Abstract
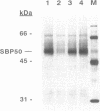
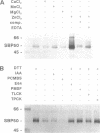
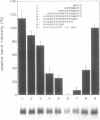
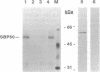
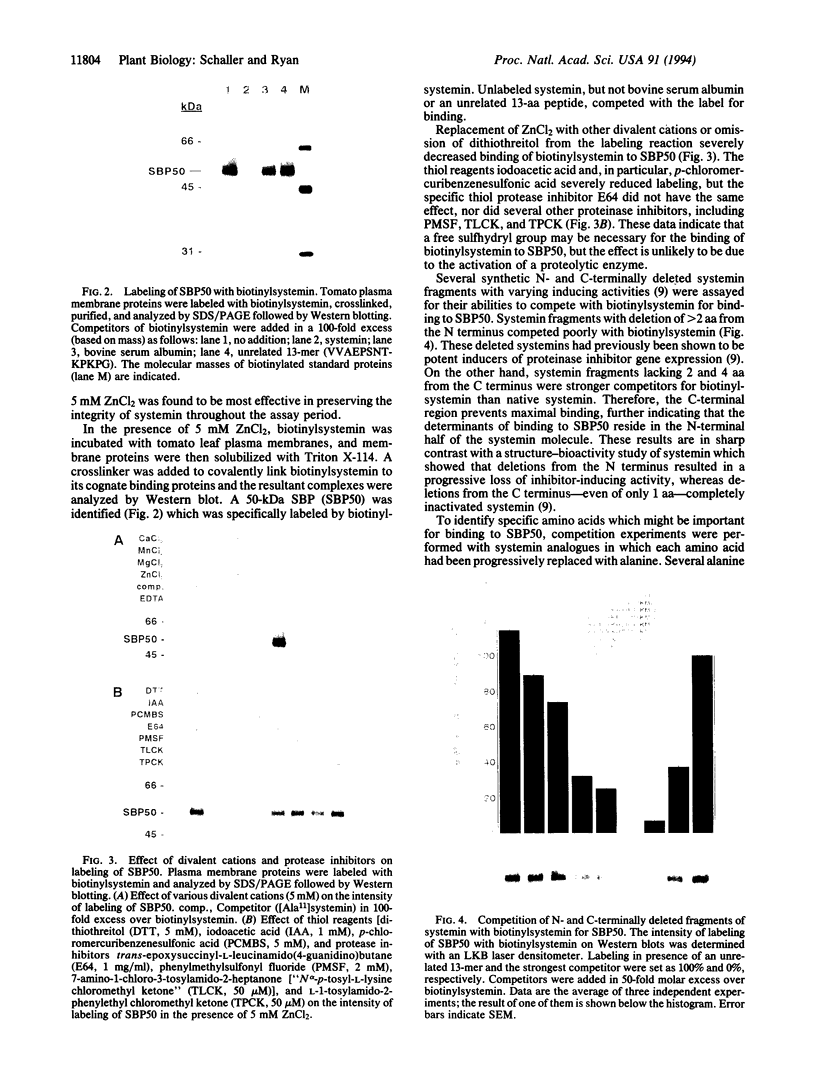
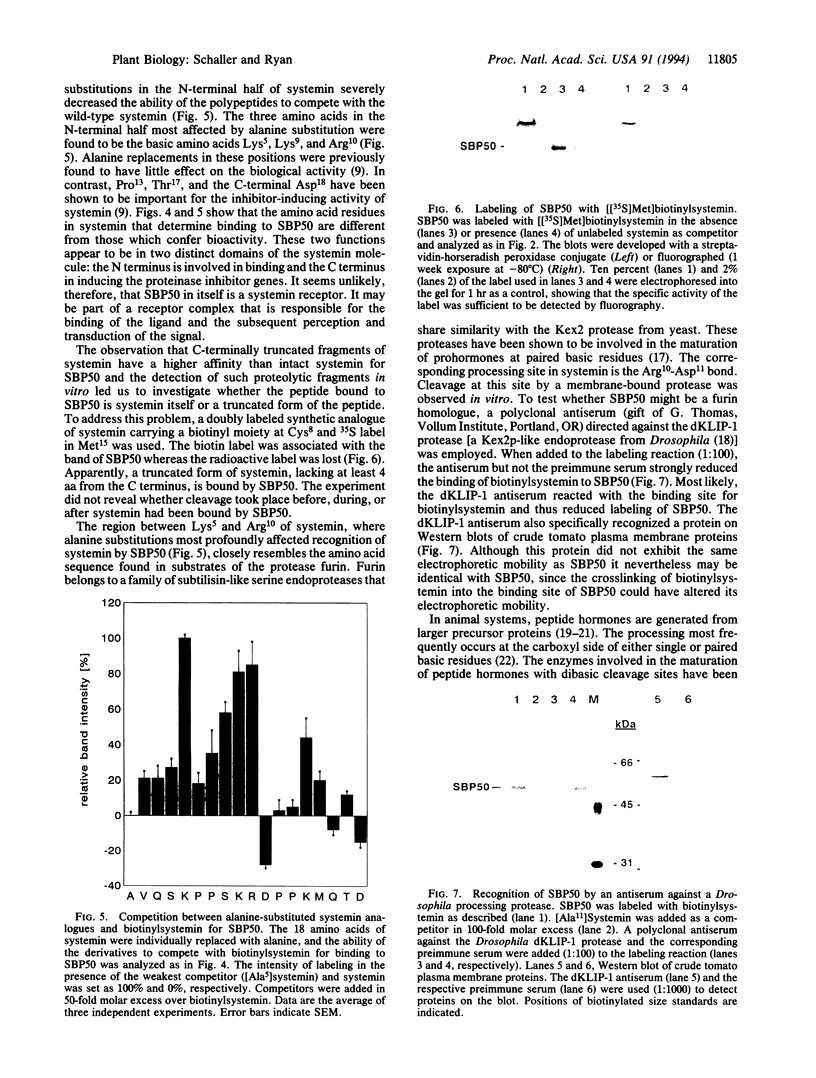
A protein of 50-kDa (SBP50) was identified in plasma membranes of tomato leaves which resembles proteases of the family of Kex2p-like prohormone convertases. To our knowledge, proteases of this class have not been reported in plants previously. A biotinylated derivative of systemin, the 18-aa polypeptide inducer of proteinase inhibitors in tomato and potato leaves, was bound by SBP50 with high specificity. When a systemin derivative was labeled with biotin at residue 8 and with [35S]methionine at position 15, the biotin moiety but not the radioactive label was bound by SBP50. At least 4 aa from the C terminus that included [35S]methionine were missing, indicating that proteolytic cleavage had occurred. Whereas residues in systemin most important for binding SBP50 appear to be located in the N-terminal half of the molecule, amino acids crucial for proteinase inhibitor induction are located within the C terminus. The residues important for binding include a cleavage site for furin, a member of the family of Kex2p-like prohormone-processing enzymes. Processing of systemin at the predicted furin cleavage site was confirmed in vitro. An antiserum against a Kex2p-like protease from Drosophila inhibited binding of biotinylsystemin to SBP50 and recognized a protein of about 60 kDa in Western blot analyses of tomato plasma membrane proteins. The data suggest a possible role for a membrane bound, furin-like protease in the mechanism of defense gene signaling by systemin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barr P. J. Mammalian subtilisins: the long-sought dibasic processing endoproteases. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90129-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. J., Oliva A. A., Jr, LaMendola J., Grens A., Bode H., Steiner D. F. Conservation of the prohormone convertase gene family in metazoa: analysis of cDNAs encoding a PC3-like protein from hydra. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6678–6682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer E. E., Pearce G., Ryan C. A. In vitro phosphorylation of plant plasma membrane proteins in response to the proteinase inhibitor inducing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1539–1542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer E. E., Ryan C. A. Interplant communication: airborne methyl jasmonate induces synthesis of proteinase inhibitors in plant leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7713–7716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer E. E., Ryan C. A. Octadecanoid Precursors of Jasmonic Acid Activate the Synthesis of Wound-Inducible Proteinase Inhibitors. Plant Cell. 1992 Feb;4(2):129–134. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.2.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher J. M., Scheller R. H. Prohormone processing and the secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16515–16518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez S., Boileau G., Zollinger L., Nault C., Rholam M., Cohen P. Site-specific mutagenesis identifies amino acid residues critical in prohormone processing. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2911–2916. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08440.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. B. Processing of pro-hormone precursor proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Dec;275(2):315–333. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90379-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatsuzawa K., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Molecular and enzymatic properties of furin, a Kex2-like endoprotease involved in precursor cleavage at Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg sites. J Biochem. 1992 Mar;111(3):296–301. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatsuzawa K., Nagahama M., Takahashi S., Takada K., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Purification and characterization of furin, a Kex2-like processing endoprotease, produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16094–16099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick J. S., Wolfgang W. J., Forte M. A., Thomas G. A unique Kex2-like endoprotease from Drosophila melanogaster is expressed in the central nervous system during early embryogenesis. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):705–717. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-00705.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka M., Nagahama M., Kim W. S., Watanabe T., Hatsuzawa K., Ikemizu J., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Arg-X-Lys/Arg-Arg motif as a signal for precursor cleavage catalyzed by furin within the constitutive secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12127–12130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung L. J., Scheller R. H. Peptide processing and targeting in the neuronal secretory pathway. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1330–1335. doi: 10.1126/science.2003219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimpel K. R., Molloy S. S., Thomas G., Leppla S. H. Anthrax toxin protective antigen is activated by a cell surface protease with the sequence specificity and catalytic properties of furin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10277–10281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGurl B., Pearce G., Orozco-Cardenas M., Ryan C. A. Structure, expression, and antisense inhibition of the systemin precursor gene. Science. 