Abstract
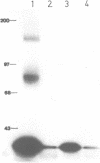
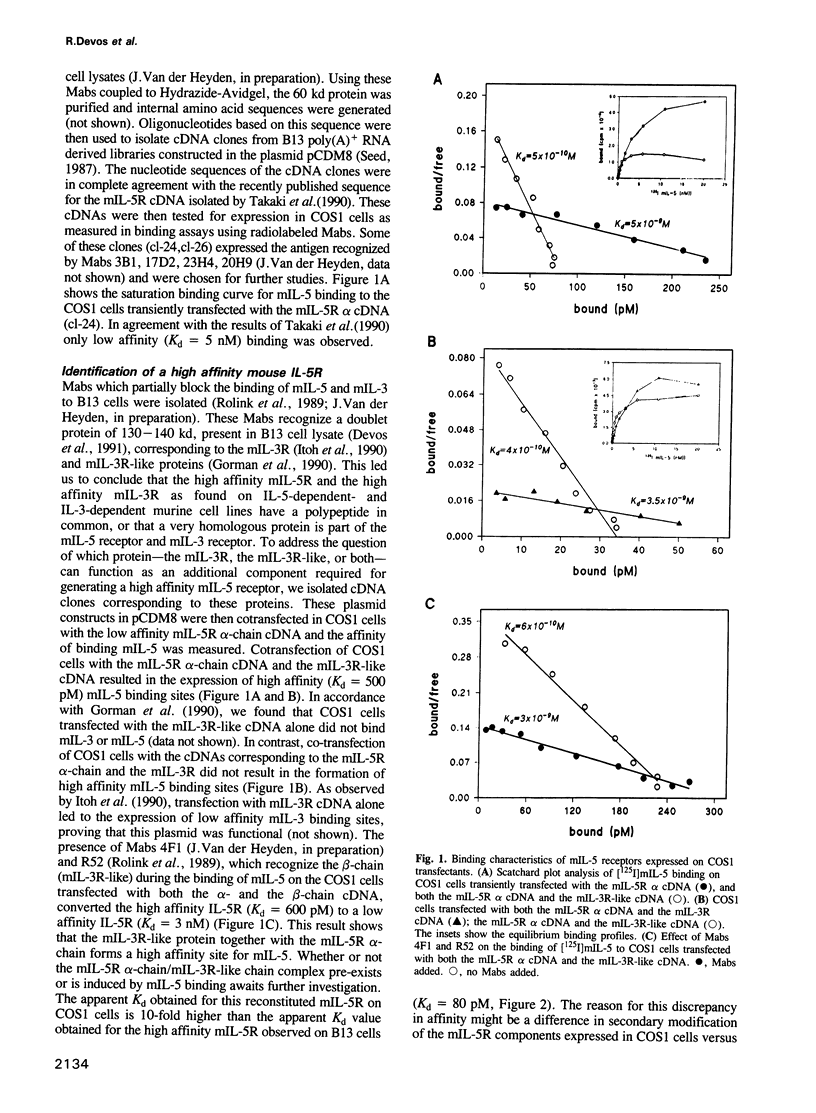
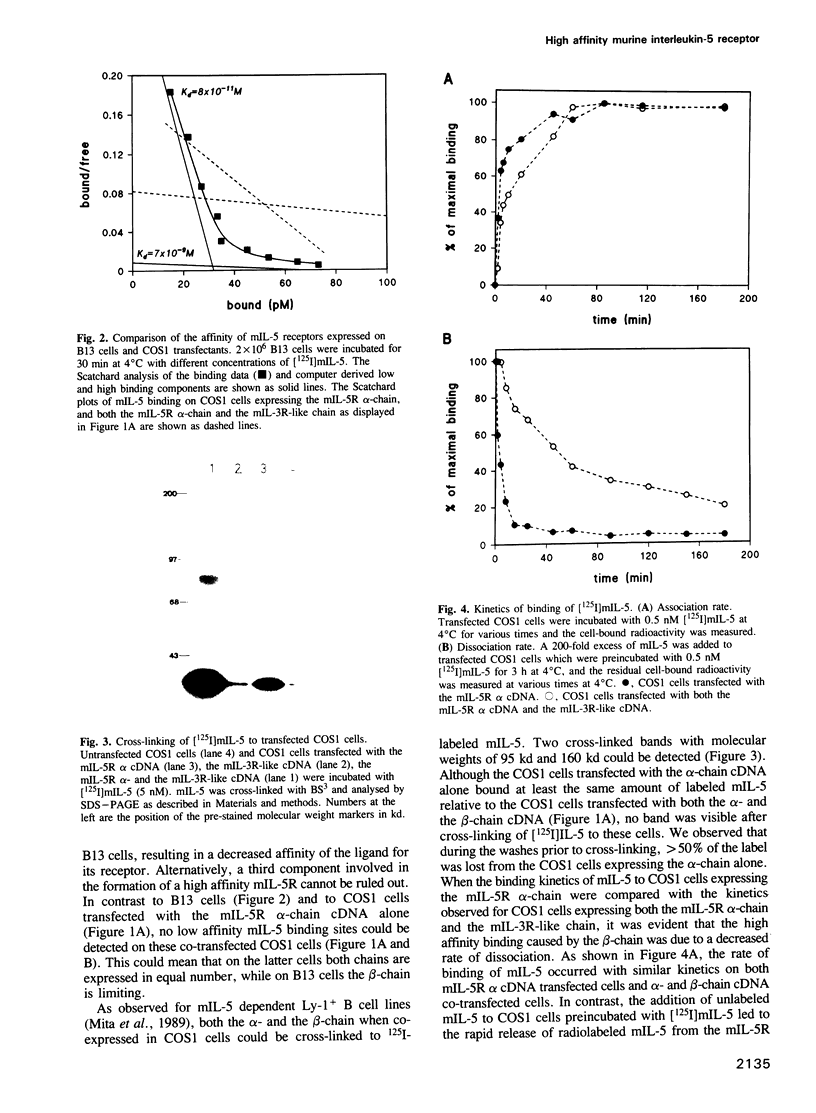
The mouse interleukin-5 receptor (mIL-5R) consists of two components one of which, the mIL-5R alpha-chain, binds mIL-5 with low affinity. Recently we demonstrated that monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) recognizing the second mIL-5R beta-chain, immunoprecipitate a p130-140 protein doublet which corresponds to the mIL-3R and the mIL-3R-like protein, the latter chain for which so far no ligand has been identified. In this study we show that a high affinity mIL-5R can be reconstituted on COS1 cells by co-expression of the mIL-5R alpha-chain with the mIL-3R-like protein (beta-chain). Cross-linking of 125I-labeled mIL-5 to the COS1 cells co-transfected with both cDNAs revealed the same pattern as in B13 cells, i.e. two proteins of 60 and 130 kd which correspond to the low affinity mIL-5R alpha-chain and the mIL-3R-like protein, respectively. The dissociation rate of mIL-5 from this reconstituted high affinity site was lower than that of the low affinity site, whereas the association rate was unchanged. Nonetheless, the apparent dissociation constant (Kd) for this reconstituted receptor was still 10-fold higher than the Kd observed for B13 cells. Although the mIL-3R is greater than 90% homologous to the mIL-3R-like protein, no increase in affinity for mIL-5 was detected on COS1 cells co-transfected with the cDNAs for the mIL-5R alpha-chain and the mIL-3R protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauw G., Van Damme J., Puype M., Vandekerckhove J., Gesser B., Ratz G. P., Lauridsen J. B., Celis J. E. Protein-electroblotting and -microsequencing strategies in generating protein data bases from two-dimensional gels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7701–7705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Seymour B. W., Hudak S., Jackson J., Rennick D. Antibody to interleukin-5 inhibits helminth-induced eosinophilia in mice. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):308–310. doi: 10.1126/science.2787531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent L. A., Strath M., Mellor A. L., Sanderson C. J. Eosinophilia in transgenic mice expressing interleukin 5. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1425–1431. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devos R., Vandekerckhove J., Rolink A., Plaetinck G., Van der Heyden J., Fiers W., Tavernier J. Amino acid sequence analysis of a mouse interleukin 5 receptor protein reveals homology with a mouse interleukin 3 receptor protein. Eur J Immunol. 1991 May;21(5):1315–1317. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., King J. A., Gough N. M., Nicola N. A. Expression cloning of a receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3667–3676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman D. M., Itoh N., Kitamura T., Schreurs J., Yonehara S., Yahara I., Arai K., Miyajima A. Cloning and expression of a gene encoding an interleukin 3 receptor-like protein: identification of another member of the cytokine receptor gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5459–5463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashida K., Kitamura T., Gorman D. M., Arai K., Yokota T., Miyajima A. Molecular cloning of a second subunit of the receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF): reconstitution of a high-affinity GM-CSF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9655–9659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isfort R. J., Stevens D., May W. S., Ihle J. N. Interleukin 3 binds to a 140-kDa phosphotyrosine-containing cell surface protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7982–7986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh N., Yonehara S., Schreurs J., Gorman D. M., Maruyama K., Ishii A., Yahara I., Arai K., Miyajima A. Cloning of an interleukin-3 receptor gene: a member of a distinct receptor gene family. Science. 