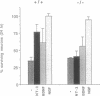
Abstract
Neurotrophin 3 (NT-3) is one of four related polypeptide growth factors that share structural and functional homology to nerve growth factor (NGF). NT-3 and its receptor, called neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 3 (Ntrk3; also called TrkC), are expressed early and throughout embryogenesis. We have inactivated the NT-3 gene in embryonic stem (ES) cells by homologous recombination. The mutated allele has been transmitted through the mouse germ line, and heterozygote intercrosses have yielded homozygous mutant newborn pups. The NT-3-deficient mutants fail to thrive and exhibit severe neurological dysfunction. Analysis of mutant embryos uncovers loss of Ntrk3/TrkC-expressing sensory neurons and abnormalities at early stages of sensory neuronal development. NT-3-deficient mice will permit further study of the role of this neurotrophin in neural development.
Full text
PDF

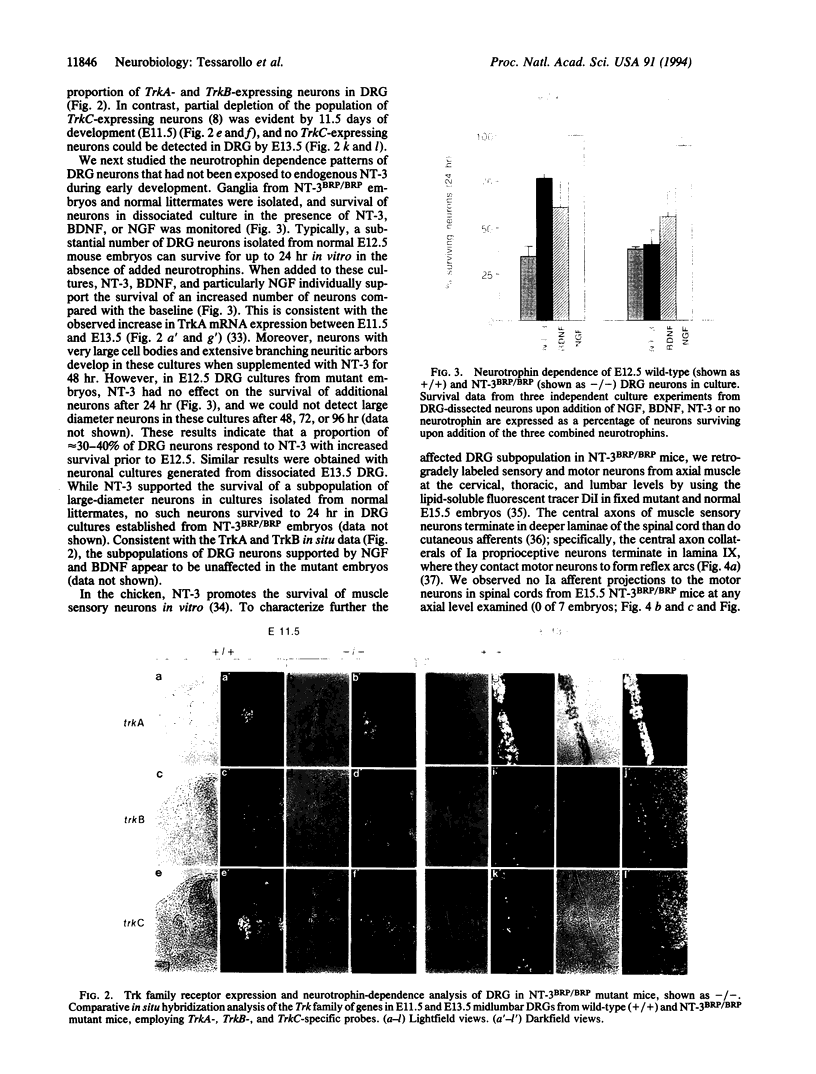

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arenas E., Persson H. Neurotrophin-3 prevents the death of adult central noradrenergic neurons in vivo. Nature. 1994 Jan 27;367(6461):368–371. doi: 10.1038/367368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Averbuch-Heller L., Pruginin M., Kahane N., Tsoulfas P., Parada L., Rosenthal A., Kalcheim C. Neurotrophin 3 stimulates the differentiation of motoneurons from avian neural tube progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3247–3251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbacid M. Nerve growth factor: a tale of two receptors. Oncogene. 1993 Aug;8(8):2033–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barde Y. A. The nerve growth factor family. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1990;2(4):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0955-2235(90)90021-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A., Raff M. C., Gaese F., Bartke I., Dechant G., Barde Y. A. A crucial role for neurotrophin-3 in oligodendrocyte development. Nature. 1994 Jan 27;367(6461):371–375. doi: 10.1038/367371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A., Schmid R., Sendnter M., Raff M. C. Multiple extracellular signals are required for long-term oligodendrocyte survival. Development. 1993 May;118(1):283–295. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkemeier L. R., Winslow J. W., Kaplan D. R., Nikolics K., Goeddel D. V., Rosenthal A. Neurotrophin-5: a novel neurotrophic factor that activates trk and trkB. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):857–866. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90287-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birren S. J., Lo L., Anderson D. J. Sympathetic neuroblasts undergo a developmental switch in trophic dependence. Development. 1993 Nov;119(3):597–610. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.3.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao M. V. Neurotrophin receptors: a window into neuronal differentiation. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):583–593. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Tapley P., Jing S. Q., Nanduri V., O'Rourke E., Lamballe F., Kovary K., Klein R., Jones K. R., Reichardt L. F. The trk tyrosine protein kinase mediates the mitogenic properties of nerve growth factor and neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):173–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90149-s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley C., Spencer S. D., Nishimura M. C., Chen K. S., Pitts-Meek S., Armanini M. P., Ling L. H., McMahon S. B., Shelton D. L., Levinson A. D. Mice lacking nerve growth factor display perinatal loss of sensory and sympathetic neurons yet develop basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1001–1011. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90378-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dechant G., Rodríguez-Tébar A., Kolbeck R., Barde Y. A. Specific high-affinity receptors for neurotrophin-3 on sympathetic neurons. J Neurosci. 1993 Jun;13(6):2610–2616. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-06-02610.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCicco-Bloom E., Friedman W. J., Black I. B. NT-3 stimulates sympathetic neuroblast proliferation by promoting precursor survival. Neuron. 