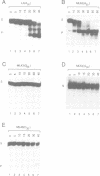
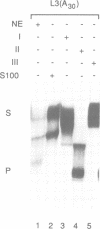
Abstract
We have identified a 3' exonuclease in HeLa cell extracts which deadenylates mammalian mRNA and leaves the mRNA body intact after poly(A) removal. Only homopolymeric adenosine tails located at the 3' end were efficiently removed by the exonuclease. The poly(A) removing activity did not require any specific sequences in the mRNA body either for poly(A) removal or for accumulation of the deadenylated mRNA. We conclude that the poly(A) removing activity is a 3' exonuclease since (i) reaction intermediates gradually lose the poly(A) tail, (ii) degradation is prevented by the presence of a cordycepin residue at the 3' end and (iii) RNAs having internally located poly(A) stretches are poor substrates for degradation. The possible involvement of the poly(A) removing enzyme in regulating mRNA translation and stability is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham A. K., Jacob S. T. Hydrolysis of poly (A) to adenine nucleotides by purified poly (A) polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2085–2087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein P., Peltz S. W., Ross J. The poly(A)-poly(A)-binding protein complex is a major determinant of mRNA stability in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):659–670. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein P., Ross J. Poly(A), poly(A) binding protein and the regulation of mRNA stability. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Sep;14(9):373–377. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. The Role of the poly(A) sequence in mammalian messenger RNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1981;10(1):1–38. doi: 10.3109/10409238109114634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Poly(A) shortening and degradation of the 3' A+U-rich sequences of human c-myc mRNA in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1697–1708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. A., Sheets M. D., Wickens M. P. Poly(A) addition during maturation of frog oocytes: distinct nuclear and cytoplasmic activities and regulation by the sequence UUUUUAU. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2151–2162. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. A., Wickens M. Poly(A) removal during oocyte maturation: a default reaction selectively prevented by specific sequences in the 3' UTR of certain maternal mRNAs. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2287–2298. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli A., Strickland S., Vassalli J. D. Meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes triggers the translation and polyadenylation of dormant tissue-type plasminogen activator mRNA. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1201–1211. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman L. E., Wormington W. M. Translational inactivation of ribosomal protein mRNAs during Xenopus oocyte maturation. Genes Dev. 1988 May;2(5):598–605. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.5.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Standart N. Do the poly(A) tail and 3' untranslated region control mRNA translation? Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):15–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90235-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus H. M., Sporin M. B. Purification and properties of a nuclear exoribonuclease from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1386–1393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L., Canellakis E. S. Adenine-rich polymer associated with rabbit reticulocyte messenger RNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):710–712. doi: 10.1038/227710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrew L. L., Dworkin-Rastl E., Dworkin M. B., Richter J. D. Poly(A) elongation during Xenopus oocyte maturation is required for translational recruitment and is mediated by a short sequence element. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):803–815. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. F., Wake S. A. An analysis of the rate of metallothionein mRNA poly(A)-shortening using RNA blot hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):7929–7943. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.7929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Accurate cleavage and polyadenylation of exogenous RNA substrate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):845–855. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Skolnik-David H., Sharp P. A. Analysis of RNA cleavage at the adenovirus-2 L3 polyadenylation site. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1929–1938. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munroe D., Jacobson A. mRNA poly(A) tail, a 3' enhancer of translational initiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3441–3455. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel R., Khoury G., Reid L. M. Regulation of insulin mRNA abundance and adenylation: dependence on hormones and matrix substrata. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):337–341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paek I., Axel R. Glucocorticoids enhance stability of human growth hormone mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1496–1507. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. G., Frim D. M., Schwartz W. J., Majzoub J. A. Vasopressin mRNA in the suprachiasmatic nuclei: daily regulation of polyadenylate tail length. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):342–344. doi: 10.1126/science.3388044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W. The poly(A) binding protein is required for poly(A) shortening and 60S ribosomal subunit-dependent translation initiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):857–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90938-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Belasco J. G., Greenberg M. E. Two distinct destabilizing elements in the c-fos message trigger deadenylation as a first step in rapid mRNA decay. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):221–231. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik-David H., Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Electrophoretic separation of polyadenylation-specific complexes. Genes Dev. 1987 Sep;1(7):672–682. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.7.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartwout S. G., Kinniburgh A. J. c-myc RNA degradation in growing and differentiating cells: possible alternate pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):288–295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varnum S. M., Wormington W. M. Deadenylation of maternal mRNAs during Xenopus oocyte maturation does not require specific cis-sequences: a default mechanism for translational control. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2278–2286. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Huarte J., Belin D., Gubler P., Vassalli A., O'Connell M. L., Parton L. A., Rickles R. J., Strickland S. Regulated polyadenylation controls mRNA translation during meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2163–2171. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. How the messenger got its tail: addition of poly(A) in the nucleus. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Jul;15(7):277–281. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90054-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickens M. In the beginning is the end: regulation of poly(A) addition and removal during early development. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Aug;15(8):320–324. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Removal of poly(A) and consequent degradation of c-fos mRNA facilitated by 3' AU-rich sequences. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):396–399. doi: 10.1038/336396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]