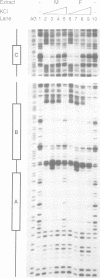
Abstract
The doublesex (dsx) gene of Drosophila melanogaster encodes both male-specific and female-specific polypeptides, whose synthesis is regulated by alternative sex-specific splicing of the primary dsx transcript. The alternative splicing of the dsx mRNA is the last known step in a cascade of regulatory gene interactions that involves both transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. Genetic studies have shown that the products of the dsx locus are required for correct somatic sexual differentiation of both sexes, and have suggested that each dsx product functions by repressing expression of terminal differentiation genes specific to the opposite sex. However, these studies have not shown whether the dsx gene products function directly to regulate the expression of target genes, or indirectly through another regulatory gene. We report here that the male- and female-specific DSX proteins, expressed in E.coli, bind directly and specifically in vitro to three DNA sequences located in an enhancer region that regulates female-specific expression of two target genes, the yolk protein genes 1 and 2. This result suggests strongly that dsx is a final regulatory gene in the hierarchy of regulatory genes controlling somatic sexual differentiation.
Full text
PDF


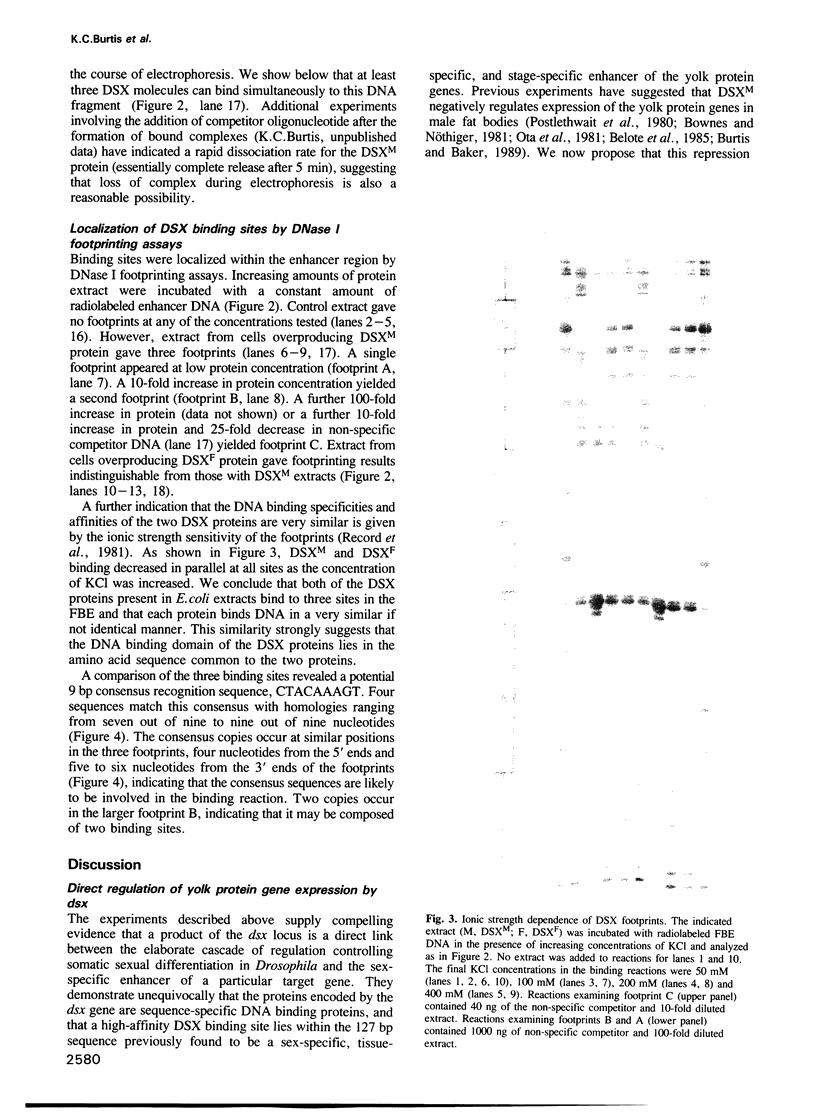


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker B. S., Belote J. M. Sex determination and dosage compensation in Drosophila melanogaster. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:345–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S., Ridge K. A. Sex and the single cell. I. On the action of major loci affecting sex determination in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1980 Feb;94(2):383–423. doi: 10.1093/genetics/94.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S. Sex in flies: the splice of life. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):521–524. doi: 10.1038/340521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell L. R., Maine E. M., Schedl P., Cline T. W. Sex-lethal, a Drosophila sex determination switch gene, exhibits sex-specific RNA splicing and sequence similarity to RNA binding proteins. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1037–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90248-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belote J. M., Baker B. S. Sex determination in Drosophila melanogaster: analysis of transformer-2, a sex-transforming locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(5):1568–1572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.5.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belote J. M., Baker B. S. Sexual behavior: its genetic control during development and adulthood in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8026–8030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belote J. M., Handler A. M., Wolfner M. F., Livak K. J., Baker B. S. Sex-specific regulation of yolk protein gene expression in Drosophila. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90148-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs R. T., Gregor P., Idriss S., Belote J. M., McKeown M. Regulation of sexual differentiation in D. melanogaster via alternative splicing of RNA from the transformer gene. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):739–747. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bownes M., Nöthiger R. Sex determining genes and vitellogenin synthesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(2):222–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00269661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Baker B. S. Drosophila doublesex gene controls somatic sexual differentiation by producing alternatively spliced mRNAs encoding related sex-specific polypeptides. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):997–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90633-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman K. B., Wolfner M. F. Determination of male-specific gene expression in Drosophila accessory glands. Dev Biol. 1988 Mar;126(1):195–202. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90253-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. W., Cline T. W. Molecular nature of the Drosophila sex determination signal and its link to neurogenesis. Science. 