Abstract
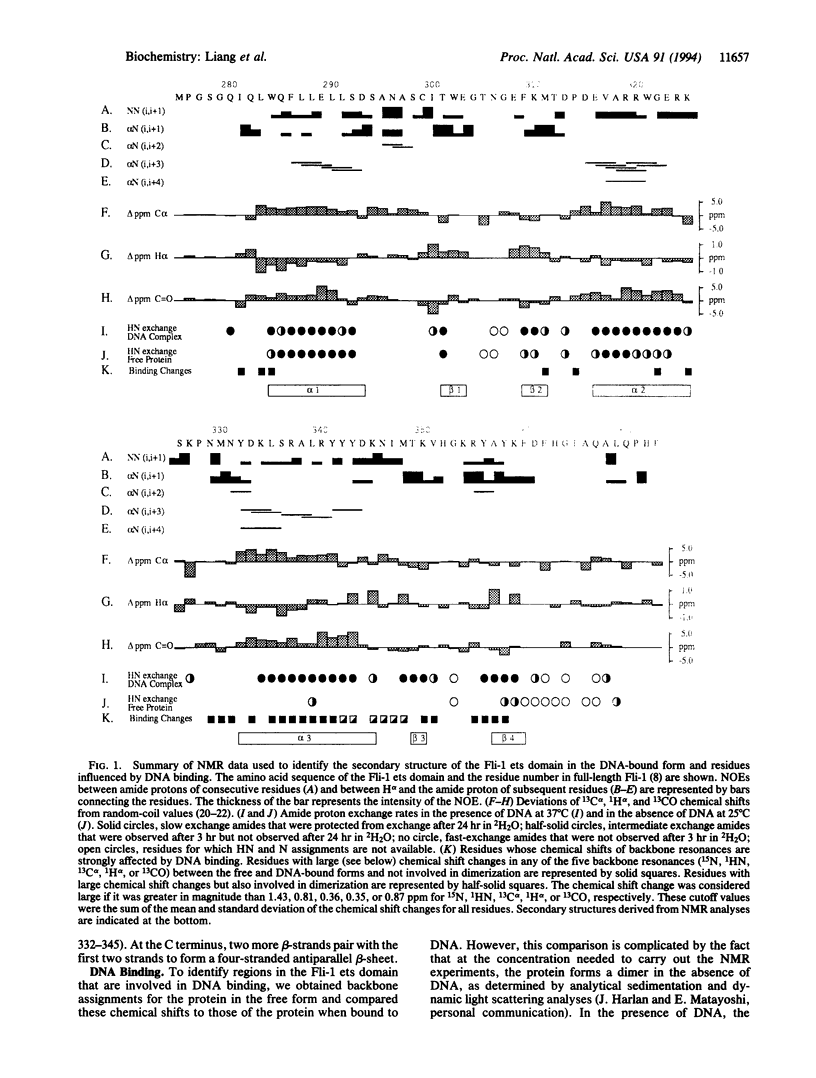
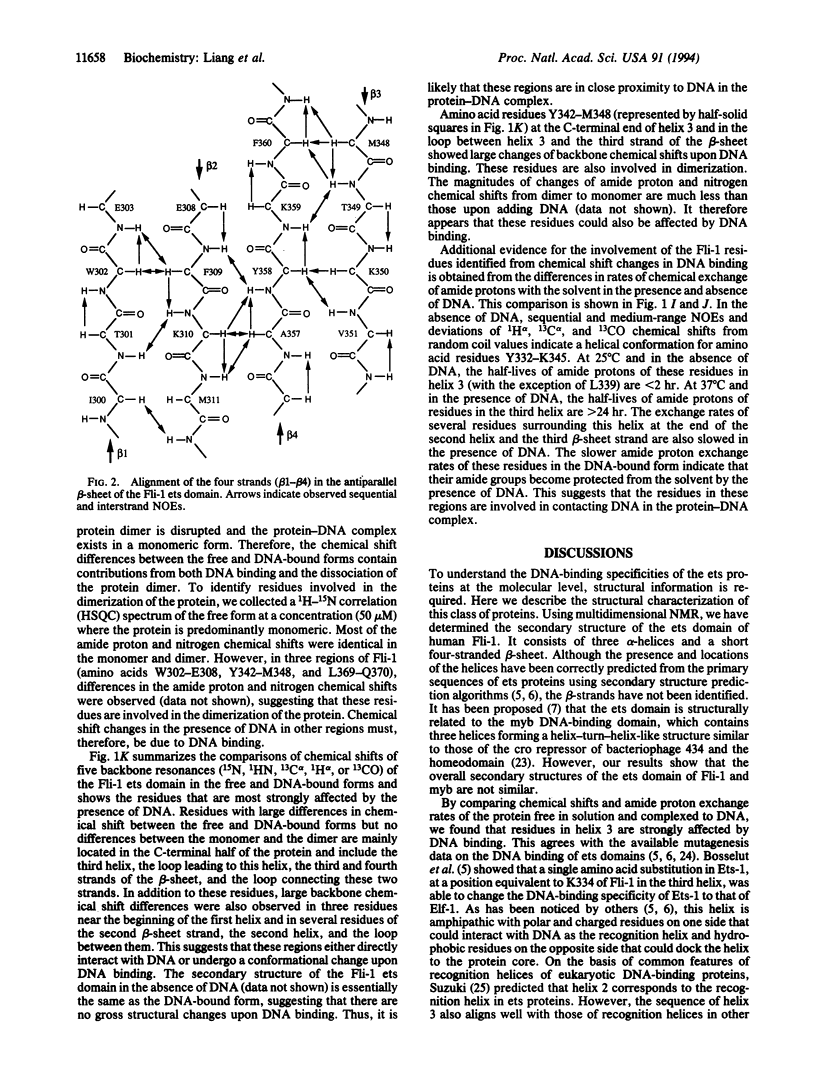
The ets family of eukaryotic transcription factors is characterized by a conserved DNA-binding domain of approximately 85 amino acids for which the three-dimensional structure is not known. By using multidimensional NMR spectroscopy, we have determined the secondary structure of the ets domain of one member of this gene family, human Fli-1, both in the free form and in a complex with a 16-bp cognate DNA site. The secondary structure of the Fli-1 ets domain consists of three alpha-helices and a short four-stranded antiparallel beta-sheet. This secondary structure arrangement resembles that of the DNA-binding domain of the catabolite gene activator protein of Escherichia coli, as well as those of several eukaryotic DNA-binding proteins including histone H5, HNF-3/fork head, and the heat shock transcription factor. Differences in chemical shifts of backbone resonances and amide exchange rates between the DNA-bound and free forms of the Fli-1 ets domain suggest that the third helix is the DNA recognition helix, as in the catabolite gene activator protein and other structurally related proteins. These results suggest that the ets domain is structurally similar to the catabolite gene activator protein family of helix-turn-helix DNA-binding proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bax A., Ikura M. An efficient 3D NMR technique for correlating the proton and 15N backbone amide resonances with the alpha-carbon of the preceding residue in uniformly 15N/13C enriched proteins. J Biomol NMR. 1991 May;1(1):99–104. doi: 10.1007/BF01874573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselut R., Levin J., Adjadj E., Ghysdael J. A single amino-acid substitution in the Ets domain alters core DNA binding specificity of Ets1 to that of the related transcription factors Elf1 and E74. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 11;21(22):5184–5191. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.22.5184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark K. L., Halay E. D., Lai E., Burley S. K. Co-crystal structure of the HNF-3/fork head DNA-recognition motif resembles histone H5. Nature. 1993 Jul 29;364(6436):412–420. doi: 10.1038/364412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delattre O., Zucman J., Plougastel B., Desmaze C., Melot T., Peter M., Kovar H., Joubert I., de Jong P., Rouleau G. Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature. 1992 Sep 10;359(6391):162–165. doi: 10.1038/359162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison C. J., Bohm A. A., Nelson H. C. Crystal structure of the DNA binding domain of the heat shock transcription factor. Science. 1994 Jan 14;263(5144):224–227. doi: 10.1126/science.8284672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janknecht R., Nordheim A. Elk-1 protein domains required for direct and SRF-assisted DNA-binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3317–3324. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Urness L. D., Thummel C. S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A., Gunther C. V., Nye J. A. The ETS-domain: a new DNA-binding motif that recognizes a purine-rich core DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1451–1453. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao X., Miesfeldt S., Yang H., Leiden J. M., Thompson C. B. The FLI-1 and chimeric EWS-FLI-1 oncoproteins display similar DNA binding specificities. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 8;269(27):18216–18222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavrothalassitis G., Fisher R. J., Smyth F., Watson D. K., Papas T. S. Structural inferences of the ETS1 DNA-binding domain determined by mutational analysis. Oncogene. 1994 Feb;9(2):425–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. A., Petersen J. M., Gunther C. V., Jonsen M. D., Graves B. J. Interaction of murine ets-1 with GGA-binding sites establishes the ETS domain as a new DNA-binding motif. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata K., Hojo H., Aimoto S., Nakai T., Nakamura H., Sarai A., Ishii S., Nishimura Y. Solution structure of a DNA-binding unit of Myb: a helix-turn-helix-related motif with conserved tryptophans forming a hydrophobic core. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6428–6432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Transcription factors: structural families and principles of DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1053–1095. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan V., Finch J. T., Graziano V., Lee P. L., Sweet R. M. Crystal structure of globular domain of histone H5 and its implications for nucleosome binding. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):219–223. doi: 10.1038/362219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1001–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1653449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuister G. W., Kim S. J., Wu C., Bax A. NMR evidence for similarities between the DNA-binding regions of Drosophila melanogaster heat shock factor and the helix-turn-helix and HNF-3/forkhead families of transcription factors. Biochemistry. 1994 Jan 11;33(1):10–16. doi: 10.1021/bi00167a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Petryniak B., Ho I. C., Thompson C. B., Leiden J. M. Evolutionarily conserved Ets family members display distinct DNA binding specificities. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1391–1399. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Hahn S. L., Giovane A. The Ets family of transcription factors. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jan 15;211(1-2):7–18. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78757-7_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wishart D. S., Sykes B. D., Richards F. M. The chemical shift index: a fast and simple method for the assignment of protein secondary structure through NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1647–1651. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




