Abstract
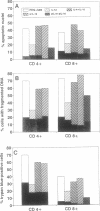
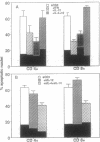
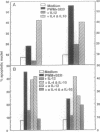
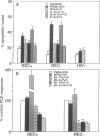
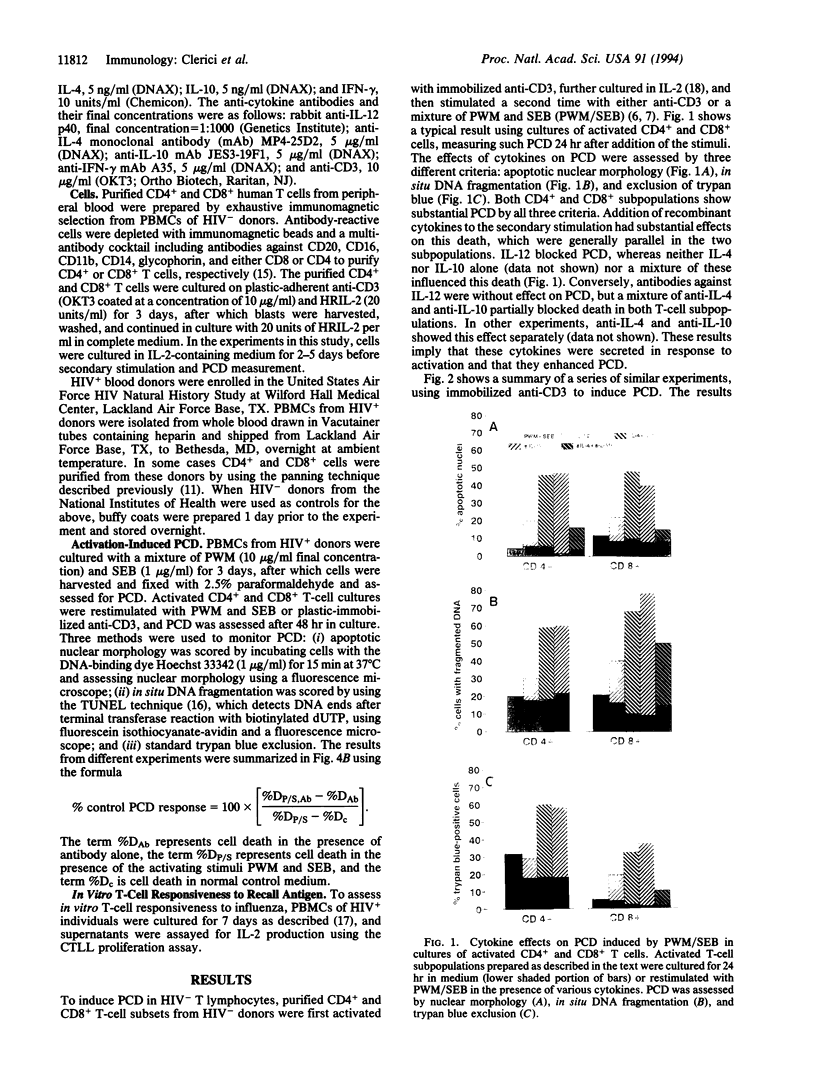
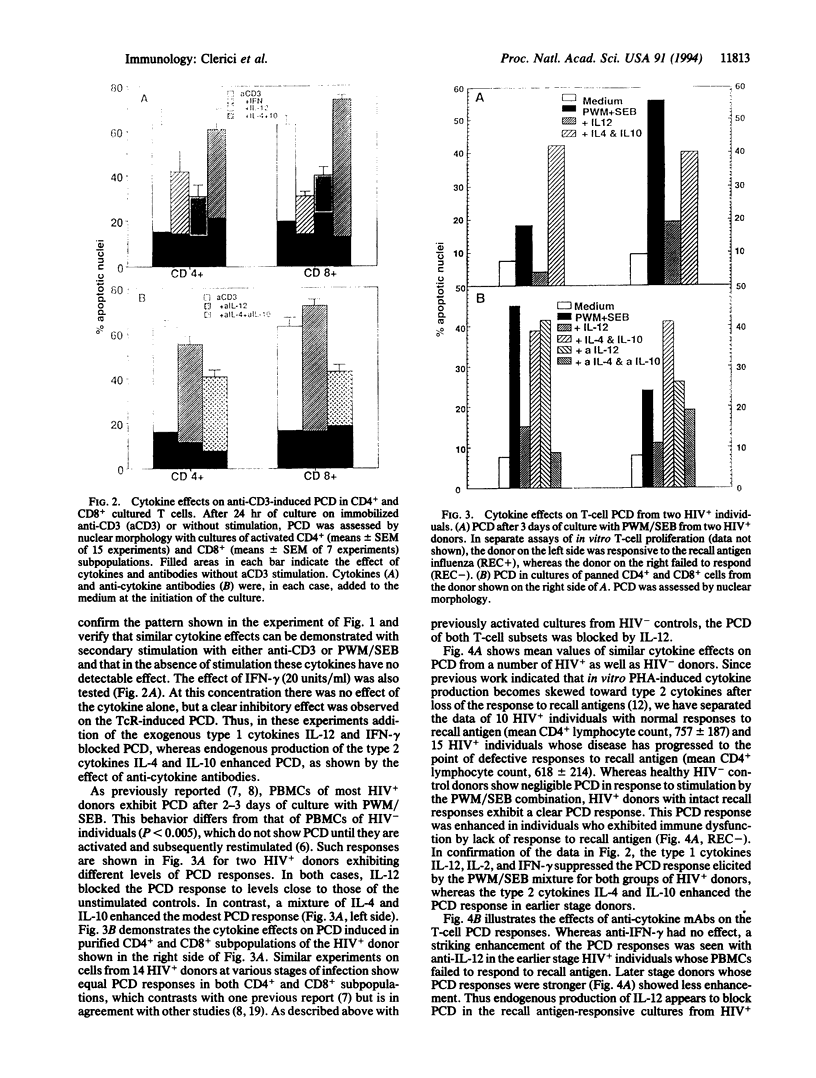
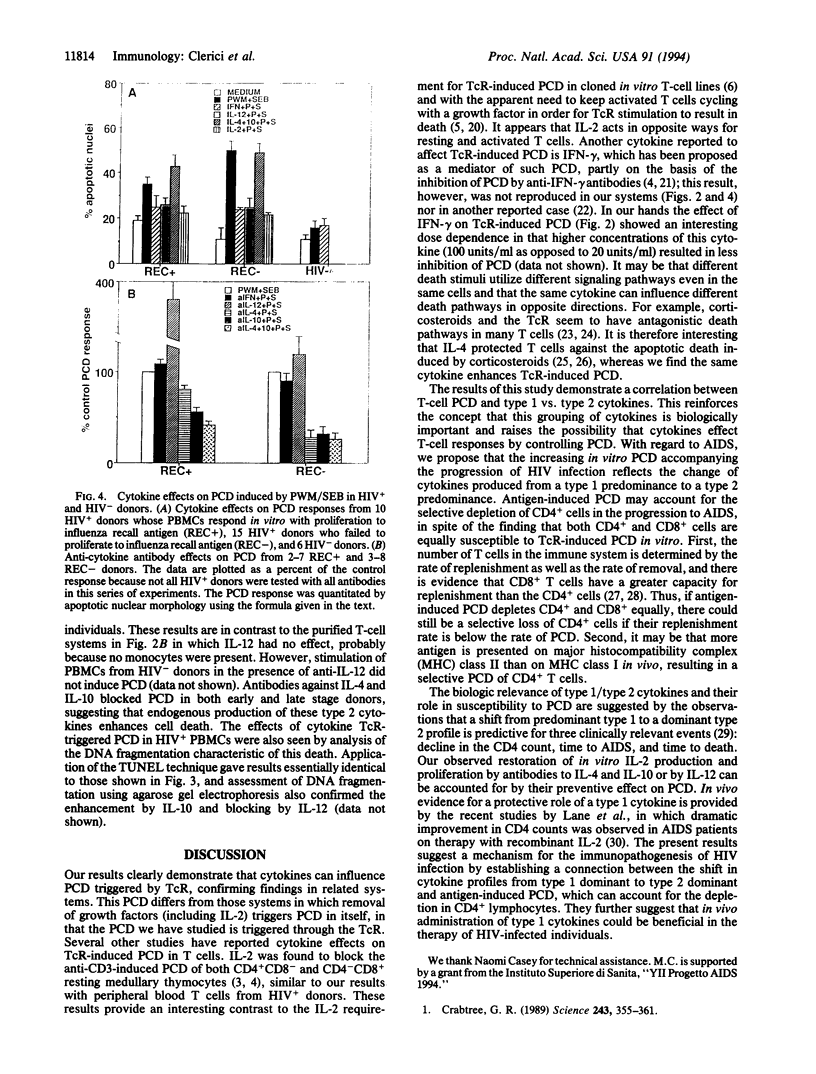
In vitro T-cell receptor-induced programmed cell death in both activated T cells from human immunodeficiency virus-seronegative (HIV-) donors and resting T cells from HIV+ donors was substantially influenced by cytokines. Addition of exogenous recombinant "type 1" lymphokines interferon gamma and interleukin 2 (IL-2), as well as the macrophage-produced IL-12, which favor cell-mediated T-cell responses, blocks both systems of T-lymphocyte programmed cell death. In contrast, the "type 2" lymphokines IL-4 and IL-10, which favor antibody responses, either had no effect or enhanced these systems of in vitro T-cell programmed cell death. A role for endogenously produced cytokines was suggested by the inhibition of T-cell receptor-mediated death by antibodies against IL-4 and IL-10 and its enhancement by anti-IL-12 in cultures containing monocytes. These results demonstrate that the functional properties of type 1 and type 2 cytokine classes may be further extended to include their effects on T-cell programmed cell death and their possible role in the pathogenesis of HIV infection.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ameisen J. C., Capron A. Cell dysfunction and depletion in AIDS: the programmed cell death hypothesis. Immunol Today. 1991 Apr;12(4):102–105. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson K., Hansen J. A., Storb R., Goehle S., Goldstein G., Thomas E. D. T-cell subpopulations identified by monoclonal antibodies after human marrow transplantation. I. Helper-inducer and cytotoxic-suppressor subsets. Blood. 1982 Jun;59(6):1292–1298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerici M., Hakim F. T., Venzon D. J., Blatt S., Hendrix C. W., Wynn T. A., Shearer G. M. Changes in interleukin-2 and interleukin-4 production in asymptomatic, human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive individuals. J Clin Invest. 1993 Mar;91(3):759–765. doi: 10.1172/JCI116294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerici M., Lucey D. R., Berzofsky J. A., Pinto L. A., Wynn T. A., Blatt S. P., Dolan M. J., Hendrix C. W., Wolf S. F., Shearer G. M. Restoration of HIV-specific cell-mediated immune responses by interleukin-12 in vitro. Science. 