Abstract
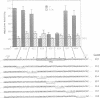
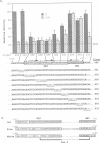
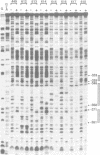
Phytochrome represses transcription of its own phyA genes within 5 min of light-triggered conversion to its active Pfr form. We have utilized microprojectile mediated gene transfer into etiolated rice seedlings to delineate sequence elements in the oat phyA3 promoter responsible for this regulation. Linker-scan mutagenesis of this promoter has identified two positive elements which together are necessary for maximal transcription in the absence of Pfr. These elements are designated PE1, centered at position -357 bp, and PE3, centered at position -96 bp. Sequence mutagenesis immediately downstream of PE3 results in maximal transcription in the presence of high Pfr levels, indicating that Pfr represses phyA3 transcription through a negatively acting sequence element. This element, designated RE1, with the sequence CATGGGCGCGG, encompasses a motif that is highly conserved in all monocot phyA promoters thus far characterized. DNase I protection analysis indicates that oat nuclear extracts contain multiple factors that bind to an array of sequence motifs, including PE1 and part of PE3, within 400 bp upstream of the oat phyA3 transcription start site. This DNA-binding pattern is not altered by Pfr. Weak binding to part of the RE1 motif is evident but also with no difference between high and low Pfr levels. We conclude that the signal transduction chain that mediates Pfr-directed repression of phyA3 transcription terminates with a negatively acting transcription factor that binds to the sequence element RE1.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruce W. B., Christensen A. H., Klein T., Fromm M., Quail P. H. Photoregulation of a phytochrome gene promoter from oat transferred into rice by particle bombardment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9692–9696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce W. B., Quail P. H. cis-acting elements involved in photoregulation of an oat phytochrome promoter in rice. Plant Cell. 1990 Nov;2(11):1081–1089. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.11.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustos M. M., Guiltinan M. J., Jordano J., Begum D., Kalkan F. A., Hall T. C. Regulation of beta-glucuronidase expression in transgenic tobacco plants by an A/T-rich, cis-acting sequence found upstream of a French bean beta-phaseolin gene. Plant Cell. 1989 Sep;1(9):839–853. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.9.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castresana C., Garcia-Luque I., Alonso E., Malik V. S., Cashmore A. R. Both positive and negative regulatory elements mediate expression of a photoregulated CAB gene from Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):1929–1936. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03030.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen A. H., Quail P. H. Structure and expression of a maize phytochrome-encoding gene. Gene. 1989 Dec 28;85(2):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90431-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnecka E., Fox P. C., Gurley W. B. In Vitro Interaction of Nuclear Proteins with the Promoter of Soybean Heat Shock Gene Gmhsp17.5E. Plant Physiol. 1990 Nov;94(3):935–943. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.3.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Cashmore A. R. Binding of a pea nuclear protein to promoters of certain photoregulated genes is modulated by phosphorylation. Plant Cell. 1989 Nov;1(11):1069–1077. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.11.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehesh K., Bruce W. B., Quail P. H. A trans-acting factor that binds to a GT-motif in a phytochrome gene promoter. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1397–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.2255908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. G., Cashmore A. R. Mutation of either G box or I box sequences profoundly affects expression from the Arabidopsis rbcS-1A promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1717–1726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst D., Oesterhelt D. Purified phytochrome influences in vitro transcription in rye nuclei. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3075–3078. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02261.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. Cohabitation of scaffold binding regions with upstream/enhancer elements of three developmentally regulated genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):521–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90877-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin P. M., Chua N. H. Spacing between GT-1 binding sites within a light-responsive element is critical for transcriptional activity. Plant Cell. 1990 May;2(5):447–455. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.5.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin P. M., Sarokin L., Memelink J., Chua N. H. Molecular light switches for plant genes. Plant Cell. 1990 May;2(5):369–378. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.5.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano G., Pichersky E., Malik V. S., Timko M. P., Scolnik P. A., Cashmore A. R. An evolutionarily conserved protein binding sequence upstream of a plant light-regulated gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7089–7093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Kay S. A., Chua N. H. Sequence-specific interactions of a pea nuclear factor with light-responsive elements upstream of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2543–2549. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Yong M. H., Cuozzo M., Kano-Murakami Y., Silverstein P., Chua N. H. Binding site requirements for pea nuclear protein factor GT-1 correlate with sequences required for light-dependent transcriptional activation of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4035–4044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03297.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey H. P., Barker R. F., Idler K. B., Murray M. G., Quail P. H. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of a gene encoding the phytochrome polypeptide from Avena. Gene. 1987;61(3):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90197-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Levine M. Divergent homeo box proteins recognize similar DNA sequences in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):858–861. doi: 10.1038/332858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen K., Laursen N. B., Jensen E. O., Marcker A., Poulsen C., Marcker K. A. HMG I-like proteins from leaf and nodule nuclei interact with different AT motifs in soybean nodulin promoters. Plant Cell. 1990 Jan;2(1):85–94. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. Ø, Marcker K. A., Schell J., Bruijn F. J. Interaction of a nodule specific, trans-acting factor with distinct DNA elements in the soybean leghaemoglobin Ibc(3) 5' upstream region. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1265–1271. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02940.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jofuku K. D., Okamuro J. K., Goldberg R. B. Interaction of an embryo DNA binding protein with a soybean lectin gene upstream region. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):734–737. doi: 10.1038/328734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordano J., Almoguera C., Thomas T. L. A sunflower helianthinin gene upstream sequence ensemble contains an enhancer and sites of nuclear protein interaction. Plant Cell. 1989 Sep;1(9):855–866. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.9.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama R., Pastan I. Molecular cloning and characterization of a human DNA binding factor that represses transcription. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90605-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay S. A., Keith B., Shinozaki K., Chua N. H. The sequence of the rice phytochrome gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2865–2866. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay S. A., Keith B., Shinozaki K., Chye M. L., Chua N. H. The rice phytochrome gene: structure, autoregulated expression, and binding of GT-1 to a conserved site in the 5' upstream region. Plant Cell. 1989 Mar;1(3):351–360. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.3.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein T. M., Roth B. A., Fromm M. E. Regulation of anthocyanin biosynthetic genes introduced into intact maize tissues by microprojectiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6681–6685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Kano-Murakami Y., Gilmartin P., Niner B., Chua N. H. A metal-dependent DNA-binding protein interacts with a constitutive element of a light-responsive promoter. Plant Cell. 1990 Sep;2(9):857–866. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.9.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lissemore J. L., Quail P. H. Rapid transcriptional regulation by phytochrome of the genes for phytochrome and chlorophyll a/b-binding protein in Avena sativa. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4840–4850. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCurdy D. W., Pratt L. H. Immunogold electron microscopy of phytochrome in Avena: identification of intracellular sites responsible for phytochrome sequestering and enhanced pelletability. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2541–2550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mösinger E., Batschauer A., Schäfer E., Apel K. Phytochrome control of in vitro transcription of specific genes in isolated nuclei from barley (Hordeum vulgare). Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;147(1):137–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08729.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R. Transcriptional repression in eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):192–197. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A mammalian high mobility group protein recognizes any stretch of six A.T base pairs in duplex DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. M., Dixon G. H. Induction by torsional stress of an altered DNA conformation 5' upstream of the gene for a high mobility group protein from trout and specific binding to flanking sequences by the gene product HMG-T. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):576–581. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Rothblum L. I. Purification and characterization of a high-mobility-group-like DNA-binding protein that stimulates rRNA synthesis in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3406–3414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]