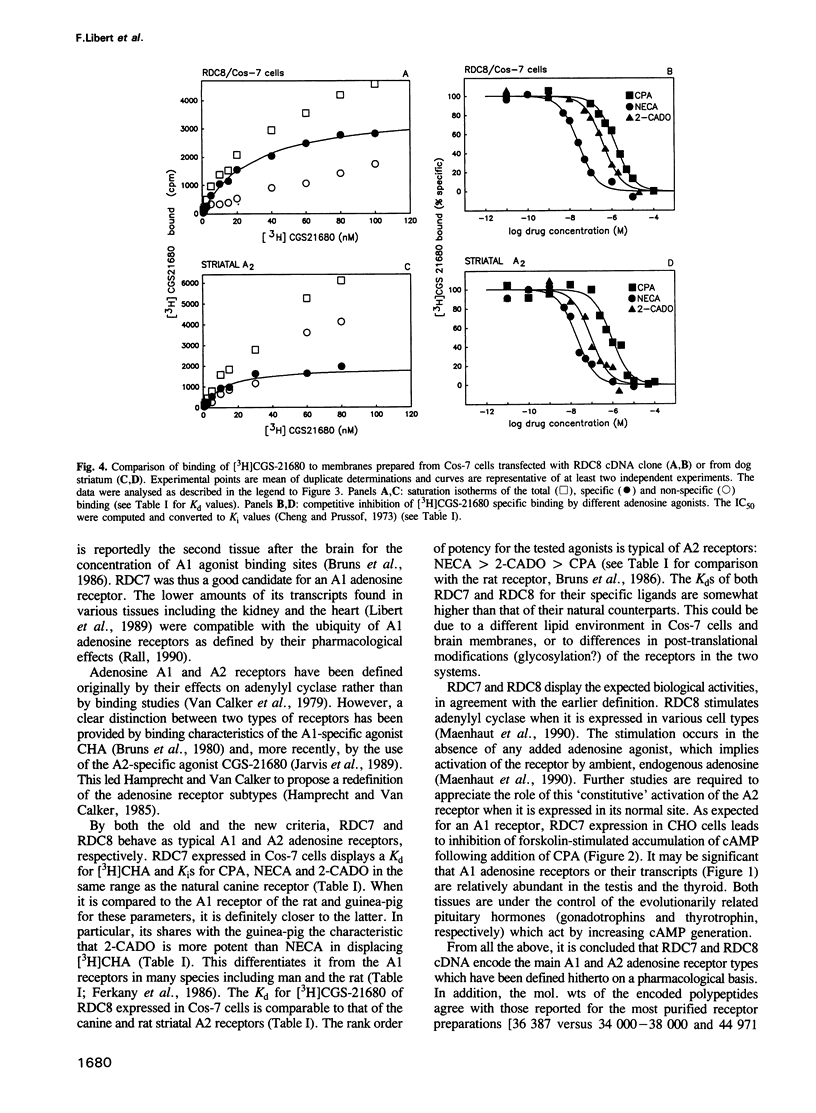
Abstract
The extensive amino acid sequence conservation among G protein-coupled receptors has been exploited to clone new members of this large family by homology screening or by PCR. Out of four such receptor cDNAs we cloned recently, RDC7 corresponds to a relatively abundant transcript in the brain cortex, the thyroid follicular cell and the testis. We have now identified RDC7 as an A1 adenosine receptor. The A1 agonist CPA [N6-cyclopentyladenosine] decreased by 80% cAMP accumulation in forskolin-stimulated CHO cells stably transfected with RDC7. Specific binding of another A1 adenosine agonist, [3H]CHA [N6-cyclohexyladenosine], was demonstrated on membranes from Cos cells transfected with a pSVL construct harbouring the RDC7 cDNA insert. The binding characteristics were similar to those of the natural brain A1 receptor. The recombinant and the natural receptors behaved also in the same way in displacement experiments involving a series of A1 adenosine agonists. The binding characteristics of RDC7 were compared to those of RDC8, another orphan receptor recently identified as an A2 adenosine receptor. The two molecular species RDC7 and RDC8 correspond clearly to the A1 and A2 receptor entities defined hitherto on a purely pharmacological basis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali H., Cunha-Melo J. R., Saul W. F., Beaven M. A. Activation of phospholipase C via adenosine receptors provides synergistic signals for secretion in antigen-stimulated RBL-2H3 cells. Evidence for a novel adenosine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):745–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrington W. W., Jacobson K. A., Hutchison A. J., Williams M., Stiles G. L. Identification of the A2 adenosine receptor binding subunit by photoaffinity crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6572–6576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrington W. W., Jacobson K. A., Stiles G. L. Glycoprotein nature of the A2-adenosine receptor binding subunit. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;38(2):177–183. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman M. I., Thomas C. G., Jr, Nayfeh S. N. Inhibition of thyrotropin-stimulated adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate formation in rat thyroid cells by an adenosine analog. Evidence that the inhibition is mediated by the putative inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1986;11(2):99–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooker G., Harper J. F., Terasaki W. L., Moylan R. D. Radioimmunoassay of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:1–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Daly J. W., Snyder S. H. Adenosine receptors in brain membranes: binding of N6-cyclohexyl[3H]adenosine and 1,3-diethyl-8-[3H]phenylxanthine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Lu G. H., Pugsley T. A. Characterization of the A2 adenosine receptor labeled by [3H]NECA in rat striatal membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):331–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. B., Gross R., Su Y. F., Perkins J. P. Regulation of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate content in human astrocytoma cells by adenosine and the adenine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5296–5303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Kobilka B. K., Strader D. J., Benovic J. L., Dohlman H. G., Frielle T., Bolanowski M. A., Bennett C. D., Rands E., Diehl R. E. Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor and homology with rhodopsin. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):75–79. doi: 10.1038/321075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eva C., Keinänen K., Monyer H., Seeburg P., Sprengel R. Molecular cloning of a novel G protein-coupled receptor that may belong to the neuropeptide receptor family. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80377-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fargin A., Raymond J. R., Lohse M. J., Kobilka B. K., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. The genomic clone G-21 which resembles a beta-adrenergic receptor sequence encodes the 5-HT1A receptor. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):358–360. doi: 10.1038/335358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Dunwiddie T. V. How does adenosine inhibit transmitter release? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Apr;9(4):130–134. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hla T., Maciag T. An abundant transcript induced in differentiating human endothelial cells encodes a polypeptide with structural similarities to G-protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9308–9313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis M. F., Schulz R., Hutchison A. J., Do U. H., Sills M. A., Williams M. [3H]CGS 21680, a selective A2 adenosine receptor agonist directly labels A2 receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Dec;251(3):888–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo T., Fukuda K., Mikami A., Maeda A., Takahashi H., Mishina M., Haga T., Haga K., Ichiyama A., Kangawa K. Cloning, sequencing and expression of complementary DNA encoding the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):411–416. doi: 10.1038/323411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert F., Parmentier M., Lefort A., Dinsart C., Van Sande J., Maenhaut C., Simons M. J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Selective amplification and cloning of four new members of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):569–572. doi: 10.1126/science.2541503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maenhaut C., Van Sande J., Libert F., Abramowicz M., Parmentier M., Vanderhaegen J. J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G., Schiffmann S. RDC8 codes for an adenosine A2 receptor with physiological constitutive activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1169–1178. