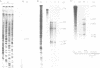Abstract
Regions 5' of the glycosomal glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gGAPDH) gene from Trypanosoma brucei were tested for their ability to promote chloramphenicol acetyl-transferase (CAT) expression on reintroduction by electroporation into the parasite. Deletion analysis mapped the gGAPDH promoter to within 403 nts of the start of translation. A transcription initiation site was mapped at around -190 nts from the ATG start codon by RNase protection and by primer extension. The higher expression of gGAPDH in bloodstream T. brucei, compared to procyclic (insect) forms, was largely attributed to differences in promoter activity. The gGAPDH promoter gave rise to relatively high CAT signals upon transfection into bloodstream T. brucei and relatively low signals in procyclic T. brucei, compared with levels resulting from transfection with the procyclic acidic repetitive protein (PARP) promoter. In addition, RNase protection data showed a higher level of gGAPDH primary transcripts in bloodstream. T. brucei. The PARP mini-exon addition region abolished transient CAT expression directed by either the gGAPDH or PARP promoters in bloodstream T. brucei implying that transplicing can be a point of stage-specific gene regulation.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allert S., Ernest I., Poliszczak A., Opperdoes F. R., Michels P. A. Molecular cloning and analysis of two tandemly linked genes for pyruvate kinase of Trypanosoma brucei. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 15;200(1):19–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb21043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltz T., Baltz D., Giroud C., Crockett J. Cultivation in a semi-defined medium of animal infective forms of Trypanosoma brucei, T. equiperdum, T. evansi, T. rhodesiense and T. gambiense. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1273–1277. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03772.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellofatto V., Cross G. A. Expression of a bacterial gene in a trypanosomatid protozoan. Science. 1989 Jun 9;244(4909):1167–1169. doi: 10.1126/science.2499047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellofatto V. The new trypanosomatid genetics. Parasitol Today. 1990 Sep;6(9):299–302. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(90)90260-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben Amar M. F., Pays A., Tebabi P., Dero B., Seebeck T., Steinert M., Pays E. Structure and transcription of the actin gene of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2166–2176. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P. Discontinuous transcription and antigenic variation in trypanosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:701–732. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun R., Schönenberger Cultivation and in vitro cloning or procyclic culture forms of Trypanosoma brucei in a semi-defined medium. Short communication. Acta Trop. 1979 Sep;36(3):289–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton C. E., Fueri J. P., Itzhaki J. E., Bellofatto V., Sherman D. R., Wisdom G. S., Vijayasarathy S., Mowatt M. R. Transcription of the procyclic acidic repetitive protein genes of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3036–3047. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. C., Swinkels B. W., Borst P. Post-transcriptional control of the differential expression of phosphoglycerate kinase genes in Trypanosoma brucei. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 20;201(2):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. T., Baudhuin P., Opperdoes F. R., de Duve C. Biogenesis of the glycosome in Trypanosoma brucei: the synthesis, translocation and turnover of glycosomal polypeptides. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1403–1411. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Standart N. Do the poly(A) tail and 3' untranslated region control mRNA translation? Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):15–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90235-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferies D., Tebabi P., Pays E. Transient activity assays of the Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein gene promoter: control of gene expression at the posttranscriptional level. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):338–343. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapler G. M., Coburn C. M., Beverley S. M. Stable transfection of the human parasite Leishmania major delineates a 30-kilobase region sufficient for extrachromosomal replication and expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1084–1094. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall G., Wilderspin A. F., Ashall F., Miles M. A., Kelly J. M. Trypanosoma cruzi glycosomal glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase does not conform to the 'hotspot' topogenic signal model. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2751–2758. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07462.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooter J. M., Borst P. Alpha-amanitin-insensitive transcription of variant surface glycoprotein genes provides further evidence for discontinuous transcription in trypanosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9457–9472. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., Kooter J. M., Loosbroek N., Borst P. Mature mRNAs of Trypanosoma brucei possess a 5' cap acquired by discontinuous RNA synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4253–4266. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Blancq S. M., Swinkels B. W., Gibson W. C., Borst P. Evidence for gene conversion between the phosphoglycerate kinase genes of Trypanosoma brucei. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 5;200(3):439–447. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90534-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michels P. A., Poliszczak A., Osinga K. A., Misset O., Van Beeumen J., Wierenga R. K., Borst P., Opperdoes F. R. Two tandemly linked identical genes code for the glycosomal glyceraldehyde-phosphate dehydrogenase in Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1049–1056. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04321.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misset O., Van Beeumen J., Lambeir A. M., Van der Meer R., Opperdoes F. R. Glyceraldehyde-phosphate dehydrogenase from Trypanosoma brucei. Comparison of the glycosomal and cytosolic isoenzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 2;162(3):501–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opperdoes F. R., Aarsen P. N., van der Meer C., Borst P. Trypanosoma brucei: an evaluation of salicylhydroxamic acid as a trypanocidal drug. Exp Parasitol. 1976 Oct;40(2):198–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(76)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opperdoes F. R. Compartmentation of carbohydrate metabolism in trypanosomes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:127–151. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osinga K. A., Swinkels B. W., Gibson W. C., Borst P., Veeneman G. H., Van Boom J. H., Michels P. A., Opperdoes F. R. Topogenesis of microbody enzymes: a sequence comparison of the genes for the glycosomal (microbody) and cytosolic phosphoglycerate kinases of Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3811–3817. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04152.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons M. Current concepts in stage-regulated gene expression in kinetoplastida. Parasitol Today. 1990 Aug;6(8):244–245. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(90)90182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons M., Nielsen B. Trypanosoma brucei: two-dimensional gel analysis of the major glycosomal proteins during the life cycle. Exp Parasitol. 1990 Apr;70(3):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(90)90109-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavé-Preux M., Aggerbeck M., Veyssier C., Bousquet-Lemercier B., Hanoune J., Barouki R. Hormonal discrimination among transcription start sites of aspartate aminotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4444–4448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pays E., Coquelet H., Tebabi P., Pays A., Jefferies D., Steinert M., Koenig E., Williams R. O., Roditi I. Trypanosoma brucei: constitutive activity of the VSG and procyclin gene promoters. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3145–3151. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pays E., Tebabi P., Pays A., Coquelet H., Revelard P., Salmon D., Steinert M. The genes and transcripts of an antigen gene expression site from T. brucei. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):835–845. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90798-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudenko G., Le Blancq S., Smith J., Lee M. G., Rattray A., Van der Ploeg L. H. Procyclic acidic repetitive protein (PARP) genes located in an unusually small alpha-amanitin-resistant transcription unit: PARP promoter activity assayed by transient DNA transfection of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3492–3504. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. F. Trypanosomatid transfection: stable introduction of DNA into protozoa. Parasitol Today. 1990 Aug;6(8):245–247. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(90)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Constitutive and inducible Saccharomyces cerevisiae promoters: evidence for two distinct molecular mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3847–3853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinkels B. W., Gibson W. C., Osinga K. A., Kramer R., Veeneman G. H., van Boom J. H., Borst P. Characterization of the gene for the microbody (glycosomal) triosephosphate isomerase of Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1291–1298. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04358.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vickerman K. Antigenic variation in trypanosomes. Nature. 1978 Jun 22;273(5664):613–617. doi: 10.1038/273613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayasarathy S., Ernest I., Itzhaki J. E., Sherman D., Mowatt M. R., Michels P. A., Clayton C. E. The genes encoding fructose bisphosphate aldolase in Trypanosoma brucei are interspersed with unrelated genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2967–2975. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zomerdijk J. C., Ouellette M., ten Asbroek A. L., Kieft R., Bommer A. M., Clayton C. E., Borst P. The promoter for a variant surface glycoprotein gene expression site in Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2791–2801. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07467.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]