Abstract
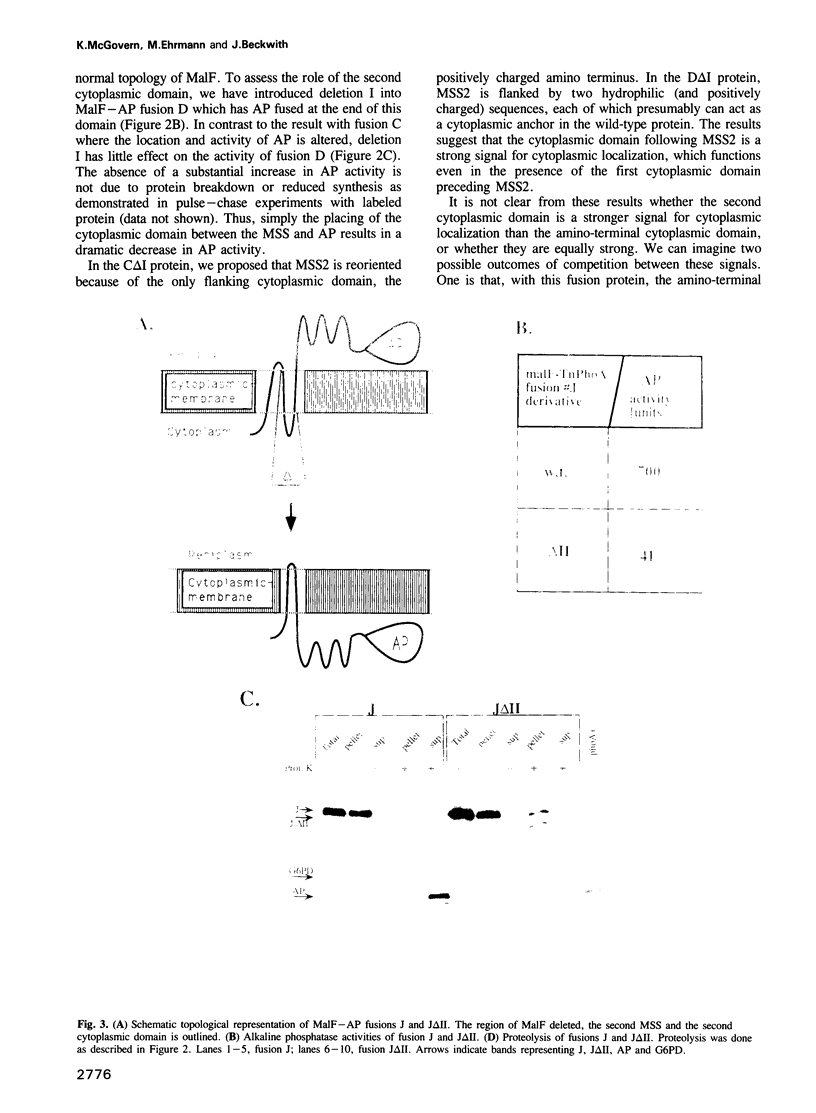
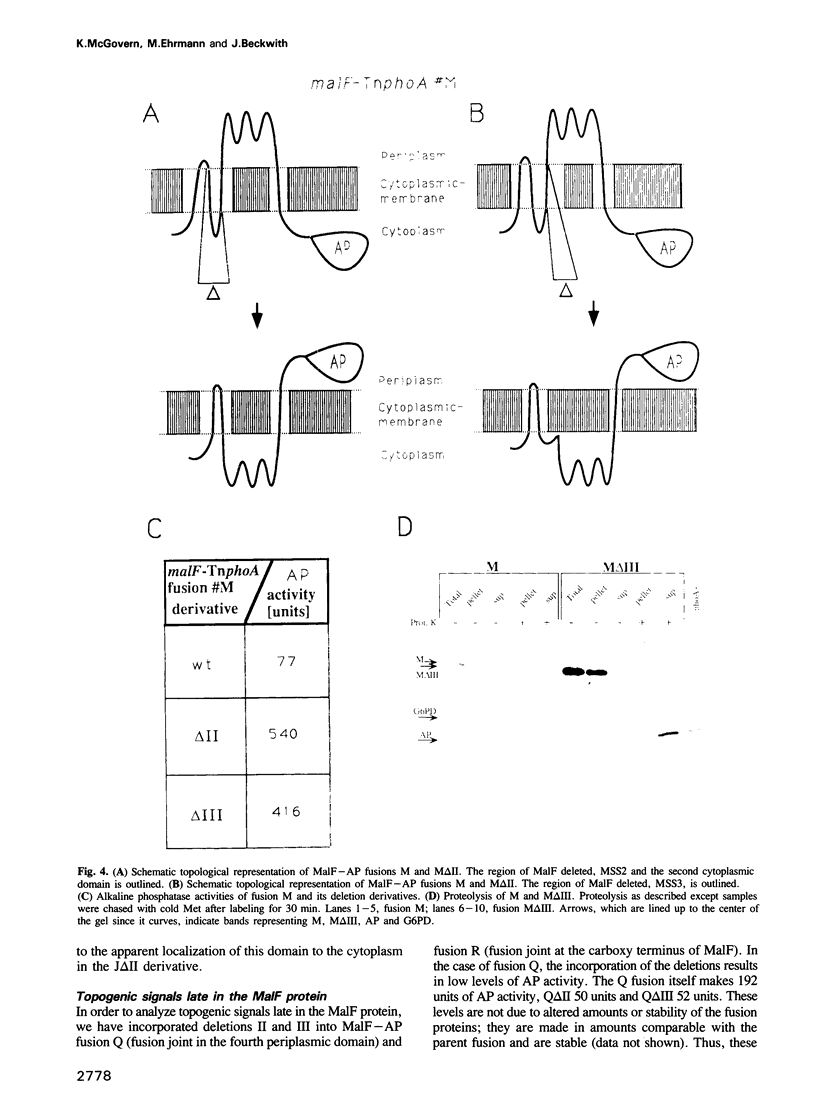
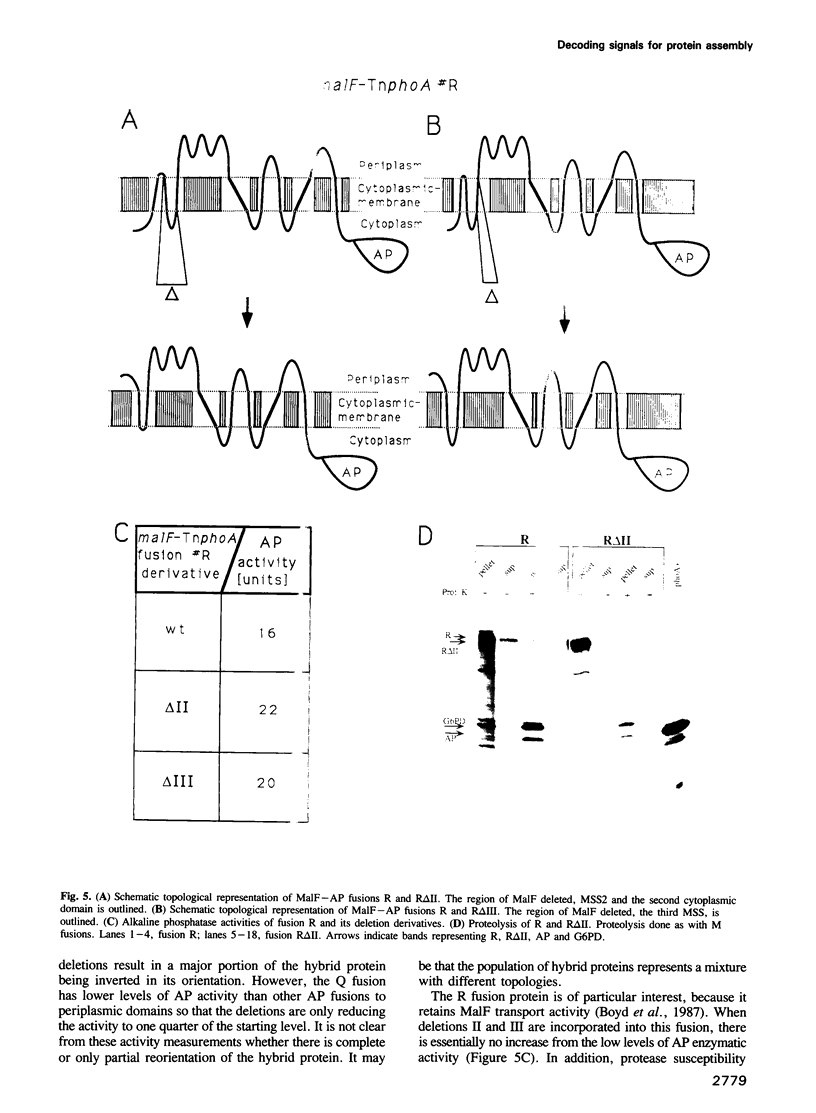
We have used genetic methods to investigate the role of the different domains of a bacterial cytoplasmic membrane protein, MalF, in determining its topology. This was done by analyzing the effects of MalF topology of deleting various domains of the protein using MalF-alkaline phosphatase fusion proteins. Our results show that the cytoplasmic domains of the protein are the pre-eminent topogenic signals. These domains contain information that determines their cytoplasmic location and, thus, the orientation of the membrane spanning segments surrounding them. Periplasmic domains do not appear to have equivalent information specifying their location and membrane spanning segments do not contain information defining their orientation in the membrane. The strength of cytoplasmic domains as topogenic signals varies, correlated with the density of positively charged amino acids within them.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akita M., Sasaki S., Matsuyama S., Mizushima S. SecA interacts with secretory proteins by recognizing the positive charge at the amino terminus of the signal peptide in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8164–8169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audigier Y., Friedlander M., Blobel G. Multiple topogenic sequences in bovine opsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5783–5787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1496–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Beckwith J. Positively charged amino acid residues can act as topogenic determinants in membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9446–9450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Beckwith J. The role of charged amino acids in the localization of secreted and membrane proteins. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1031–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90378-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Manoil C., Beckwith J. Determinants of membrane protein topology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8525–8529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson A. L., Nikaido H. Overproduction, solubilization, and reconstitution of the maltose transport system from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4254–4260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrmann M., Boyd D., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of membrane protein topology by a sandwich gene fusion approach. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7574–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froshauer S., Beckwith J. The nucleotide sequence of the gene for malF protein, an inner membrane component of the maltose transport system of Escherichia coli. Repeated DNA sequences are found in the malE-malF intercistronic region. