Abstract
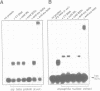
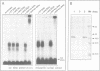
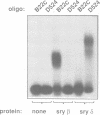
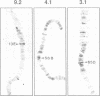
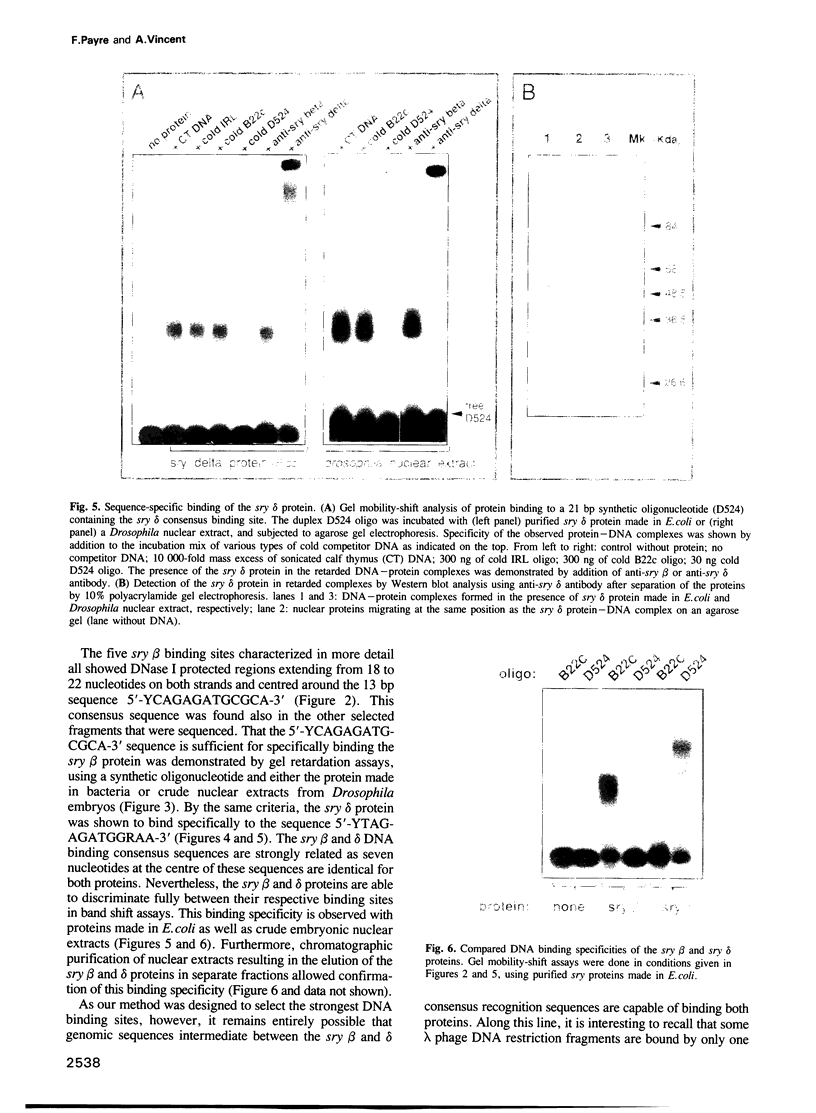
The closely related Drosophila serendipity (sry) beta (beta) and delta (delta) Cys2-His2 zinc finger proteins show partly overlapping in vitro DNA binding specificities and distinct patterns of binding sites on polytene chromosomes. Using a newly developed procedure, we identified genomic DNA targets for these two proteins. Both the sry beta and delta proteins protect an 18-22 base region from DNase I digestion within each analysed genomic binding site, that includes a 13 bp consensus sequence. The consensus recognition sites sry beta 5'-YCAGAGATGCGCA-3' and sry delta 5'-YTAGAGATGGRAA-3' thus differ by nucleotides at four out of 13 positions. They are determinant for specific binding of the sry beta and delta proteins, respectively, produced in Escherichia coli or present in Drosophila embryos. We further show that sry beta is the major (if not exclusive) Drosophila nuclear protein that specifically binds the 5'-CAGAGTGCGC-3' sequence. The identified sry beta genomic targets are all contained within single-copy DNA in euchromatic regions of the genome. Two out of the five characterized in detail map at cytological positions coincident with binding sites of the native sry beta protein on polytene chromosomes.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg J. M. Zinc finger domains: hypotheses and current knowledge. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:405–421. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Selection of DNA binding sites by regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Jun;13(6):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90085-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedenkapp H., Borgmeyer U., Sippel A. E., Klempnauer K. H. Viral myb oncogene encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):835–837. doi: 10.1038/335835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Tjian R. Transcription factors that activate the Ultrabithorax promoter in developmentally staged extracts. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):699–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T. J., Postma J. P., Brown R. S., Argos P. A model for the tertiary structure of the 28 residue DNA-binding motif ('zinc finger') common to many eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Protein Eng. 1988 Sep;2(3):209–218. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Thomas G. H., Elgin S. C. Drosophila nuclear proteins bind to regions of alternating C and T residues in gene promoters. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1487–1490. doi: 10.1126/science.2781290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. The GLI gene encodes a nuclear protein which binds specific sequences in the human genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):634–642. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knöchel W., Pöting A., Köster M., el Baradi T., Nietfeld W., Bouwmeester T., Pieler T. Evolutionary conserved modules associated with zinc fingers in Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6097–6100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer-Safer P. R., Levine M., Ward D. C. Immunological method for mapping genes on Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay R. D. Binding of a simian virus 40 T antigen-related protein to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 25;145(3):471–488. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90540-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli J., Gibson T. J., Vesque C., Charnay P. Base sequence discrimination by zinc-finger DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):175–178. doi: 10.1038/349175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pankratz M. J., Jäckle H. Making stripes in the Drosophila embryo. Trends Genet. 1990 Sep;6(9):287–292. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90234-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payre F., Noselli S., Lefrère V., Vincent A. The closely related Drosophila sry beta and sry delta zinc finger proteins show differential embryonic expression and distinct patterns of binding sites on polytene chromosomes. Development. 1990 Sep;110(1):141–149. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payre F., Vincent A. Finger proteins and DNA-specific recognition: distinct patterns of conserved amino acids suggest different evolutionary modes. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 18;234(2):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80091-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payre F., Yanicostas C., Vincent A. Serendipity delta, a Drosophila zinc finger protein present in embryonic nuclei at the onset of zygotic gene transcription. Dev Biol. 1989 Dec;136(2):469–480. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90272-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. An underlying repeat in some transcriptional control sequences corresponding to half a double helical turn of DNA. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90866-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh R., Aicher W., Gaul U., Côté S., Preiss A., Maier D., Seifert E., Nauber U., Schröder C., Kemler R. A conserved family of nuclear proteins containing structural elements of the finger protein encoded by Krüppel, a Drosophila segmentation gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90817-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., LeBowitz J. H., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Molecular cloning of an enhancer binding protein: isolation by screening of an expression library with a recognition site DNA. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):415–423. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L., Danna K. J. Method to identify genomic targets of DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3274–3278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A., Colot H. V., Rosbash M. Sequence and structure of the serendipity locus of Drosophila melanogaster. A densely transcribed region including a blastoderm-specific gene. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):149–166. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90265-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent A. TFIIIA and homologous genes. The 'finger' proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jun 11;14(11):4385–4391. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.11.4385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]