Abstract
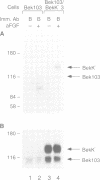
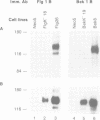
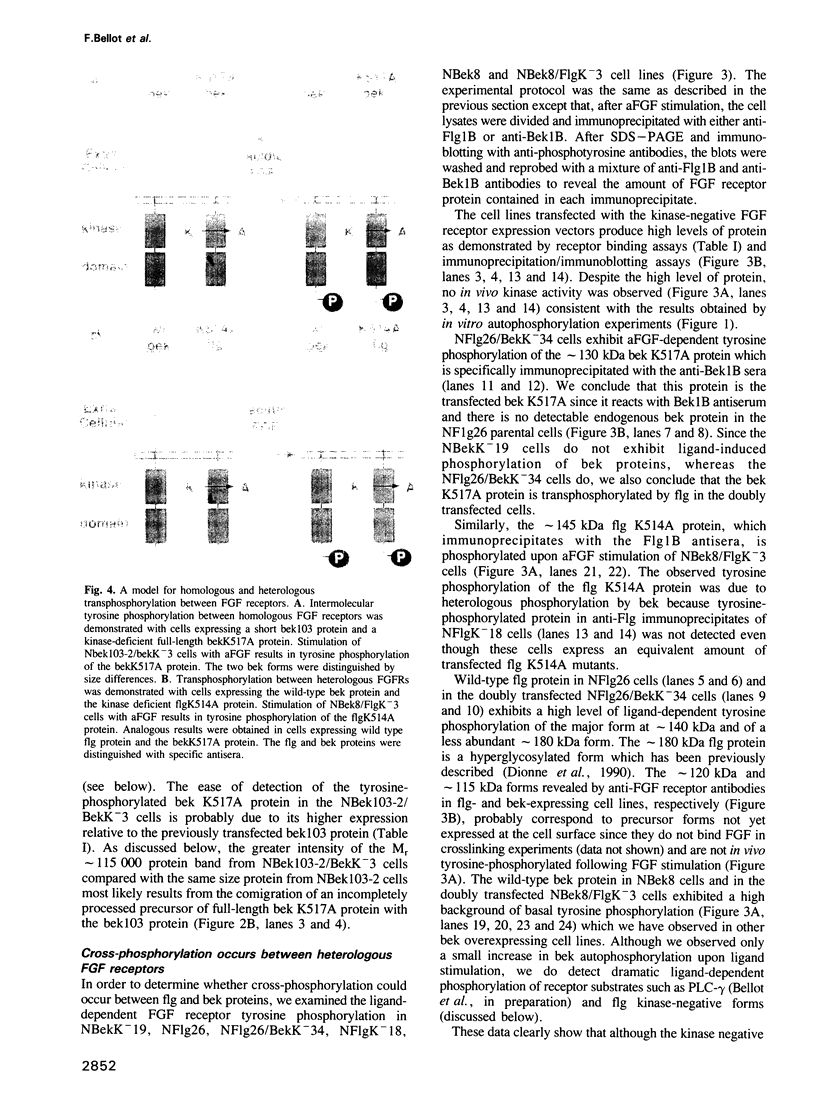
Recent evidence shows that different fibroblast growth factors (FGF) bind with similar high affinities to two FGF receptors (FGFR) called flg and bek. In order to explore the mechanism of FGFR tyrosine autophosphorylation, we have generated cell lines which co-express a kinase-negative mutant of FGFR and an active form of FGFR. The following transfected NIH 3T3 cells were generated: (i) cells which express a shorter truncated form of bek (two Ig domains) together with a kinase-negative mutant of full length bek (bek K517A), (ii) cells which express wild-type bek together with kinase-negative flg (flg K514A) and (iii) cells co-expressing wild-type flg together with bek K517A. Immunoprecipitations with either bek-or flg-specific antisera followed by immunoblotting indicated that the double transfectants express the desired receptor species. The addition of acidic FGF (aFGF) to the various cell lines followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-FGFR antibodies and immunoblotting with anti-phosphotyrosine specific antibodies indicated that aFGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of the kinase-negative FGFR mutants. These results show that tyrosine autophosphorylation of the kinase-negative FGFR is mediated by a transphosphorylation mechanism and that both homologous (bek----bek) and heterologous (bek----flg and flg----bek) transphosphorylation occurs in living cells. Recent evidence shows that tyrosine autophosphorylation of receptors with tyrosine kinase activities is essential for mediating interactions with signaling molecules. Therefore, heterologous transphosphorylation could amplify the response of cells to various forms of FGFs and their cognate receptors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D., Koch C. A., Grey L., Ellis C., Moran M. F., Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2173144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beguinot F., Smith R. J., Kahn C. R., Maron R., Moses A. C., White M. F. Phosphorylation of insulin-like growth factor I receptor by insulin receptor tyrosine kinase in intact cultured skeletal muscle cells. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3222–3228. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. S., Lazar C. S., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Requirement for intrinsic protein tyrosine kinase in the immediate and late actions of the EGF receptor. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):820–823. doi: 10.1038/328820a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionne C. A., Crumley G., Bellot F., Kaplow J. M., Searfoss G., Ruta M., Burgess W. H., Jaye M., Schlessinger J. Cloning and expression of two distinct high-affinity receptors cross-reacting with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2685–2692. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07454.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing J. R., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Ligand and protein kinase C downmodulate the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor by independent mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2890–2896. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammacher A., Mellström K., Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Isoform-specific induction of actin reorganization by platelet-derived growth factor suggests that the functionally active receptor is a dimer. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2489–2495. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori Y., Odagiri H., Nakatani H., Miyagawa K., Naito K., Sakamoto H., Katoh O., Yoshida T., Sugimura T., Terada M. K-sam, an amplified gene in stomach cancer, is a member of the heparin-binding growth factor receptor genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5983–5987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Dull T. J., Felder S., Van Obberghen E., Bellot F., Szapary D., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Point mutation at the ATP binding site of EGF receptor abolishes protein-tyrosine kinase activity and alters cellular routing. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90147-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Kris R. M., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Evidence that autophosphorylation of solubilized receptors for epidermal growth factor is mediated by intermolecular cross-phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):925–929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honegger A. M., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Evidence for epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced intermolecular autophosphorylation of the EGF receptors in living cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4035–4044. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J. Z., Kan M. K., McKeehan K., McBride G., Adams P., McKeehan W. L. Fibroblast growth factor receptors from liver vary in three structural domains. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):665–668. doi: 10.1126/science.1846977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssaint E., Blanquet P. R., Champion-Arnaud P., Gesnel M. C., Torriglia A., Courtois Y., Breathnach R. Related fibroblast growth factor receptor genes exist in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8180–8184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller T., Hood L. Diversity of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:1–63. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60639-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh N., Terachi T., Ohta M., Seo M. K. The complete amino acid sequence of the shorter form of human basic fibroblast growth factor receptor deduced from its cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 15;169(2):680–685. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90384-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., Burgess W. H., Shaw A. B., Drohan W. N. Biological equivalence of natural bovine and recombinant human alpha-endothelial cell growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16612–16617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., Lyall R. M., Mudd R., Schlessinger J., Sarver N. Expression of acidic fibroblast growth factor cDNA confers growth advantage and tumorigenesis to Swiss 3T3 cells. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):963–969. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. E., Lee P. L., Lu J., Williams L. T. Diverse forms of a receptor for acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4728–4736. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan M., DiSorbo D., Hou J. Z., Hoshi H., Mansson P. E., McKeehan W. L. High and low affinity binding of heparin-binding growth factor to a 130-kDa receptor correlates with stimulation and inhibition of growth of a differentiated human hepatoma cell. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11306–11313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan K., Johnson D. E., Williams L. T., Hayman M. J. Isolation of an additional member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family, FGFR-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1095–1099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth S., Paulson K. E., Hanafusa H. Novel tyrosine kinase identified by phosphotyrosine antibody screening of cDNA libraries. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5541–5544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. L., Johnson D. E., Cousens L. S., Fried V. A., Williams L. T. Purification and complementary DNA cloning of a receptor for basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):57–60. doi: 10.1126/science.2544996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansukhani A., Moscatelli D., Talarico D., Levytska V., Basilico C. A murine fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor expressed in CHO cells is activated by basic FGF and Kaposi FGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4378–4382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Li N., Koch A., Mohammadi M., Hurwitz D. R., Zilberstein A., Ullrich A., Pawson T., Schlessinger J. The tyrosine phosphorylated carboxyterminus of the EGF receptor is a binding site for GAP and PLC-gamma. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4375–4380. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07887.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., Maegawa H., Lee J., Dull T. J., Ulrich A., Olefsky J. M. A mutant insulin receptor with defective tyrosine kinase displays no biologic activity and does not undergo endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14663–14671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Fleming T. P., Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Ron D., Aaronson S. A. Expression cDNA cloning of the KGF receptor by creation of a transforming autocrine loop. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):72–75. doi: 10.1126/science.1846048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musci T. J., Amaya E., Kirschner M. W. Regulation of the fibroblast growth factor receptor in early Xenopus embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8365–8369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen J., Mäkelä T. P., Eerola E., Korhonen J., Hirvonen H., Claesson-Welsh L., Alitalo K. FGFR-4, a novel acidic fibroblast growth factor receptor with a distinct expression pattern. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1347–1354. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquale E. B. A distinctive family of embryonic protein-tyrosine kinase receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5812–5816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquale E. B., Singer S. J. Identification of a developmentally regulated protein-tyrosine kinase by using anti-phosphotyrosine antibodies to screen a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5449–5453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by allosteric receptor oligomerization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Nov;13(11):443–447. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soos M. A., Siddle K. Immunological relationships between receptors for insulin and insulin-like growth factor I. Evidence for structural heterogeneity of insulin-like growth factor I receptors involving hybrids with insulin receptors. Biochem J. 1989 Oct 15;263(2):553–563. doi: 10.1042/bj2630553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorkin A., Westermark B., Heldin C. H., Claesson-Welsh L. Effect of receptor kinase inactivation on the rate of internalization and degradation of PDGF and the PDGF beta-receptor. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(3):469–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.3.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugden B., Marsh K., Yates J. A vector that replicates as a plasmid and can be efficiently selected in B-lymphoblasts transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):410–413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada T., Qian X. L., Greene M. I. Intermolecular association of the p185neu protein and EGF receptor modulates EGF receptor function. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1339–1347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90697-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T. Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1564–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2538922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. M., Cheadle C., Foulke J. S., Jr, Drohan W. N., Sarver N. Utilization of an Epstein-Barr virus replicon as a eukaryotic expression vector. Gene. 1988;62(2):171–185. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90556-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]