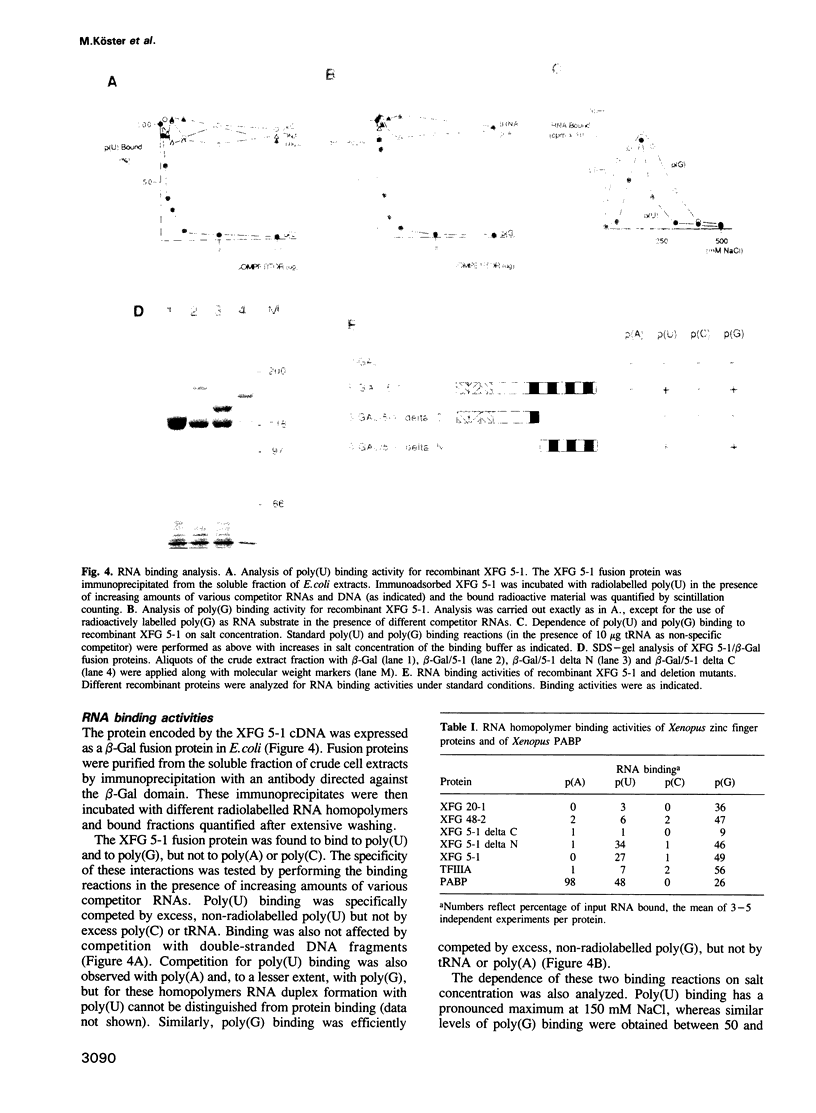
Abstract
Large multigene families of zinc finger proteins are expressed in vertebrates. One way of approaching their function is to characterize their structure, expression and biochemical properties. XFG 5-1 is a Xenopus zinc finger protein which is widely transcribed in oocytes, embryos and adult tissues. It carries a novel, non-finger repeat structure, which is common to a subfamily of Xenopus zinc finger proteins. The bacterially expressed protein exhibits specific RNA homopolymer binding activities with the zinc finger domain being sufficient for this ability. These findings suggest that XFG 5-1 serves a general biological function involving its RNA binding capacity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bandziulis R. J., Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):431–437. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellefroid E. J., Lecocq P. J., Benhida A., Poncelet D. A., Belayew A., Martial J. A. The human genome contains hundreds of genes coding for finger proteins of the Krüppel type. DNA. 1989 Jul-Aug;8(6):377–387. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellefroid E. J., Poncelet D. A., Lecocq P. J., Revelant O., Martial J. A. The evolutionarily conserved Krüppel-associated box domain defines a subfamily of eukaryotic multifingered proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3608–3612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury K., Deutsch U., Gruss P. A multigene family encoding several "finger" structures is present and differentially active in mammalian genomes. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):771–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The Drosophila developmental gene, engrailed, encodes a sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):630–635. doi: 10.1038/318630a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont J. N. Oogenesis in Xenopus laevis (Daudin). I. Stages of oocyte development in laboratory maintained animals. J Morphol. 1972 Feb;136(2):153–179. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051360203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellington A. D., Szostak J. W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):818–822. doi: 10.1038/346818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Blanco M. A., Jamison S. F., Sharp P. A. Identification and purification of a 62,000-dalton protein that binds specifically to the polypyrimidine tract of introns. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1874–1886. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg A. M., King B. O., Roeder R. G. Xenopus 5S gene transcription factor, TFIIIA: characterization of a cDNA clone and measurement of RNA levels throughout development. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):479–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90455-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Gough N. M., Dunn A. R., de Blaquiere J. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA clones of the murine myb proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2003–2008. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03884.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guddat U., Bakken A. H., Pieler T. Protein-mediated nuclear export of RNA: 5S rRNA containing small RNPs in xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):619–628. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90665-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda B. M., Roeder R. G. Association of a 5S gene transcription factor with 5S RNA and altered levels of the factor during cell differentiation. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho K. E., Darby M. K., Crawford E. T., Brown D. D. A finger protein structurally similar to TFIIIA that binds exclusively to 5S RNA in Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90809-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpel R. L., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S. Interactions of retroviral structural proteins with single-stranded nucleic acids. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):4961–4967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knöchel W., Pöting A., Köster M., el Baradi T., Nietfeld W., Bouwmeester T., Pieler T. Evolutionary conserved modules associated with zinc fingers in Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6097–6100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Varnum S. M., Wormington W. M., Melton D. A. The mRNA encoding elongation factor 1-alpha (EF-1 alpha) is a major transcript at the midblastula transition in Xenopus. Dev Biol. 1989 May;133(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90300-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köster M., Pieler T., Pöting A., Knöchel W. The finger motif defines a multigene family represented in the maternal mRNA of Xenopus laevis oocytes. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1735–1741. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03002.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muriel W. J., Cole J., Lehmann A. R. Molecular analysis of ouabain-resistant mutants of the mouse lymphoma cell line L5178Y. Mutagenesis. 1987 Sep;2(5):383–389. doi: 10.1093/mutage/2.5.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nietfeld W., Mentzel H., Pieler T. The Xenopus laevis poly(A) binding protein is composed of multiple functionally independent RNA binding domains. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3699–3705. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nietfeld W., el-Baradi T., Mentzel H., Pieler T., Köster M., Pöting A., Knöchel W. Second-order repeats in Xenopus laevis finger proteins. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 20;208(4):639–659. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., Wegnez M. Isolation of a 7S particle from Xenopus laevis oocytes: a 5S RNA-protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):241–245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard B., le Maire M., Wegnez M., Denis H. Biochemical Research on oogenesis. Composition of the 42-S storage particles of Xenopus laevix oocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(2):359–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh R., Aicher W., Gaul U., Côté S., Preiss A., Maier D., Seifert E., Nauber U., Schröder C., Kemler R. A conserved family of nuclear proteins containing structural elements of the finger protein encoded by Krüppel, a Drosophila segmentation gene. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90817-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano J. E. Purified lupus antigen La recognizes an oligouridylate stretch common to the 3' termini of RNA polymerase III transcripts. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. Classification and purification of proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles by RNA-binding specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2237–2241. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Baradi T., Bouwmeester T., Giltay R., Pieler T. The maternal store of zinc finger protein encoding mRNAs in fully grown Xenopus oocytes is not required for early embryogenesis. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1407–1413. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07661.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]