Abstract
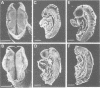
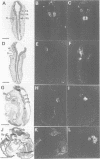
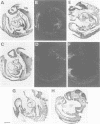
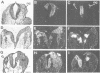
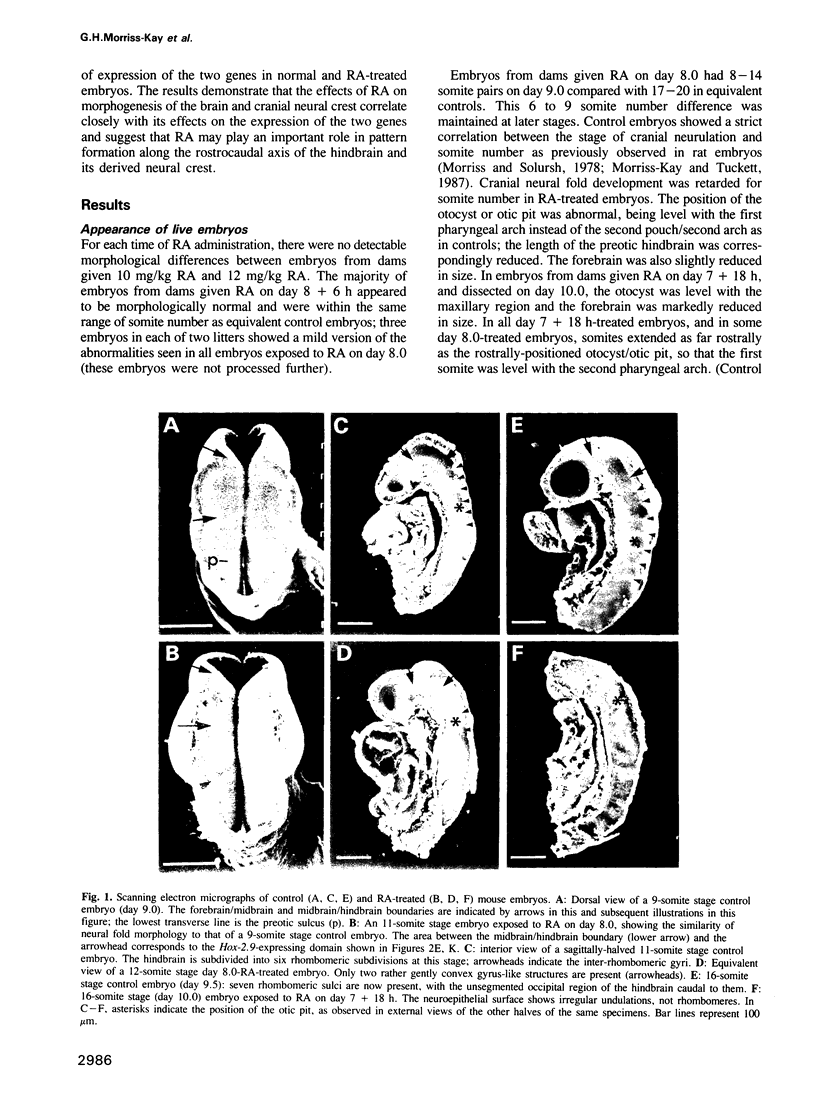
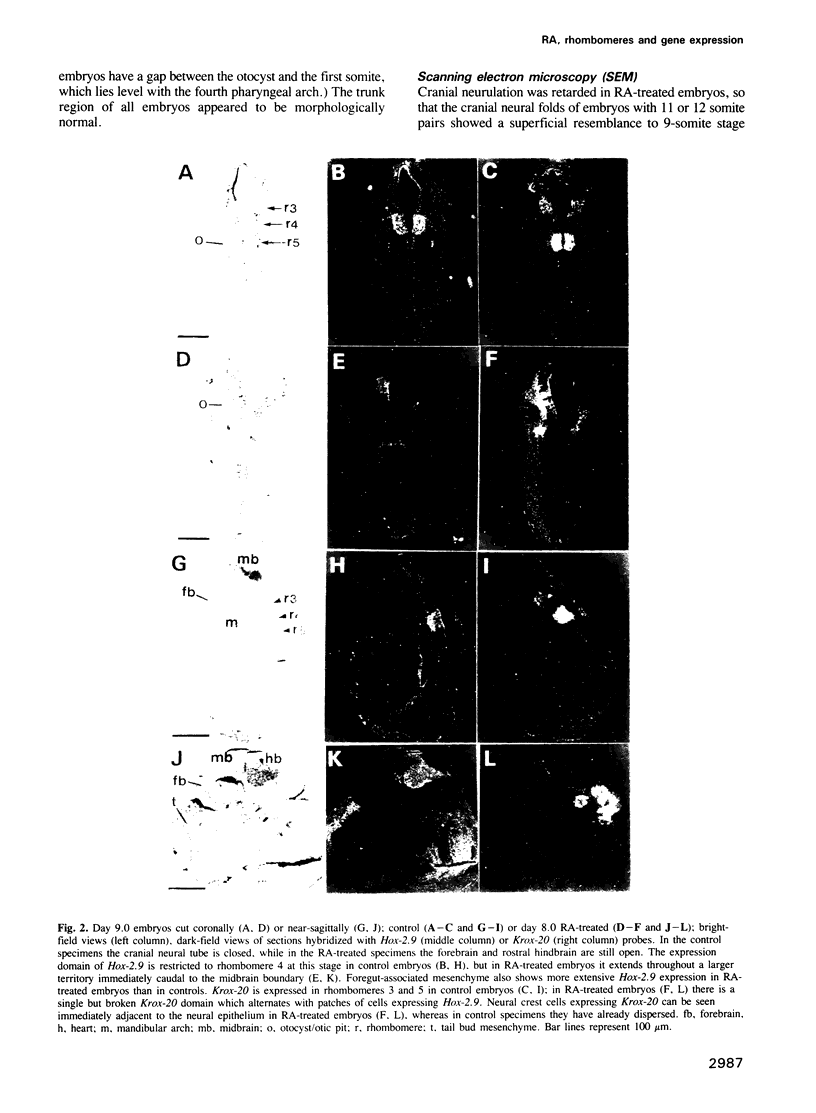
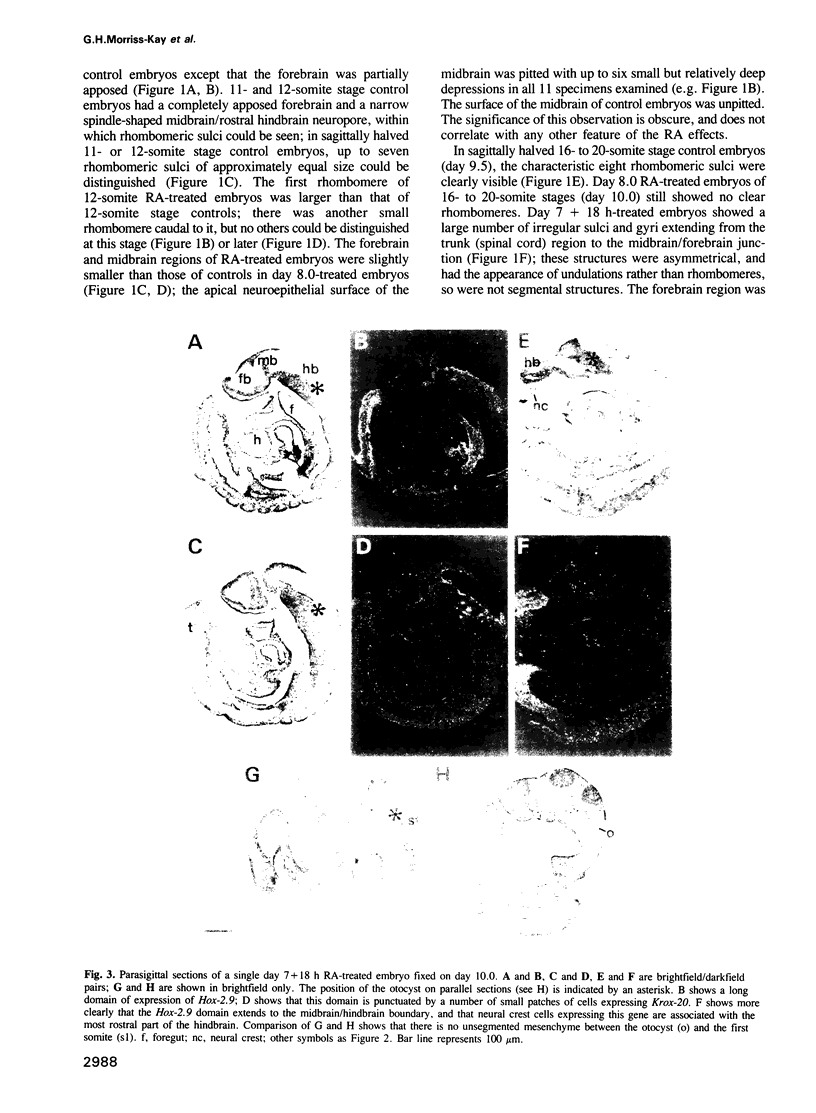
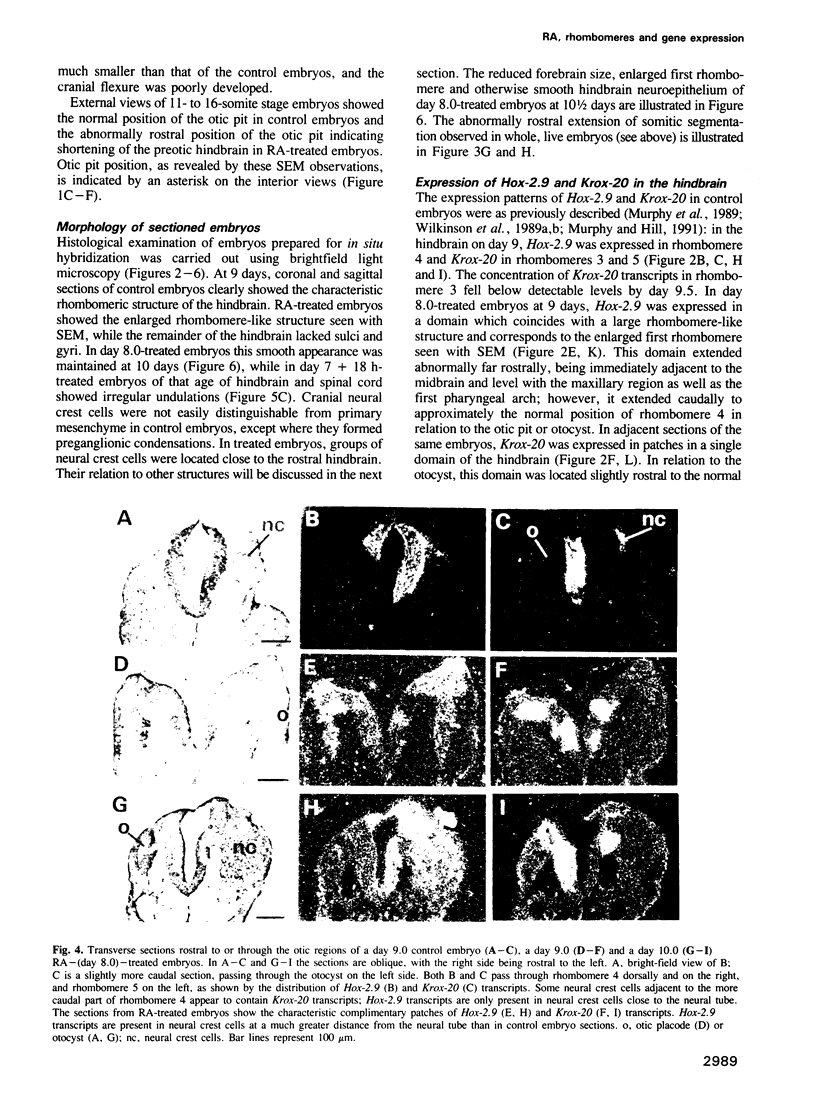
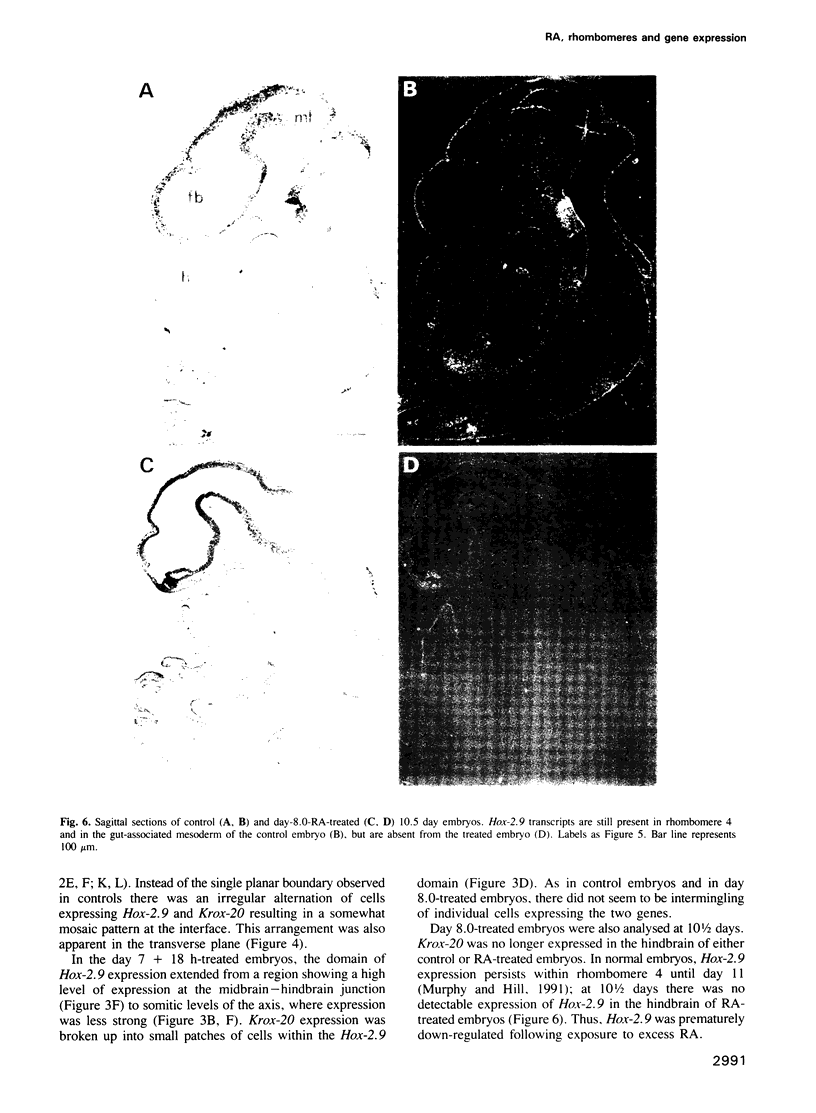
Mouse embryos were exposed to maternally administered RA on day 8.0 or day 7 3/4 of development, i.e. at or just before the differentiation of the cranial neural plate, and before the start of segmentation. On day 9.0, the RA-treated embryos had a shorter preotic hindbrain than the controls and clear rhombomeric segmentation was absent. These morphological effects were correlated with alterations in the spatiotemporal distribution patterns of two genes, Hox-2.9 and Krox-20, which are expressed in the otic and preotic hindbrain and in specific neural crest cell populations. Hox-2.9 was expressed throughout the preotic hindbrain region, instead of being confined to rhombomere 4. Krox-20 was not expressed rostral to the Hox-2.9 domain, i.e. its normal rhombomere 3 domain was absent. The Hox-2.9/Krox-20 boundary was ill-defined, with patches of alternating expression of the two genes. In migrating neural crest cells, Hox-2.9 expression was both abnormally extensive and abnormally prolonged. Neural crest cells expressing Krox-20 remained close to the neural tube. Embryos exposed to RA on day 8 1/4 appeared to be morphologically normal. We suggest that early events leading to rhombomeric segmentation and rhombomere-specific gene expression are specifically vulnerable to raised RA levels, and may require RA levels lower than those in the region of somitic segmentation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boylan J. F., Gudas L. J. Overexpression of the cellular retinoic acid binding protein-I (CRABP-I) results in a reduction in differentiation-specific gene expression in F9 teratocarcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):965–979. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand N. J., Petkovich M., Chambon P. Characterization of a functional promoter for the human retinoic acid receptor-alpha (hRAR-alpha). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6799–6806. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand N., Petkovich M., Krust A., Chambon P., de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Identification of a second human retinoic acid receptor. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):850–853. doi: 10.1038/332850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Janssen-Timmen U., Mattéi M. G., Zerial M., Bravo R., Charnay P. Structure, chromosome location, and expression of the mouse zinc finger gene Krox-20: multiple gene products and coregulation with the proto-oncogene c-fos. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):787–797. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. W., De Robertis E. M. Differential activation of Xenopus homeo box genes by mesoderm-inducing growth factors and retinoic acid. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1910–1916. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson D., Graham E., Sime C., Hill R. A gene with sequence similarity to Drosophila engrailed is expressed during the development of the neural tube and vertebrae in the mouse. Development. 1988 Oct;104(2):305–316. doi: 10.1242/dev.104.2.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. A., Joyner A. L. Expression patterns of the homeo box-containing genes En-1 and En-2 and the proto-oncogene int-1 diverge during mouse development. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1736–1744. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. A., Noble-Topham S. E., Rossant J., Joyner A. L. Expression of the homeo box-containing gene En-2 delineates a specific region of the developing mouse brain. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):361–371. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dencker L., Annerwall E., Busch C., Eriksson U. Localization of specific retinoid-binding sites and expression of cellular retinoic-acid-binding protein (CRABP) in the early mouse embryo. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):343–352. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durston A. J., Timmermans J. P., Hage W. J., Hendriks H. F., de Vries N. J., Heideveld M., Nieuwkoop P. D. Retinoic acid causes an anteroposterior transformation in the developing central nervous system. