Abstract
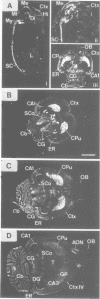
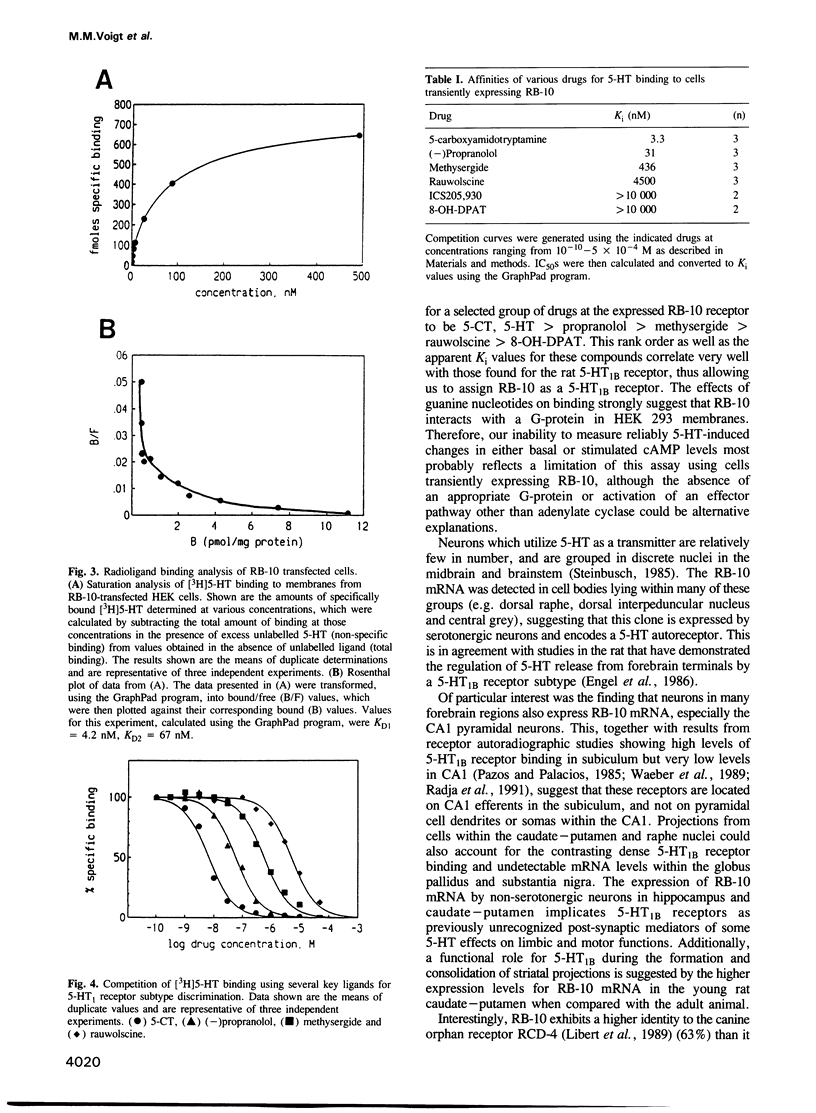
To date, there have been at least eight different receptors for the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-HT) identified in the central nervous system. These receptors fall into four pharmacological classes: 5-HT1, 5-HT2, 5-HT3 and 5-HT4. The 5-HT1 class has been shown to contain at least four pharmacologically distinct subtypes, 5-HT1A-D. Of these, cDNAs encoding the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1C receptors have been previously characterized. We now report the cloning and expression of a rat brain cDNA encoding another member of the 5-HT1 receptor family. Transient expression of this clone demonstrated high-affinity binding of [3H]5-HT with a pharmacological profile corresponding to that of the 5-HT1B subtype: 5-CT, 5-HT greater than propranolol greater than methysergide greater than rauwolscine greater than 8-OH-DPAT. In situ hybridization revealed expression of cognate mRNA within cells of the dorsal and median raphe nuclei, consistent with previous reports that the 5-HT1B receptor acts as an autoreceptor on 5-HT terminals in this species. mRNA expression was also detected in cells within the CA1 region of hippocampus, striatum, layer 4 of cortex and in the cerebellum, suggesting a previously unrecognized post-synaptic role for the 5-HT1B receptor.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert P. R., Zhou Q. Y., Van Tol H. H., Bunzow J. R., Civelli O. Cloning, functional expression, and mRNA tissue distribution of the rat 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5825–5832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Schofield P. R., Sprengel R. Amino-terminal leucine-rich repeats in gonadotropin receptors determine hormone selectivity. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1885–1890. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07714.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Bouhelal R., Sebben M., Cory R., Bockaert J. A nonclassical 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor positively coupled with adenylate cyclase in the central nervous system. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;34(6):880–887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Sebben M., Bockaert J. Pharmacology of 5-hydroxytryptamine-1A receptors which inhibit cAMP production in hippocampal and cortical neurons in primary culture. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;33(2):178–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazer A., Maayani S., Wolfe B. B. Subtypes of receptors for serotonin. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:307–348. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.001515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glennon R. A. Serotonin receptors: clinical implications. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1990 Spring;14(1):35–47. doi: 10.1016/s0149-7634(05)80158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamblin M. W., Metcalf M. A. Primary structure and functional characterization of a human 5-HT1D-type serotonin receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):143–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausdorff W. P., Bouvier M., O'Dowd B. F., Irons G. P., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation sites on two domains of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor are involved in distinct pathways of receptor desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12657–12665. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrick-Davis K., Titeler M. Detection and characterization of the serotonin 5-HT 1D receptor in rat and human brain. J Neurochem. 1988 May;50(5):1624–1631. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb03052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuring R. E., Peroutka S. J. Characterization of a novel 3H-5-hydroxytryptamine binding site subtype in bovine brain membranes. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):894–903. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00894.