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80909-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy K. M., Snyder S. H. Adenosine receptors in rat testes: labeling with 3H-cyclohexyladenosine. Life Sci. 1981 Feb 23;28(8):917–920. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata H. A1 adenosine receptor of rat testis membranes. Purification and partial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):671–677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata H. Purification of A1 adenosine receptor from rat brain membranes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16545–16551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Structure of the adrenergic and related receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:67–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmentier M., Libert F., Maenhaut C., Lefort A., Gérard C., Perret J., Van Sande J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Molecular cloning of the thyrotropin receptor. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1620–1622. doi: 10.1126/science.2556796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret J., Ludgate M., Libert F., Gerard C., Dumont J. E., Vassart G., Parmentier M. Stable expression of the human TSH receptor in CHO cells and characterization of differentially expressing clones. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 28;171(3):1044–1050. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90789-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prémont J., Perez M., Bockaert J. Adenosine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in rat striatal homogenates and its relationship to dopamine- and Ca2+-sensitive adenylate cyclases. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Jul;13(4):662–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. A., Sebastião A. M. Adenosine receptors and calcium: basis for proposing a third (A3) adenosine receptor. Prog Neurobiol. 1986;26(3):179–209. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(86)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roger P. P., Van Heuverswyn B., Lambert C., Reuse S., Vassart G., Dumont J. E. Antagonistic effects of thyrotropin and epidermal growth factor on thyroglobulin mRNA level in cultured thyroid cells. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):239–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09189.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross P. C., Figler R. A., Corjay M. H., Barber C. M., Adam N., Harcus D. R., Lynch K. R. RTA, a candidate G protein-coupled receptor: cloning, sequencing, and tissue distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3052–3056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann S. N., Libert F., Vassart G., Dumont J. E., Vanderhaeghen J. J. A cloned G protein-coupled protein with a distribution restricted to striatal medium-sized neurons. Possible relationship with D1 dopamine receptor. Brain Res. 1990 Jun 11;519(1-2):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90097-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Adenosine as a neuromodulator. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1985;8:103–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.08.030185.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel A. M. Guanine nucleotide binding proteins and signal transduction. Vitam Horm. 1988;44:47–101. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60693-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles G. L. Photoaffinity cross-linked A1 adenosine receptor-binding subunits. Homologous glycoprotein expression by different tissues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 15;261(23):10839–10843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Candelore M. R., Rands E., Hill W. S., Dixon R. A. Conserved aspartic acid residues 79 and 113 of the beta-adrenergic receptor have different roles in receptor function. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10267–10271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Sande J., Dumont J. E. Effects of thyrotropin, prostaglandin E1 and iodide on cyclic 3',5'-AMP concentration in dog thyroid slices. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 28;313(2):320–328. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velu T. J., Beguinot L., Vass W. C., Zhang K., Pastan I., Lowy D. R. Retroviruses expressing different levels of the normal epidermal growth factor receptor: biological properties and new bioassay. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Feb;39(2):153–166. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Calker D., Müller M., Hamprecht B. Adenosine regulates via two different types of receptors, the accumulation of cyclic AMP in cultured brain cells. J Neurochem. 1979 Nov;33(5):999–1005. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb05236.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]