1993 Dec;11(6):1101–1111. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90223-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernfors P., Lee K. F., Jaenisch R. Mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor develop with sensory deficits. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):147–150. doi: 10.1038/368147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernfors P., Lee K. F., Kucera J., Jaenisch R. Lack of neurotrophin-3 leads to deficiencies in the peripheral nervous system and loss of limb proprioceptive afferents. Cell. 1994 May 20;77(4):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90213-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fariñas I., Jones K. R., Backus C., Wang X. Y., Reichardt L. F. Severe sensory and sympathetic deficits in mice lacking neurotrophin-3. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):658–661. doi: 10.1038/369658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson C. E., Camu W., Mettling C., Gouin A., Poulsen K., Karihaloo M., Rullamas J., Evans T., McMahon S. B., Armanini M. P. Neurotrophins promote motor neuron survival and are present in embryonic limb bud. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):266–270. doi: 10.1038/363266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hory-Lee F., Russell M., Lindsay R. M., Frank E. Neurotrophin 3 supports the survival of developing muscle sensory neurons in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2613–2617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip N. Y., Ibáez C. F., Nye S. H., McClain J., Jones P. F., Gies D. R., Belluscio L., Le Beau M. M., Espinosa R., 3rd, Squinto S. P. Mammalian neurotrophin-4: structure, chromosomal localization, tissue distribution, and receptor specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3060–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. R., Fariñas I., Backus C., Reichardt L. F. Targeted disruption of the BDNF gene perturbs brain and sensory neuron development but not motor neuron development. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):989–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90377-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalcheim C., Carmeli C., Rosenthal A. Neurotrophin 3 is a mitogen for cultured neural crest cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1661–1665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Nanduri V., Jing S. A., Lamballe F., Tapley P., Bryant S., Cordon-Cardo C., Jones K. R., Reichardt L. F., Barbacid M. The trkB tyrosine protein kinase is a receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90628-c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Silos-Santiago I., Smeyne R. J., Lira S. A., Brambilla R., Bryant S., Zhang L., Snider W. D., Barbacid M. Disruption of the neurotrophin-3 receptor gene trkC eliminates la muscle afferents and results in abnormal movements. Nature. 1994 Mar 17;368(6468):249–251. doi: 10.1038/368249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R., Smeyne R. J., Wurst W., Long L. K., Auerbach B. A., Joyner A. L., Barbacid M. Targeted disruption of the trkB neurotrophin receptor gene results in nervous system lesions and neonatal death. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):113–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsching S. The neurotrophic factor concept: a reexamination. J Neurosci. 1993 Jul;13(7):2739–2748. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-07-02739.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamballe F., Klein R., Barbacid M. trkC, a new member of the trk family of tyrosine protein kinases, is a receptor for neurotrophin-3. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):967–979. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1154–1162. doi: 10.1126/science.3306916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisonpierre P. C., Belluscio L., Squinto S., Ip N. Y., Furth M. E., Lindsay R. M., Yancopoulos G. D. Neurotrophin-3: a neurotrophic factor related to NGF and BDNF. Science. 