Abstract
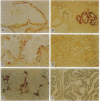
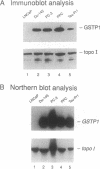
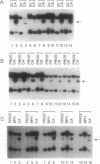
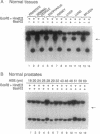
Hypermethylation of regulatory sequences at the locus of the pi-class glutathione S-transferase gene GSTP1 was detected in 20 of 20 human prostatic carcinoma tissue specimens studied but not in normal tissues or prostatic tissues exhibiting benign hyperplasia. In addition, a striking decrease in GSTP1 expression was found to accompany human prostatic carcinogenesis. Immunohistochemical staining with anti-GSTP1 antibodies failed to detect the enzyme in 88 of 91 prostatic carcinomas analyzed. In vitro, GSTP1 expression was limited to human prostatic cancer cell lines containing GSTP1 alleles with hypomethylated promoter sequences; a human prostatic cancer cell line containing only hypermethylated GSTP1 promoter sequences did not express GSTP1 mRNA or polypeptides. Methylation of cytidine nucleotides in GSTP1 regulatory sequences constitutes the most common genomic alteration yet described for human prostate cancer.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antequera F., Boyes J., Bird A. High levels of de novo methylation and altered chromatin structure at CpG islands in cell lines. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):503–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylin S. B., Makos M., Wu J. J., Yen R. W., de Bustros A., Vertino P., Nelkin B. D. Abnormal patterns of DNA methylation in human neoplasia: potential consequences for tumor progression. Cancer Cells. 1991 Oct;3(10):383–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boring C. C., Squires T. S., Tong T., Montgomery S. Cancer statistics, 1994. CA Cancer J Clin. 1994 Jan-Feb;44(1):7–26. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.44.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyes J., Bird A. DNA methylation inhibits transcription indirectly via a methyl-CpG binding protein. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1123–1134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brothman A. R., Lesho L. J., Somers K. D., Wright G. L., Jr, Merchant D. J. Phenotypic and cytogenetic characterization of a cell line derived from primary prostatic carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1989 Nov 15;44(5):898–903. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. R., Daar I. O., Krug J. R., Maquat L. E. Characterization of the functional gene and several processed pseudogenes in the human triosephosphate isomerase gene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1694–1706. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B. S., Carter H. B., Isaacs J. T. Epidemiologic evidence regarding predisposing factors to prostate cancer. Prostate. 1990;16(3):187–197. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990160302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B. S., Ewing C. M., Ward W. S., Treiger B. F., Aalders T. W., Schalken J. A., Epstein J. I., Isaacs W. B. Allelic loss of chromosomes 16q and 10q in human prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8751–8755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedar H. DNA methylation and gene activity. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):3–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles B., Ketterer B. The role of glutathione and glutathione transferases in chemical carcinogenesis. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(1):47–70. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell I. G., Dixon K. H., Pemble S. E., Ketterer B., Taylor J. B. The structure of the human glutathione S-transferase pi gene. Biochem J. 1988 Oct 1;255(1):79–83. doi: 10.1042/bj2550079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel V. Glutathione S-transferases: gene structure and regulation of expression. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1993;28(3):173–207. doi: 10.3109/10409239309086794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holliday R. The inheritance of epigenetic defects. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):163–170. doi: 10.1126/science.3310230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horoszewicz J. S., Leong S. S., Kawinski E., Karr J. P., Rosenthal H., Chu T. M., Mirand E. A., Murphy G. P. LNCaP model of human prostatic carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1983 Apr;43(4):1809–1818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iizumi T., Yazaki T., Kanoh S., Kondo I., Koiso K. Establishment of a new prostatic carcinoma cell line (TSU-Pr1). J Urol. 1987 Jun;137(6):1304–1306. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)44488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A., Buckley J. D. The role of DNA methylation in cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1990;54:1–23. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60806-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. A. DNA methylation and cancer. Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;46(2):461–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juan C. C., Hwang J. L., Liu A. A., Whang-Peng J., Knutsen T., Huebner K., Croce C. M., Zhang H., Wang J. C., Liu L. F. Human DNA topoisomerase I is encoded by a single-copy gene that maps to chromosome region 20q12-13.2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8910–8913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaighn M. E., Narayan K. S., Ohnuki Y., Lechner J. F., Jones L. W. Establishment and characterization of a human prostatic carcinoma cell line (PC-3). Invest Urol. 1979 Jul;17(1):16–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kautiainen T. L., Jones P. A. DNA methyltransferase levels in tumorigenic and nontumorigenic cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1594–1598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet I., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Cedar H. DNA methylation affects the formation of active chromatin. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet I., Yisraeli J., Cedar H. Effect of regional DNA methylation on gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2560–2564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. D., Meehan R. R., Henzel W. J., Maurer-Fogy I., Jeppesen P., Klein F., Bird A. Purification, sequence, and cellular localization of a novel chromosomal protein that binds to methylated DNA. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90610-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makos M., Nelkin B. D., Lerman M. I., Latif F., Zbar B., Baylin S. B. Distinct hypermethylation patterns occur at altered chromosome loci in human lung and colon cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannervik B., Awasthi Y. C., Board P. G., Hayes J. D., Di Ilio C., Ketterer B., Listowsky I., Morgenstern R., Muramatsu M., Pearson W. R. Nomenclature for human glutathione transferases. Biochem J. 1992 Feb 15;282(Pt 1):305–306. doi: 10.1042/bj2820305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Chilcote R., Ryan P. M. Human triosephosphate isomerase cDNA and protein structure. Studies of triosephosphate isomerase deficiency in man. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3748–3753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeal J. E., Bostwick D. G. Intraductal dysplasia: a premalignant lesion of the prostate. Hum Pathol. 1986 Jan;17(1):64–71. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80156-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. S., Cowan K. H., Goldsmith M. E. Structure of the human genomic glutathione S-transferase-pi gene. Gene. 1989 Jan 30;75(1):3–11. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90377-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. S., Goldsmith M. E., Cowan K. H. Regulation of human glutathione S-transferase pi gene transcription: influence of 5'-flanking sequences and trans-activating factors which recognize AP-1-binding sites. Gene. 1990 Apr 16;88(2):215–225. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90034-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscow J. A., Townsend A. J., Cowan K. H. Elevation of pi class glutathione S-transferase activity in human breast cancer cells by transfection of the GST pi gene and its effect on sensitivity to toxins. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):22–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscow J. A., Townsend A. J., Goldsmith M. E., Whang-Peng J., Vickers P. J., Poisson R., Legault-Poisson S., Myers C. E., Cowan K. H. Isolation of the human anionic glutathione S-transferase cDNA and the relation of its gene expression to estrogen-receptor content in primary breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6518–6522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. G., Kastan M. B. DNA strand breaks: the DNA template alterations that trigger p53-dependent DNA damage response pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1815–1823. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani-Fujita N., Fujita T., Aoike A., Osifchin N. E., Robbins P. D., Sakai T. CpG methylation inactivates the promoter activity of the human retinoblastoma tumor-suppressor gene. Oncogene. 1993 Apr;8(4):1063–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett C. B., Lu A. Y. Glutathione S-transferases: gene structure, regulation, and biological function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:743–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestera T., Holtzclaw W. D., Zhang Y., Talalay P. Chemical and molecular regulation of enzymes that detoxify carcinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2965–2969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prochaska H. J., Santamaria A. B., Talalay P. Rapid detection of inducers of enzymes that protect against carcinogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2394–2398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushmore T. H., Pickett C. B. Glutathione S-transferases, structure, regulation, and therapeutic implications. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11475–11478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidegård J., Pero R. W., Markowitz M. M., Roush G., Miller D. G., Beattie E. J. Isoenzyme(s) of glutathione transferase (class Mu) as a marker for the susceptibility to lung cancer: a follow up study. Carcinogenesis. 1990 Jan;11(1):33–36. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidegård J., Pero R. W., Miller D. G., Beattie E. J. A glutathione transferase in human leukocytes as a marker for the susceptibility to lung cancer. Carcinogenesis. 1986 May;7(5):751–753. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.5.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidegård J., Vorachek W. R., Pero R. W., Pearson W. R. Hereditary differences in the expression of the human glutathione transferase active on trans-stilbene oxide are due to a gene deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7293–7297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone K. R., Mickey D. D., Wunderli H., Mickey G. H., Paulson D. F. Isolation of a human prostate carcinoma cell line (DU 145). Int J Cancer. 1978 Mar 15;21(3):274–281. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910210305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrier P., Townsend A. J., Coindre J. M., Triche T. J., Cowan K. H. An immunohistochemical study of pi class glutathione S-transferase expression in normal human tissue. Am J Pathol. 1990 Oct;137(4):845–853. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida S., Sato K. Glutathione transferases and cancer. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1992;27(4-5):337–384. doi: 10.3109/10409239209082566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia C. L., Cowell I. G., Dixon K. H., Pemble S. E., Ketterer B., Taylor J. B. Glutathione transferase pi its minimal promoter and downstream cis-acting element. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Apr 15;176(1):233–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90914-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Talalay P., Cho C. G., Posner G. H. A major inducer of anticarcinogenic protective enzymes from broccoli: isolation and elucidation of structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2399–2403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bustros A., Nelkin B. D., Silverman A., Ehrlich G., Poiesz B., Baylin S. B. The short arm of chromosome 11 is a "hot spot" for hypermethylation in human neoplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5693–5697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Nelkin B. D., Celano P., Yen R. W., Falco J. P., Hamilton S. R., Baylin S. B. High expression of the DNA methyltransferase gene characterizes human neoplastic cells and progression stages of colon cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3470–3474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]