Abstract
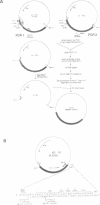
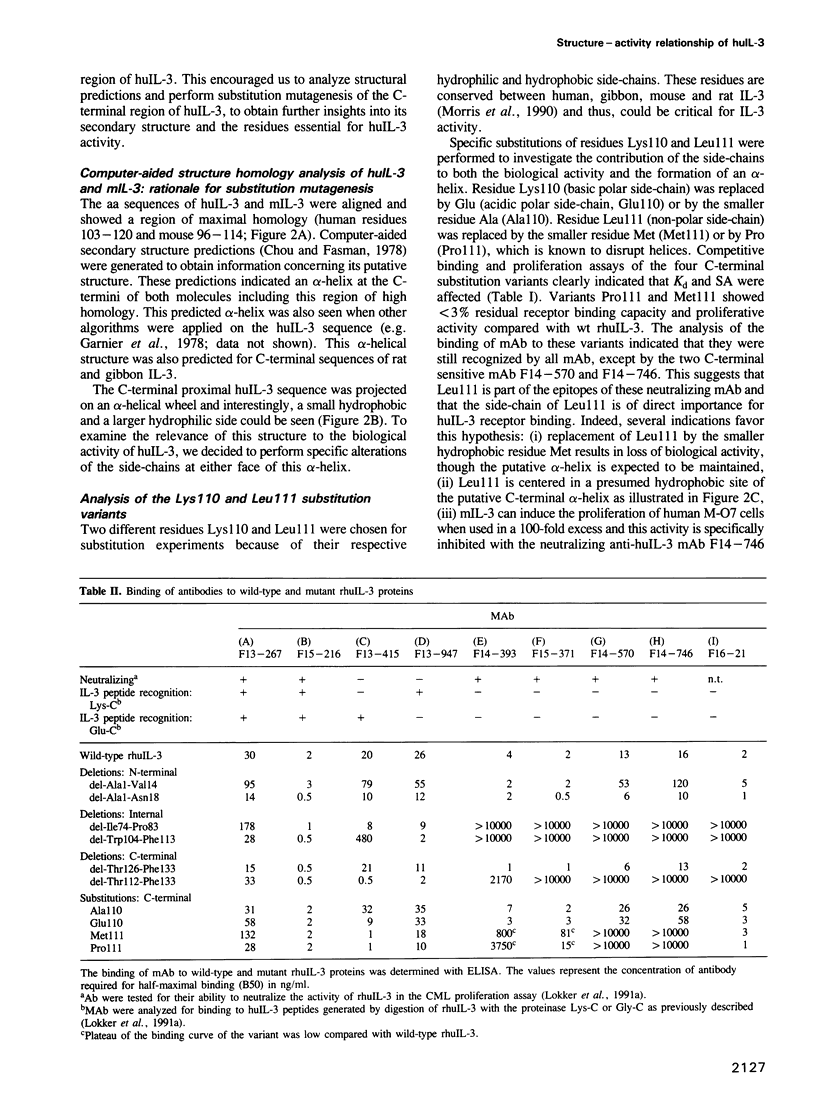
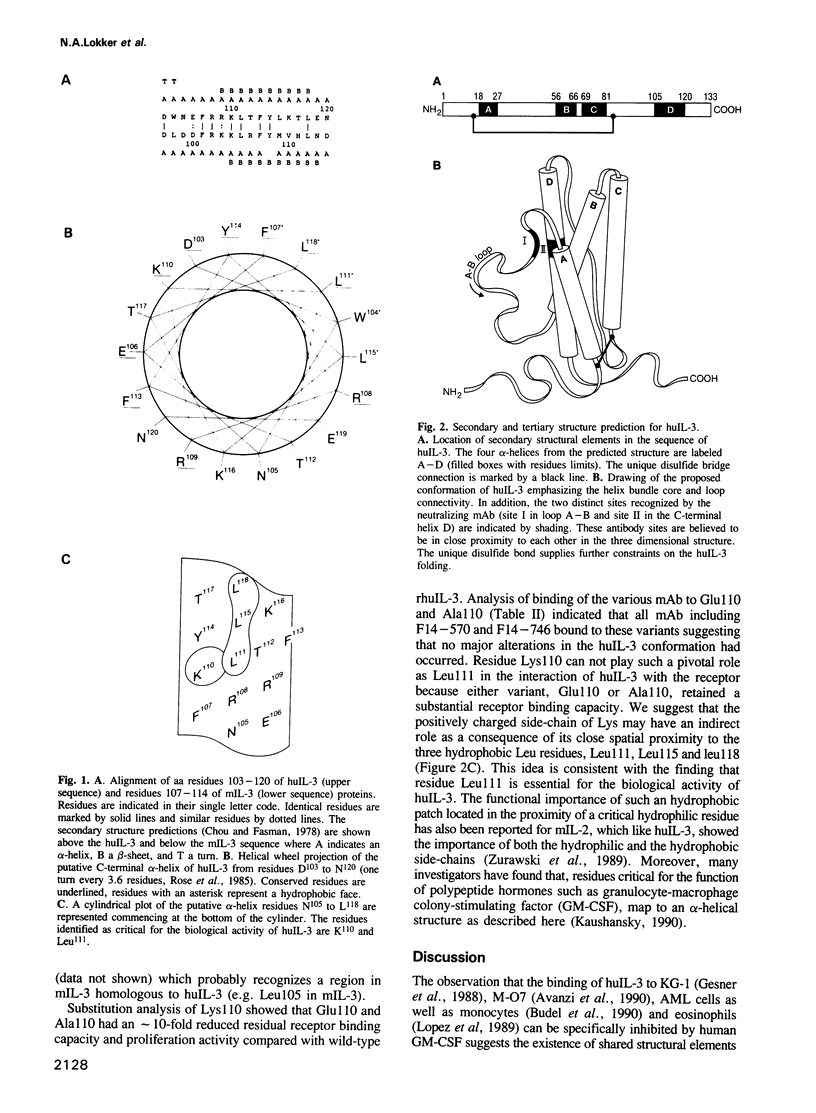
A structure-activity relationship study of human interleukin-3 (huIL-3) was performed by functional analysis of huIL-3 deletion and substitution variants combined with epitope mapping of huIL-3 specific neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (mAb). Analysis of the huIL-3 variants was accomplished by defining their capacity to compete with wild-type huIL-3 for binding to the huIL-3 receptor and to induce the proliferation of the huIL-3 dependent cell line M-O7. HuIL-3 variants with either 14 amino acids (aa) deleted from the N-terminus or eight aa from the C-terminus retained full biological activity in vitro. An huIL-3 variant, with 18 N-terminal aa deleted, exhibited a greater than 7-fold reduced receptor binding capacity and proliferative activity. No biological activity could be detected with a variant where 22 C-terminal aa have been deleted. Neutralizing mAb recognizing presumed discontinuous epitopes failed to interact with the latter deletion variant indicating a possible location of their epitopes within the C-terminal region. Computer-aided structure prediction and sequence homology analysis of this region indicated the presence of an amphiphilic alpha-helix with highly conserved residues like Lys110 and Leu111. Substitution of Lys110 with either Glu or Ala resulted in variants with a 10-fold reduced activity in the receptor binding assay and the proliferation assay. Further variants, where Leu111 was substituted by Pro or Met, were totally inactive in these assays. Analysis of the binding of the two neutralizing mAb to these substitution variants showed that they did not bind to either of the Leu111 variants suggesting that Leu111 is part of an active site. Based on our results, a possible model for the structure of the huIL-3 molecule can be constructed with two active sites in close proximity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Meguid S. S., Shieh H. S., Smith W. W., Dayringer H. E., Violand B. N., Bentle L. A. Three-dimensional structure of a genetically engineered variant of porcine growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6434–6437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avanzi G. C., Lista P., Giovinazzo B., Miniero R., Saglio G., Benetton G., Coda R., Cattoretti G., Pegoraro L. Selective growth response to IL-3 of a human leukaemic cell line with megakaryoblastic features. Br J Haematol. 1988 Jul;69(3):359–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1988.tb02374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. A., Grossman A. D., Gross C. A. A gene regulating the heat shock response in Escherichia coli also affects proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6779–6783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F. Haemopoietic receptors and helical cytokines. Immunol Today. 