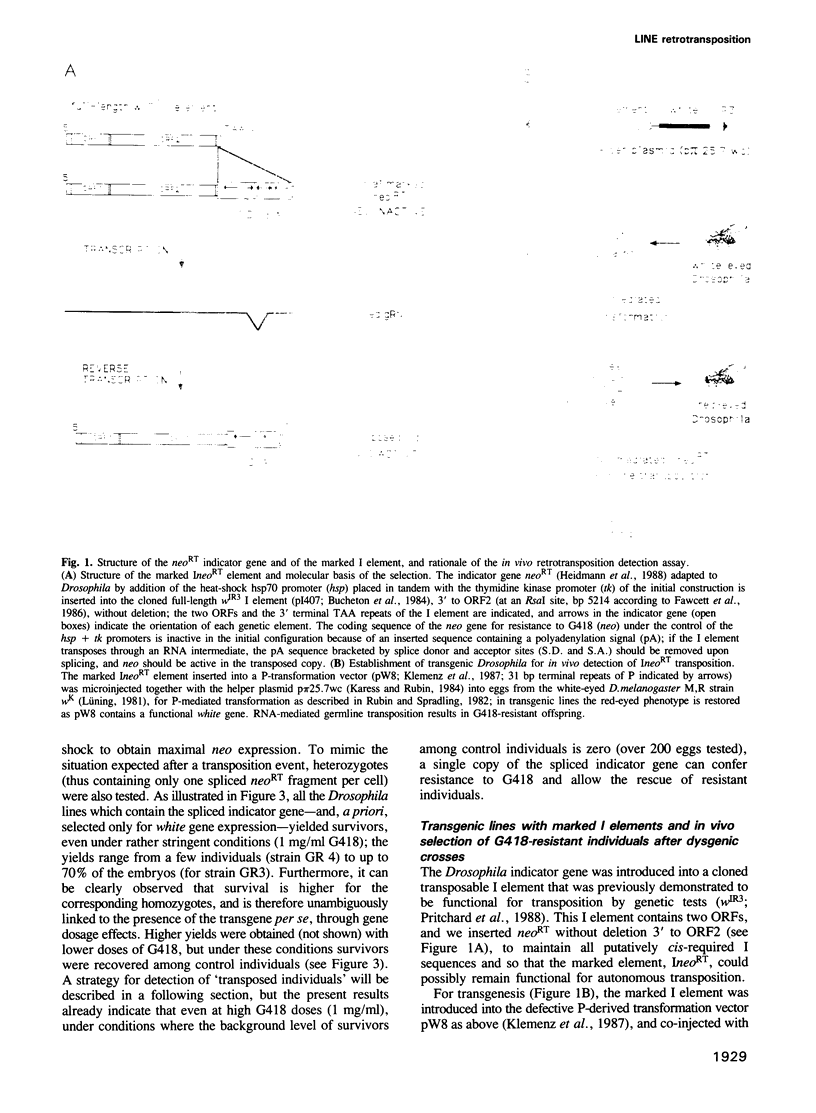
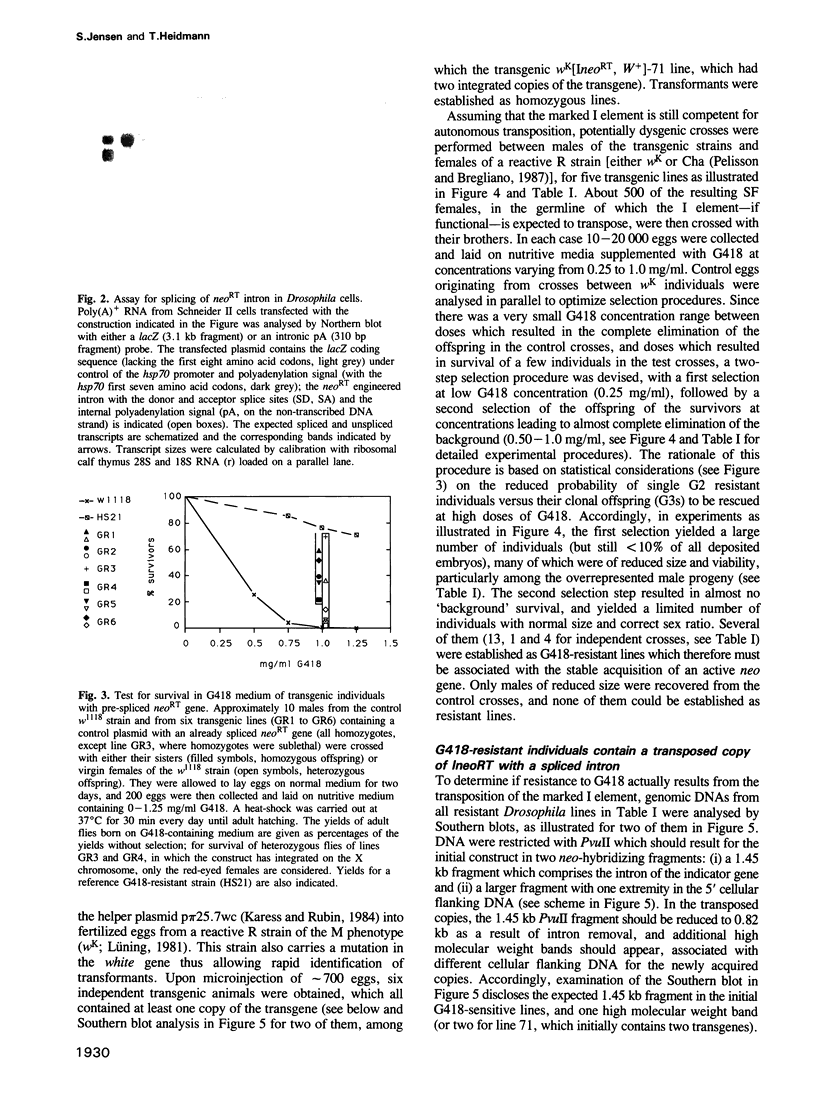
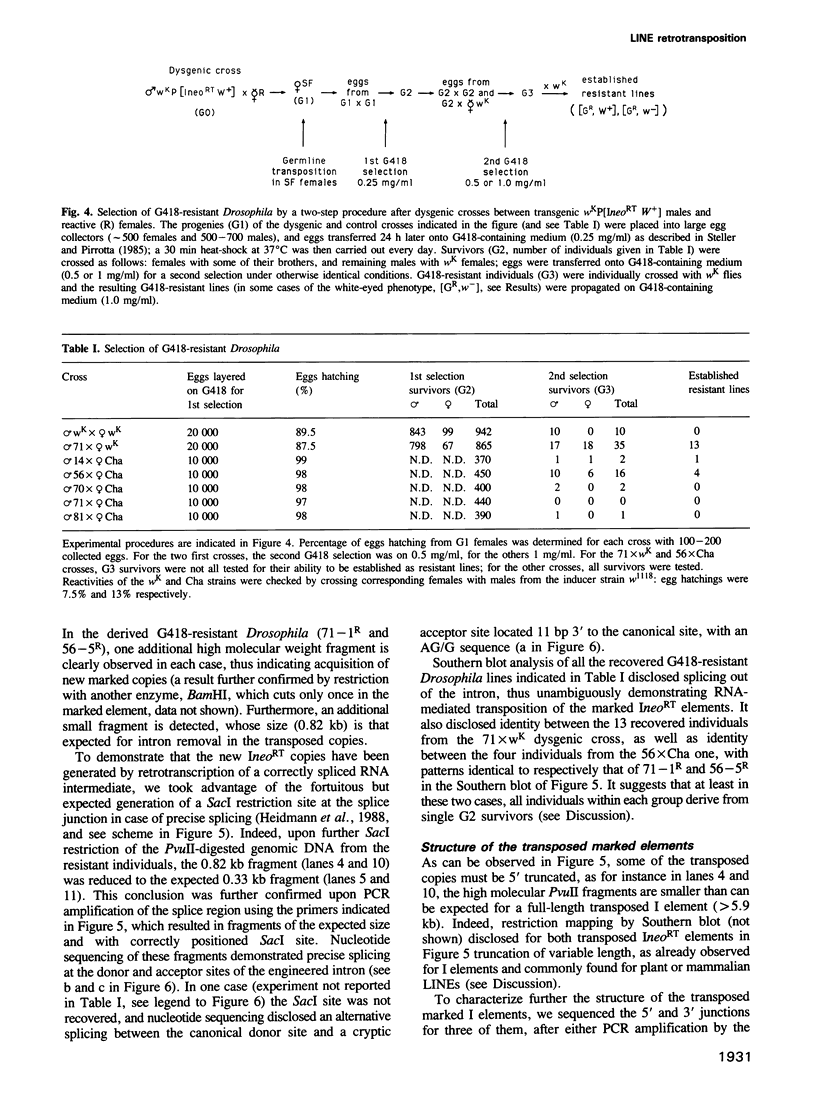
Abstract
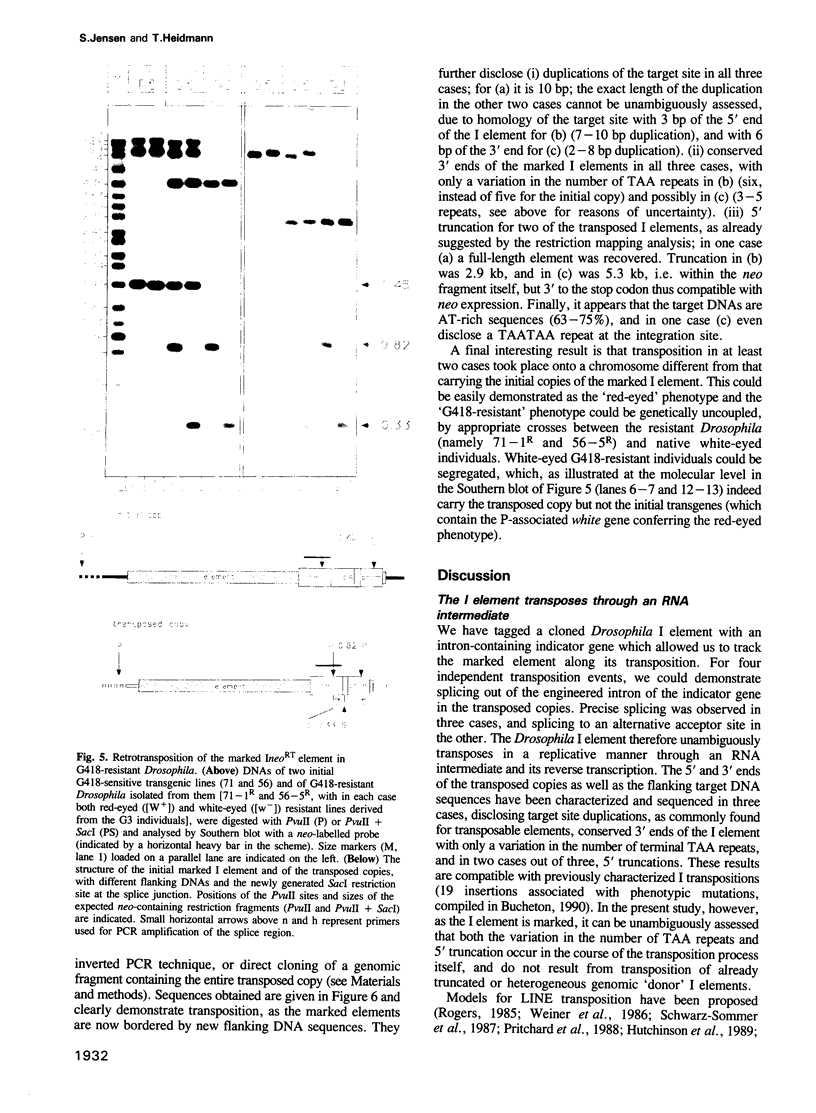
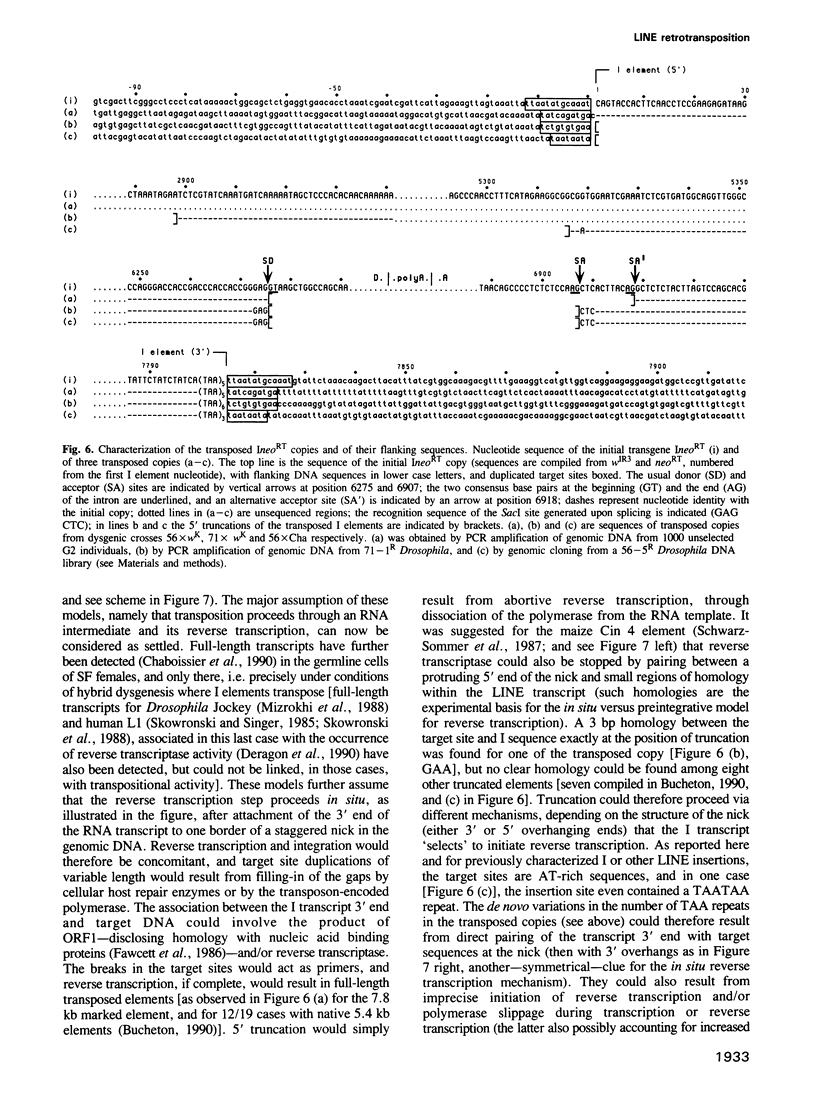
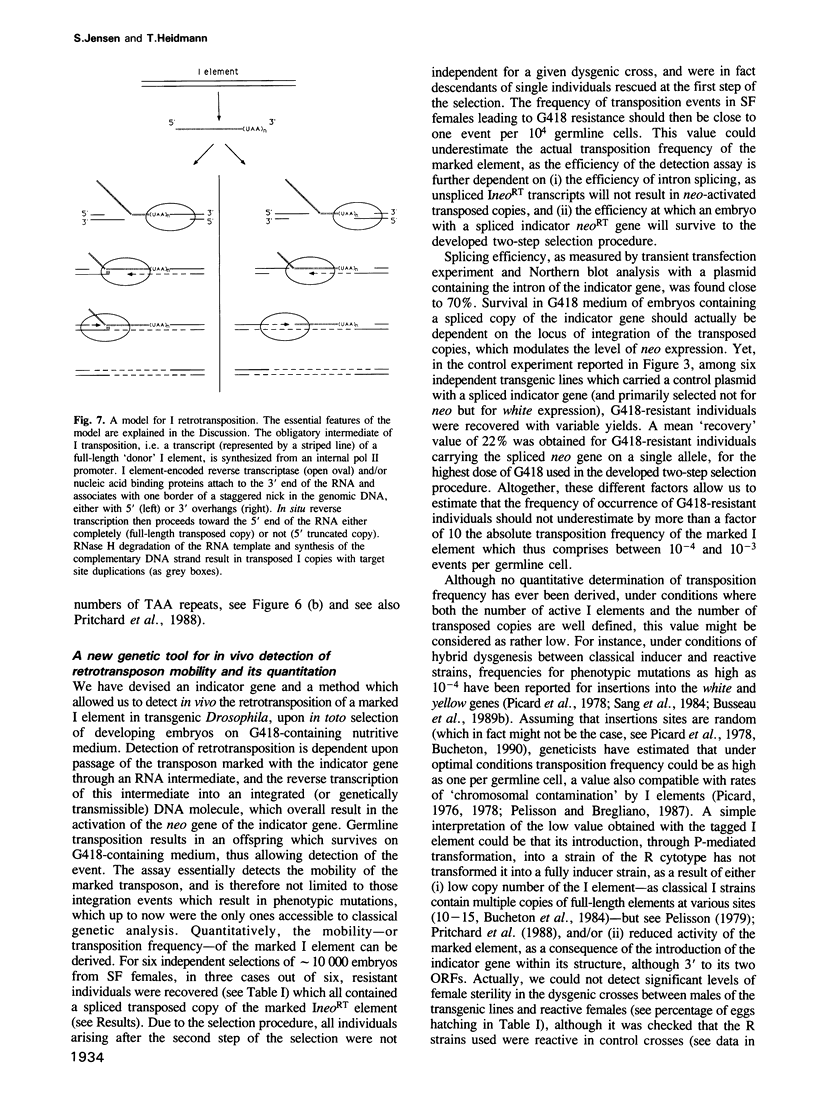
We have marked a cloned Drosophila transposable element--the I element--with an engineered neomycin-containing indicator gene, whose expression is conditioned by passage of the transposon through an RNA intermediate. Mobility of the marked element introduced into Drosophila as a transgene could be detected in vivo, upon in toto selection of developing embryos on G418-containing medium. For resistant individuals, Southern blot analysis and nucleotide sequencing after PCR amplification disclosed transposition of the marked element into new loci, with target site duplications and splicing out of the intron in the indicator gene. It demonstrates that the I element, which is closely related to the widespread mammalian LINEs, transposes through an RNA intermediate, as up to now only conjectured from sequence singularities of this class of 'non-viral retrotransposons'. The developed indicator gene provides a potent new genetic tool for detection and quantitative analysis of retrotransposon mobility and its regulation as it occurs in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abad P., Vaury C., Pélisson A., Chaboissier M. C., Busseau I., Bucheton A. A long interspersed repetitive element--the I factor of Drosophila teissieri--is able to transpose in different Drosophila species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8887–8891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. J., Parks C., Parker-Thornburg J., Mortin M. A., Pelham H. R. The use of promoter fusions in Drosophila genetics: isolation of mutations affecting the heat shock response. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):979–991. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90432-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bregliano J. C., Picard G., Bucheton A., Pelisson A., Lavige J. M., L'Heritier P. Hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1980 Feb 8;207(4431):606–611. doi: 10.1126/science.6766221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucheton A. I transposable elements and I-R hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila. Trends Genet. 