Abstract
To further an understanding of the mechanism of constitutional chromosomal rearrangement, the translocation breakpoints of two X-autosome translocations carried by females with Duchenne or Becker muscular dystrophy have been mapped, cloned and sequenced. Breakpoints were mapped to specific introns within the dystrophin gene and intron sequences spanning the two breakpoints were cloned and used as probes to identify DNA fragments containing the translocation junctions. The junction-containing fragments were cloned after amplification by inverse PCR or single-specific-primer PCR. Sequence through the junctions and the autosomal regions spanning the breakpoints identified the mechanism of rearrangement as non-homologous exchange with minor additions or deletions (0-8 nucleotides) at the breakpoints. Paternal origin of these X-autosome translocations, coupled with evidence for non-transmission of X-autosome translocations through male meiosis suggested that the translocations were the result of a post-meiotic rearrangement in spermiogenesis.
Full text
PDF

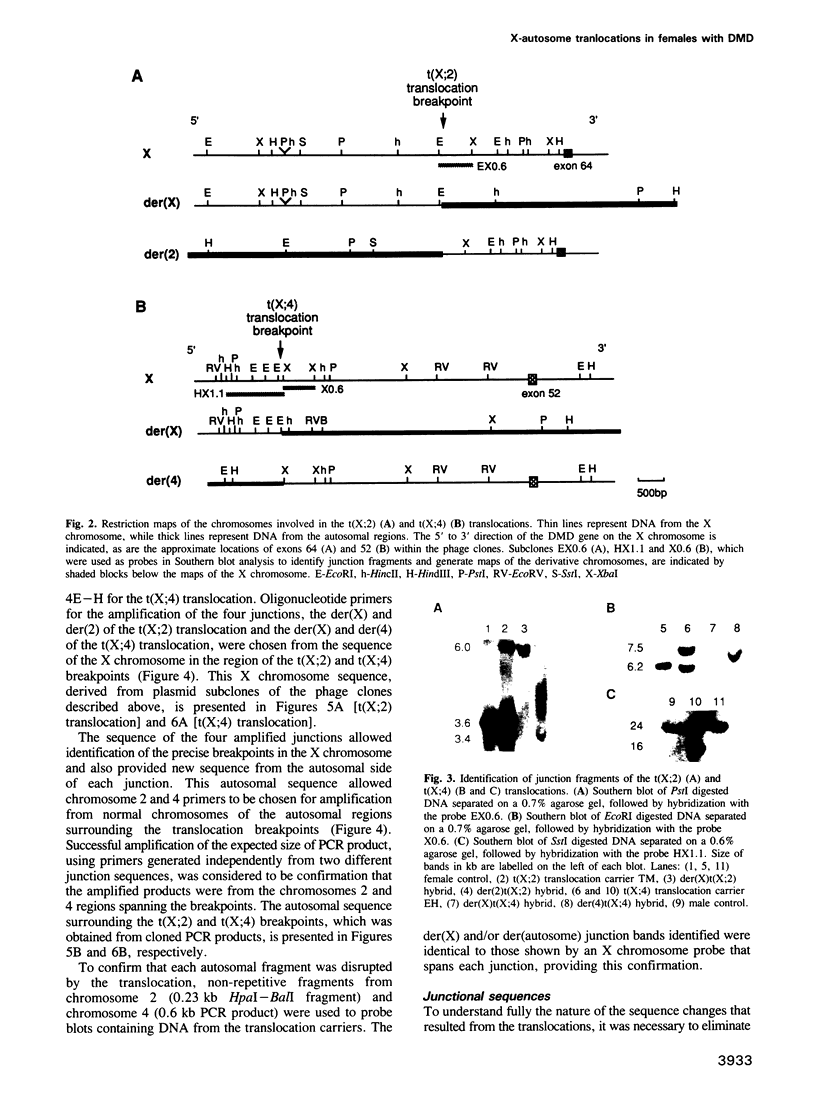
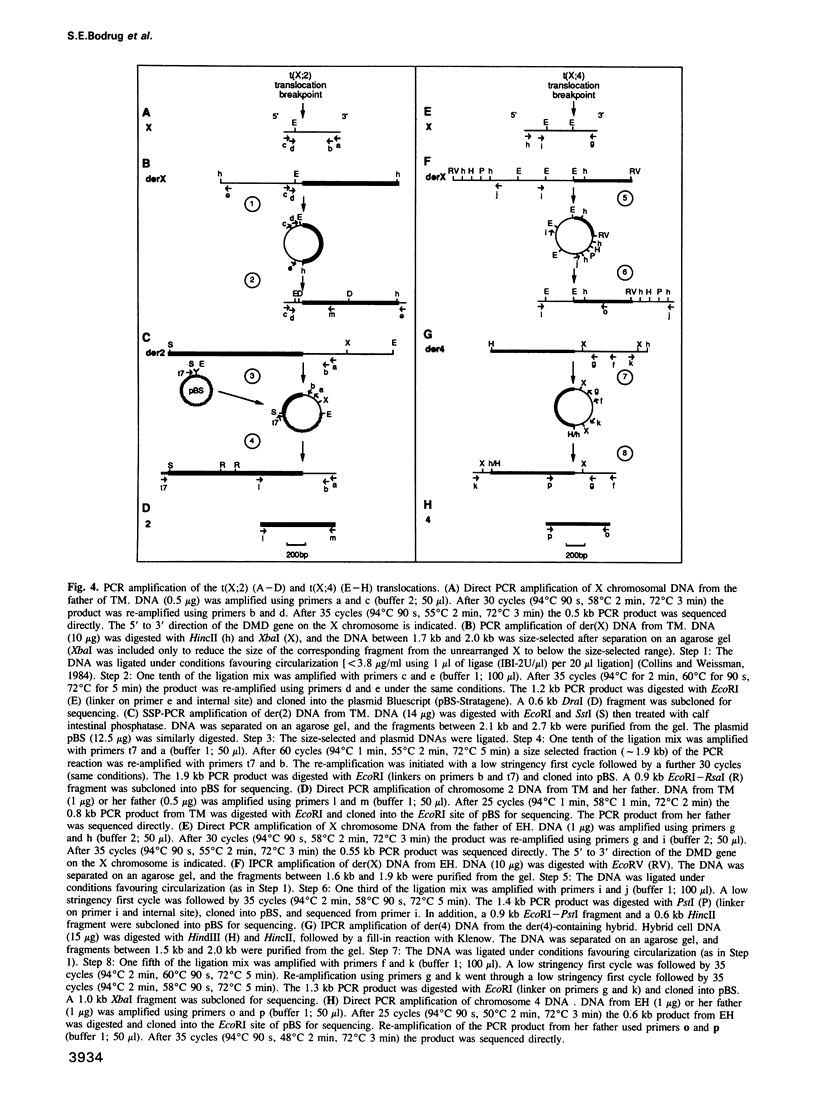





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldridge J., Kunkel L., Bruns G., Tantravahi U., Lalande M., Brewster T., Moreau E., Wilson M., Bromley W., Roderick T. A strategy to reveal high-frequency RFLPs along the human X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 May;36(3):546–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bae Y. S., Kawasaki I., Ikeda H., Liu L. F. Illegitimate recombination mediated by calf thymus DNA topoisomerase II in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2076–2080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Burgess R. R., Champoux J. J. Nucleotide sequence preference at rat liver and wheat germ type 1 DNA topoisomerase breakage sites in duplex SV40 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3097–3114. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodrug S. E., Burghes A. H., Ray P. M., Worton R. G. Mapping of four translocation breakpoints within the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Genomics. 1989 Jan;4(1):101–104. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90321-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodrug S. E., Ray P. N., Gonzalez I. L., Schmickel R. D., Sylvester J. E., Worton R. G. Molecular analysis of a constitutional X-autosome translocation in a female with muscular dystrophy. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1620–1624. doi: 10.1126/science.3629260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodrug S. E., Roberson J. R., Weiss L., Ray P. N., Worton R. G., Van Dyke D. L. Prenatal identification of a girl with a t(X;4)(p21;q35) translocation: molecular characterisation, paternal origin, and association with muscular dystrophy. J Med Genet. 1990 Jul;27(7):426–432. doi: 10.1136/jmg.27.7.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm T., Mengle-Gaw L., Kees U. R., Spurr N., Lavenir I., Forster A., Rabbitts T. H. Alternating purine-pyrimidine tracts may promote chromosomal translocations seen in a variety of human lymphoid tumours. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2621–2631. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd Y., Buckle V. J. Cytogenetic heterogeneity of translocations associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin Genet. 1986 Feb;29(2):108–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1986.tb01232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd Y., Buckle V., Holt S., Munro E., Hunter D., Craig I. Muscular dystrophy in girls with X;autosome translocations. J Med Genet. 1986 Dec;23(6):484–490. doi: 10.1136/jmg.23.6.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd Y., Cockburn D., Holt S., Munro E., Van Ommen G. J., Gillard B., Affara N., Ferguson-Smith M., Craig I. Mapping of 12 translocation breakpoints in the Xp21 region with respect to the locus for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;48(1):28–34. doi: 10.1159/000132581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandley A. C. Origins of genetic disease. Lancet. 