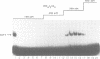
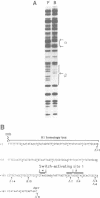
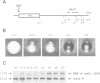
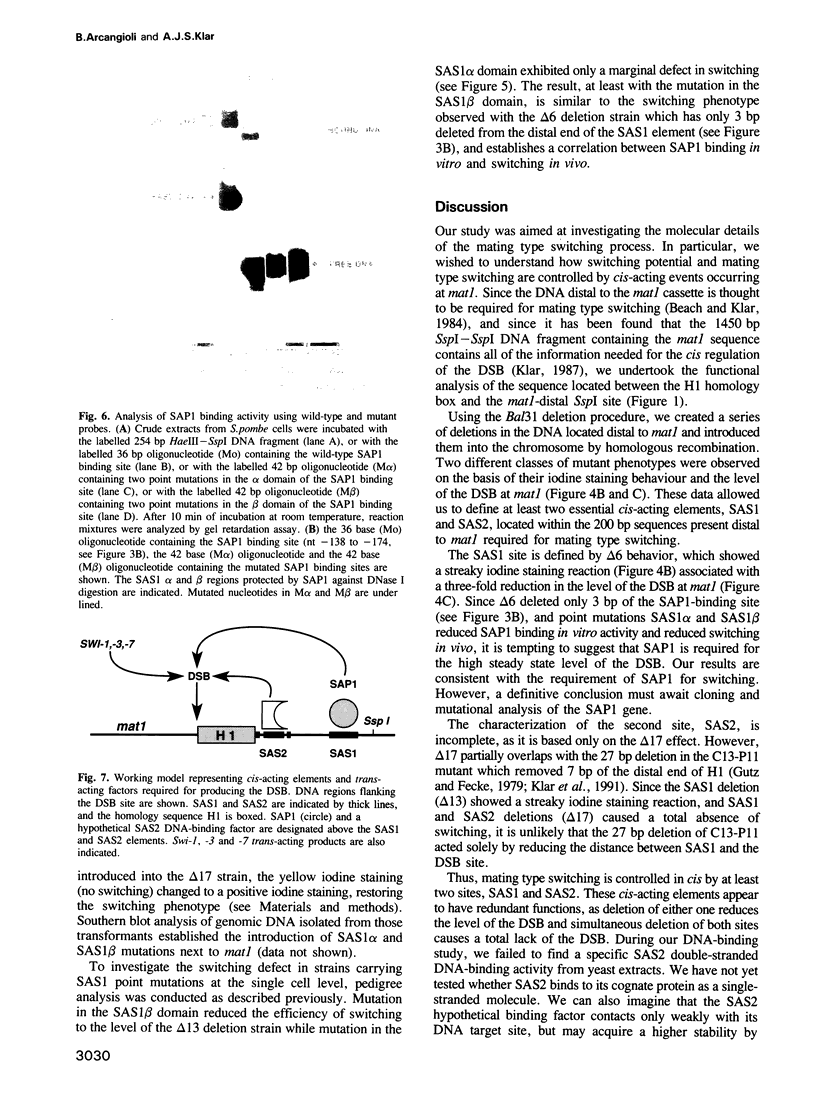
Abstract
The pattern of parental DNA strand inheritance at the mating type locus (mat1) determines the pattern of mat1 switching in a cell lineage by regulating the formation of the site-specific double-stranded break (DSB) required for mating type interconversion in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. To study the molecular basis of this programmable cell type change, we conducted structural and functional analyses of the DNA sequence flanking the DSB at mat1. We have identified and characterized a DNA-binding activity that interacts with a specific sequence located 140 bp from the DSB site. Deletion analysis of DNA sequences located distal to mat1 cassette revealed the presence of at least two switch-activating sites (SAS1 and SAS2), both of which are required for generating an efficient level of DSBs and consequently, for efficient switching. We found that SAS1 overlaps with the target site of the DNA-binding activity called SAP1 (for switch-activating protein). Point mutations generated in the SAS1 element that adversely affect binding of SAP1 protein in vitro were found to reduce the efficiency of switching in vivo, suggesting the requirement of SAP1 for switching. Pedigree analysis revealed that SAS1 is equally required for initial switching (one switch in four grand-daughters of a cell) and for consecutive switching (where the sister of a recently switched cell switches again), indicating that the two developmentally asymmetric cell divisions required to generate a particular pattern of switching share the same molecular control mechanism.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcangioli B., Lescure B. Identification of proteins involved in the regulation of yeast iso- 1-cytochrome C expression by oxygen. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2627–2633. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach D. H., Klar A. J. Rearrangements of the transposable mating-type cassettes of fission yeast. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):603–610. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egel R., Beach D. H., Klar A. J. Genes required for initiation and resolution steps of mating-type switching in fission yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3481–3485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutz H., Doe F. J. Two Different h Mating Types in SCHIZOSACCHAROMYCES POMBE. Genetics. 1973 Aug;74(4):563–569. doi: 10.1093/genetics/74.4.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Burke J., Smith M., Klar A., Beach D. Four mating-type genes control sexual differentiation in the fission yeast. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1537–1547. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02973.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Bonaduce M. J., Cafferkey R. The mechanism of fission yeast mating type interconversion: seal/replicate/cleave model of replication across the double-stranded break site at mat1. Genetics. 1991 Mar;127(3):489–496. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.3.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J. Differentiated parental DNA strands confer developmental asymmetry on daughter cells in fission yeast. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):466–470. doi: 10.1038/326466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Miglio L. M. Initiation of meiotic recombination by double-strand DNA breaks in S. pombe. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90348-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Strathern J. N., Abraham J. A. Involvement of double-strand chromosomal breaks for mating-type switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:77–88. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Strathern J. N., Hicks J. B. A position-effect control for gene transposition: state of expression of yeast mating-type genes affects their ability to switch. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):517–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J. The developmental fate of fission yeast cells is determined by the pattern of inheritance of parental and grandparental DNA strands. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1407–1415. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08256.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostriken R., Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B., Heffron F. A site-specific endonuclease essential for mating-type switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEUPOLD U. Studies on recombination in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1958;23:161–170. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1958.023.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K., Stillman D., Kipling D. Both positive and negative regulators of HO transcription are required for mother-cell-specific mating-type switching in yeast. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90236-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff J. A., Chen E. Y., Heffron F. A 24-base-pair DNA sequence from the MAT locus stimulates intergenic recombination in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7831–7835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen O., Egel R. Mapping the double-strand breaks at the mating-type locus in fission yeast by genomic sequencing. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):269–276. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg P. W., Stern M. J., Clark I., Herskowitz I. Activation of the yeast HO gene by release from multiple negative controls. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):567–577. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90235-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J. N., Klar A. J., Hicks J. B., Abraham J. A., Ivy J. M., Nasmyth K. A., McGill C. Homothallic switching of yeast mating type cassettes is initiated by a double-stranded cut in the MAT locus. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90418-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]