1990 Mar 23;247(4949 Pt 1):1446–1451. doi: 10.1126/science.247.4949.1446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Zanca D., Barbacid M., Parada L. F. Expression of the trk proto-oncogene is restricted to the sensory cranial and spinal ganglia of neural crest origin in mouse development. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):683–694. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlio J. P., Ernfors P., Jaber M., Persson H. Molecular cloning of rat trkC and distribution of cells expressing messenger RNAs for members of the trk family in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1992 Dec;51(3):513–532. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90292-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruit K. G., Elliott J. L., Osborne P. A., Yan Q., Snider W. D. Selective dependence of mammalian dorsal root ganglion neurons on nerve growth factor during embryonic development. Neuron. 1992 Mar;8(3):573–587. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90284-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell L., Schneider R., Kolbeck R., Barde Y. A., Schwab M. E. Neurotrophin-3 enhances sprouting of corticospinal tract during development and after adult spinal cord lesion. Nature. 1994 Jan 13;367(6459):170–173. doi: 10.1038/367170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sendtner M., Holtmann B., Kolbeck R., Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor prevents the death of motoneurons in newborn rats after nerve section. Nature. 1992 Dec 24;360(6406):757–759. doi: 10.1038/360757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeyne R. J., Klein R., Schnapp A., Long L. K., Bryant S., Lewin A., Lira S. A., Barbacid M. Severe sensory and sympathetic neuropathies in mice carrying a disrupted Trk/NGF receptor gene. Nature. 1994 Mar 17;368(6468):246–249. doi: 10.1038/368246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soppet D., Escandon E., Maragos J., Middlemas D. S., Reid S. W., Blair J., Burton L. E., Stanton B. R., Kaplan D. R., Hunter T. The neurotrophic factors brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 are ligands for the trkB tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):895–903. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90396-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Montgomery C., Geske R., Bradley A. Targeted disruption of the c-src proto-oncogene leads to osteopetrosis in mice. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):693–702. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90499-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squinto S. P., Stitt T. N., Aldrich T. H., Davis S., Bianco S. M., Radziejewski C., Glass D. J., Masiakowski P., Furth M. E., Valenzuela D. M. trkB encodes a functional receptor for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 but not nerve growth factor. Cell. 1991 May 31;65(5):885–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90395-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swiatek P. J., Gridley T. Perinatal lethality and defects in hindbrain development in mice homozygous for a targeted mutation of the zinc finger gene Krox20. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2071–2084. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessarollo L., Tsoulfas P., Martin-Zanca D., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Parada L. F. trkC, a receptor for neurotrophin-3, is widely expressed in the developing nervous system and in non-neuronal tissues. Development. 1993 Jun;118(2):463–475. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.2.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsoulfas P., Soppet D., Escandon E., Tessarollo L., Mendoza-Ramirez J. L., Rosenthal A., Nikolics K., Parada L. F. The rat trkC locus encodes multiple neurogenic receptors that exhibit differential response to neurotrophin-3 in PC12 cells. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):975–990. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90212-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela D. M., Maisonpierre P. C., Glass D. J., Rojas E., Nuñez L., Kong Y., Gies D. R., Stitt T. N., Ip N. Y., Yancopoulos G. D. Alternative forms of rat TrkC with different functional capabilities. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):963–974. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]