1990 Jun 16;335(8703):1462–1463. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91490-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Weissman S. M. Directional cloning of DNA fragments at a large distance from an initial probe: a circularization method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6812–6816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson R. P. Post-meiotic gene expression. Trends Genet. 1990 Aug;6(8):264–269. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90209-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faed M. J., Lamont M. A., Baxby K. Cytogenetic and histological studies of testicular biopsies from subfertile men with chromosome anomaly. J Med Genet. 1982 Feb;19(1):49–56. doi: 10.1136/jmg.19.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossberger D. Minipreps of DNA from bacteriophage lambda. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6737–6737. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haluska F. G., Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. Oncogene activation by chromosome translocation in human malignancy. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:321–345. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heery D. M., Gannon F., Powell R. A simple method for subcloning DNA fragments from gel slices. Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):173–173. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90158-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P. S., Smithies O., Mager D. L. Molecular analysis of deletions in the human beta-globin gene cluster: deletion junctions and locations of breakpoints. Genomics. 1990 Feb;6(2):226–237. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90561-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Brown R. H., Jr, Kunkel L. M. Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90579-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofker M. H., van Ommen G. J., Bakker E., Burmeister M., Pearson P. L. Development of additional RFLP probes near the locus for Duchenne muscular dystrophy by cosmid cloning of the DXS84 (754) locus. Hum Genet. 1986 Nov;74(3):270–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00282547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden J. J., Smith A., MacLeod P. M., Masotti R., Duncan A. M. Xp21/autosome translocations. Case report and risk for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin Genet. 1986 Jun;29(6):516–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Beggs A. H., Moyer M., Scherpf S., Heindrich K., Bettecken T., Meng G., Müller C. R., Lindlöf M., Kaariainen H. The molecular basis for Duchenne versus Becker muscular dystrophy: correlation of severity with type of deletion. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Oct;45(4):498–506. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Hoffman E. P., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogan S. C., Doherty M., Gitschier J. An improved method for prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases by analysis of amplified DNA sequences. Application to hemophilia A. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):985–990. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krowczynska A. M., Rudders R. A., Krontiris T. G. The human minisatellite consensus at breakpoints of oncogene translocations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1121–1127. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Love D. R., England S. B., Speer A., Marsden R. F., Bloomfield J. F., Roche A. L., Cross G. S., Mountford R. C., Smith T. J., Davies K. E. Sequences of junction fragments in the deletion-prone region of the dystrophin gene. Genomics. 1991 May;10(1):57–67. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90484-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madan K. Balanced structural changes involving the human X: effect on sexual phenotype. Hum Genet. 1983;63(3):216–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00284652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Ayme S., Giraud F. X-autosome translocations: cytogenetic characteristics and their consequences. Hum Genet. 