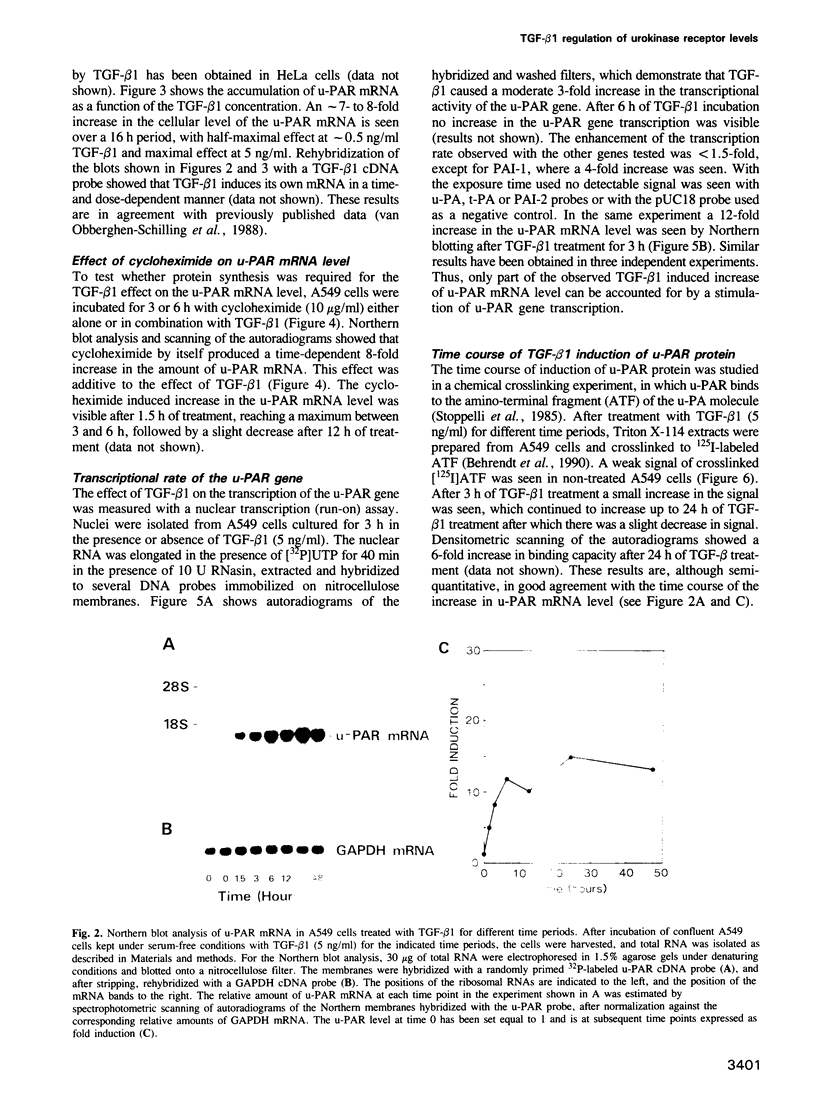
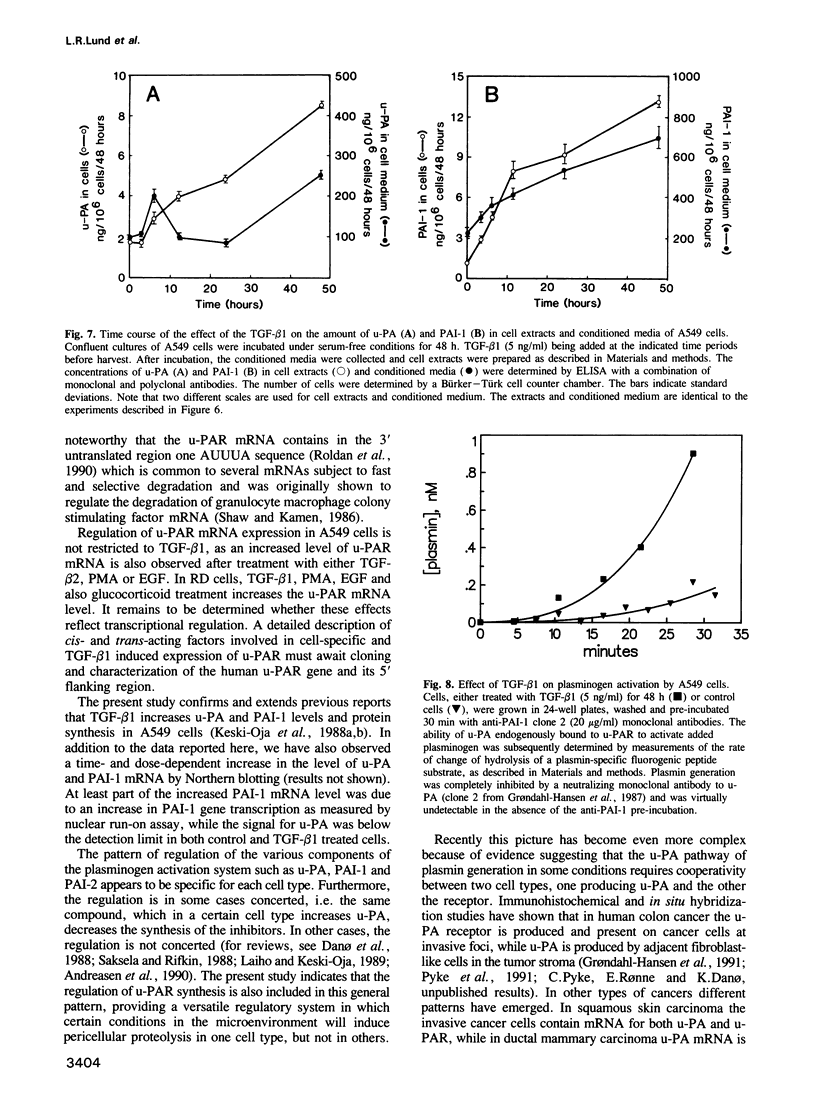
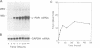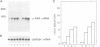Abstract
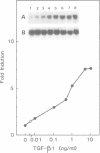
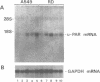
We have compared the cell-specific expression and regulation of the receptor for urokinase-type plasminogen activator (u-PAR) by transforming growth factor beta type 1 (TGF-beta 1) in 10 human cell lines derived from both normal and neoplastic tissues. The basal expression of u-PAR mRNA as well as its response to TGF-beta 1 varied strongly between different cell lines; however, five out of the 10 cell lines responded to TGF-beta 1 by an increase in the u-PAR mRNA level. Among these, A549 cells were selected for a detailed elucidation of the molecular mechanism involved in TGF-beta 1 regulation of u-PAR mRNA expression. TGF-beta 1 caused an early increase in u-PAR mRNA level, with a maximal 15-fold enhancement after 24 h of treatment. This was paralleled by an increase in u-PAR protein as detected by crosslinking studies with radiolabeled ligand, and also resulted in an increase in cell surface plasmin generation. The protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide also increased the level of u-PAR mRNA in a time-dependent fashion and when both cycloheximide and TGF-beta 1 were used, an additive effect was seen. Nuclear run-on experiments demonstrated only a moderate (3-fold) increase in the u-PAR gene transcription rate after exposure of the cells to TGF-beta 1 for 3 h compared with a 12-fold increase in the mRNA level. TGF-beta 1 also caused an increase of both u-PA and PAI-1 antigens, while there was no detectable effect on t-PA.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen P. A., Georg B., Lund L. R., Riccio A., Stacey S. N. Plasminogen activator inhibitors: hormonally regulated serpins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Jan 2;68(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen P. A., Riccio A., Welinder K. G., Douglas R., Sartorio R., Nielsen L. S., Oppenheimer C., Blasi F., Danø K. Plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1: reactive center and amino-terminal heterogeneity determined by protein and cDNA sequencing. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajpai A., Baker J. B. Cryptic urokinase binding sites on human foreskin fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 17;133(2):475–482. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90931-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard J. A., Lyons R. M., Moses H. L. The cell biology of transforming growth factor beta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 1;1032(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(90)90013-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrendt N., Ploug M., Patthy L., Houen G., Blasi F., Danø K. The ligand-binding domain of the cell surface receptor for urokinase-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7842–7847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrendt N., Rønne E., Ploug M., Petri T., Løber D., Nielsen L. S., Schleuning W. D., Blasi F., Appella E., Danø K. The human receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. NH2-terminal amino acid sequence and glycosylation variants. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6453–6460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi F., Vassalli J. D., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator: proenzyme, receptor, and inhibitors. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):801–804. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Florent G., Kim P., Brattain M. Determination of the levels of urokinase and its receptor in human colon carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 1;48(11):3112–3116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubellis M. V., Andreasen P., Ragno P., Mayer M., Danø K., Blasi F. Accessibility of receptor-bound urokinase to type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4828–4832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubellis M. V., Nolli M. L., Cassani G., Blasi F. Binding of single-chain prourokinase to the urokinase receptor of human U937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):15819–15822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubellis M. V., Wun T. C., Blasi F. Receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of urokinase is caused by its specific inhibitor PAI-1. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1079–1085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Jarrett J. A., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Bell J. R., Assoian R. K., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Goeddel D. V. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):701–705. doi: 10.1038/316701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F. Polypeptide growth factors: roles in normal and abnormal cell growth. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:443–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis V., Scully M. F., Kakkar V. V. Plasminogen activation initiated by single-chain urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Potentiation by U937 monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2185–2188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis V., Wun T. C., Behrendt N., Rønne E., Danø K. Inhibition of receptor-bound urokinase by plasminogen-activator inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9904–9908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher A., Mühlhauser J., Carpentier J. L., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. The receptor for urokinase type plasminogen activator polarizes expression of the protease to the leading edge of migrating monocytes and promotes degradation of enzyme inhibitor complexes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):783–792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher A., Wohlwend A., Belin D., Schleuning W. D., Vassalli J. D. Characterization of the cellular binding site for the urokinase-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1180–1189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giard D. J., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J., Arnstein P., Kersey J. H., Dosik H., Parks W. P. In vitro cultivation of human tumors: establishment of cell lines derived from a series of solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1417–1423. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøndahl-Hansen J., Agerlin N., Munkholm-Larsen P., Bach F., Nielsen L. S., Dombernowsky P., Danø K. Sensitive and specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its application to plasma from patients with breast cancer. J Lab Clin Med. 1988 Jan;111(1):42–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøndahl-Hansen J., Ralfkiaer E., Kirkeby L. T., Kristensen P., Lund L. R., Danø K. Localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in stromal cells in adenocarcinomas of the colon in humans. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jan;138(1):111–117. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøndahl-Hansen J., Ralfkiaer E., Nielsen L. S., Kristensen P., Frentz G., Danø K. Immunohistochemical localization of urokinase- and tissue-type plasminogen activators in psoriatic skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Jan;88(1):28–32. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12464827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. H., Christensen E. I., Ebbesen P., Gliemann J., Andreasen P. A. Lysosomal degradation of receptor-bound urokinase-type plasminogen activator is enhanced by its inhibitors in human trophoblastic choriocarcinoma cells. Cell Regul. 1990 Dec;1(13):1043–1056. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.13.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keski-Oja J., Blasi F., Leof E. B., Moses H. L. Regulation of the synthesis and activity of urokinase plasminogen activator in A549 human lung carcinoma cells by transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):451–459. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keski-Oja J., Raghow R., Sawdey M., Loskutoff D. J., Postlethwaite A. E., Kang A. H., Moses H. L. Regulation of mRNAs for type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor, fibronectin, and type I procollagen by transforming growth factor-beta. Divergent responses in lung fibroblasts and carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3111–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen P., Eriksen J., Danø K. Localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator messenger RNA in the normal mouse by in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Mar;39(3):341–349. doi: 10.1177/39.3.1899685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Keski-Oja J. Growth factors in the regulation of pericellular proteolysis: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 May 15;49(10):2533–2553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Saksela O., Andreasen P. A., Keski-Oja J. Enhanced production and extracellular deposition of the endothelial-type plasminogen activator inhibitor in cultured human lung fibroblasts by transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2403–2410. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D. A., Pircher R., Krycève-Martinerie C., Jullien P. Normal embryo fibroblasts release transforming growth factors in a latent form. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Oct;121(1):184–188. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund L. R., Georg B., Nielsen L. S., Mayer M., Danø K., Andreasen P. A. Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1: cell-specific and differentiation-induced expression and regulation in human cell lines, as determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1988 Nov;60(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(88)90118-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund L. R., Riccio A., Andreasen P. A., Nielsen L. S., Kristensen P., Laiho M., Saksela O., Blasi F., Danø K. Transforming growth factor-beta is a strong and fast acting positive regulator of the level of type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor mRNA in WI-38 human lung fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1281–1286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02365.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund L. R., Rønne E., Roldan A. L., Behrendt N., Rømer J., Blasi F., Danø K. Urokinase receptor mRNA level and gene transcription are strongly and rapidly increased by phorbol myristate acetate in human monocyte-like U937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5177–5181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Gentry L. E., Purchio A. F., Moses H. L. Mechanism of activation of latent recombinant transforming growth factor beta 1 by plasmin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1361–1367. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Keski-Oja J., Moses H. L. Proteolytic activation of latent transforming growth factor-beta from fibroblast-conditioned medium. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1659–1665. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons R. M., Moses H. L. Transforming growth factors and the regulation of cell proliferation. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Feb 14;187(3):467–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M., Lund L. R., Riccio A., Skouv J., Nielsen L. S., Stacey S. N., Danø K., Andreasen P. A. Plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 protein, mRNA and gene transcription are increased by phorbol esters in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15688–15693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister R. M., Melnyk J., Finkelstein J. Z., Adams E. C., Jr, Gardner M. B. Cultivation in vitro of cells derived from a human rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer. 1969 Sep;24(3):520–526. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196909)24:3<520::aid-cncr2820240313>3.0.co;2-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen L. S., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Huang J. Y., Kristensen P., Danø K. Monoclonal antibodies to human 54,000 molecular weight plasminogen activator inhibitor from fibrosarcoma cells--inhibitor neutralization and one-step affinity purification. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Apr 30;55(2):206–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen L. S., Kellerman G. M., Behrendt N., Picone R., Danø K., Blasi F. A 55,000-60,000 Mr receptor protein for urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Identification in human tumor cell lines and partial purification. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2358–2363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nykjaer A., Petersen C. M., Christensen E. I., Davidsen O., Gliemann J. Urokinase receptors in human monocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 22;1052(3):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttinen R. P., Kobayashi S., Bornstein P. Transforming growth factor beta increases mRNA for matrix proteins both in the presence and in the absence of changes in mRNA stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1105–1108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picone R., Kajtaniak E. L., Nielsen L. S., Behrendt N., Mastronicola M. R., Cubellis M. V., Stoppelli M. P., Pedersen S., Danø K., Blasi F. Regulation of urokinase receptors in monocytelike U937 cells by phorbol ester phorbol myristate acetate. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):693–702. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploug M., Rønne E., Behrendt N., Jensen A. L., Blasi F., Danø K. Cellular receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. Carboxyl-terminal processing and membrane anchoring by glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1926–1933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Freaney D. E., Plescia J., Miles L. A. The plasminogen system and cell surfaces: evidence for plasminogen and urokinase receptors on the same cell type. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2411–2420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gunning P., Blau H., Kedes L. Human actin genes are single copy for alpha-skeletal and alpha-cardiac actin but multicopy for beta- and gamma-cytoskeletal genes: 3' untranslated regions are isotype specific but are conserved in evolution. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1783–1791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyke C., Kristensen P., Ralfkiaer E., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Eriksen J., Blasi F., Danø K. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is expressed in stromal cells and its receptor in cancer cells at invasive foci in human colon adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol. 1991 May;138(5):1059–1067. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccio A., Lund L. R., Sartorio R., Lania A., Andreasen P. A., Danø K., Blasi F. The regulatory region of the human plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1) gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):2805–2824. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.2805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzino A. Transforming growth factor-beta: multiple effects on cell differentiation and extracellular matrices. Dev Biol. 1988 Dec;130(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90337-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Anzano M. A., Wakefield L. M., Roche N. S., Stern D. F., Sporn M. B. Type beta transforming growth factor: a bifunctional regulator of cellular growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):119–123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Flanders K. C., Kondaiah P., Thompson N. L., Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Wakefield L., Rossi P., de Crombrugghe B., Heine U., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor beta: biochemistry and roles in embryogenesis, tissue repair and remodeling, and carcinogenesis. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1988;44:157–197. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571144-9.50010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Rifkin D. B. Cell-associated plasminogen activation: regulation and physiological functions. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:93–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Rifkin D. B. Inhibition of endothelial cell movement by pericytes and smooth muscle cells: activation of a latent transforming growth factor-beta 1-like molecule by plasmin during co-culture. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):309–315. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Tsuboi R., Lyons R., Moses H., Rifkin D. B. Characterization of the activation of latent TGF-beta by co-cultures of endothelial cells and pericytes or smooth muscle cells: a self-regulating system. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):757–763. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawdey M., Podor T. J., Loskutoff D. J. Regulation of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Induction by transforming growth factor-beta, lipopolysaccharide, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10396–10401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleuning W. D., Medcalf R. L., Hession C., Rothenbühler R., Shaw A., Kruithof E. K. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 2: regulation of gene transcription during phorbol ester-mediated differentiation of U-937 human histiocytic lymphoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4564–4567. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Blume J. E., Nielsen D. A. Regulation of messenger RNA stability in eukaryotic cells. Bioessays. 1987 May;6(5):221–226. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Autocrine growth factors and cancer. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):745–747. doi: 10.1038/313745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wakefield L. M., de Crombrugghe B. Some recent advances in the chemistry and biology of transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1039–1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. W., Pöllänen J., Tapiovaara H., Leung K. C., Sim P. S., Salonen E. M., Rønne E., Behrendt N., Danø K., Vaheri A. Activation of pro-urokinase and plasminogen on human sarcoma cells: a proteolytic system with surface-bound reactants. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1987–1995. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Corti A., Soffientini A., Cassani G., Blasi F., Assoian R. K. Differentiation-enhanced binding of the amino-terminal fragment of human urokinase plasminogen activator to a specific receptor on U937 monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4939–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Tacchetti C., Cubellis M. V., Corti A., Hearing V. J., Cassani G., Appella E., Blasi F. Autocrine saturation of pro-urokinase receptors on human A431 cells. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90782-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Roche N. S., Flanders K. C., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Transforming growth factor beta 1 positively regulates its own expression in normal and transformed cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7741–7746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Baccino D., Belin D. A cellular binding site for the Mr 55,000 form of the human plasminogen activator, urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):86–92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verde P., Stoppelli M. P., Galeffi P., Di Nocera P., Blasi F. Identification and primary sequence of an unspliced human urokinase poly(A)+ RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4727–4731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakefield L. M., Smith D. M., Masui T., Harris C. C., Sporn M. B. Distribution and modulation of the cellular receptor for transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):965–975. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]