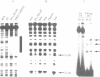Abstract
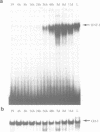
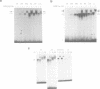
Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor-1 alpha (HNF-1 alpha) and HNF-1 beta are homeodomain-containing transcription factors which interact with the GTTAATNATTAAC motif essential to the function of more than 15 promoters selectively expressed in the liver. These homeoproteins can form homo- and heterodimers in solution and share identical DNA-binding domains but have different transcriptional activation properties. During retinoic acid (RA) induced differentiation of F9 embryonal carcinoma (EC) cells, which stimulates aspects of pre-implantation embryogenesis, both HNF-1 beta mRNA and immunoreactive DNA-binding activity are strongly induced approximately 24 h post RA-treatment. In contrast, HNF-1 alpha mRNA increases approximately 4-fold after 5 days, concomitant with elevation of HNF-1 alpha DNA-binding activity and expression of the HNF-1 target gene alpha-fetoprotein. These results indicate that HNF-1 alpha and -1 beta expression can be controlled by regulatory hierarchies downstream of primary RA-response genes, and suggest that independent regulatory mechanisms for these factors can confer distinct and interactive developmental functions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumhueter S., Courtois G., Crabtree G. R. A variant nuclear protein in dedifferentiated hepatoma cells binds to the same functional sequences in the beta fibrinogen gene promoter as HNF-1. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2485–2493. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03095.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Yaniv M., Cortese R. Hepatocyte dedifferentiation and extinction is accompanied by a block in the synthesis of mRNA coding for the transcription factor HNF1/LFB1. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2257–2263. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouard T., Blumenfeld M., Bach I., Vandekerckhove J., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. A distal dimerization domain is essential for DNA-binding by the atypical HNF1 homeodomain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 11;18(19):5853–5863. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.19.5853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Baumhueter S., Crabtree G. R. Purified hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 interacts with a family of hepatocyte-specific promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7937–7941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Morgan J. G., Campbell L. A., Fourel G., Crabtree G. R. Interaction of a liver-specific nuclear factor with the fibrinogen and alpha 1-antitrypsin promoters. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):688–692. doi: 10.1126/science.3499668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durand D. B., Shaw J. P., Bush M. R., Replogle R. E., Belagaje R., Crabtree G. R. Characterization of antigen receptor response elements within the interleukin-2 enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1715–1724. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerman M. H., Godbout R., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. Tissue-specific transcription of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene promoter is dependent on HNF-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4204–4212. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frain M., Swart G., Monaci P., Nicosia A., Stämpfli S., Frank R., Cortese R. The liver-specific transcription factor LF-B1 contains a highly diverged homeobox DNA binding domain. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90877-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardon E. M., Frain M., Paonessa G., Cortese R. Two distinct factors interact with the promoter regions of several liver-specific genes. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1711–1719. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Rollier A., Tronche F., Ott M. O., Yaniv M., Weiss M. C. The rat albumin promoter is composed of six distinct positive elements within 130 nucleotides. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4750–4758. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan B. L., Taylor A., Adamson E. Cell interactions modulate embryonal carcinoma cell differentiation into parietal or visceral endoderm. Nature. 1981 May 21;291(5812):235–237. doi: 10.1038/291235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. J., Conley P. B., Hsieh C. L., Francke U., Crabtree G. R. Molecular cloning, functional expression, and chromosomal localization of mouse hepatocyte nuclear factor 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9838–9842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRosa G. J., Gudas L. J. Early retinoic acid-induced F9 teratocarcinoma stem cell gene ERA-1: alternate splicing creates transcripts for a homeobox-containing protein and one lacking the homeobox. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3906–3917. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Schibler U. A glycosylated liver-specific transcription factor stimulates transcription of the albumin gene. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1179–1187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maire P., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The role of cis-acting promoter elements in tissue-specific albumin gene expression. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.2711183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel D. B., Hansen L. P., Graves M. K., Conley P. B., Crabtree G. R. HNF-1 alpha and HNF-1 beta (vHNF-1) share dimerization and homeo domains, but not activation domains, and form heterodimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1042–1056. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2075–2087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S. P., Garbern J., Odenwald W. F., Lazzarini R. A., Linney E. Differential expression of the homeobox gene Hox-1.3 in F9 embryonal carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5587–5591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Monaci P., Tomei L., De Francesco R., Nuzzo M., Stunnenberg H., Cortese R. A myosin-like dimerization helix and an extra-large homeodomain are essential elements of the tripartite DNA binding structure of LFB1. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1225–1236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90687-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Identification of a novel lymphoid specific octamer binding protein (OTF-2B) by proteolytic clipping bandshift assay (PCBA). EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4221–4229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03319.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. W., Vogt T. F., Croke M. E., Tilghman S. M. Tissue-specific activation of a cloned alpha-fetoprotein gene during differentiation of a transfected embryonal carcinoma cell line. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):562–567. doi: 10.1038/310562a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasios G. W., Gold J. D., Petkovich M., Chambon P., Gudas L. J. A retinoic acid-responsive element is present in the 5' flanking region of the laminin B1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9099–9103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt T. F., Compton R. S., Scott R. W., Tilghman S. M. Differential requirements for cellular enhancers in stem and differentiated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):487–500. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young P. R., Tilghman S. M. Induction of alpha-fetoprotein synthesis in differentiating F9 teratocarcinoma cells is accompanied by a genome-wide loss of DNA methylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):898–907. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]