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):140–144. doi: 10.1038/340140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H., Dreyer C. A retinoic acid receptor expressed in the early development of Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1991 Jan;5(1):94–104. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser S., Keynes R., Lumsden A. Segmentation in the chick embryo hindbrain is defined by cell lineage restrictions. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):431–435. doi: 10.1038/344431a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Boyle M., Martin G. R. Isolation of the mouse Hox-2.9 gene; analysis of embryonic expression suggests that positional information along the anterior-posterior axis is specified by mesoderm. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):589–607. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R. The murine and Drosophila homeobox gene complexes have common features of organization and expression. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt P., Wilkinson D., Krumlauf R. Patterning the vertebrate head: murine Hox 2 genes mark distinct subpopulations of premigratory and migrating cranial neural crest. Development. 1991 May;112(1):43–50. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraft J. C., Kochhar D. M., Scott W. J., Nau H. Low teratogenicity of 13-cis-retinoic acid (isotretinoin) in the mouse corresponds to low embryo concentrations during organogenesis: comparison to the all-trans isomer. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 15;87(3):474–482. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(87)90253-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Zelent A., Chambon P. A third human retinoic acid receptor, hRAR-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammer E. J., Chen D. T., Hoar R. M., Agnish N. D., Benke P. J., Braun J. T., Curry C. J., Fernhoff P. M., Grix A. W., Jr, Lott I. T. Retinoic acid embryopathy. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 3;313(14):837–841. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510033131401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morriss-Kay G., Tuckett F. Fluidity of the neural epithelium during forebrain formation in rat embryos. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;8:433–449. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_8.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morriss G. M. Morphogenesis of the malformations induced in rat embryos by maternal hypervitaminosis A. J Anat. 1972 Nov;113(Pt 2):241–250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morriss G. M., Steele C. E. Comparison of the effects of retinol and retinoic acid on postimplantation rat embryos in vitro. Teratology. 1977 Feb;15(1):109–119. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420150115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P., Davidson D. R., Hill R. E. Segment-specific expression of a homoeobox-containing gene in the mouse hindbrain. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):156–159. doi: 10.1038/341156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P., Hill R. E. Expression of the mouse labial-like homeobox-containing genes, Hox 2.9 and Hox 1.6, during segmentation of the hindbrain. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):61–74. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols D. H. Formation and distribution of neural crest mesenchyme to the first pharyngeal arch region of the mouse embryo. Am J Anat. 1986 Jun;176(2):221–231. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001760210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noden D. M. The role of the neural crest in patterning of avian cranial skeletal, connective, and muscle tissues. Dev Biol. 1983 Mar;96(1):144–165. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noji S., Nohno T., Koyama E., Muto K., Ohyama K., Aoki Y., Tamura K., Ohsugi K., Ide H., Taniguchi S. Retinoic acid induces polarizing activity but is unlikely to be a morphogen in the chick limb bud. Nature. 1991 Mar 7;350(6313):83–86. doi: 10.1038/350083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie H., Webster W. S. Parameters determining isotretinoin teratogenicity in rat embryo culture. Teratology. 1991 Jan;43(1):71–81. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420430109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberte E., Dolle P., Chambon P., Morriss-Kay G. Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid binding proteins. II. Their differential pattern of transcription during early morphogenesis in mouse embryos. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):45–60. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Acampora D., Arcioni L., Andrews P. W., Boncinelli E., Mavilio F. Sequential activation of HOX2 homeobox genes by retinoic acid in human embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):763–766. doi: 10.1038/346763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sive H. L., Draper B. W., Harland R. M., Weintraub H. Identification of a retinoic acid-sensitive period during primary axis formation in Xenopus laevis. Genes Dev. 1990 Jun;4(6):932–942. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.6.932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner C. M., Gudas L. J. Mouse cellular retinoic acid binding protein: cloning, complementary DNA sequence, and messenger RNA expression during the retinoic acid-induced differentiation of F9 wild type and RA-3-10 mutant teratocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 15;49(6):1497–1504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. S., Morriss-Kay G. M. Analysis of cranial neural crest cell migration and early fates in postimplantation rat chimaeras. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1986 Nov;98:21–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. S., Morriss-Kay G. The development and distribution of the cranial neural crest in the rat embryo. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;240(2):403–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00222353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuckett F., Lim L., Morriss-Kay G. M. The ontogenesis of cranial neuromeres in the rat embryo. I. A scanning electron microscope and kinetic study. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Jun;87:215–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuckett F., Morriss-Kay G. M. The ontogenesis of cranial neuromeres in the rat embryo. II. A transmission electron microscope study. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Aug;88:231–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaessen M. J., Meijers J. H., Bootsma D., Van Kessel A. G. The cellular retinoic-acid-binding protein is expressed in tissues associated with retinoic-acid-induced malformations. Development. 1990 Oct;110(2):371–378. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.2.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanek N., Gardiner D. M., Muneoka K., Bryant S. V. Conversion by retinoic acid of anterior cells into ZPA cells in the chick wing bud. Nature. 1991 Mar 7;350(6313):81–83. doi: 10.1038/350081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster W. S., Johnston M. C., Lammer E. J., Sulik K. K. Isotretinoin embryopathy and the cranial neural crest: an in vivo and in vitro study. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol. 1986;6(3):211–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bailes J. A., Champion J. E., McMahon A. P. A molecular analysis of mouse development from 8 to 10 days post coitum detects changes only in embryonic globin expression. Development. 1987 Apr;99(4):493–500. doi: 10.1242/dev.99.4.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bailes J. A., McMahon A. P. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to specific neural cells in the developing mouse embryo. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90664-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bhatt S., Chavrier P., Bravo R., Charnay P. Segment-specific expression of a zinc-finger gene in the developing nervous system of the mouse. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):461–464. doi: 10.1038/337461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bhatt S., Cook M., Boncinelli E., Krumlauf R. Segmental expression of Hox-2 homoeobox-containing genes in the developing mouse hindbrain. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):405–409. doi: 10.1038/341405a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Peters G., Dickson C., McMahon A. P. Expression of the FGF-related proto-oncogene int-2 during gastrulation and neurulation in the mouse. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):691–695. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02864.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Krust A., Petkovich M., Kastner P., Chambon P. Cloning of murine alpha and beta retinoic acid receptors and a novel receptor gamma predominantly expressed in skin. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):714–717. doi: 10.1038/339714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]