Abstract
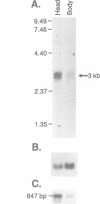
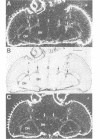
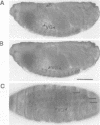
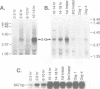
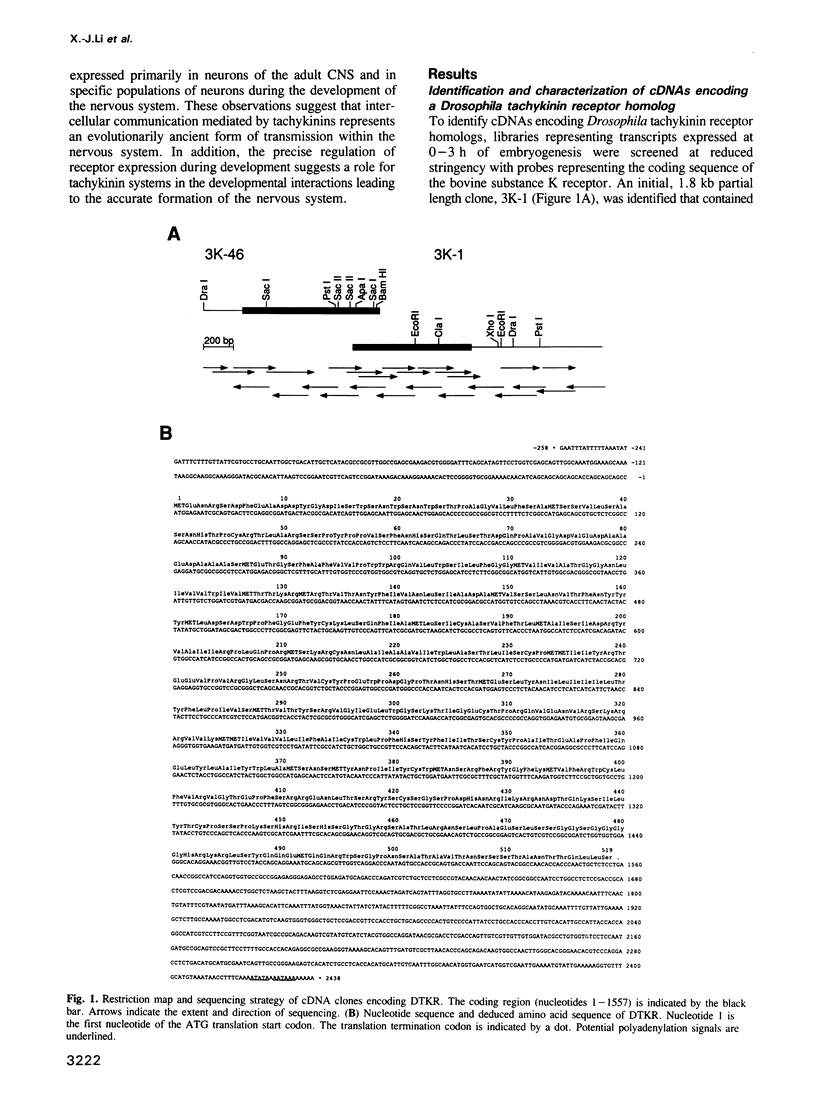
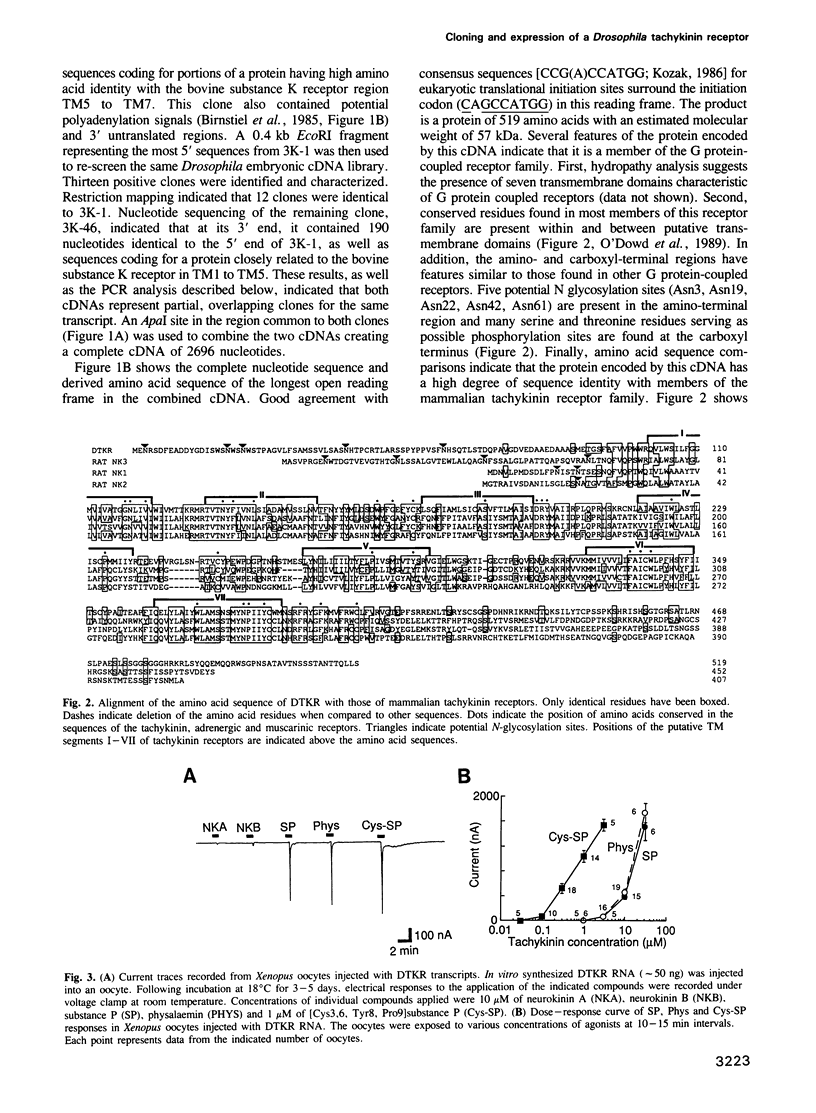
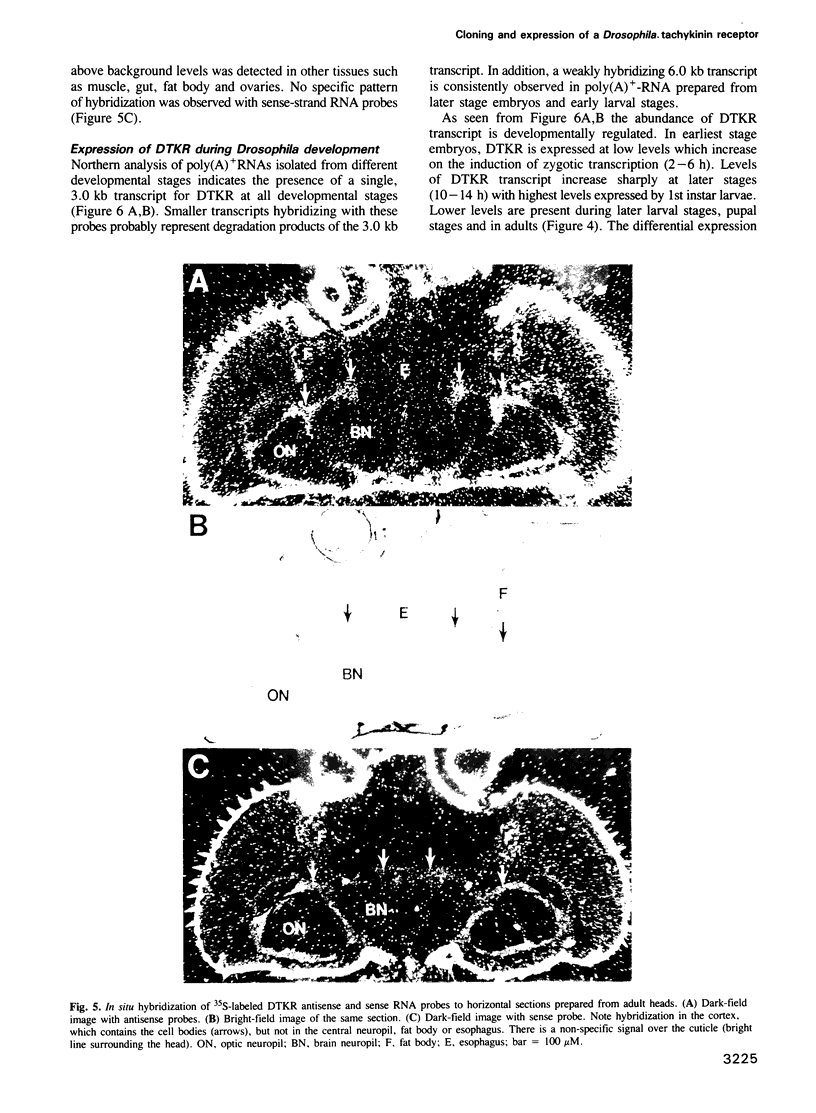
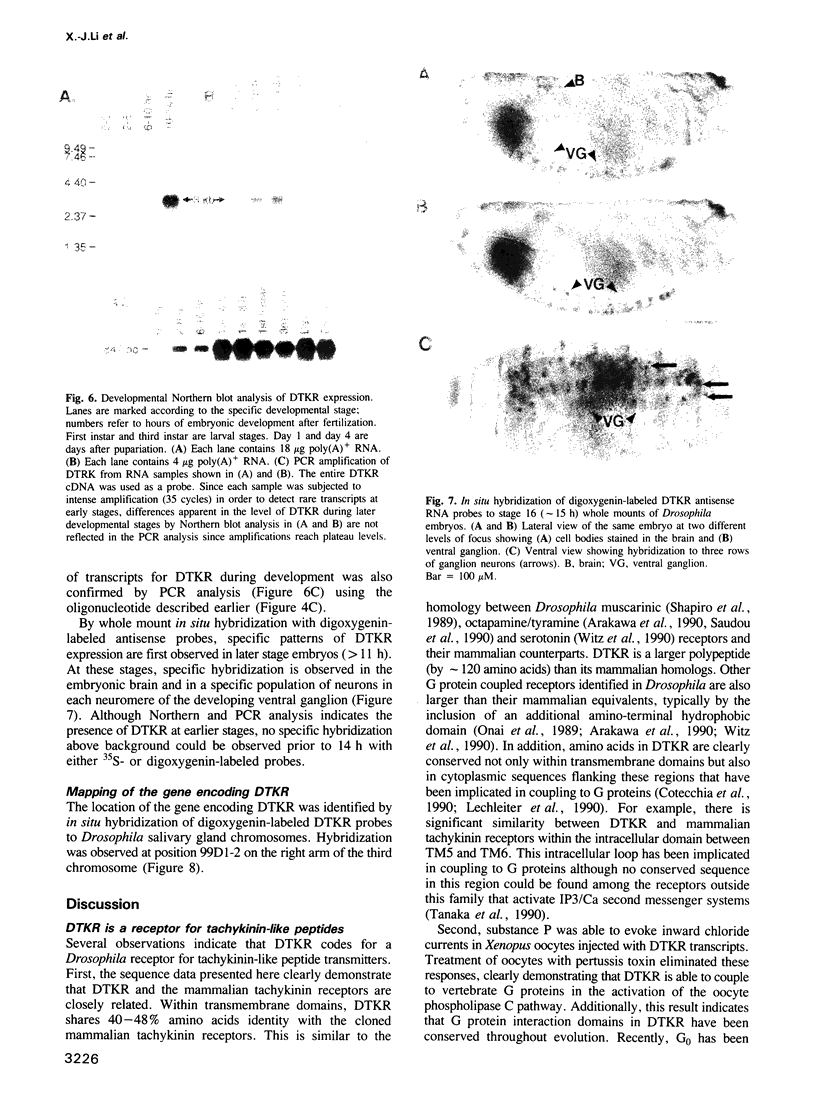
We identified clones encoding a Drosophila receptor for tachykinin-like peptides by low stringency screening of an embryonic cDNA library with probes from the bovine substance K receptor. The cDNAs encode a seven transmembrane domain protein (DTKR) of 519 amino acids with 40-48% amino acid identity to mammalian tachykinin receptors within transmembrane regions. Xenopus oocytes injected with DTKR cRNAs showed selective responses to vertebrate substance P, its agonists and not to other vertebrate tachykinin peptides. These responses were eliminated by treatment of oocytes with pertussis toxin. In the adult fly, Northern and PCR analysis demonstrated preferential expression of DTKR in the head; in situ hybridization indicated that DTKR is accumulated in the cell bodies of neurons in the adult CNS. The levels of DTKR transcript are regulated during development. Northern and PCR amplification analysis showed that while DTKR transcripts are present at all stages, high levels of expression occur in later stages of embryogenesis (starting at 10-14 h), coinciding with the beginning of major periods of neural development. Whole mount embryo in situ hybridization demonstrated that DTKR is expressed at these later stages of embryogenesis (11-15 h) in the brain and in a specific subset of neurons in each neuromere of the developing ventral ganglion. The gene encoding DTKR was mapped by in situ hybridization to a single location at 99D on the right arm of chromosome 3. These observations demonstrate that the tachykinin family of peptide transmitters and their receptors represent an evolutionarily ancient form of cellular communication within the nervous system.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arakawa S., Gocayne J. D., McCombie W. R., Urquhart D. A., Hall L. M., Fraser C. M., Venter J. C. Cloning, localization, and permanent expression of a Drosophila octopamine receptor. Neuron. 1990 Mar;4(3):343–354. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90047-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedeczky I., Kiss J. Z., Somogyi P. Light and electron microscopic localization of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the cerebral ganglion of locust with a monoclonal antibody. Histochemistry. 