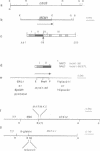
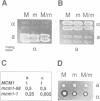
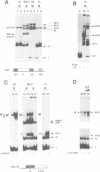
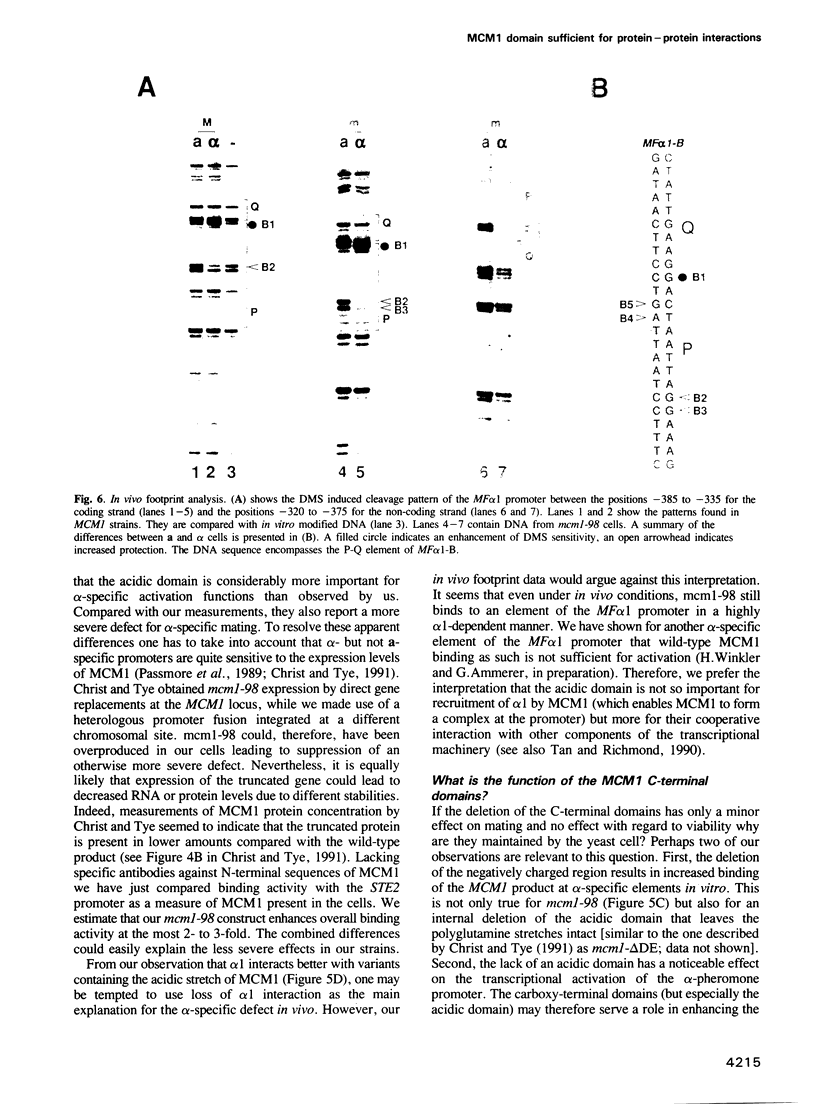
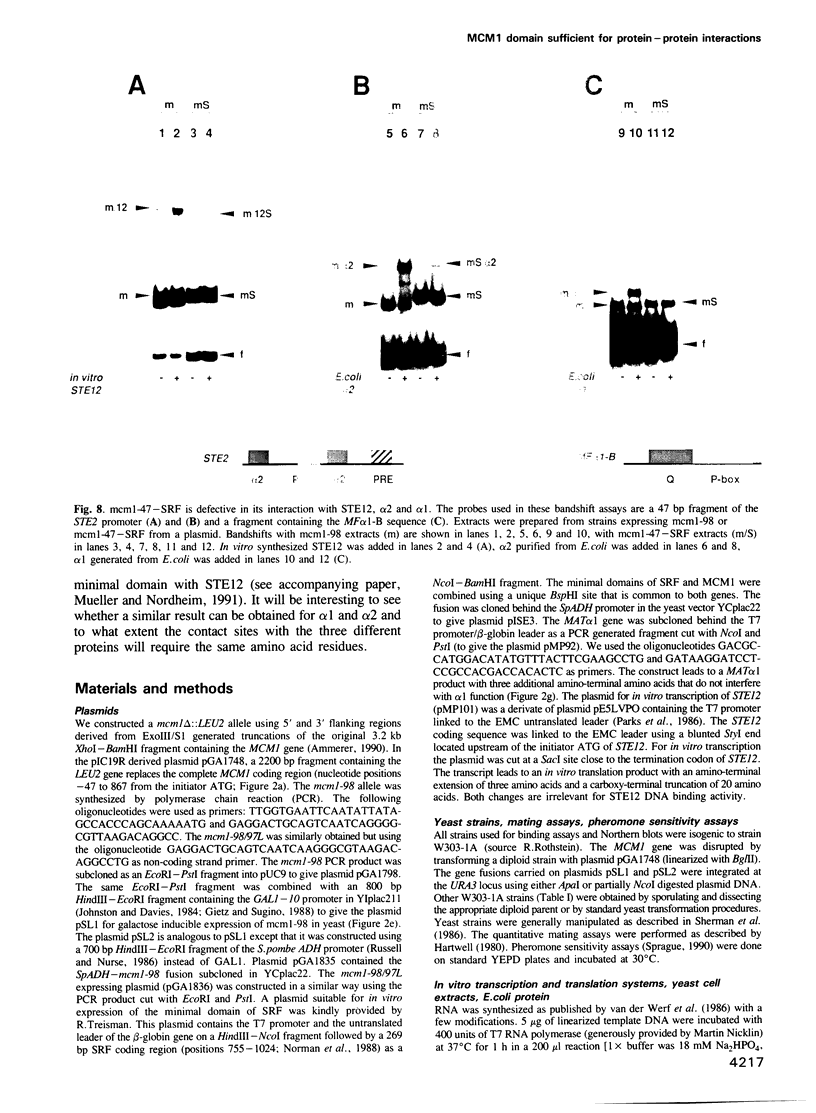
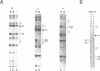Abstract
The MCM1 gene encodes an essential DNA binding protein that, in cooperation with the transactivators alpha 1 and STE12 and the repressor alpha 2, confers mating specificity to haploid yeast cells. We show that the amino-terminal third of the MCM1 protein is sufficient for the physical interaction with these factors. A strain expressing just 98 amino acids encompassing the oligomerization and DNA binding domains of MCM1 is viable and mating competent. This motif exhibits considerable similarity to a domain of the mammalian transcription factor SRF. A 98 amino acid hybrid gene coding for the MCM1 DNA binding domain and SRF dimerization domain is sufficient for viability but not for the expression of mating type specific genes. In vitro binding studies suggest that a region of approximately 50 amino acids of MCM1 is essential for providing contacts with alpha 1, alpha 2 and STE12.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammerer G. Identification, purification, and cloning of a polypeptide (PRTF/GRM) that binds to mating-specific promoter elements in yeast. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):299–312. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A., Sprague G. F., Jr MAT alpha 1 protein, a yeast transcription activator, binds synergistically with a second protein to a set of cell-type-specific genes. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):681–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christ C., Tye B. K. Functional domains of the yeast transcription/replication factor MCM1. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):751–763. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan J. W., Fields S. Cell-type-specific transcription in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Feb 16;1088(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90051-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan J. W., Kirkman C., Fields S. The yeast STE12 protein binds to the DNA sequence mediating pheromone induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5703–5707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois E., Bercy J., Messenguy F. Characterization of two genes, ARGRI and ARGRIII required for specific regulation of arginine metabolism in yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Apr;207(1):142–148. doi: 10.1007/BF00331501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Ammerer G. STE12, a protein involved in cell-type-specific transcription and signal transduction in yeast, is part of protein-DNA complexes. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1349–1361. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Chaleff D. T., Sprague G. F., Jr Yeast STE7, STE11, and STE12 genes are required for expression of cell-type-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):551–556. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson G., Schier A., LeMotte P., Gehring W. J. The specificities of Sex combs reduced and Antennapedia are defined by a distinct portion of each protein that includes the homeodomain. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1087–1103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90386-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz R. D., Sugino A. New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):527–534. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90185-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae unresponsive to cell division control by polypeptide mating hormone. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):811–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes T. E., Sengupta P., Cochran B. H. The human c-fos serum response factor and the yeast factors GRM/PRTF have related DNA-binding specificities. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1713–1722. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Mahadevan S., Struhl K. Structural and functional characterization of the short acidic transcriptional activation region of yeast GCN4 protein. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):635–640. doi: 10.1038/333635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. L., Hartwell L. H. Courtship in S. cerevisiae: both cell types choose mating partners by responding to the strongest pheromone signal. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90507-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis E. E., Clark K. L., Sprague G. F., Jr The yeast transcription activator PRTF, a homolog of the mammalian serum response factor, is encoded by the MCM1 gene. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):936–945. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis E. E., Hagen D. C., Sprague G. F., Jr Identification of a DNA segment that is necessary and sufficient for alpha-specific gene control in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: implications for regulation of alpha-specific and a-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):309–320. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. Transcriptional regulation by dimerization: two sides to an incestuous relationship. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):9–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90207-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keleher C. A., Goutte C., Johnson A. D. The yeast cell-type-specific repressor alpha 2 acts cooperatively with a non-cell-type-specific protein. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):927–936. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90449-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronstad J. W., Holly J. A., MacKay V. L. A yeast operator overlaps an upstream activation site. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90491-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma H., Yanofsky M. F., Meyerowitz E. M. AGL1-AGL6, an Arabidopsis gene family with similarity to floral homeotic and transcription factor genes. Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):484–495. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maine G. T., Sinha P., Tye B. K. Mutants of S. cerevisiae defective in the maintenance of minichromosomes. Genetics. 1984 Mar;106(3):365–385. doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.3.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Runswick M., Pollock R., Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C. Encephalomyocarditis virus 3C protease: efficient cell-free expression from clones which link viral 5' noncoding sequences to the P3 region. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):376–384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.376-384.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore S., Elble R., Tye B. K. A protein involved in minichromosome maintenance in yeast binds a transcriptional enhancer conserved in eukaryotes. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):921–935. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passmore S., Maine G. T., Elble R., Christ C., Tye B. K. Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein involved in plasmid maintenance is necessary for mating of MAT alpha cells. J Mol Biol. 1988 Dec 5;204(3):593–606. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Prezant T., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator binds to two upstream activation sites of different sequence. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90751-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price C., Nasmyth K., Schuster T. A general approach to the isolation of cell cycle-regulated genes in the budding yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1991 Apr 5;218(3):543–556. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90700-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. cdc25+ functions as an inducer in the mitotic control of fission yeast. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90546-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saluz H., Jost J. P. A simple high-resolution procedure to study DNA methylation and in vivo DNA-protein interactions on a single-copy gene level in higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2602–2606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröter H., Mueller C. G., Meese K., Nordheim A. Synergism in ternary complex formation between the dimeric glycoprotein p67SRF, polypeptide p62TCF and the c-fos serum response element. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1123–1130. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08218.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Schröter H., Nordheim A. The ability of a ternary complex to form over the serum response element correlates with serum inducibility of the human c-fos promoter. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):563–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90579-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer H., Beltrán J. P., Huijser P., Pape H., Lönnig W. E., Saedler H., Schwarz-Sommer Z. Deficiens, a homeotic gene involved in the control of flower morphogenesis in Antirrhinum majus: the protein shows homology to transcription factors. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):605–613. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08152.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr Assay of yeast mating reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:77–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94008-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr Combinatorial associations of regulatory proteins and the control of cell type in yeast. Adv Genet. 1990;27:33–62. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60023-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J., Hicks J., Herskowitz I. Control of cell type in yeast by the mating type locus. The alpha 1-alpha 2 hypothesis. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 15;147(3):357–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90488-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S., Ammerer G., Richmond T. J. Interactions of purified transcription factors: binding of yeast MAT alpha 1 and PRTF to cell type-specific, upstream activating sequences. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4255–4264. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03323.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S., Richmond T. J. DNA binding-induced conformational change of the yeast transcriptional activator PRTF. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):367–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90373-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. The SRE: a growth factor responsive transcriptional regulator. Semin Cancer Biol. 1990 Feb;1(1):47–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. L., Herskowitz I. Sequences upstream of the STE6 gene required for its expression and regulation by the mating type locus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2536–2540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bradley J., Wimmer E., Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA by purified T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]