1990 Oct;11(10):350–354. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90139-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budel L. M., Elbaz O., Hoogerbrugge H., Delwel R., Mahmoud L. A., Löwenberg B., Touw I. P. Common binding structure for granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-3 on human acute myeloid leukemia cells and monocytes. Blood. 1990 Apr 1;75(7):1439–1445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Role of disulfide bridges in determining the biological activity of interleukin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7897–7901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins L., Tsien W. H., Seals C., Hakimi J., Weber D., Bailon P., Hoskings J., Greene W. C., Toome V., Ju G. Identification of specific residues of human interleukin 2 that affect binding to the 70-kDa subunit (p70) of the interleukin 2 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7709–7713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. C., Hapel A. J., Ymer S., Cohen D. R., Johnson R. M., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Molecular cloning of cDNA for murine interleukin-3. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):233–237. doi: 10.1038/307233a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., King J. A., Gough N. M., Nicola N. A. Expression cloning of a receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3667–3676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh N., Yonehara S., Schreurs J., Gorman D. M., Maruyama K., Ishii A., Yahara I., Arai K., Miyajima A. Cloning of an interleukin-3 receptor gene: a member of a distinct receptor gene family. Science. 1990 Jan 19;247(4940):324–327. doi: 10.1126/science.2404337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushansky K., Brown C. B., O'Hara P. J. Molecular modeling of human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Int J Cell Cloning. 1990 Jan;8 (Suppl 1):26–34. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530080704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaushansky K., Shoemaker S. G., Alfaro S., Brown C. Hematopoietic activity of granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor is dependent upon two distinct regions of the molecule: functional analysis based upon the activities of interspecies hybrid growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1213–1217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krüttgen A., Rose-John S., Möller C., Wroblowski B., Wollmer A., Müllberg J., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Heinrich P. C. Structure-function analysis of human interleukin-6. Evidence for the involvement of the carboxy-terminus in function. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuga T., Komatsu Y., Yamasaki M., Sekine S., Miyaji H., Nishi T., Sato M., Yokoo Y., Asano M., Okabe M. Mutagenesis of human granulocyte colony stimulating factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Feb 28;159(1):103–111. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92410-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurimoto Y., de Weck A. L., Dahinden C. A. Interleukin 3-dependent mediator release in basophils triggered by C5a. J Exp Med. 1989 Aug 1;170(2):467–479. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.2.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lokker N. A., Strittmatter U., Steiner C., Fagg B., Graff P., Kocher H. P., Zenke G. Mapping the epitopes of neutralizing anti-human IL-3 monoclonal antibodies. Implications for structure-activity relationship. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 1;146(3):893–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez A. F., Eglinton J. M., Gillis D., Park L. S., Clark S., Vadas M. A. Reciprocal inhibition of binding between interleukin 3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor to human eosinophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7022–7026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry D. A., Minasian E., Leach S. J. Conformational homologies among cytokines: interleukins and colony stimulating factors. J Mol Recognit. 1988 Jun;1(3):107–110. doi: 10.1002/jmr.300010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose G. D., Geselowitz A. R., Lesser G. J., Lee R. H., Zehfus M. H. Hydrophobicity of amino acid residues in globular proteins. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):834–838. doi: 10.1126/science.4023714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semon D., Movva N. R., Smith T. F., el Alama M., Davies J. Plasmid-determined bleomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Plasmid. 1987 Jan;17(1):46–53. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(87)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valent P., Besemer J., Muhm M., Majdic O., Lechner K., Bettelheim P. Interleukin 3 activates human blood basophils via high-affinity binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5542–5546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Ciarletta A. B., Temple P. A., Chung M. P., Kovacic S., Witek-Giannotti J. S., Leary A. C., Kriz R., Donahue R. E., Wong G. G. Human IL-3 (multi-CSF): identification by expression cloning of a novel hematopoietic growth factor related to murine IL-3. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):3–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski S. M., Zurawski G. Mouse interleukin-2 structure-function studies: substitutions in the first alpha-helix can specifically inactivate p70 receptor binding and mutations in the fifth alpha-helix can specifically inactivate p55 receptor binding. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2583–2590. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08397.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]