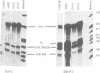Abstract
Many cellular and viral genes are parts of complex transcription units containing multiple splicing choices. During the course of an adenoviral replicative cycle, different spliced versions of a single gene predominate, depending on the stage of infection. This is true for several adenoviral genes. In this paper we show for the viral E1B transcription unit that splice site usage regulates this process. The change in alternative splicing in this system does not depend on the sequence of the transcribed genes. Non-adenoviral genes, such as the SV40 early region and the polyoma early region, which normally show little or no regulation of spliced RNA product formation, become regulated for mRNA production after insertion into the adenoviral genome. Additional studies show that E1B splicing regulation in adenovirus is a cis effect. Staggered infections using two discernable viral genomes resulted in a situation where both early and late genomes exist in the same nucleus. Neither genome was able to impose its regulated splicing pattern on the other, indicating that the cue for the switch in viral gene splicing is not directly dependent on global changes in trans-acting splicing factors. This suggests a model where the signal for changes in RNA processing for the E1B gene is linked to the state of the DNA template or its localization within nuclear subcompartments.
Full text
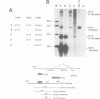
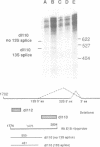
PDF


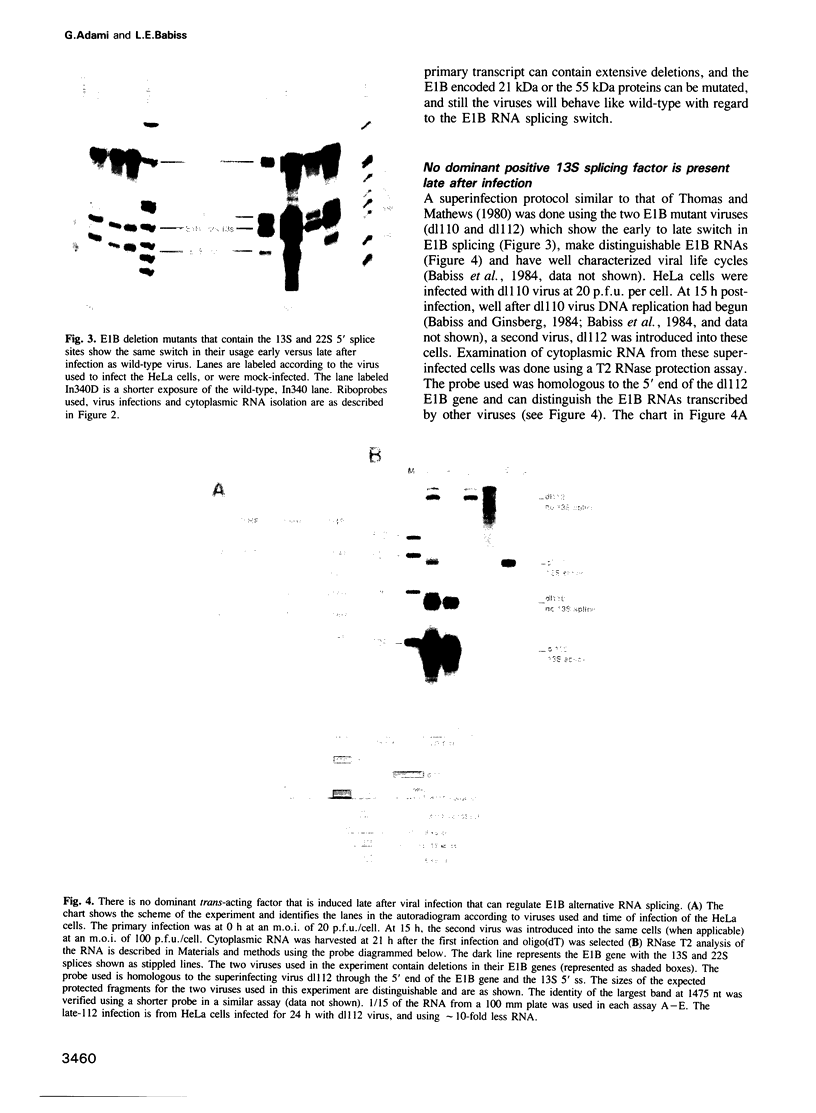





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adami G. R., Babiss L. E. The efficiency of adenovirus transformation of rodent cells is inversely related to the rate of viral E1A gene expression. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3427–3436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3427-3436.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adami G., Nevins J. R. Splice site selection dominates over poly(A) site choice in RNA production from complex adenovirus transcription units. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2107–2116. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03050.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Fisher P. B., Ginsberg H. S. Effect on transformation of mutations in the early region 1b-encoded 21- and 55-kilodalton proteins of adenovirus 5. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):389–395. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.389-395.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Ginsberg H. S. Adenovirus type 5 early region 1b gene product is required for efficient shutoff of host protein synthesis. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):202–212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.202-212.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barone M. V., Henchcliffe C., Baralle F. E., Paolella G. Cell type specific trans-acting factors are involved in alternative splicing of human fibronectin pre-mRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1079–1085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Osheim Y. N. Splice site selection, rate of splicing, and alternative splicing on nascent transcripts. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):754–765. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodnar J. W., Hanson P. I., Polvino-Bodnar M., Zempsky W., Ward D. C. The terminal regions of adenovirus and minute virus of mice DNAs are preferentially associated with the nuclear matrix in infected cells. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4344–4353. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4344-4353.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Nadal-Ginard B. Developmentally induced, muscle-specific trans factors control the differential splicing of alternative and constitutive troponin T exons. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):793–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90617-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossland L. D., Raskas H. J. Identification of adenovirus genes that require template replication for expression. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):737–748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.737-748.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eperon L. P., Graham I. R., Griffiths A. D., Eperon I. C. Effects of RNA secondary structure on alternative splicing of pre-mRNA: is folding limited to a region behind the transcribing RNA polymerase? Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falck-Pedersen E., Logan J. Regulation of poly(A) site selection in adenovirus. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):532–541. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.532-541.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint S. J., Beltz G. A., Linzer D. I. Synthesis and processing of simian virus 40-specific RNA in adenovirus-infected, simian virus 40-transformed human cells. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):335–359. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80339-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. B., Berk A. J. Cis-acting induction of adenovirus transcription. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):683–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Manley J. L. A protein factor, ASF, controls cell-specific alternative splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearing P., Shenk T. The adenovirus type 5 E1A transcriptional control region contains a duplicated enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):695–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes D. H., Steitz J. A. Correct in vivo splicing of the mouse immunoglobulin kappa light-chain pre-mRNA is dependent on 5' splice-site position even in the absence of transcription. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1448–1459. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Alwine J. C., Dhar R., Gruss P., Lai C. J., Segal S., Seif I. Regulation of SV40 gene expression through RNA splicing. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):41–54. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. The essential pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 influences 5' splice site selection by activating proximal sites. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Singer R. H., Marselle L. M. Highly localized tracks of specific transcripts within interphase nuclei visualized by in situ hybridization. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90924-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Splice commitment dictates neuron-specific alternative RNA processing in calcitonin/CGRP gene expression. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):517–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppard K. N., Shenk T. The adenovirus E1B 55 kd protein influences mRNA transport via an intranuclear effect on RNA metabolism. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2329–2336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08360.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T. Mechanisms of alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):33–34. doi: 10.1126/science.1824726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark D. F., Berg P. A third splice site in SV40 early mRNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):55–62. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massie B., Gluzman Y., Hassell J. A. Construction of a helper-free recombinant adenovirus that expresses polyomavirus large T antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2872–2883. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moen P. T., Jr, Fox E., Bodnar J. W. Adenovirus and minute virus of mice DNAs are localized at the nuclear periphery. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):513–520. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Courtois G., Eng C., Berk A. Complete transformation by adenovirus 2 requires both E1A proteins. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):951–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90045-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Control of adenovirus E1B mRNA synthesis by a shift in the activities of RNA splice sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):966–972. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Resolving the functions of overlapping viral genes by site-specific mutagenesis at a mRNA splice site. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):380–384. doi: 10.1038/295380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S., Williams G. T. The intron requirement for immunoglobulin gene expression is dependent upon the promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6713–6724. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phi-Van L., von Kries J. P., Ostertag W., Strätling W. H. The chicken lysozyme 5' matrix attachment region increases transcription from a heterologous promoter in heterologous cells and dampens position effects on the expression of transfected genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2302–2307. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaack J., Ho W. Y., Freimuth P., Shenk T. Adenovirus terminal protein mediates both nuclear matrix association and efficient transcription of adenovirus DNA. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1197–1208. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebel C. W., Rio D. C. Regulated splicing of the Drosophila P transposable element third intron in vitro: somatic repression. Science. 1990 Jun 8;248(4960):1200–1208. doi: 10.1126/science.2161558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisodia S. S., Sollner-Webb B., Cleveland D. W. Specificity of RNA maturation pathways: RNAs transcribed by RNA polymerase III are not substrates for splicing or polyadenylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3602–3612. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. W., Patton J. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Alternative splicing in the control of gene expression. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:527–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosnowski B. A., Belote J. M., McKeown M. Sex-specific alternative splicing of RNA from the transformer gene results from sequence-dependent splice site blockage. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):449–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90426-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. J., Halbert D. N., Raskas H. J. Regulation of integrated adenovirus sequences during adenovirus infection of transformed cells. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):860–871. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.860-871.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. J., McGrogan M., Raskas H. J. Regulation of the appearance of cytoplasmic RNAs from region 1 of the adenovirus 2 genome. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):395–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. P., Mathews M. B. DNA replication and the early to late transition in adenovirus infection. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen A., Pettersson U. Organization of early region 1B of human adenovirus type 2: identification of four differentially spliced mRNAs. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):383–391. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.383-391.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Grodzicker T., Stillman B. W. Mutations in the gene encoding the adenovirus early region 1B 19,000-molecular-weight tumor antigen cause the degradation of chromosomal DNA. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):410–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.410-419.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. C., Darnell J. E., Jr Control of messenger RNA concentration by differential cytoplasmic half-life. Adenovirus messenger RNAs from transcription units 1A and 1B. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):231–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90537-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachar Z., Chou T. B., Bingham P. M. Evidence that a regulatory gene autoregulates splicing of its transcript. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4105–4111. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Wilson R. C., Efstratiadis A. Autonomous splicing and complementation of in vivo-assembled spliceosomes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):765–777. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhai Z. H., Nickerson J. A., Krochmalnic G., Penman S. Alterations in nuclear matrix structure after adenovirus infection. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1007–1018. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1007-1018.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]