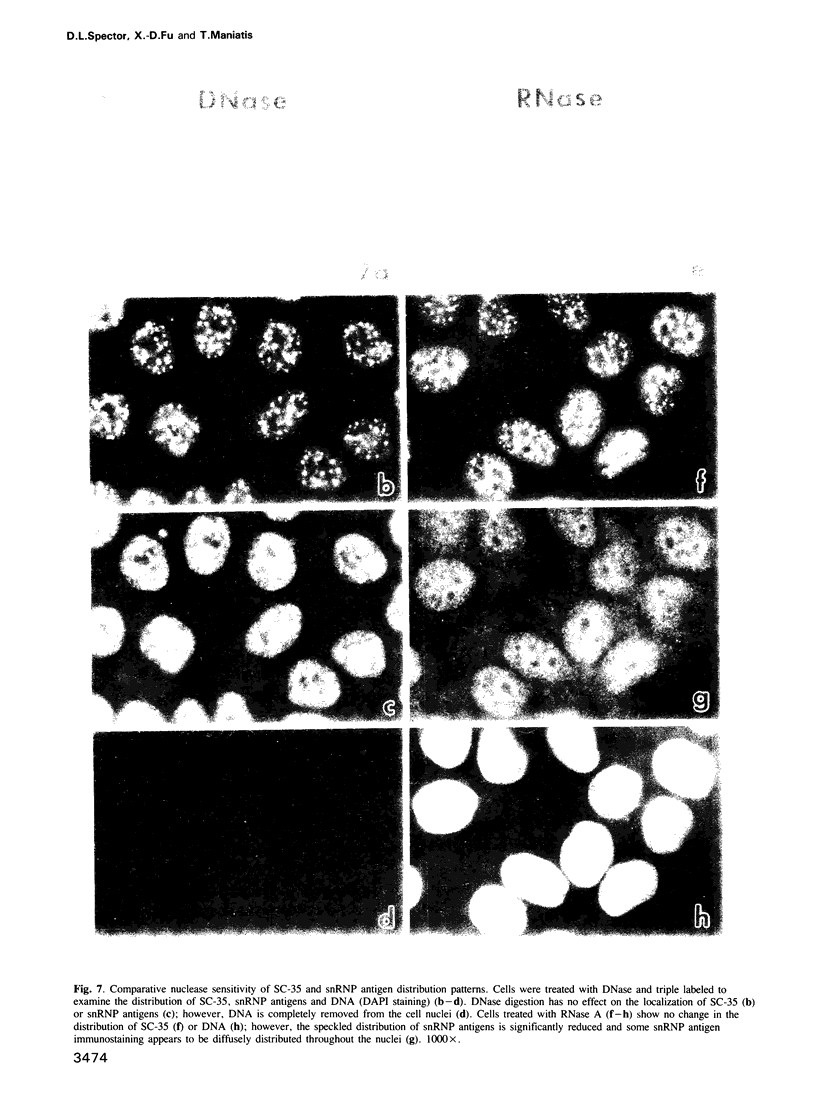
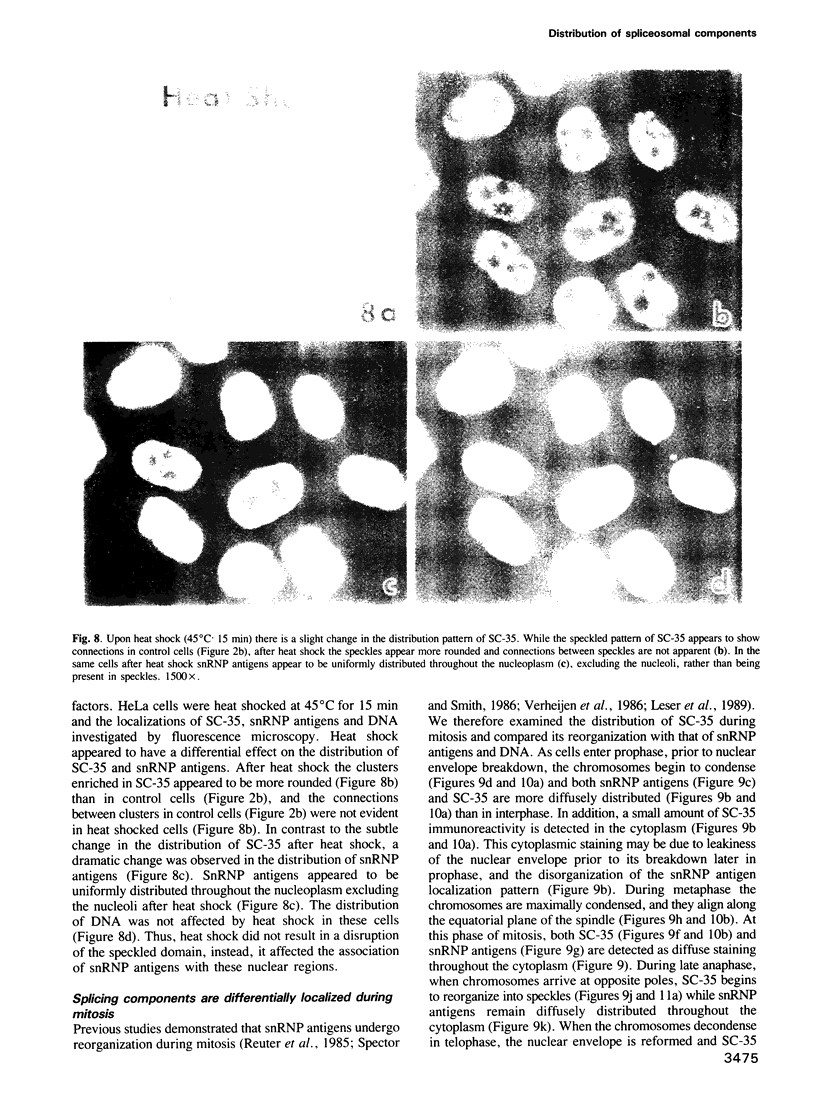
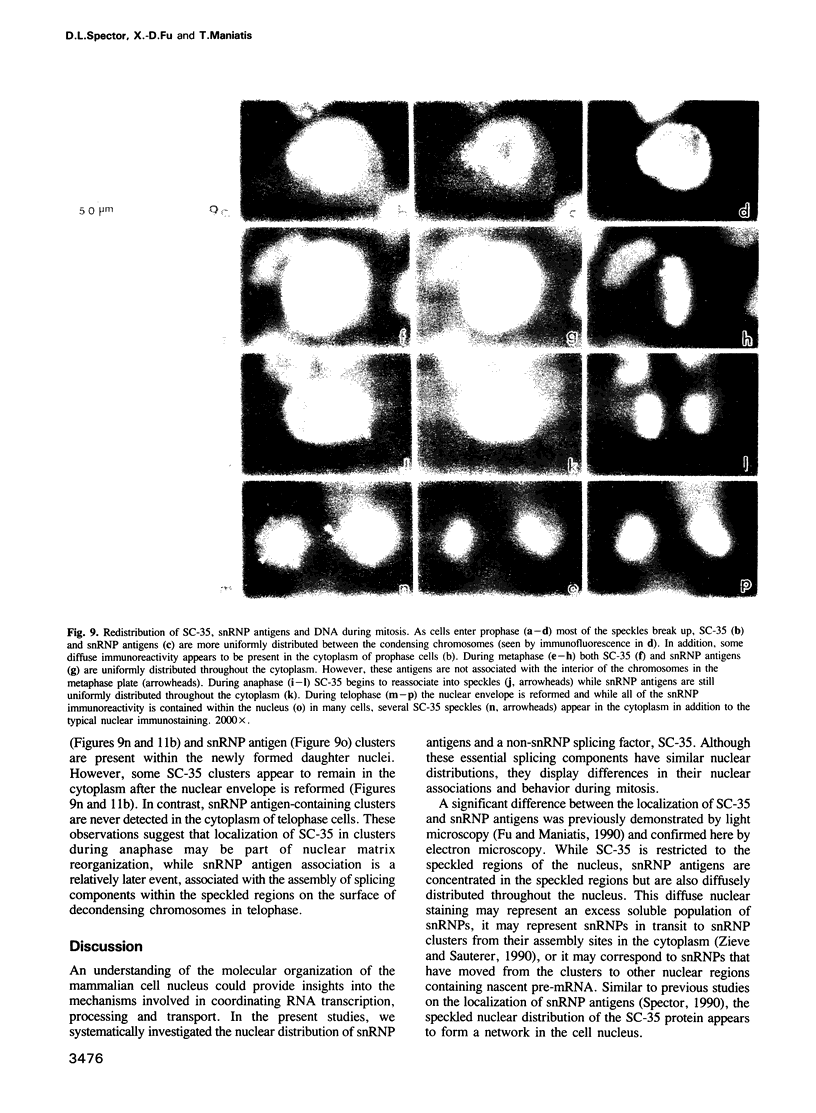
Abstract
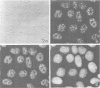
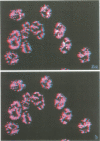
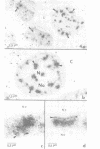
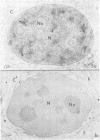
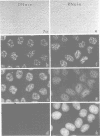
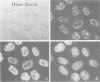
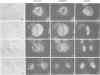
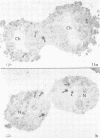
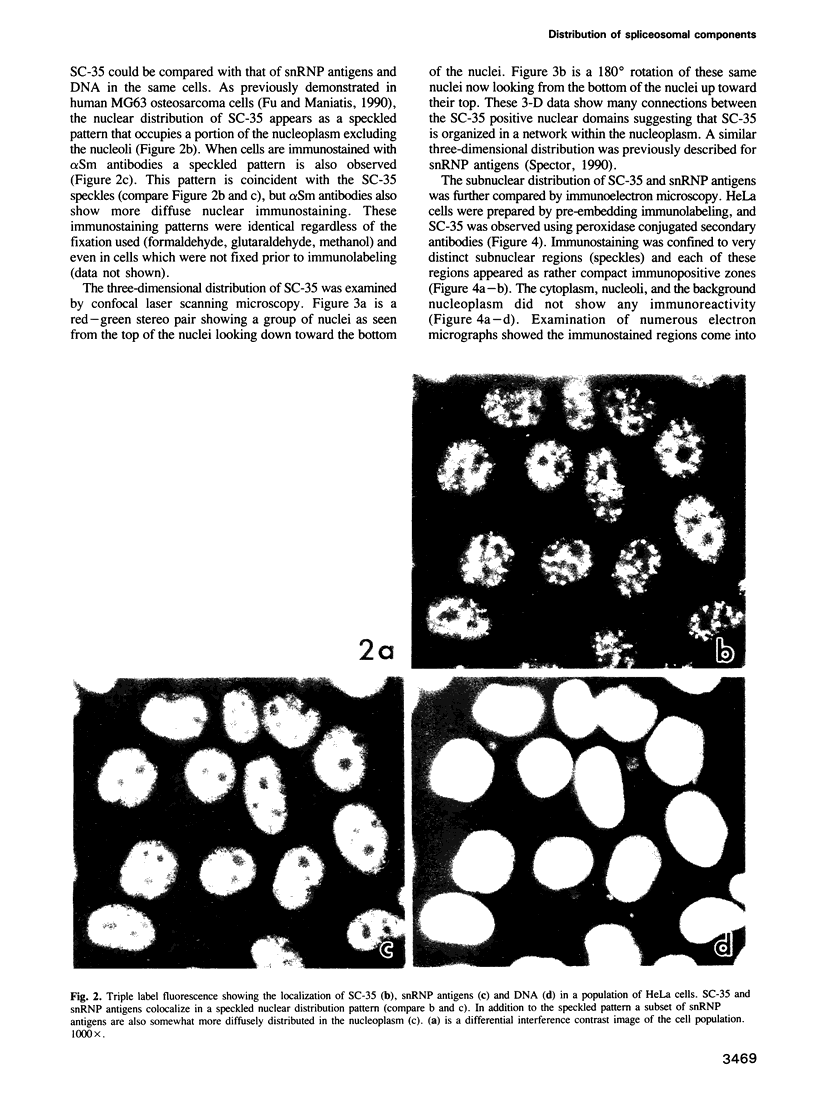
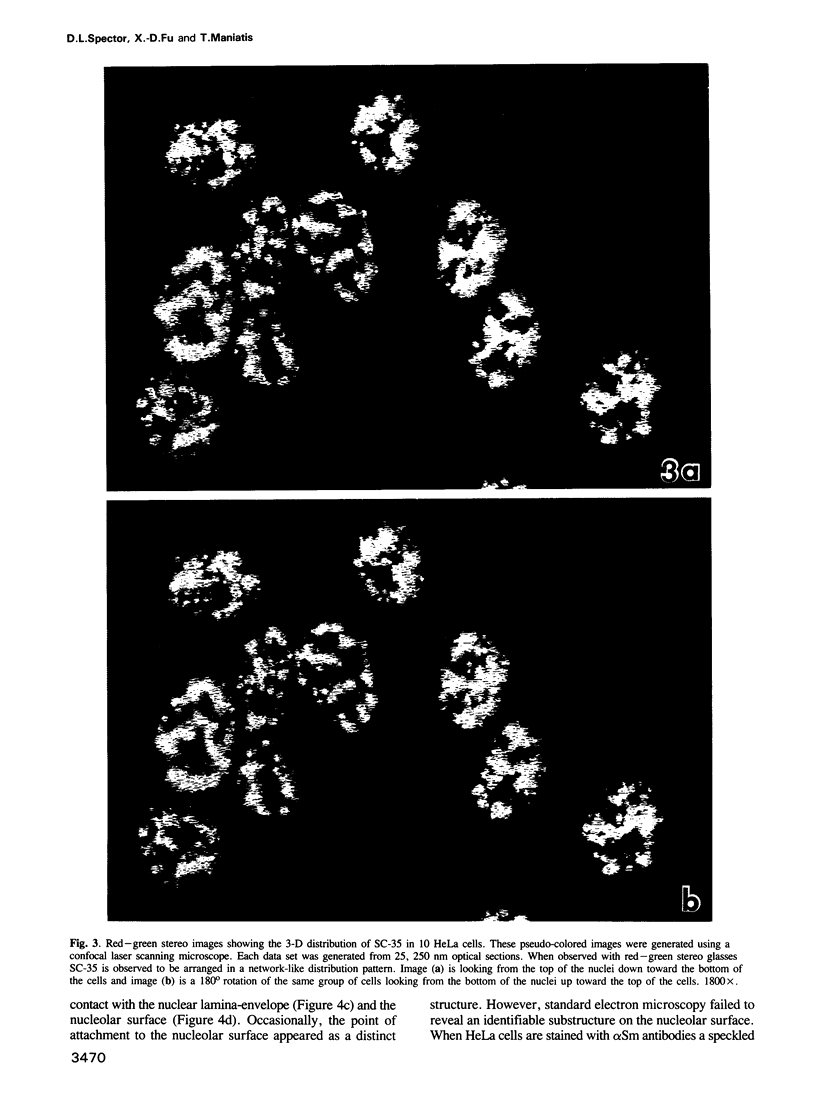
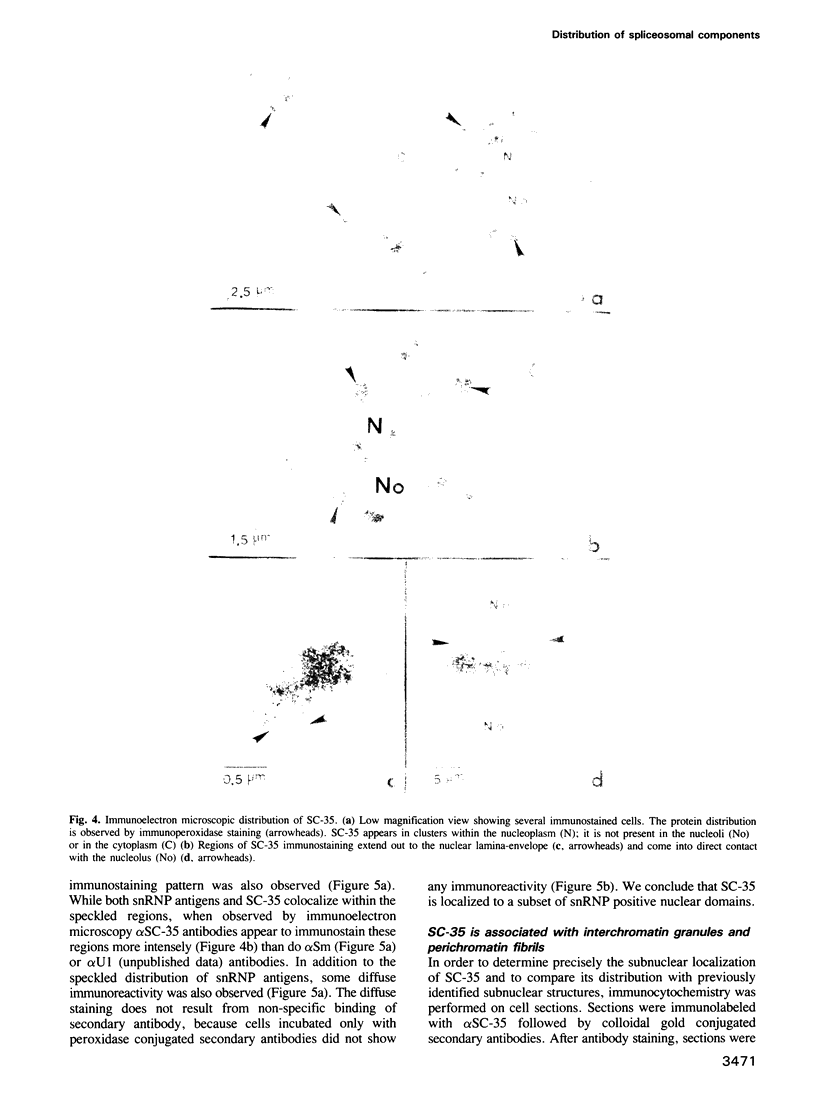
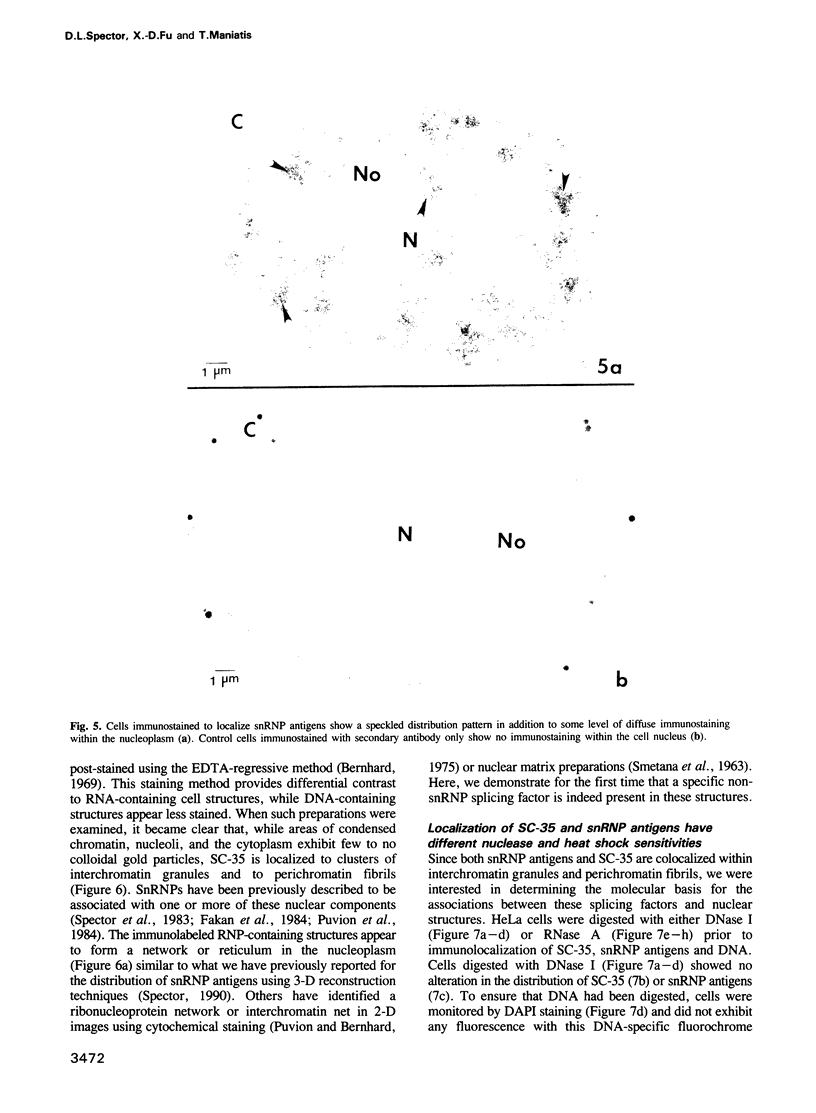
SC-35 is a non-snRNP spliceosome component that is specifically recognized by the anti-spliceosome monoclonal antibody alpha SC-35. In this paper we provide direct evidence that SC-35 is an essential splicing factor and we examine the immunolocalization of SC-35 by confocal laser scanning microscopy and by electron microscopy. We have found that the speckled staining pattern observed by fluorescence microscopy corresponds to structures previously designated as interchromatin granules and perichromatin fibrils. Although snRNP antigens are also concentrated in these nuclear regions, we show that the two types of spliceosome components are localized through different molecular interactions: The distribution of SC-35 was not affected by treatment with DNase I or RNase A, or when the cells were heat shocked. In contrast, snRNP antigens become diffusely distributed after RNase A digestion or heat shock. Examination of cells at different stages of mitosis revealed that the SC-35 speckled staining pattern is lost during prophase and speckles containing SC-35 begin to reform in the cytoplasm of anaphase cells. In contrast, snRNP antigens do not associate with speckled regions until late in telophase. These studies reveal a dynamic pattern of assembly and disassembly of the splicing factor SC-35 into discrete nuclear structures that colocalize with interchromatin granules and perichromatin fibrils. These subnuclear regions may therefore be nuclear organelles involved in the assembly of spliceosomes, or splicing itself.