1991 Mar 1;251(4997):1071–1074. doi: 10.1126/science.1900130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian M. J., Shepherd B. M., Wensink P. C. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer from the Drosophila yolk protein 1 gene. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):859–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90560-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goutte C., Johnson A. D. a1 protein alters the DNA binding specificity of alpha 2 repressor. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):875–882. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90429-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Johnson A. D. Homeo domain of the yeast repressor alpha 2 is a sequence-specific DNA-binding domain but is not sufficient for repression. Science. 1987 Aug 28;237(4818):1007–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.2887035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., England B., Tjian R. Characterization of Drosophila transcription factors that activate the tandem promoters of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):965–977. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Goutte C., Johnson A. D. The yeast cell-type-specific repressor alpha 2 acts cooperatively with a non-cell-type-specific protein. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):927–936. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90449-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagoshi R. N., McKeown M., Burtis K. C., Belote J. M., Baker B. S. The control of alternative splicing at genes regulating sexual differentiation in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):229–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90384-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota T., Fukunaga A., Kawabe M., Oishi K. Interactions between sex-transformation mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Hemolymph vitellogenins and gonad morphology. Genetics. 1981 Nov-Dec;99(3-4):429–441. doi: 10.1093/genetics/99.3-4.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwait J. H., Bownes M., Jowett T. Sexual phenotype and vitellogenin synthesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90123-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Mazur S. J., Melançon P., Roe J. H., Shaner S. L., Unger L. Double helical DNA: conformations, physical properties, and interactions with ligands. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:997–1024. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.005025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salz H. K., Maine E. M., Keyes L. N., Samuels M. E., Cline T. W., Schedl P. The Drosophila female-specific sex-determination gene, Sex-lethal, has stage-, tissue-, and sex-specific RNAs suggesting multiple modes of regulation. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):708–719. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd B., Garabedian M. J., Hung M. C., Wensink P. C. Developmental control of Drosophila yolk protein 1 gene by cis-acting DNA elements. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:521–526. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slee R., Bownes M. Sex determination in Drosophila melanogaster. Q Rev Biol. 1990 Jun;65(2):175–204. doi: 10.1086/416718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosnowski B. A., Belote J. M., McKeown M. Sex-specific alternative splicing of RNA from the transformer gene results from sequence-dependent splice site blockage. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90426-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmann-Zwicky M., Amrein H., Nöthiger R. Genetic control of sex determination in Drosophila. Adv Genet. 1990;27:189–237. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenlund A., Botchan M. R. The E2 trans-activator can act as a repressor by interfering with a cellular transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):123–136. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. Developmental regulation of two 5S ribosomal RNA genes. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1626–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfner M. F. Sex-specific gene expression in somatic tissues of Drosophila melanogaster. Trends Genet. 1988 Dec;4(12):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90052-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]