1993 Dec 10;262(5140):1721–1724. doi: 10.1126/science.7903123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerici M., Shearer G. M. A TH1-->TH2 switch is a critical step in the etiology of HIV infection. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerici M., Stocks N. I., Zajac R. A., Boswell R. N., Lucey D. R., Via C. S., Shearer G. M. Detection of three distinct patterns of T helper cell dysfunction in asymptomatic, human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive patients. Independence of CD4+ cell numbers and clinical staging. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1892–1899. doi: 10.1172/JCI114376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerici M., Wynn T. A., Berzofsky J. A., Blatt S. P., Hendrix C. W., Sher A., Coffman R. L., Shearer G. M. Role of interleukin-10 in T helper cell dysfunction in asymptomatic individuals infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Clin Invest. 1994 Feb;93(2):768–775. doi: 10.1172/JCI117031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R. Contingent genetic regulatory events in T lymphocyte activation. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):355–361. doi: 10.1126/science.2783497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. Multifactorial nature of human immunodeficiency virus disease: implications for therapy. Science. 1993 Nov 12;262(5136):1011–1018. doi: 10.1126/science.8235617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavrieli Y., Sherman Y., Ben-Sasson S. A. Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):493–501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gougeon M. L., Garcia S., Heeney J., Tschopp R., Lecoeur H., Guetard D., Rame V., Dauguet C., Montagnier L. Programmed cell death in AIDS-related HIV and SIV infections. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 Jun;9(6):553–563. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groux H., Monte D., Plouvier B., Capron A., Ameisen J. C. CD3-mediated apoptosis of human medullary thymocytes and activated peripheral T cells: respective roles of interleukin-1, interleukin-2, interferon-gamma and accessory cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jul;23(7):1623–1629. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groux H., Torpier G., Monté D., Mouton Y., Capron A., Ameisen J. C. Activation-induced death by apoptosis in CD4+ T cells from human immunodeficiency virus-infected asymptomatic individuals. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):331–340. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horgan K. J., Van Seventer G. A., Shimizu Y., Shaw S. Hyporesponsiveness of "naive" (CD45RA+) human T cells to multiple receptor-mediated stimuli but augmentation of responses by co-stimuli. Eur J Immunol. 1990 May;20(5):1111–1118. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata M., Hanaoka S., Sato K. Rescue of thymocytes and T cell hybridomas from glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis by stimulation via the T cell receptor/CD3 complex: a possible in vitro model for positive selection of the T cell repertoire. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Mar;21(3):643–648. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabelitz D., Pohl T., Pechhold K. Activation-induced cell death (apoptosis) of mature peripheral T lymphocytes. Immunol Today. 1993 Jul;14(7):338–339. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leino L., Lilius E. M., Nikoskelainen J., Pelliniemi T. T., Rajamäki A. The reappearance of 10 differentiation antigens on peripheral blood lymphocytes after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1991 Nov;8(5):339–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J. Interleukin-2 programs mouse alpha beta T lymphocytes for apoptosis. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):858–861. doi: 10.1038/353858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Janeway C. A., Jr Interferon gamma plays a critical role in induced cell death of effector T cell: a possible third mechanism of self-tolerance. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1735–1739. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucey D. R., Melcher G. P., Hendrix C. W., Zajac R. A., Goetz D. W., Butzin C. A., Clerici M., Warner R. D., Abbadessa S., Hall K. Human immunodeficiency virus infection in the US Air Force: seroconversions, clinical staging, and assessment of a T helper cell functional assay to predict change in CD4+ T cell counts. J Infect Dis. 1991 Oct;164(4):631–637. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.4.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyaard L., Otto S. A., Jonker R. R., Mijnster M. J., Keet R. P., Miedema F. Programmed death of T cells in HIV-1 infection. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):217–219. doi: 10.1126/science.1352911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Migliorati G., Nicoletti I., Pagliacci M. C., D'Adamio L., Riccardi C. Interleukin-4 protects double-negative and CD4 single-positive thymocytes from dexamethasone-induced apoptosis. Blood. 1993 Mar 1;81(5):1352–1358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieto M. A., González A., López-Rivas A., Diaz-Espada F., Gambón F. IL-2 protects against anti-CD3-induced cell death in human medullary thymocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 1;145(5):1364–1368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., Rush B. J., Abrams S. I., Wang R. Sensitivity of T cells to anti-CD3-stimulated suicide is independent of functional phenotype. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jun;22(6):1655–1658. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., White C. L., Loh D. Y., Meleedy-Rey P. Receptor-stimulated death pathway is opened by antigen in mature T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2151–2155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin A., Adams D. H., Henkart P. A. Protease inhibitors selectively block T cell receptor-triggered programmed cell death in a murine T cell hybridoma and activated peripheral T cells. J Exp Med. 1993 Nov 1;178(5):1693–1700. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. IL-12: initiation cytokine for cell-mediated immunity. Science. 1993 Apr 23;260(5107):496–497. doi: 10.1126/science.8097337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Williams G. T., Kingston R., Jenkinson E. J., Owen J. J. Antibodies to CD3/T-cell receptor complex induce death by apoptosis in immature T cells in thymic cultures. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):181–184. doi: 10.1038/337181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharchuk C. M., Merćep M., Chakraborti P. K., Simons S. S., Jr, Ashwell J. D. Programmed T lymphocyte death. Cell activation- and steroid-induced pathways are mutually antagonistic. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 15;145(12):4037–4045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubiaga A. M., Munoz E., Huber B. T. IL-4 and IL-2 selectively rescue Th cell subsets from glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 1;149(1):107–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]