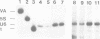Abstract
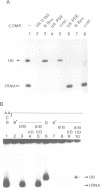
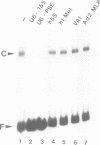
Transcription factors, required for the basal expression of the mouse U6 gene were identified in extracts from HeLa cells. This gene is transcribed at least four times more efficiently than its human counterpart in extracts from mouse or HeLa cells and hence provides an excellent in vitro system for the identification of transcription factors involved in the basal expression of mammalian U6 genes. At least four separate protein components were found to be required in addition to RNA polymerase III for correct synthesis of U6 RNA in vitro. These correspond to: (i) TFIIIB; (ii) a heat labile activity contained in a protein fraction enriched in TFIID; (iii) an, as yet, uncharacterized component contained in the flow-through upon rechromatography on phosphocellulose, and finally; (iv) a protein specifically binding to the mouse U6 gene promoter and transactivating its expression. Transcription factors IIIA and IIIC are not involved in mammalian U6 transcription in vitro. The U6-specific transcription factor has a molecular mass of approximately 90 +/- 10 kDa. It specifically binds to the U6 gene from bp -42 to -78 on the coding and from bp -37 to -79 on the non-coding strand thereby centrally encompassing the PSE motif of the mouse U6 promoter. The binding activity of this protein is correlated with the efficiency with which the U6 gene is transcribed in vitro, thereby indicating a crucial role of the PSE-binding protein for U6 transcription.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndt-Jovin D. J., Jovin T. M., Bähr W., Frischauf A. M., Marquardt M. Covalent attachment of DNA to agarose. Improved synthesis and use in affinity chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun;54(2):411–418. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bark C., Weller P., Zabielski J., Janson L., Pettersson U. A distant enhancer element is required for polymerase III transcription of a U6 RNA gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):356–359. doi: 10.1038/328356a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Guthrie C. Transcription of a yeast U6 snRNA gene requires a polymerase III promoter element in a novel position. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1345–1356. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Murgo S., Ebel J. P., Krol A., Tebb G., Mattaj L. W. A common octamer motif binding protein is involved in the transcription of U6 snRNA by RNA polymerase III and U2 snRNA by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G., Henning D., Wright D., Reddy R. Upstream regulatory elements are necessary and sufficient for transcription of a U6 RNA gene by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):503–512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C., Patterson B. Spliceosomal snRNAs. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:387–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn D., Wingender E., Seifart K. H. Transcription complexes for various class III genes differ in parameters of formation and stability towards salt. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 20;193(2):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90221-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knuth M. W., Gunderson S. I., Thompson N. E., Strasheim L. A., Burgess R. R. Purification and characterization of proximal sequence element-binding protein 1, a transcription activating protein related to Ku and TREF that binds the proximal sequence element of the human U1 promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17911–17920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Maser R. L., Calvet J. P., Pederson T. U6 small nuclear RNA is transcribed by RNA polymerase III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8575–8579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Transcription of a human U6 small nuclear RNA gene in vivo withstands deletion of intragenic sequences but not of an upstream TATATA box. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7371–7379. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Upstream elements required for efficient transcription of a human U6 RNA gene resemble those of U1 and U2 genes even though a different polymerase is used. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):196–204. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R. RNA polymerase III transcription of genes that lack internal control regions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 17;1088(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90146-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Hernandez N. A 7 bp mutation converts a human RNA polymerase II snRNA promoter into an RNA polymerase III promoter. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90402-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margottin F., Dujardin G., Gérard M., Egly J. M., Huet J., Sentenac A. Participation of the TATA factor in transcription of the yeast U6 gene by RNA polymerase C. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):424–426. doi: 10.1126/science.1989075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Dathan N. A., Parry H. D., Carbon P., Krol A. Changing the RNA polymerase specificity of U snRNA gene promoters. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimori T., Hardin J. A. Mechanism of interaction between Ku protein and DNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10375–10379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moenne A., Camier S., Anderson G., Margottin F., Beggs J., Sentenac A. The U6 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is transcribed by RNA polymerase C (III) in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):271–277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohshima Y., Okada N., Tani T., Itoh Y., Itoh M. Nucleotide sequences of mouse genomic loci including a gene or pseudogene for U6 (4.8S) nuclear RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):5145–5158. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R. Transcription of a U6 small nuclear RNA gene in vitro. Transcription of a mouse U6 small nuclear RNA gene in vitro by RNA polymerase III is dependent on transcription factor(s) different from transcription factors IIIA, IIIB, and IIIC. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):15980–15984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves W. H., Sthoeger Z. M. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding the p70 (Ku) lupus autoantigen. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5047–5052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H. R., Waldschmidt R., Jahn D., Seifart K. H. Purification of human transcription factor IIIC and its binding to the gene for ribosomal 5S RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5003–5016. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H. R., Waldschmidt R., Seifart K. H. Human transcription factor IIIC contains a polypeptide of 55 kDa specifically binding to Pol III genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4743–4750. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Sklar V. E., Jaehning J. A., Weinmann R., Roeder R. G. Isolation and partial characterization of the multiple forms of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase in the mouse myeloma, MOPC 315. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):5889–5897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifart K. H., Wang L., Waldschmidt R., Jahn D., Wingender E. Purification of human transcription factor IIIA and its interaction with a chemically synthesized gene encoding human 5 S rRNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1702–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmen K. A., Bernués J., Parry H. D., Stunnenberg H. G., Berkenstam A., Cavallini B., Egly J. M., Mattaj I. W. TFIID is required for in vitro transcription of the human U6 gene by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1853–1862. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg T. H., Mathews D. E., Durbin R. D., Burgess R. R. Tagetitoxin: a new inhibitor of eukaryotic transcription by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):499–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldschmidt R., Jahn D., Seifart K. H. Purification of transcription factor IIIB from HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13350–13356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingart S., Sommer U., Gerhold H., Seifart K. H. Transcription of the alpha A-globin gene of the duck. Development of a homologous in vitro system and identification of trans-acting factors. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jul 15;183(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaneva M., Ochs R., McRorie D. K., Zweig S., Busch H. Purification of an 86-70 kDa nuclear DNA-associated protein complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 26;841(1):22–29. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaneva M., Wen J., Ayala A., Cook R. cDNA-derived amino acid sequence of the 86-kDa subunit of the Ku antigen. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13407–13411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]