1990 Jan 19;247(4940):324–327. doi: 10.1126/science.2404337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanakura Y., Druker B., Cannistra S. A., Furukawa Y., Torimoto Y., Griffin J. D. Signal transduction of the human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-3 receptors involves tyrosine phosphorylation of a common set of cytoplasmic proteins. Blood. 1990 Aug 15;76(4):706–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanakura Y., Druker B., Wood K. W., Mamon H. J., Okuda K., Roberts T. M., Griffin J. D. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-3 induce rapid phosphorylation and activation of the proto-oncogene Raf-1 in a human factor-dependent myeloid cell line. Blood. 1991 Jan 15;77(2):243–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. Analysis of radioligand binding experiments. A collection of computer programs for the IBM PC. J Pharmacol Methods. 1985 Nov;14(3):213–228. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(85)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minamoto S., Mori H., Hatakeyama M., Kono T., Doi T., Ide T., Uede T., Taniguchi T. Characterization of the heterodimeric complex of human IL-2 receptor alpha.beta chains reconstituted in a mouse fibroblast cell line, L929. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 1;145(7):2177–2182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mita S., Tominaga A., Hitoshi Y., Sakamoto K., Honjo T., Akagi M., Kikuchi Y., Yamaguchi N., Takatsu K. Characterization of high-affinity receptors for interleukin 5 on interleukin 5-dependent cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2311–2315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Schreurs J., Miyajima A., Wang J. Y. Hematopoietic growth factors activate the tyrosine phosphorylation of distinct sets of proteins in interleukin-3-dependent murine cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2214–2218. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata Y., Yamaguchi N., Hitoshi Y., Tominaga A., Takatsu K. Interleukin 5 and interleukin 3 induce serine and tyrosine phosphorylations of several cellular proteins in an interleukin 5-dependent cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Dec 31;173(3):1102–1108. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80899-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaetinck G., Van der Heyden J., Tavernier J., Faché I., Tuypens T., Fischkoff S., Fiers W., Devos R. Characterization of interleukin 5 receptors on eosinophilic sublines from human promyelocytic leukemia (HL-60) cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):683–691. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A. G., Melchers F., Palacios R. Monoclonal antibodies reactive with the mouse interleukin 5 receptor. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1693–1701. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. An LFA-3 cDNA encodes a phospholipid-linked membrane protein homologous to its receptor CD2. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):840–842. doi: 10.1038/329840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher A., Coffman R. L., Hieny S., Scott P., Cheever A. W. Interleukin 5 is required for the blood and tissue eosinophilia but not granuloma formation induced by infection with Schistosoma mansoni. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):61–65. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen P. H., Mui A. L., Murthy S. C., Krystal G. Interleukin-3, GM-CSF, and TPA induce distinct phosphorylation events in an interleukin 3-dependent multipotential cell line. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):406–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen P., Mui A. L., Krystal G. Interleukin-3 stimulates the tyrosine phosphorylation of the 140-kilodalton interleukin-3 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19253–19258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaki S., Tominaga A., Hitoshi Y., Mita S., Sonoda E., Yamaguchi N., Takatsu K. Molecular cloning and expression of the murine interleukin-5 receptor. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4367–4374. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsu K., Tominaga A., Harada N., Mita S., Matsumoto M., Takahashi T., Kikuchi Y., Yamaguchi N. T cell-replacing factor (TRF)/interleukin 5 (IL-5): molecular and functional properties. Immunol Rev. 1988 Feb;102:107–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier J., Devos R., Van der Heyden J., Hauquier G., Bauden R., Fache I., Kawashima E., Vandekerckhove J., Contreras R., Fiers W. Expression of human and murine interleukin-5 in eukaryotic systems. DNA. 1989 Sep;8(7):491–501. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohyama K., Lee K. H., Tashiro K., Kinashi T., Honjo T. Establishment of an interleukin-5-dependent subclone from an interleukin-3-dependent murine hemopoietic progenitor cell line, LyD9, and its malignant transformation by autocrine secretion of interleukin-5. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1823–1830. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08307.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga A., Mita S., Kikuchi Y., Hitoshi Y., Takatsu K., Nishikawa S., Ogawa M. Establishment of IL-5-dependent early B cell lines by long-term bone marrow cultures. Growth Factors. 1989;1(2):135–146. doi: 10.3109/08977198909029123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga A., Takaki S., Koyama N., Katoh S., Matsumoto R., Migita M., Hitoshi Y., Hosoya Y., Yamauchi S., Kanai Y. Transgenic mice expressing a B cell growth and differentiation factor gene (interleukin 5) develop eosinophilia and autoantibody production. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):429–437. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umland S. P., Go N. F., Cupp J. E., Howard M. Responses of B cells from autoimmune mice to IL-5. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1528–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel G. D. Interleukin 5 regulation of peritoneal Ly-1 B lymphocyte proliferation, differentiation and autoantibody secretion. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Sep;19(9):1701–1707. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi N., Hitoshi Y., Mita S., Hosoya Y., Murata Y., Kikuchi Y., Tominaga A., Takatsu K. Characterization of the murine interleukin 5 receptor by using a monoclonal antibody. Int Immunol. 1990;2(2):181–187. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.2.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi Y., Matsui T., Kasahara T., Etoh S., Tominaga A., Takatsu K., Miura Y., Suda T. In vivo changes of hemopoietic progenitors and the expression of the interleukin 5 gene in eosinophilic mice infected with Toxocara canis. Exp Hematol. 1990 Dec;18(11):1152–1157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]