1990 Jan;6(1):16–21. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucheton A., Paro R., Sang H. M., Pelisson A., Finnegan D. J. The molecular basis of I-R hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: identification, cloning, and properties of the I factor. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90536-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busseau I., Pelisson A., Bucheton A. Characterization of 5' truncated transposed copies of the I factor in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 12;17(17):6939–6945. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.17.6939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busseau I., Pelisson A., Bucheton A. I elements of Drosophila melanogaster generate specific chromosomal rearrangements during transposition. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Aug;218(2):222–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00331272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
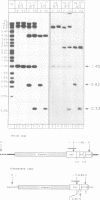
- Chaboissier M. C., Busseau I., Prosser J., Finnegan D. J., Bucheton A. Identification of a potential RNA intermediate for transposition of the LINE-like element I factor in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3557–3563. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07566.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ambrosio E., Waitzkin S. D., Witney F. R., Salemme A., Furano A. V. Structure of the highly repeated, long interspersed DNA family (LINE or L1Rn) of the rat. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):411–424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deragon J. M., Sinnett D., Labuda D. Reverse transcriptase activity from human embryonal carcinoma cells NTera2D1. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3363–3368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Casari G. Related polypeptides are encoded by Drosophila F elements, I factors, and mammalian L1 sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5843–5847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P. Close relationship between non-viral retroposons in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):4041–4052. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.4041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dührsen U., Stahl J., Gough N. M. In vivo transformation of factor-dependent hemopoietic cells: role of intracisternal A-particle transposition for growth factor gene activation. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1087–1096. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G. Drosophila retrotransposons: interactions with genome. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:33–105. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60582-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning T. G., Singer M. F. LINE-1: a mammalian transposable element. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 8;910(3):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90112-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. H., Lister C. K., Kellett E., Finnegan D. J. Transposable elements controlling I-R hybrid dysgenesis in D. melanogaster are similar to mammalian LINEs. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90815-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Kuhara S., Takenaka O., Sakaki Y. L1 family of repetitive DNA sequences in primates may be derived from a sequence encoding a reverse transcriptase-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):625–628. doi: 10.1038/321625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelrigg T., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Transformation of white locus DNA in drosophila: dosage compensation, zeste interaction, and position effects. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann O., Heidmann T. Retrotransposition of a mouse IAP sequence tagged with an indicator gene. Cell. 1991 Jan 11;64(1):159–170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90217-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann T., Heidmann O., Nicolas J. F. An indicator gene to demonstrate intracellular transposition of defective retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2219–2223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Gehring W. J. Regulation and function of the Drosophila segmentation gene fushi tarazu. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):963–974. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohjoh H., Minakami R., Sakaki Y. Selective cloning and sequence analysis of the human L1 (LINE-1) sequences which transposed in the relatively recent past. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4099–4104. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of P transposable element functions in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Wong C., Youssoufian H., Scott A. F., Phillips D. G., Antonarakis S. E. Haemophilia A resulting from de novo insertion of L1 sequences represents a novel mechanism for mutation in man. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):164–166. doi: 10.1038/332164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel B. E., ole-MoiYoi O. K., Young J. R. Ingi, a 5.2-kb dispersed sequence element from Trypanosoma brucei that carries half of a smaller mobile element at either end and has homology with mammalian LINEs. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1465–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Weber U., Gehring W. J. The white gene as a marker in a new P-element vector for gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):3947–3959. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.3947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb D. D., Padgett R. W., Hardies S. C., Shehee W. R., Comer M. B., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd The sequence of a large L1Md element reveals a tandemly repeated 5' end and several features found in retrotransposons. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):168–182. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrokhi L. J., Georgieva S. G., Ilyin Y. V. jockey, a mobile Drosophila element similar to mammalian LINEs, is transcribed from the internal promoter by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):685–691. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse B., Rotherg P. G., South V. J., Spandorfer J. M., Astrin S. M. Insertional mutagenesis of the myc locus by a LINE-1 sequence in a human breast carcinoma. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):87–90. doi: 10.1038/333087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Alley M. R., Cullingford T. E., Driver A., Sanderson M. J. DNA sequence of the Doc retroposon in the white-one mutant of Drosophila melanogaster and of secondary insertions in the phenotypically altered derivatives white-honey and white-eosin. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jan;225(1):17–24. doi: 10.1007/BF00282637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard G., Bregliano J. C., Bucheton A., Lavige J. M., Pelisson A., Kidwell M. G. Non-mendelian female sterility and hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Genet Res. 1978 Nov;32(3):275–287. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300018772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard G. Non-mendelian female sterility in Drosophila melanogaster: hereditary transmission of I factor. Genetics. 1976 May;83(1):107–123. doi: 10.1093/genetics/83.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priimägi A. F., Mizrokhi L. J., Ilyin Y. V. The Drosophila mobile element jockey belongs to LINEs and contains coding sequences homologous to some retroviral proteins. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchard M. A., Dura J. M., Pélisson A., Bucheton A., Finnegan D. J. A cloned I-factor is fully functional in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):533–540. doi: 10.1007/BF00330491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pélisson A. The I-R system of hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: influence on SF females sterility of their inducer and reactive paternal chromosomes. Heredity (Edinb) 1979 Dec;43(3):423–428. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1979.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. H. The origin and evolution of retroposons. Int Rev Cytol. 1985;93:187–279. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61375-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F. Use of a recombinant retrovirus to study post-implantation cell lineage in mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sang H. M., Pélisson A., Bucheton A., Finnegan D. J. Molecular lesions associated with white gene mutations induced by I-R hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3079–3085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02262.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider I. Cell lines derived from late embryonic stages of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1972 Apr;27(2):353–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Leclercq L., Göbel E., Saedler H. Cin4, an insert altering the structure of the A1 gene in Zea mays, exhibits properties of nonviral retrotransposons. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3873–3880. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02727.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Keerikatte V. Novel use of polymerase chain reaction to amplify cellular DNA adjacent to an integrated provirus. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1924–1928. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1924-1928.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J., Fanning T. G., Singer M. F. Unit-length line-1 transcripts in human teratocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1385–1397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowronski J., Singer M. F. Expression of a cytoplasmic LINE-1 transcript is regulated in a human teratocarcinoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6050–6054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. A transposable P vector that confers selectable G418 resistance to Drosophila larvae. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):167–171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swergold G. D. Identification, characterization, and cell specificity of a human LINE-1 promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6718–6729. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchenio T., Heidmann T. Defective retroviruses can disperse in the human genome by intracellular transposition. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2113–2118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2113-2118.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner A. M., Deininger P. L., Efstratiadis A. Nonviral retroposons: genes, pseudogenes, and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:631–661. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Eickbush T. H. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3353–3362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu H., Boeke J. D. Localization of sequences required in cis for yeast Ty1 element transposition near the long terminal repeats: analysis of mini-Ty1 elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2695–2702. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]