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer D., Engel G., Kalkman H. O. Molecular pharmacology of 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 recognition sites in rat and pig brain membranes: radioligand binding studies with [3H]5-HT, [3H]8-OH-DPAT, (-)[125I]iodocyanopindolol, [3H]mesulergine and [3H]ketanserin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov 26;118(1-2):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90658-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Huang K. N., Livelli T. J., Axel R., Jessell T. M. The 5HT2 receptor defines a family of structurally distinct but functionally conserved serotonin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):928–932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., MacDermott A. B., Axel R., Jessell T. M. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA encoding the serotonin 1c receptor. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):558–564. doi: 10.1126/science.3399891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Frielle T., Collins S., Yang-Feng T., Kobilka T. S., Francke U., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. An intronless gene encoding a potential member of the family of receptors coupled to guanine nucleotide regulatory proteins. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):75–79. doi: 10.1038/329075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonhardt S., Herrick-Davis K., Titeler M. Detection of a novel serotonin receptor subtype (5-HT1E) in human brain: interaction with a GTP-binding protein. J Neurochem. 1989 Aug;53(2):465–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert F., Parmentier M., Lefort A., Dinsart C., Van Sande J., Maenhaut C., Simons M. J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Selective amplification and cloning of four new members of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):569–572. doi: 10.1126/science.2541503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markstein R., Hoyer D., Engel G. 5-HT1A-receptors mediate stimulation of adenylate cyclase in rat hippocampus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Aug;333(4):335–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00500006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. J., Bylund D. B. Characterization of serotonin-1B receptors negatively coupled to adenylate cyclase in OK cells, a renal epithelial cell line from the opossum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 May;249(2):535–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazos A., Palacios J. M. Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of serotonin receptors in the rat brain. I. Serotonin-1 receptors. Brain Res. 1985 Nov 4;346(2):205–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90856-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J. Pharmacological differentiation and characterization of 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, and 5-HT1C binding sites in rat frontal cortex. J Neurochem. 1986 Aug;47(2):529–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb04532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pritchett D. B., Bach A. W., Wozny M., Taleb O., Dal Toso R., Shih J. C., Seeburg P. H. Structure and functional expression of cloned rat serotonin 5HT-2 receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4135–4140. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeffter P., Hoyer D. 5-Hydroxytryptamine 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors mediating inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity. Pharmacological comparison with special reference to the effects of yohimbine, rauwolscine and some beta-adrenoceptor antagonists. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;340(3):285–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00168512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waeber C., Dietl M. M., Hoyer D., Palacios J. M. 5.HT1 receptors in the vertebrate brain. Regional distribution examined by autoradiography. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;340(5):486–494. doi: 10.1007/BF00260602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner P., Voigt M., Keinänen K., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. Cloning of a putative high-affinity kainate receptor expressed predominantly in hippocampal CA3 cells. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):742–744. doi: 10.1038/351742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]