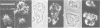Abstract
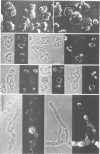
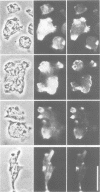
A soluble actin binding protein of Dictyostelium discoideum cells has been extracted and purified from precipitated actin-myosin complexes. This protein with a relative molecular mass of 55 kDa has been named coronin because of its association with crown-shaped cell surface projections of growth-phase D. discoideum cells. In aggregating cells, which respond most sensitively to the chemoattractant cyclic AMP, coronin is accumulated at the front where surface projections are directed towards a cAMP source. Since these cells can quickly change shape and polarity, it follows that coronin is rapidly reshuffled within the cells during motion and chemotactic orientation. The cDNA derived sequence of coronin indicates a protein of 49 kDa, consisting of an amino-terminal domain with similarities to the beta subunits of G proteins and a carboxy-terminal domain with a high tendency for alpha-helical structure. It is hypothesized that coronin is implicated in the transmission of chemotactic signals from cAMP receptors in the plasma membrane through G proteins to the cortical cytoskeleton, whose structure and activity is locally modulated.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- André E., Brink M., Gerisch G., Isenberg G., Noegel A., Schleicher M., Segall J. E., Wallraff E. A Dictyostelium mutant deficient in severin, an F-actin fragmenting protein, shows normal motility and chemotaxis. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):985–995. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengtsson T., Särndahl E., Stendahl O., Andersson T. Involvement of GTP-binding proteins in actin polymerization in human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2921–2925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlot C. H., Devreotes P. N., Spudich J. A. Chemoattractant-elicited increases in Dictyostelium myosin phosphorylation are due to changes in myosin localization and increases in kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3918–3926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlot C. H., Spudich J. A., Devreotes P. N. Chemoattractant-elicited increases in myosin phosphorylation in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomblies L., Biegelmann E., Döring V., Gerisch G., Krafft-Czepa H., Noegel A. A., Schleicher M., Humbel B. M. Membrane-enclosed crystals in Dictyostelium discoideum cells, consisting of developmentally regulated proteins with sequence similarities to known esterases. J Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;110(3):669–679. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.3.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink M., Gerisch G., Isenberg G., Noegel A. A., Segall J. E., Wallraff E., Schleicher M. A Dictyostelium mutant lacking an F-actin cross-linking protein, the 120-kD gelation factor. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1477–1489. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claviez M., Brink M., Gerisch G. Cytoskeletons from a mutant of Dictyostelium discoideum with flattened cells. J Cell Sci. 1986 Dec;86:69–82. doi: 10.1242/jcs.86.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devreotes P. N., Zigmond S. H. Chemotaxis in eukaryotic cells: a focus on leukocytes and Dictyostelium. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:649–686. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.003245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drubin D. G., Mulholland J., Zhu Z. M., Botstein D. Homology of a yeast actin-binding protein to signal transduction proteins and myosin-I. Nature. 1990 Jan 18;343(6255):288–290. doi: 10.1038/343288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckerskorn C., Mewes W., Goretzki H., Lottspeich F. A new siliconized-glass fiber as support for protein-chemical analysis of electroblotted proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):509–519. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichinger L., Noegel A. A., Schleicher M. Domain structure in actin-binding proteins: expression and functional characterization of truncated severin. J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;112(4):665–676. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.4.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fechheimer M., Murdock D., Carney M., Glover C. V. Isolation and sequencing of cDNA clones encoding the Dictyostelium discoideum 30,000-dalton actin-bundling protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):2883–2889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fechheimer M., Taylor D. L. Isolation and characterization of a 30,000-dalton calcium-sensitive actin cross-linking protein from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4514–4520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fechheimer M., Zigmond S. H. Changes in cytoskeletal proteins of polymorphonuclear leukocytes induced by chemotactic peptides. Cell Motil. 1983;3(4):349–361. doi: 10.1002/cm.970030406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. R., Merkl R., Gerisch G. Quantitative analysis of cell motility and chemotaxis in Dictyostelium discoideum by using an image processing system and a novel chemotaxis chamber providing stationary chemical gradients. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):973–984. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong H. K., Amatruda T. T., 3rd, Birren B. W., Simon M. I. Distinct forms of the beta subunit of GTP-binding regulatory proteins identified by molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3792–3796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Lynch T. J., Brzeska H., Korn E. D. Myosin I is located at the leading edges of locomoting Dictyostelium amoebae. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):328–331. doi: 10.1038/341328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Keller H. U. Chemotactic reorientation of granulocytes stimulated with micropipettes containing fMet-Leu-Phe. J Cell Sci. 1981 Dec;52:1–10. doi: 10.1242/jcs.52.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Noegel A. A., Schleicher M. Genetic alteration of proteins in actin-based motility systems. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:607–628. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.003135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gribskov M., Burgess R. R. Sigma factors from E. coli, B. subtilis, phage SP01, and phage T4 are homologous proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6745–6763. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelsema C. L., Axelrod J. Stimulation of phospholipase A2 activity in bovine rod outer segments by the beta gamma subunits of transducin and its inhibition by the alpha subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung G., Hammer J. A., 3rd Generation and characterization of Dictyostelium cells deficient in a myosin I heavy chain isoform. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):1955–1964. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Kusakabe K., Oinuma M., Ui M. A novel mechanism for the inhibition of adenylate cyclase via inhibitory GTP-binding proteins. Calmodulin-dependent inhibition of the cyclase catalyst by the beta gamma-subunits of GTP-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):11897–11900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P. S., Sun T. J., Saxe C. L., 3rd, Kimmel A. R., Johnson R. L., Devreotes P. N. A chemoattractant receptor controls development in Dictyostelium discoideum. Science. 1988 Sep 16;241(4872):1467–1472. doi: 10.1126/science.3047871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai A., Hadwiger J. A., Pupillo M., Firtel R. A. Molecular genetic analysis of two G alpha protein subunits in Dictyostelium. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1220–1228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. C., Wu X. W., Gibbs R. A., Cook R. G., Muzny D. M., Caskey C. T. Generation of cDNA probes directed by amino acid sequence: cloning of urate oxidase. Science. 1988 Mar 11;239(4845):1288–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.3344434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logothetis D. E., Kurachi Y., Galper J., Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. The beta gamma subunits of GTP-binding proteins activate the muscarinic K+ channel in heart. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):321–326. doi: 10.1038/325321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Losada A., Nanjundiah V., Konijn T. M. Signal input for a chemotactic response in the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4991–4993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McRobbie S. J., Newell P. C. Changes in actin associated with the cytoskeleton following chemotactic stimulation of dictyostelium discoideum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pupillo M., Kumagai A., Pitt G. S., Firtel R. A., Devreotes P. N. Multiple alpha subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding proteins in Dictyostelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4892–4896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richey B., Cayley D. S., Mossing M. C., Kolka C., Anderson C. F., Farrar T. C., Record M. T., Jr Variability of the intracellular ionic environment of Escherichia coli. Differences between in vitro and in vivo effects of ion concentrations on protein-DNA interactions and gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7157–7164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryba N. J., Pottinger J. D., Keen J. N., Findlay J. B. Sequence of the beta-subunit of the phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C-directed GTP-binding protein from squid (Loligo forbesi) photoreceptors. Biochem J. 1991 Jan 1;273(Pt 1):225–228. doi: 10.1042/bj2730225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheel J., Ziegelbauer K., Kupke T., Humbel B. M., Noegel A. A., Gerisch G., Schleicher M. Hisactophilin, a histidine-rich actin-binding protein from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 15;264(5):2832–2839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleicher M., Gerisch G., Isenberg G. New actin-binding proteins from Dictyostelium discoideum. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2095–2100. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02096.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J. E., Gerisch G. Genetic approaches to cytoskeleton function and the control of cell motility. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;1(1):44–50. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(89)80035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanini M., De Martino C., Zamboni L. Fixation of ejaculated spermatozoa for electron microscopy. Nature. 1967 Oct 14;216(5111):173–174. doi: 10.1038/216173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therrien S., Naccache P. H. Guanine nucleotide-induced polymerization of actin in electropermeabilized human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1125–1132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus M. A., Warrick H. M., Spudich J. A. Multiple actin-based motor genes in Dictyostelium. Cell Regul. 1989 Nov;1(1):55–63. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A., Haarer B., Field J., Gerst J., Pollard T. D., Brown S., Wigler M. Evidence for a functional link between profilin and CAP in the yeast S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):497–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallraff E., Schleicher M., Modersitzki M., Rieger D., Isenberg G., Gerisch G. Selection of Dictyostelium mutants defective in cytoskeletal proteins: use of an antibody that binds to the ends of alpha-actinin rods. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):61–67. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessels D., Soll D. R., Knecht D., Loomis W. F., De Lozanne A., Spudich J. Cell motility and chemotaxis in Dictyostelium amebae lacking myosin heavy chain. Dev Biol. 1988 Jul;128(1):164–177. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90279-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteway M., Hougan L., Dignard D., Thomas D. Y., Bell L., Saari G. C., Grant F. J., O'Hara P., MacKay V. L. The STE4 and STE18 genes of yeast encode potential beta and gamma subunits of the mating factor receptor-coupled G protein. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90249-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Levitsky H. I., Kreel B. J. Cell polarity: an examination of its behavioral expression and its consequences for polymorphonuclear leukocyte chemotaxis. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):585–592. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zot A. S., Potter J. D. Structural aspects of troponin-tropomyosin regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:535–559. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Voorn L., Gebbink M., Plasterk R. H., Ploegh H. L. Characterization of a G-protein beta-subunit gene from the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1990 May 5;213(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]