1992 Mar 20;255(5051):1570–1573. doi: 10.1126/science.1549783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy S. S., Bresnahan P. A., Leppla S. H., Klimpel K. R., Thomas G. Human furin is a calcium-dependent serine endoprotease that recognizes the sequence Arg-X-X-Arg and efficiently cleaves anthrax toxin protective antigen. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16396–16402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco-Cardenas M., McGurl B., Ryan C. A. Expression of an antisense prosystemin gene in tomato plants reduces resistance toward Manduca sexta larvae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8273–8276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce G., Johnson S., Ryan C. A. Structure-activity of deleted and substituted systemin, an 18-amino acid polypeptide inducer of plant defensive genes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):212–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce G., Strydom D., Johnson S., Ryan C. A. A polypeptide from tomato leaves induces wound-inducible proteinase inhibitor proteins. Science. 1991 Aug 23;253(5022):895–897. doi: 10.1126/science.253.5022.895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pēna-Cortés H., Sánchez-Serrano J. J., Mertens R., Willmitzer L., Prat S. Abscisic acid is involved in the wound-induced expression of the proteinase inhibitor II gene in potato and tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9851–9855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan C. A. Quantitative determination of soluble cellular proteins by radial diffusion in agar gels containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jun;19(3):434–440. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Berger A. On the size of the active site in proteases. I. Papain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 20;27(2):157–162. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Smeekens S. P., Ohagi S., Chan S. J. The new enzymology of precursor processing endoproteases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23435–23438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautman R., Cowan K. M., Wagner G. G. Data processing for radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1971 Oct;8(10):901–916. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90429-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Nakagawa T., Ikemizu J., Nagahama M., Murakami K., Nakayama K. Sequence requirements for precursor cleavage within the constitutive secretory pathway. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8270–8274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Uemura M., Niki T., Sakai A., Gusta L. V. Partition of membrane particles in aqueous two-polymer phase system and its practical use for purification of plasma membranes from plants. Plant Physiol. 1983 May;72(1):105–114. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]