1982;61(4):295–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00276593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Zuk D., Einat P., Zeelon E., Levy Z., Neuman S., Yaffe D. Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene product is not identical in muscle and brain. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):76–78. doi: 10.1038/337076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochman H., Gerber A. S., Hartl D. L. Genetic applications of an inverse polymerase chain reaction. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):621–623. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quack B., Speed R. M., Luciani J. M., Noel B., Guichaoua M., Chandley A. C. Meiotic analysis of two human reciprocal X-autosome translocations. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1988;48(1):43–47. doi: 10.1159/000132583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson D. O., Boyd Y., Cockburn D., Collinson M. N., Craig I., Jacobs P. A. The parental origin of de novo X-autosome translocations in females with Duchenne muscular dystrophy revealed by M27 beta methylation analysis. Genet Res. 1990 Oct-Dec;56(2-3):135–140. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300035217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca J., Mezquita C. DNA topoisomerase II activity in nonreplicating, transcriptionally inactive, chicken late spermatids. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1855–1860. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03581.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth D. B., Chang X. B., Wilson J. H. Comparison of filler DNA at immune, nonimmune, and oncogenic rearrangements suggests multiple mechanisms of formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):3049–3057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.3049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey P. G., Whittaker P. A., Southern E. M. Removal of repeated sequences from hybridisation probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):1905–1922. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.1905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyamala V., Ames G. F. Genome walking by single-specific-primer polymerase chain reaction: SSP-PCR. Gene. 1989 Dec 7;84(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90132-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzner J. R., Muller M. T. A consensus sequence for cleavage by vertebrate DNA topoisomerase II. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5533–5556. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thode S., Schäfer A., Pfeiffer P., Vielmetter W. A novel pathway of DNA end-to-end joining. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90340-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triglia T., Peterson M. G., Kemp D. J. A procedure for in vitro amplification of DNA segments that lie outside the boundaries of known sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8186–8186. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worton R. G., Thompson M. W. Genetics of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:601–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ommen G. J., Bertelson C., Ginjaar H. B., den Dunnen J. T., Bakker E., Chelly J., Matton M., van Essen A. J., Bartley J., Kunkel L. M. Long-range genomic map of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene: isolation and use of J66 (DXS268), a distal intragenic marker. Genomics. 1987 Dec;1(4):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(87)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Feltz M. J., Shivji M. K., Allen P. B., Heisterkamp N., Groffen J., Wiedemann L. M. Nucleotide sequence of both reciprocal translocation junction regions in a patient with Ph positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, with a breakpoint within the first intron of the BCR gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):1–10. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]