Abstract
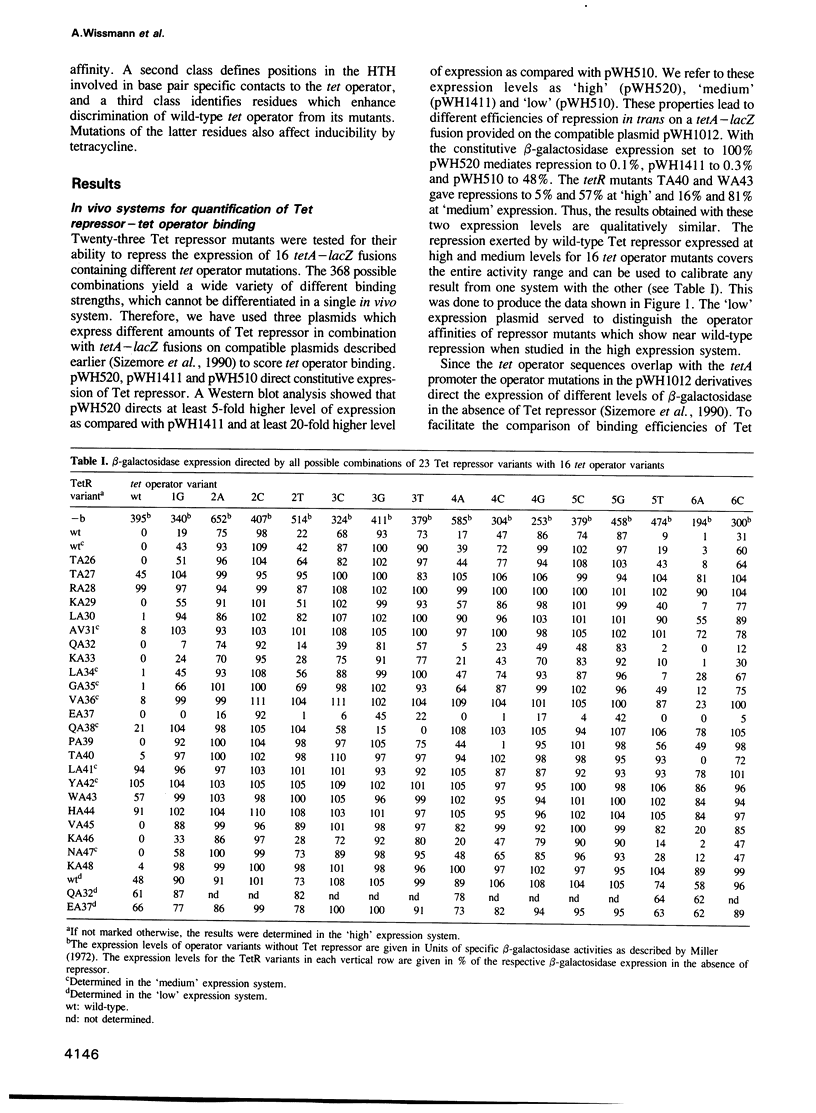
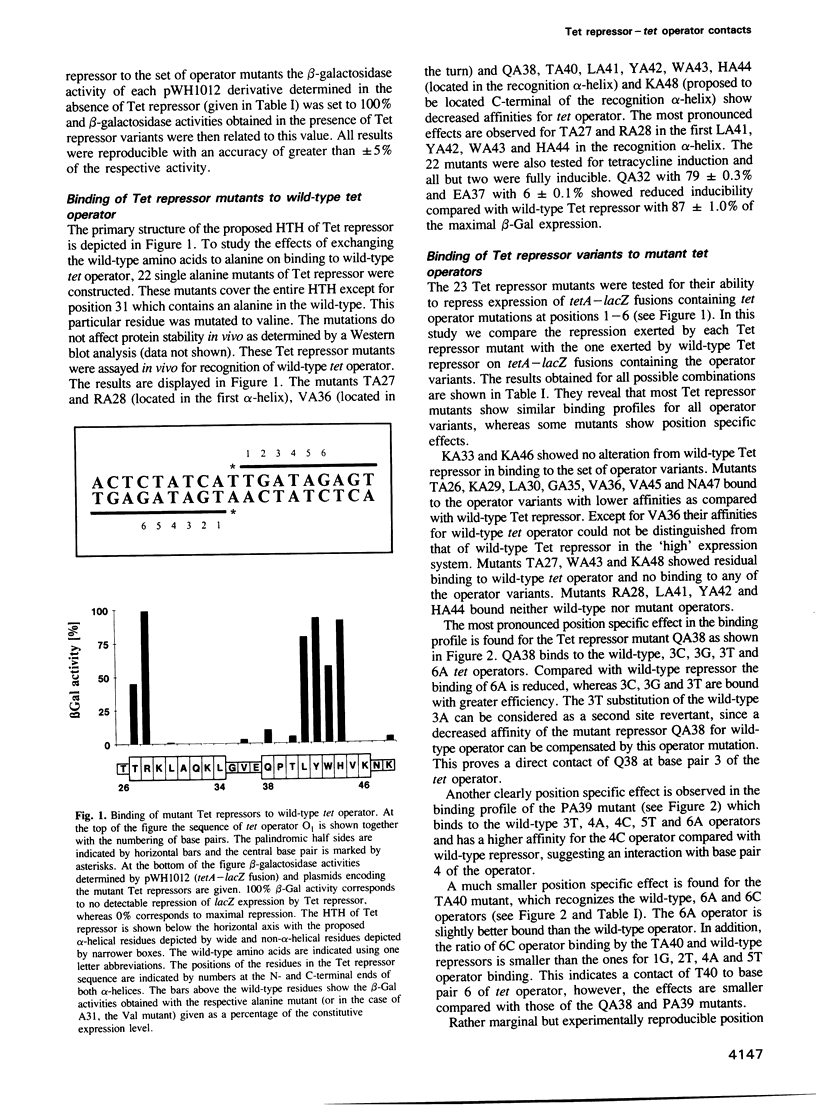
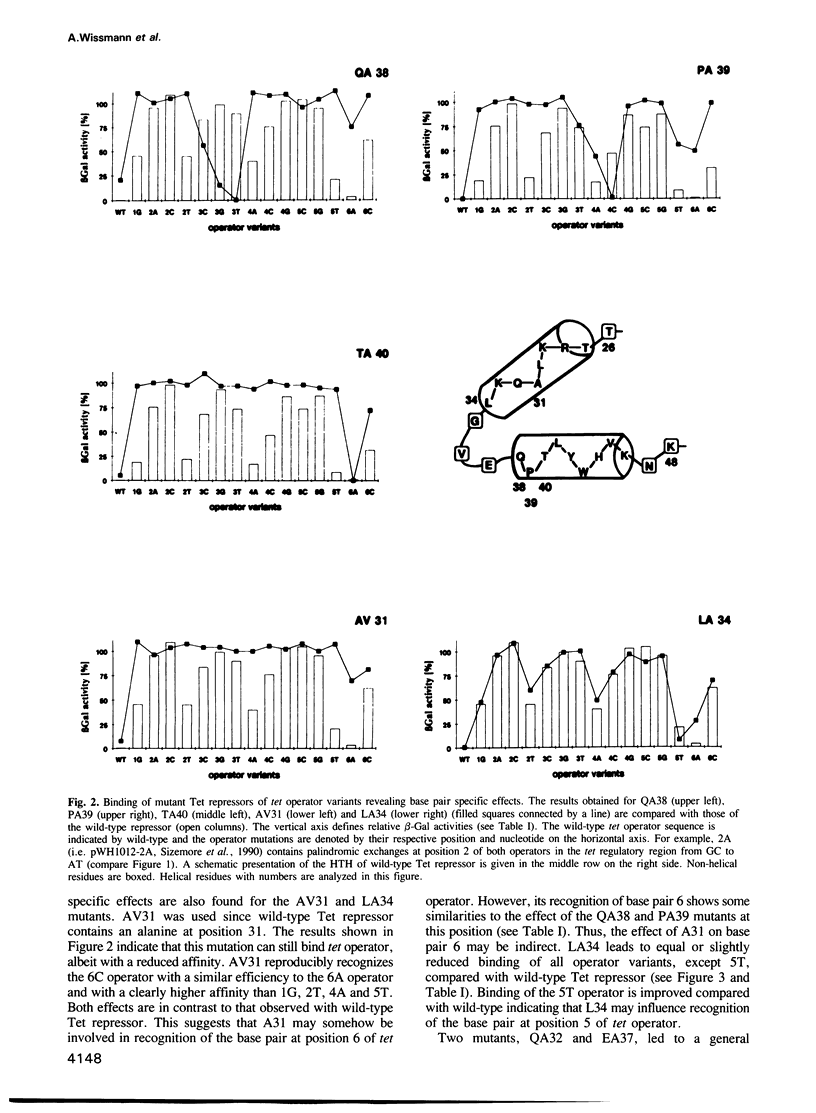
Each of 22 amino acids in the proposed alpha-helix-turn-alpha-helix operator binding motif of the Tn10 encoded Tet repressor was replaced by alanine and one residue was replaced by valine to determine their role in tet operator recognition by a 'loss of contact' analysis with 16 operator variants. One class of amino acids consisting of T27 and R28 in the first alpha-helix and L41, Y42, W43 and H44 in the recognition alpha-helix are quantitatively most important for wild-type operator binding. These residues are probably involved in the structural architecture of the motif. A second class of residues is quantitatively less important for binding, but determines specificity by forming base pair specific contacts to three positions in tet operator. This property is most clearly demonstrated for Q38 and P39 and to a lesser extent for T40 at the N-terminus of the recognition alpha-helix. The contacted operator base pairs indicate that the N-terminus of the recognition alpha-helix is located towards the palindromic center in the repressor-operator complex. Although the orientation of the recognition alpha-helix in the Tet repressor-tet operator complex is inversed as compared with the lambda- and 434 repressor-operator complexes, the reduced operator binding of the TA27 mutation in the first alpha-helix suggests that the hydrogen bonding networks connecting the two alpha-helices may be similar in these proteins.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
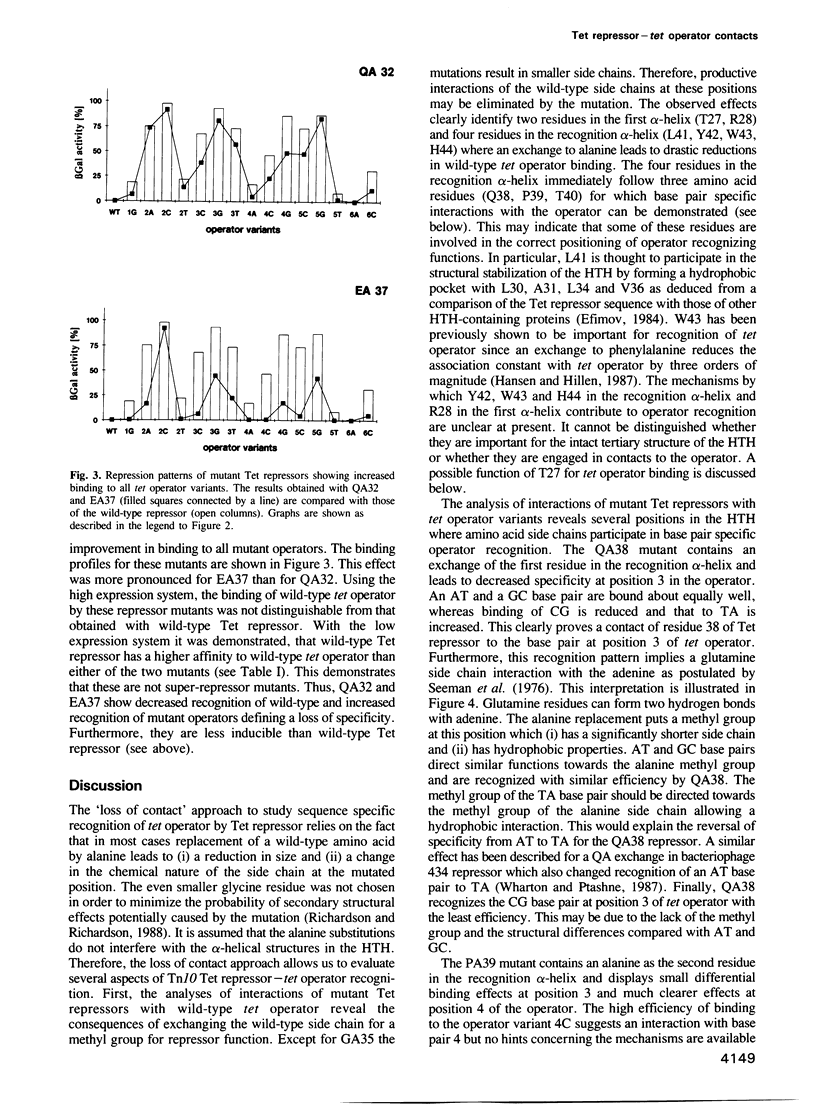



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aggarwal A. K., Rodgers D. W., Drottar M., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Recognition of a DNA operator by the repressor of phage 434: a view at high resolution. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):899–907. doi: 10.1126/science.3187531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschmied L., Baumeister R., Pfleiderer K., Hillen W. A threonine to alanine exchange at position 40 of Tet repressor alters the recognition of the sixth base pair of tet operator from GC to AT. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):4011–4017. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03290.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boelens R., Scheek R. M., van Boom J. H., Kaptein R. Complex of lac repressor headpiece with a 14 base-pair lac operator fragment studied by two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jan 5;193(1):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90638-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H. Evidence for a contact between glutamine-18 of lac repressor and base pair 7 of lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):303–307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H. Use of "loss-of-contact" substitutions to identify residues involved in an amino acid-base pair contact: effect of substitution of Gln18 of lac repressor by Gly, Ser, and Leu. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1985 Oct;3(2):281–297. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1985.10508417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efimov A. V. A novel super-secondary structure of proteins and the relation between the structure and the amino acid sequence. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 23;166(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen D., Altschmied L., Hillen W. Engineered Tet repressor mutants with single tryptophan residues as fluorescent probes. Solvent accessibilities of DNA and inducer binding sites and interaction with tetracycline. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14030–14035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen D., Hillen W. Tryptophan in alpha-helix 3 of Tet repressor forms a sequence-specific contact with tet operator in solution. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12269–12274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison S. C., Aggarwal A. K. DNA recognition by proteins with the helix-turn-helix motif. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:933–969. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.004441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuer C., Hillen W. Tet repressor-tet operator contacts probed by operator DNA-modification interference studies. J Mol Biol. 1988 Aug 5;202(3):407–415. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90274-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Ptashne M. Homologous interactions of lambda repressor and lambda Cro with the lambda operator. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):925–933. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90015-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isackson P. J., Bertrand K. P. Dominant negative mutations in the Tn10 tet repressor: evidence for use of the conserved helix-turn-helix motif in DNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6226–6230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan S. R., Pabo C. O. Structure of the lambda complex at 2.5 A resolution: details of the repressor-operator interactions. Science. 1988 Nov 11;242(4880):893–899. doi: 10.1126/science.3187530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisters-Woike B., Lehming N., Sartorius J., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. A model of the lac repressor-operator complex based on physical and genetic data. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jun 1;198(2):411–419. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehming N., Sartorius J., Kisters-Woike B., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. Mutant lac repressors with new specificities hint at rules for protein--DNA recognition. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):615–621. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08153.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otwinowski Z., Schevitz R. W., Zhang R. G., Lawson C. L., Joachimiak A., Marmorstein R. Q., Luisi B. F., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of trp repressor/operator complex at atomic resolution. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):321–329. doi: 10.1038/335321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Aggarwal A. K., Jordan S. R., Beamer L. J., Obeysekare U. R., Harrison S. C. Conserved residues make similar contacts in two repressor-operator complexes. Science. 1990 Mar 9;247(4947):1210–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.2315694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postle K., Nguyen T. T., Bertrand K. P. Nucleotide sequence of the repressor gene of the TN10 tetracycline resistance determinant. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 25;12(12):4849–4863. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.12.4849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C. Amino acid preferences for specific locations at the ends of alpha helices. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1648–1652. doi: 10.1126/science.3381086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A. Sequence-specific recognition of double helical nucleic acids by proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):804–808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sizemore C., Wissmann A., Gülland U., Hillen W. Quantitative analysis of Tn10 Tet repressor binding to a complete set of tet operator mutants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2875–2880. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. D., Bertrand K. P. Mutations in the Tn10 tet repressor that interfere with induction. Location of the tetracycline-binding domain. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):949–959. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. Structural studies of protein-nucleic acid interaction: the sources of sequence-specific binding. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Aug;23(3):205–280. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton R. P., Ptashne M. A new-specificity mutant of 434 repressor that defines an amino acid-base pair contact. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):888–891. doi: 10.1038/326888a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wissmann A., Wray L. V., Jr, Somaggio U., Baumeister R., Geissendörfer M., Hillen W. Selection for Tn10 tet repressor binding to tet operator in Escherichia coli: isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants and combinatorial mutagenesis in the DNA binding motif. Genetics. 1991 Jun;128(2):225–232. doi: 10.1093/genetics/128.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolberger C., Dong Y. C., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. Structure of a phage 434 Cro/DNA complex. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):789–795. doi: 10.1038/335789a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]