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):10896–10903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froshauer S., Green G. N., Boyd D., McGovern K., Beckwith J. Genetic analysis of the membrane insertion and topology of MalF, a cytoplasmic membrane protein of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 5;200(3):501–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90539-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann E., Rapoport T. A., Lodish H. F. Predicting the orientation of eukaryotic membrane-spanning proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5786–5790. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heijne G. The distribution of positively charged residues in bacterial inner membrane proteins correlates with the trans-membrane topology. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3021–3027. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings M. L. Topography of membrane proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:999–1027. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.005031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähnig F. Structure predictions of membrane proteins are not that bad. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):93–95. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90188-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laws J. K., Dalbey R. E. Positive charges in the cytoplasmic domain of Escherichia coli leader peptidase prevent an apolar domain from functioning as a signal. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2095–2099. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03618.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li P., Beckwith J., Inouye H. Alteration of the amino terminus of the mature sequence of a periplasmic protein can severely affect protein export in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7685–7689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp J., Flint N., Haeuptle M. T., Dobberstein B. Structural requirements for membrane assembly of proteins spanning the membrane several times. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2013–2022. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. A genetic approach to analyzing membrane protein topology. Science. 1986 Sep 26;233(4771):1403–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.3529391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Mekalanos J. J., Beckwith J. Alkaline phosphatase fusions: sensors of subcellular location. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):515–518. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.515-518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Inouye H., Oliver D., Beckwith J. Mutations that alter the signal sequence of alkaline phosphatase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):366–374. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.366-374.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson I., von Heijne G. Fine-tuning the topology of a polytopic membrane protein: role of positively and negatively charged amino acids. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1135–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90390-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxender D. L., Anderson J. J., Daniels C. J., Landick R., Gunsalus R. P., Zurawski G., Yanofsky C. Amino-terminal sequence and processing of the precursor of the leucine-specific binding protein, and evidence for conformational differences between the precursor and the mature form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2005–2009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J. Correlation of competence for export with lack of tertiary structure of the mature species: a study in vivo of maltose-binding protein in E. coli. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90074-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers R. G., Harris C. R., Knowles J. R. A conservative amino acid substitution, arginine for lysine, abolishes export of a hybrid protein in Escherichia coli. Implications for the mechanism of protein secretion. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):20082–20088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczesna-Skorupa E., Kemper B. NH2-terminal substitutions of basic amino acids induce translocation across the microsomal membrane and glycosylation of rabbit cytochrome P450IIC2. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1237–1243. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels H. P., Spiess M. Insertion of a multispanning membrane protein occurs sequentially and requires only one signal sequence. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):61–70. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane K., Akiyama Y., Ito K., Mizushima S. A positively charged region is a determinant of the orientation of cytoplasmic membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21166–21171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial M., Huylebroeck D., Garoff H. Foreign transmembrane peptides replacing the internal signal sequence of transferrin receptor allow its translocation and membrane binding. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):147–155. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90365-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu H. Y., Dalbey R. E. Both a short hydrophobic domain and a carboxyl-terminal hydrophilic region are important for signal function in the Escherichia coli leader peptidase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11833–11838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Control of topology and mode of assembly of a polytopic membrane protein by positively charged residues. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):456–458. doi: 10.1038/341456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G., Gavel Y. Topogenic signals in integral membrane proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jul 1;174(4):671–678. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14150.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]