Abstract
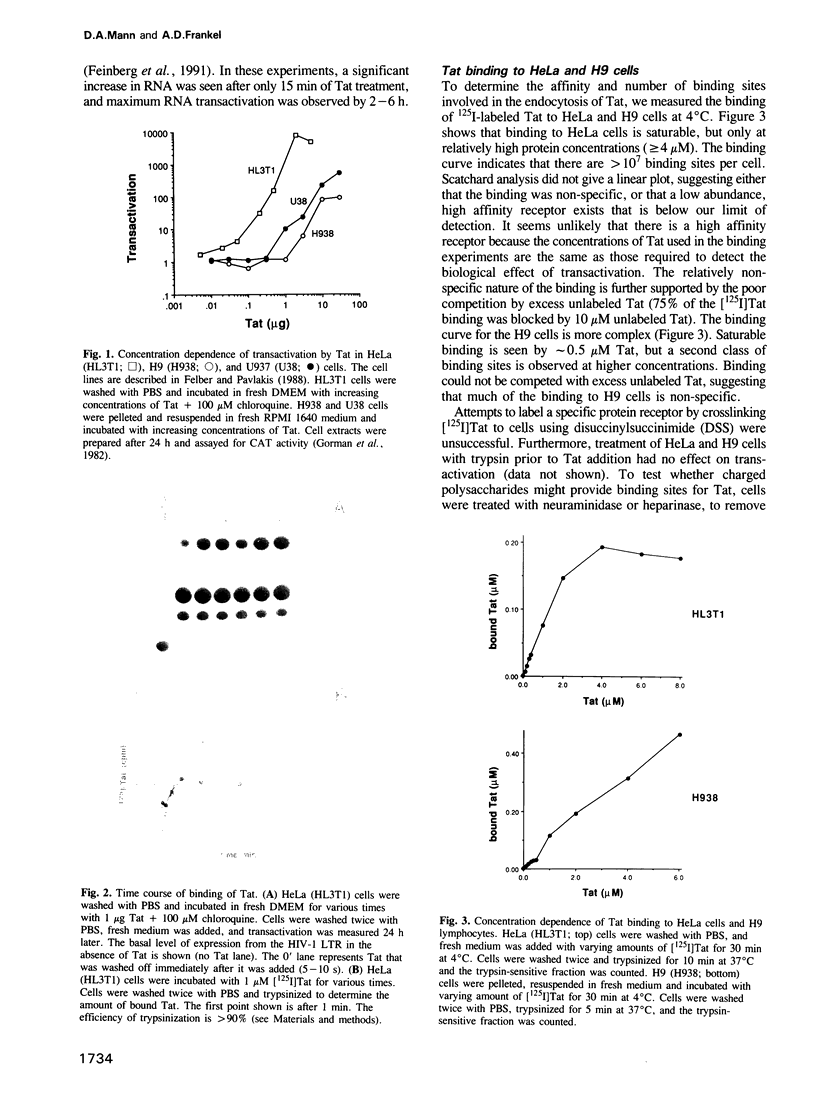
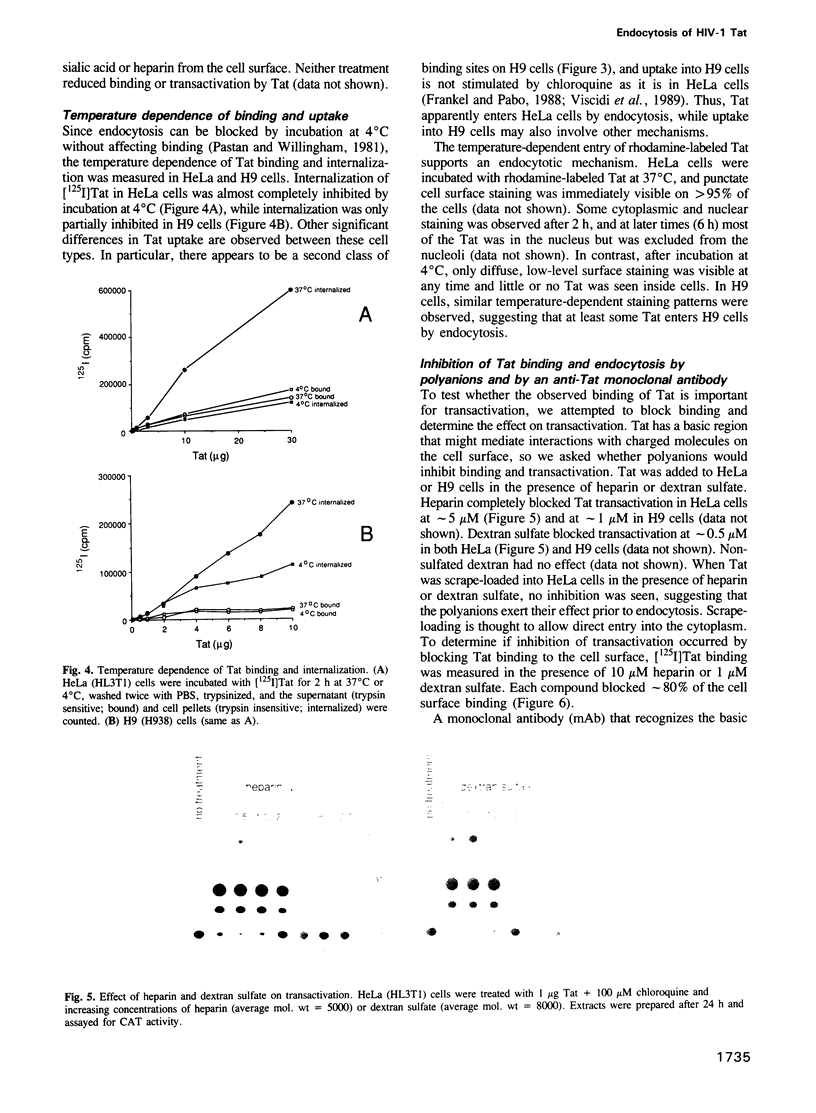
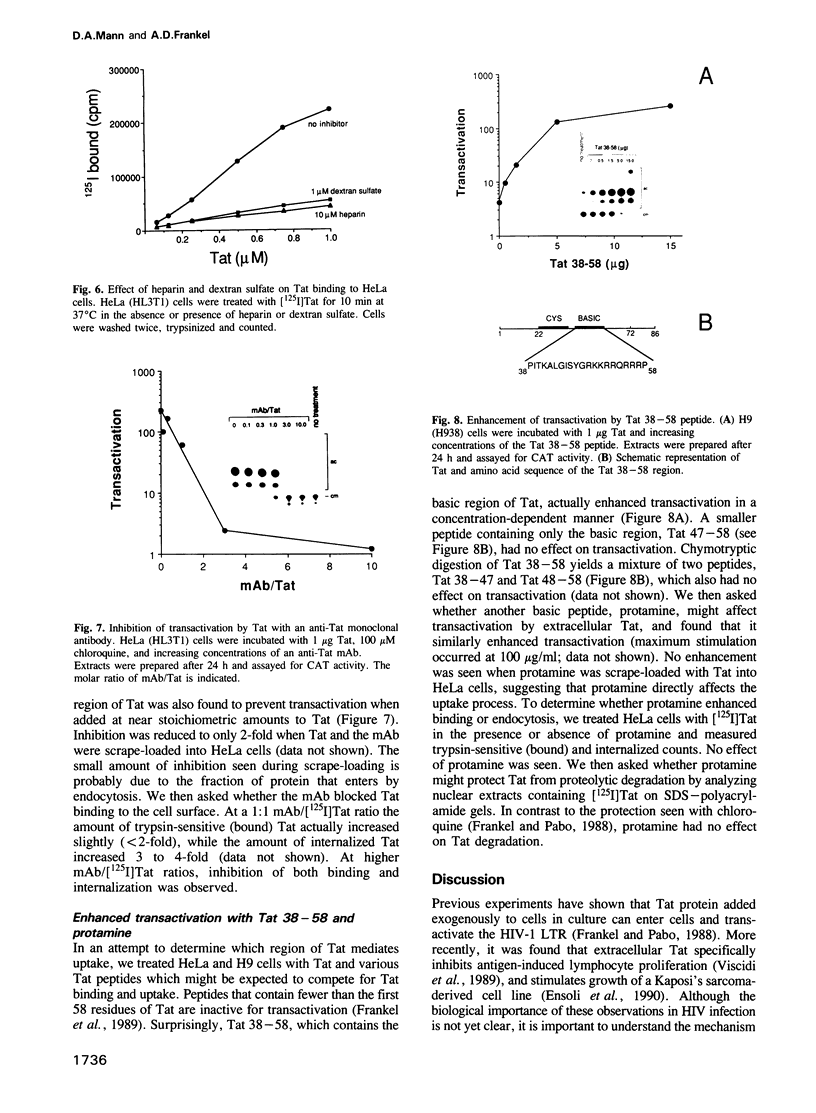
The human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) Tat protein has previously been shown to transactivate the HIV-1-LTR when added exogenously to HeLa, H9 lymphocytic and U937 promonocytic cells growing in culture. Here we show that Tat enters these cells by adsorptive endocytosis. Tat appears to bind non-specifically to the cell surface, with greater than 10(7) sites per cell. A specific receptor was not detected by protein crosslinking experiments, and uptake was not affected by treating cells with trypsin, heparinase or neuraminidase. Uptake and transactivation could be inhibited by incubation with heparin, dextran sulfate, an anti-Tat monoclonal antibody, or by incubation at 4 degrees C. In contrast, transactivation by Tat was markedly stimulated by the addition of basic peptides, such as Tat 38-58 or protamine. Fluorescence experiments with rhodamine-conjugated Tat show punctate staining on the cell surface and then localization to the cytoplasm and nucleus. The lack of a specific receptor makes it unclear whether Tat uptake is biologically important in HIV infection, however, the efficiency of uptake raises the possibility that Tat may be useful for delivery of protein molecules into cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behr J. P., Demeneix B., Loeffler J. P., Perez-Mutul J. Efficient gene transfer into mammalian primary endocrine cells with lipopolyamine-coated DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6982–6986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake D. A., Debouck C., Biesecker G. Identification of an Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) cell adhesion site in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transactivation protein, tat. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1275–1281. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnan B. J., Biancalana S., Hudson D., Frankel A. D. Analysis of arginine-rich peptides from the HIV Tat protein reveals unusual features of RNA-protein recognition. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):201–210. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus occurs via a bimodal mechanism. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., Lee W. M. Nuclear and nucleolar targeting sequences of c-erb-A, c-myb, N-myc, p53, HSP70, and HIV tat proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18019–18023. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton A. I., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A. The trans-activator gene of the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III is required for replication. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo S., Kubota S., Siomi H., Adachi A., Oroszlan S., Maki M., Hatanaka M. A region of basic amino-acid cluster in HIV-1 Tat protein is essential for trans-acting activity and nucleolar localization. Virus Genes. 1989 Nov;3(2):99–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00125123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Barillari G., Salahuddin S. Z., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Tat protein of HIV-1 stimulates growth of cells derived from Kaposi's sarcoma lesions of AIDS patients. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):84–86. doi: 10.1038/345084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Fuerst T. R., Moss B. Use of vaccinia virus vectors to study the synthesis, intracellular localization, and action of the human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):450–457. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. A quantitative bioassay for HIV-1 based on trans-activation. Science. 1988 Jan 8;239(4836):184–187. doi: 10.1126/science.3422113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Feinberg M. B., Josephs S. F., Harper M. E., Marselle L. M., Reyes G., Gonda M. A., Aldovini A., Debouk C., Gallo R. C. The trans-activator gene of HTLV-III is essential for virus replication. 1986 Mar 27-Apr 2Nature. 320(6060):367–371. doi: 10.1038/320367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Biancalana S., Hudson D. Activity of synthetic peptides from the Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7397–7401. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Bredt D. S., Pabo C. O. Tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus forms a metal-linked dimer. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):70–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2832944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Chen L., Cotter R. J., Pabo C. O. Dimerization of the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus: a cysteine-rich peptide mimics the normal metal-linked dimer interface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6297–6300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Pabo C. O. Cellular uptake of the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1189–1193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. A., Harrich D., Pearson L., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. B. Functional domains required for tat-induced transcriptional activation of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3143–3147. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03181.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A. Bioassay for trans-activation using purified human immunodeficiency virus tat-encoded protein: trans-activation requires mRNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):821–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Malim M. H., Cullen B. R. Mutational analysis of the conserved basic domain of human immunodeficiency virus tat protein. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1181–1187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1181-1187.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Perkins A., Heimer E. P., Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus gene expression is mediated by nuclear events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6364–6368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuppuswamy M., Subramanian T., Srinivasan A., Chinnadurai G. Multiple functional domains of Tat, the trans-activator of HIV-1, defined by mutational analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3551–3561. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lokeshwar V. B., Huang S. S., Huang J. S. Protamine enhances epidermal growth factor (EGF)-stimulated mitogenesis by increasing cell surface EGF receptor number. Implications for existence of cryptic EGF receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19318–19326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Zsak L., Zuckermann F., Sugg N., Kern H., Ben-Porat T. Interaction of glycoprotein gIII with a cellular heparinlike substance mediates adsorption of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):278–286. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.278-286.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Capon D. J. Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy R. F., Jorgensen E. D., Cantor C. R. Kinetics of histone endocytosis in Chinese hamster ovary cells. A flow cytofluorometric analysis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1695–1701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Isolation and analysis of nuclear RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:234–241. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I. H., Willingham M. C. Journey to the center of the cell: role of the receptosome. Science. 