Abstract
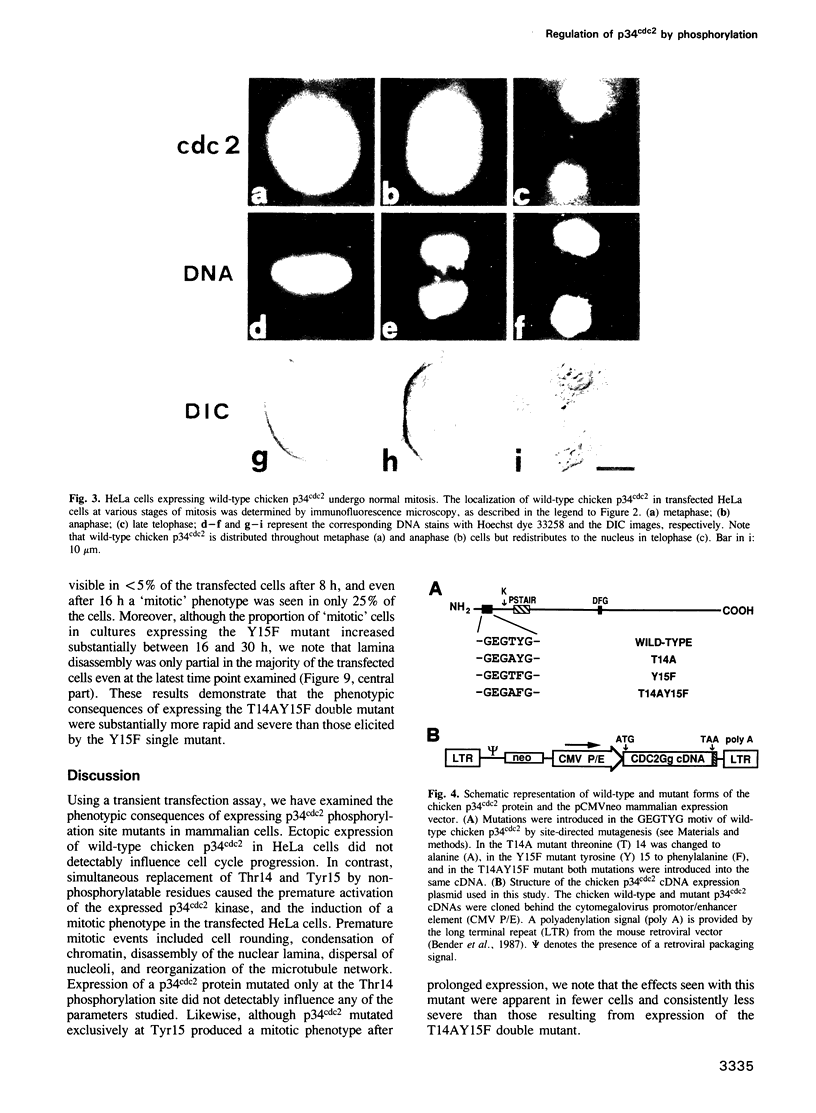
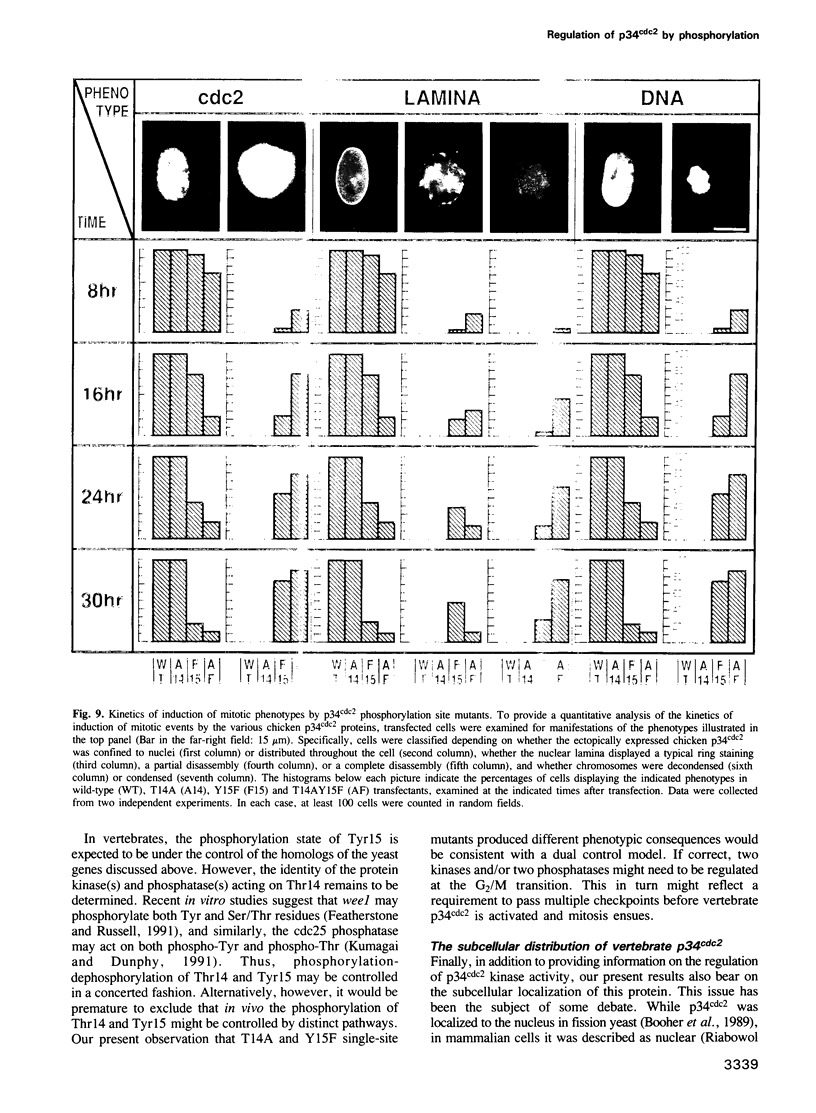
In vertebrates, entry into mitosis is accompanied by dephosphorylation of p34cdc2 kinase on threonine 14 (Thr14) and tyrosine 15 (Tyr15). To examine the role of these residues in controlling p34cdc2 kinase activation, and hence the onset of mitosis, we replaced Thr14 and/or Tyr15 by non-phosphorylatable residues and transfected wild-type and mutant chicken p34cdc2 cDNAs into HeLa cells. While expression of wild-type p34cdc2 did not interfere with normal cell cycle progression, p34cdc2 carrying mutations at both Thr14 and Tyr15 displayed increased histone H1 kinase activity and rapidly induced premature mitotic events, including chromosome condensation and lamina disassembly. No phenotype was observed in response to mutation of only Thr14, and although single-site mutation at Tyr15 did induce premature mitotic events, effects were partial and their onset was delayed. These results identify both Thr14 and Tyr15 as sites of negative regulation of vertebrate p34cdc2 kinase, and they suggest that dephosphorylation of p34cdc2 represents the rate-limiting step controlling entry of vertebrate cells into mitosis.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akhurst R. J., Flavin N. B., Worden J., Lee M. G. Intracellular localisation and expression of mammalian CDC2 protein during myogenic differentiation. Differentiation. 1989 Mar;40(1):36–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1989.tb00811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailly E., Dorée M., Nurse P., Bornens M. p34cdc2 is located in both nucleus and cytoplasm; part is centrosomally associated at G2/M and enters vesicles at anaphase. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):3985–3995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08581.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender M. A., Palmer T. D., Gelinas R. E., Miller A. D. Evidence that the packaging signal of Moloney murine leukemia virus extends into the gag region. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1639–1646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1639-1646.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booher R. N., Alfa C. E., Hyams J. S., Beach D. H. The fission yeast cdc2/cdc13/suc1 protein kinase: regulation of catalytic activity and nuclear localization. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):485–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90429-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorée M. Control of M-phase by maturation-promoting factor. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;2(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90018-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G. Cell cycle control in eukaryotes: molecular mechanisms of cdc2 activation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):378–383. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducommun B., Draetta G., Young P., Beach D. Fission yeast cdc25 is a cell-cycle regulated protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 28;167(1):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91765-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Newport J. W. Unraveling of mitotic control mechanisms. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):925–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch T., Nurse P. Mutation of fission yeast cell cycle control genes abolishes dependence of mitosis on DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):665–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90669-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Featherstone C., Russell P. Fission yeast p107wee1 mitotic inhibitor is a tyrosine/serine kinase. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):808–811. doi: 10.1038/349808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Félix M. A., Labbé J. C., Dorée M., Hunt T., Karsenti E. Triggering of cyclin degradation in interphase extracts of amphibian eggs by cdc2 kinase. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):379–382. doi: 10.1038/346379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Minshull J., Lohka M., Glotzer M., Hunt T., Maller J. L. Cyclin is a component of maturation-promoting factor from Xenopus. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90599-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giordano A., Whyte P., Harlow E., Franza B. R., Jr, Beach D., Draetta G. A 60 kd cdc2-associated polypeptide complexes with the E1A proteins in adenovirus-infected cells. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):981–990. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90949-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Matsuda S., Shiina N., Kosako H., Shiokawa K., Akiyama T., Ohta K., Sakai H. In vitro effects on microtubule dynamics of purified Xenopus M phase-activated MAP kinase. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):251–254. doi: 10.1038/349251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Moreno S., Tonks N. K., Nurse P. Complementation of the mitotic activator, p80cdc25, by a human protein-tyrosine phosphatase. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1573–1576. doi: 10.1126/science.1703321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Nurse P. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the fission yeast cdc2+ protein kinase regulates entry into mitosis. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):39–45. doi: 10.1038/342039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Maturation promoting factor, cyclin and the control of M-phase. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;1(2):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(89)90099-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilmartin J. V., Wright B., Milstein C. Rat monoclonal antitubulin antibodies derived by using a new nonsecreting rat cell line. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):576–582. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Differential phosphorylation of vertebrate p34cdc2 kinase at the G1/S and G2/M transitions of the cell cycle: identification of major phosphorylation sites. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):305–316. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07951.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Nigg E. A. Structure and developmental expression of the chicken CDC2 kinase. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3071–3078. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08458.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. The cdc25 protein controls tyrosine dephosphorylation of the cdc2 protein in a cell-free system. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):903–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90315-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe J. C., Picard A., Peaucellier G., Cavadore J. C., Nurse P., Doree M. Purification of MPF from starfish: identification as the H1 histone kinase p34cdc2 and a possible mechanism for its periodic activation. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90963-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb N. J., Fernandez A., Watrin A., Labbé J. C., Cavadore J. C. Microinjection of p34cdc2 kinase induces marked changes in cell shape, cytoskeletal organization, and chromatin structure in mammalian fibroblasts. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):151–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90725-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J. Mitotic control by metaphase-promoting factor and cdc proteins. J Cell Sci. 1989 Feb;92(Pt 2):131–135. doi: 10.1242/jcs.92.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren K., Walworth N., Booher R., Dembski M., Kirschner M., Beach D. mik1 and wee1 cooperate in the inhibitory tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1111–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijer L., Arion D., Golsteyn R., Pines J., Brizuela L., Hunt T., Beach D. Cyclin is a component of the sea urchin egg M-phase specific histone H1 kinase. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2275–2282. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minshull J., Pines J., Golsteyn R., Standart N., Mackie S., Colman A., Blow J., Ruderman J. V., Wu M., Hunt T. The role of cyclin synthesis, modification and destruction in the control of cell division. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1989;12:77–97. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1989.supplement_12.8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Hayles J., Nurse P. Regulation of p34cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90850-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Nurse P., Russell P. Regulation of mitosis by cyclic accumulation of p80cdc25 mitotic inducer in fission yeast. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):549–552. doi: 10.1038/344549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Nurse P. Substrates for p34cdc2: in vivo veritas? Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):549–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90463-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morla A. O., Draetta G., Beach D., Wang J. Y. Reversible tyrosine phosphorylation of cdc2: dephosphorylation accompanies activation during entry into mitosis. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90415-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin synthesis drives the early embryonic cell cycle. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):275–280. doi: 10.1038/339275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Dominoes and clocks: the union of two views of the cell cycle. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):614–621. doi: 10.1126/science.2683077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Solomon M. J., Kirschner M. W. The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of maturation promoting factor activity. Nature. 1989 May 25;339(6222):280–286. doi: 10.1038/339280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Schäfer G., Hilz H., Eppenberger H. M. Cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase type II is associated with the Golgi complex and with centrosomes. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P. Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):503–508. doi: 10.1038/344503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmani S. A., Pu R. T., Morris N. R. Mitotic induction and maintenance by overexpression of a G2-specific gene that encodes a potential protein kinase. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90385-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard A., Capony J. P., Brautigan D. L., Dorée M. Involvement of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A in the control of M phase-promoting factor activity in starfish. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3347–3354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Human cyclin A is adenovirus E1A-associated protein p60 and behaves differently from cyclin B. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):760–763. doi: 10.1038/346760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. Isolation of a human cyclin cDNA: evidence for cyclin mRNA and protein regulation in the cell cycle and for interaction with p34cdc2. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):833–846. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J., Hunter T. p34cdc2: the S and M kinase? New Biol. 1990 May;2(5):389–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riabowol K., Draetta G., Brizuela L., Vandre D., Beach D. The cdc2 kinase is a nuclear protein that is essential for mitosis in mammalian cells. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90914-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. cdc25+ functions as an inducer in the mitotic control of fission yeast. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90546-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Glotzer M., Lee T. H., Philippe M., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin activation of p34cdc2. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1013–1024. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stick R., Angres B., Lehner C. F., Nigg E. A. The fates of chicken nuclear lamin proteins during mitosis: evidence for a reversible redistribution of lamin B2 between inner nuclear membrane and elements of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):397–406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausfeld U., Labbé J. C., Fesquet D., Cavadore J. C., Picard A., Sadhu K., Russell P., Dorée M. Dephosphorylation and activation of a p34cdc2/cyclin B complex in vitro by human CDC25 protein. Nature. 1991 May 16;351(6323):242–245. doi: 10.1038/351242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson K. I., Farrell K. M., Ruderman J. V. The clam embryo protein cyclin A induces entry into M phase and the resumption of meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90801-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]