1982;75(1):123–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00492539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. M., Leeman S. E. Isolation of a sialogogic peptide from bovine hypothalamic tissue and its characterization as substance P. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4784–4790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie M. J., Adelman J. P., Douglass J., North R. A. Expression of a cloned rat brain potassium channel in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):221–224. doi: 10.1126/science.2539643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Exum S., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regions of the alpha 1-adrenergic receptor involved in coupling to phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis and enhanced sensitivity of biological function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2896–2900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Salhy M., Abou-el-Ela R., Falkmer S., Grimelius L., Wilander E. Immunohistochemical evidence of gastro-entero-pancreatic neurohormonal peptides of vertebrate type in the nervous system of the larva of a dipteran insect, the hoverfly, Eristalis aeneus. Regul Pept. 1980 Dec;1(3):187–204. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(80)90271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangawa K., Minamino N., Fukuda A., Matsuo H. Neuromedin K: a novel mammalian tachykinin identified in porcine spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):533–540. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90813-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Goto K., Ogawa T., Sugita Y., Kanazawa I. Pharmacological characterization of novel mammalian tachykinins, neurokinin alpha and neurokinin beta. Neurosci Res. 1984 Dec;2(1-2):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(84)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavielle S., Chassaing G., Ploux O., Loeuillet D., Besseyre J., Julien S., Marquet A., Convert O., Beaujouan J. C., Torrens Y. Analysis of tachykinin binding site interactions using constrained analogues of tachykinins. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 1;37(1):41–49. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90753-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleiter J., Hellmiss R., Duerson K., Ennulat D., David N., Clapham D., Peralta E. Distinct sequence elements control the specificity of G protein activation by muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4381–4390. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist T., Nässel D. R. Substance P-, FMRFamide-, and gastrin/cholecystokinin-like immunoreactive neurons in the thoraco-abdominal ganglia of the flies Drosophila and Calliphora. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Apr 8;294(2):161–178. doi: 10.1002/cne.902940202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggio J. E. Tachykinins. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1988;11:13–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.11.030188.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masu Y., Nakayama K., Tamaki H., Harada Y., Kuno M., Nakanishi S. cDNA cloning of bovine substance-K receptor through oocyte expression system. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):836–838. doi: 10.1038/329836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty T. M., Padrell E., Carty D. J., Omri G., Landau E. M., Iyengar R. Go protein as signal transducer in the pertussis toxin-sensitive phosphatidylinositol pathway. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):79–82. doi: 10.1038/343079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nässel D. R., Lundquist T., Hög A., Grimelius L. Substance P-like immunoreactive neurons in the nervous system of Drosophila. Brain Res. 1990 Jan 22;507(2):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90276-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Structure of the adrenergic and related receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:67–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onai T., FitzGerald M. G., Arakawa S., Gocayne J. D., Urquhart D. A., Hall L. M., Fraser C. M., McCombie W. R., Venter J. C. Cloning, sequence analysis and chromosome localization of a Drosophila muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. FEBS Lett. 1989 Sep 25;255(2):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quan F., Wolfgang W. J., Forte M. A. The Drosophila gene coding for the alpha subunit of a stimulatory G protein is preferentially expressed in the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4321–4325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Drapeau G., Dion S., Couture R. New selective agonists for neurokinin receptors: pharmacological tools for receptor characterization. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Aug;9(8):290–295. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saudou F., Amlaiky N., Plassat J. L., Borrelli E., Hen R. Cloning and characterization of a Drosophila tyramine receptor. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3611–3617. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07572.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoofs L., Holman G. M., Hayes T. K., Nachman R. J., De Loof A. Locustatachykinin I and II, two novel insect neuropeptides with homology to peptides of the vertebrate tachykinin family. FEBS Lett. 1990 Feb 26;261(2):397–401. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80601-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R. A., Wakimoto B. T., Subers E. M., Nathanson N. M. Characterization and functional expression in mammalian cells of genomic and cDNA clones encoding a Drosophila muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):9039–9043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.9039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigemoto R., Yokota Y., Tsuchida K., Nakanishi S. Cloning and expression of a rat neuromedin K receptor cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):623–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thambi N. C., Quan F., Wolfgang W. J., Spiegel A., Forte M. Immunological and molecular characterization of Go alpha-like proteins in the Drosophila central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18552–18560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrens Y., Daguet De Montety M. C., el Etr M., Beaujouan J. C., Glowinski J. Tachykinin receptors of the NK1 type (substance P) coupled positively to phospholipase C on cortical astrocytes from the newborn mouse in primary culture. J Neurochem. 1989 Jun;52(6):1913–1918. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witz P., Amlaiky N., Plassat J. L., Maroteaux L., Borrelli E., Hen R. Cloning and characterization of a Drosophila serotonin receptor that activates adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8940–8944. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota Y., Sasai Y., Tanaka K., Fujiwara T., Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Kakizuka A., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA for rat substance P receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17649–17652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]