1981 Oct 30;214(4520):504–509. doi: 10.1126/science.6170111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Carlotti F. Mutational analysis of the conserved cysteine-rich region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat protein. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1864–1868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1864-1868.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S., Perkins A., Purcell R., Joung K., Sia R., Burghoff R., Haseltine W. A., Rosen C. A. Structural and functional characterization of human immunodeficiency virus tat protein. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.1-8.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryser H. J., Hancock R. Histones and basic polyamino acids stimulate the uptake of albumin by tumor cells in culture. Science. 1965 Oct 22;150(3695):501–503. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3695.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siomi H., Shida H., Maki M., Hatanaka M. Effects of a highly basic region of human immunodeficiency virus Tat protein on nucleolar localization. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1803–1807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1803-1807.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Rosen C., Wong-Staal F., Salahuddin S. Z., Popovic M., Arya S., Gallo R. C., Haseltine W. A. Trans-acting transcriptional regulation of human T-cell leukemia virus type III long terminal repeat. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):171–173. doi: 10.1126/science.2981427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viscidi R. P., Mayur K., Lederman H. M., Frankel A. D. Inhibition of antigen-induced lymphocyte proliferation by Tat protein from HIV-1. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1606–1608. doi: 10.1126/science.2556795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks K. M., Ampe C., Schultz S. C., Steitz T. A., Crothers D. M. Fragments of the HIV-1 Tat protein specifically bind TAR RNA. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1281–1285. doi: 10.1126/science.2205002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis W., Brown J. H., Cusack S., Paulson J. C., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the influenza virus haemagglutinin complexed with its receptor, sialic acid. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):426–431. doi: 10.1038/333426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WuDunn D., Spear P. G. Initial interaction of herpes simplex virus with cells is binding to heparan sulfate. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.52-58.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