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ast G., Goldblatt D., Offen D., Sperling J., Sperling R. A novel splicing factor is an integral component of 200S large nuclear ribonucleoprotein (InRNP) particles. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):425–432. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07964.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachellerie J. P., Puvion E., Zalta J. P. Ultrastructural organization and biochemical characterization of chromatin - RNA - protein complexes isolated from mammalian cell nuclei. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Oct 15;58(2):327–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard W. A new staining procedure for electron microscopical cytology. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 May;27(3):250–265. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)80016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindereif A., Green M. R. Identification and functional analysis of mammalian splicing factors. Genet Eng (N Y) 1990;12:201–224. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-0641-2_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond U. Heat shock but not other stress inducers leads to the disruption of a sub-set of snRNPs and inhibition of in vitro splicing in HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3509–3518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03227.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Pepperkok R., Sproat B. S., Ansorge W., Swanson M. S., Lamond A. I. In vivo detection of snRNP-rich organelles in the nuclei of mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1863–1873. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Tollervey D., Pepperkok R., Barabino S. M., Merdes A., Brunner C., Zamore P. D., Green M. R., Hurt E., Lamond A. I. Mammalian nuclei contain foci which are highly enriched in components of the pre-mRNA splicing machinery. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):195–206. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07936.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciejek E. M., Nordstrom J. L., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Ribonucleic acid precursors are associated with the chick oviduct nuclear matrix. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):4945–4953. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Bernhard W. Localisation of rapidly and slowly labelled nuclear RNA as visualized by high resolution autoradiography. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jul;67(1):129–141. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90628-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Leser G., Martin T. E. Ultrastructural distribution of nuclear ribonucleoproteins as visualized by immunocytochemistry on thin sections. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):358–363. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Nobis P. Ultrastructural localization of transcription sites and of RNA distribution during the cell cycle of synchronized CHO cells. Exp Cell Res. 1978 May;113(2):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90373-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Puvion E., Sphor G. Localization and characterization of newly synthesized nuclear RNA in isolate rat hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Apr;99(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90690-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakan S., Puvion E. The ultrastructural visualization of nucleolar and extranucleolar RNA synthesis and distribution. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;65:255–299. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61962-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Factor required for mammalian spliceosome assembly is localized to discrete regions in the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):437–441. doi: 10.1038/343437a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Callan H. G. The sphere organelle contains small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6635–6639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Manley J. L. A protein factor, ASF, controls cell-specific alternative splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. Purification and characterization of pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 from HeLa cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1158–1171. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. The essential pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 influences 5' splice site selection by activating proximal sites. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):35–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T. Multiple factors including the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1 and U2 are necessary for pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner E. A., Lerner M. R., Janeway C. A., Jr, Steitz J. A. Monoclonal antibodies to nucleic acid-containing cellular constituents: probes for molecular biology and autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2737–2741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leser G. P., Fakan S., Martin T. E. Ultrastructural distribution of ribonucleoprotein complexes during mitosis. snRNP antigens are contained in mitotic granule clusters. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;50(2):376–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mariman E. C., van Eekelen C. A., Reinders R. J., Berns A. J., van Venrooij W. J. Adenoviral heterogeneous nuclear RNA is associated with the host nuclear matrix during splicing. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 5;154(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90420-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monneron A., Bernhard W. Fine structural organization of the interphase nucleus in some mammalian cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 May;27(3):266–288. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)80017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyman U., Hallman H., Hadlaczky G., Pettersson I., Sharp G., Ringertz N. R. Intranuclear localization of snRNP antigens. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):137–144. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potashkin J. A., Derby R. J., Spector D. L. Differential distribution of factors involved in pre-mRNA processing in the yeast cell nucleus. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3524–3534. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puvion E., Bernhard W. Ribonucleoprotein components in liver cell nuclei as visualized by cryoultramicrotomy. J Cell Biol. 1975 Oct;67(1):200–214. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.1.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puvion E., Viron A., Assens C., Leduc E. H., Jeanteur P. Immunocytochemical identification of nuclear structures containing snRNPs in isolated rat liver cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1984 May;87(2):180–189. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(84)80077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raska I., Ochs R. L., Salamin-Michel L. Immunocytochemistry of the cell nucleus. Electron Microsc Rev. 1990;3(2):301–353. doi: 10.1016/0892-0354(90)90006-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. Protein composition of mammalian spliceosomes assembled in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8031–8035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter R., Appel B., Bringmann P., Rinke J., Lührmann R. 5'-Terminal caps of snRNAs are reactive with antibodies specific for 2,2,7-trimethylguanosine in whole cells and nuclear matrices. Double-label immunofluorescent studies with anti-m3G antibodies and with anti-RNP and anti-Sm autoantibodies. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Oct;154(2):548–560. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90179-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter R., Appel B., Rinke J., Lührmann R. Localization and structure of snRNPs during mitosis. Immunofluorescent and biochemical studies. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Jul;159(1):63–79. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(85)80038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Zamore P. D., Green M. R. A factor, U2AF, is required for U2 snRNP binding and splicing complex assembly. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90509-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier W. H., Reddy R., Busch H. Identification of an antigenic protein recognized by anti-Sm autoantibody. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1982 Oct;6(10):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(82)90003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shukla R. R., Dominski Z., Zwierzynski T., Kole R. Inactivation of splicing factors in HeLa cells subjected to heat shock. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20377–20383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. C., Harris S. G., Zillmann M., Berget S. M. Evidence that a nuclear matrix protein participates in premessenger RNA splicing. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Jun;182(2):521–533. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. C., Ochs R. L., Fernandez E. A., Spector D. L. Macromolecular domains containing nuclear protein p107 and U-snRNP protein p28: further evidence for an in situ nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biochem. 1986 May;70(2):151–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00229430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. C., Spector D. L., Woodcock C. L., Ochs R. L., Bhorjee J. Alterations in chromatin conformation are accompanied by reorganization of nonchromatin domains that contain U-snRNP protein p28 and nuclear protein p107. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):560–567. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L. Colocalization of U1 and U2 small nuclear RNPs by immunocytochemistry. Biol Cell. 1984;51(1):109–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L. Higher order nuclear organization: three-dimensional distribution of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):147–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Schrier W. H., Busch H. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of snRNPs. Biol Cell. 1983;49(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. L., Smith H. C. Redistribution of U-snRNPs during mitosis. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Mar;163(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90560-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen R., Kuijpers H., Vooijs P., Van Venrooij W., Ramaekers F. Distribution of the 70K U1 RNA-associated protein during interphase and mitosis. Correlation with other U RNP particles and proteins of the nuclear matrix. J Cell Sci. 1986 Dec;86:173–190. doi: 10.1242/jcs.86.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Hunt B. F. A subset of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle antigens is a component of the nuclear matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Apr 14;105(3):1224–1232. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91099-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright-Sandor L. G., Reichlin M., Tobin S. L. Alteration by heat shock and immunological characterization of Drosophila small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;108(6):2007–2016. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.6.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z. A., Murphy C., Callan H. G., Gall J. G. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in the amphibian germinal vesicle: loops, spheres, and snurposomes. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):465–483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost H. J., Lindquist S. RNA splicing is interrupted by heat shock and is rescued by heat shock protein synthesis. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):185–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90382-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamore P. D., Green M. R. Biochemical characterization of U2 snRNP auxiliary factor: an essential pre-mRNA splicing factor with a novel intranuclear distribution. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):207–214. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07937.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamore P. D., Green M. R. Identification, purification, and biochemical characterization of U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein auxiliary factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9243–9247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Parent A., Silverstein S., Efstratiadis A. Pre-mRNA splicing and the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):111–120. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Wilson R. C., Efstratiadis A. Autonomous splicing and complementation of in vivo-assembled spliceosomes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):765–777. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G. W., Sauterer R. A. Cell biology of the snRNP particles. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1990;25(1):1–46. doi: 10.3109/10409239009090604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]