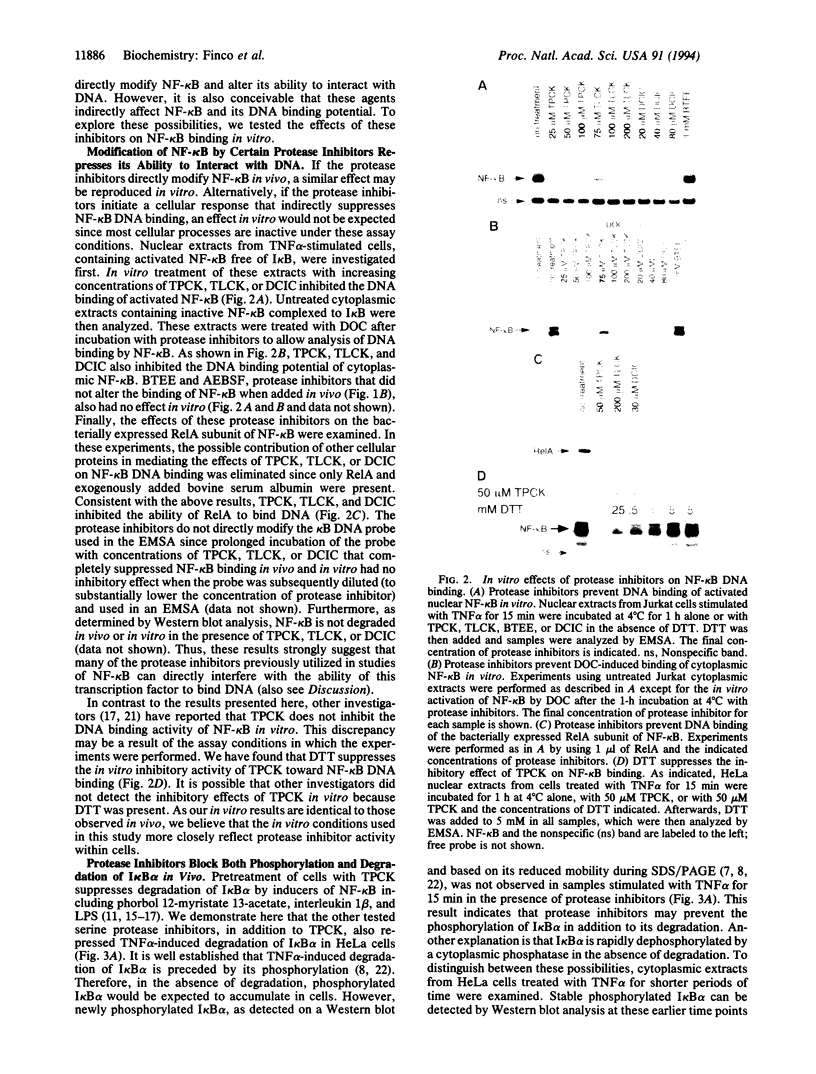
Abstract
The ubiquitous transcription factor NF-kappa B is regulated by its cytoplasmic inhibitor I kappa B. A variety of cellular stimuli cause the dissociation of NF-kappa B from I kappa B, allowing NF-kappa B to translocate to the nucleus and regulate gene expression. Although the activation of NF-kappa B in vivo is associated with the phosphorylation and degradation of I kappa B alpha, it has remained unclear how each of these events contributes to this process. Recently, studies utilizing protease inhibitors have suggested that the proteolysis of I kappa B alpha is a necessary event in the activation of NF-kappa B. We demonstrate in this study that these and an additional protease inhibitor also completely repress inducible phosphorylation of I kappa B alpha. This surprising result suggests a more complex role of proteases in NF-kappa B activation. In addition, data presented here indicate that many of these inhibitors also directly modify NF-kappa B and inhibit its DNA binding activity. Due to the pleiotropic effects of these protease inhibitors, it is difficult to conclude from their use how I kappa B alpha phosphorylation and degradation contribute to NF-kappa B activation. In the present study, a more direct approach demonstrates that phosphorylation of I kappa B alpha alone is not sufficient for NF-kappa B activation.
Full text
PDF
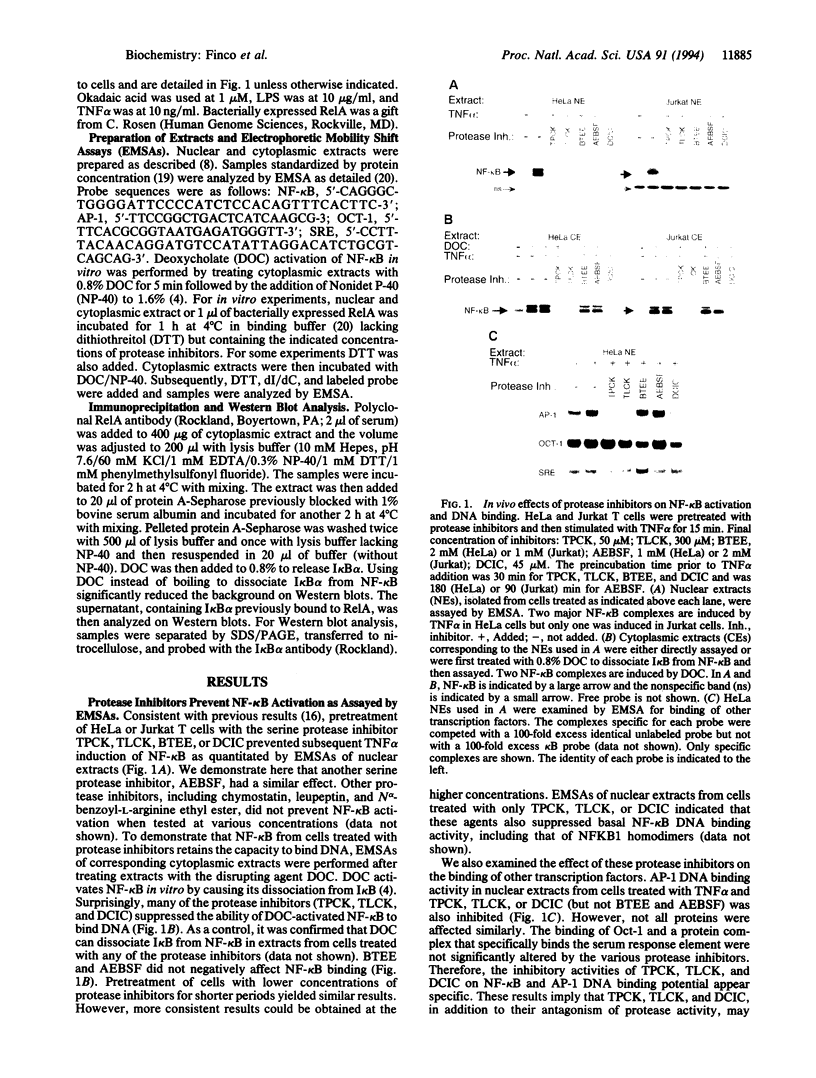


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Finco T. S., Nantermet P. V., Baldwin A. S., Jr Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 lead to phosphorylation and loss of I kappa B alpha: a mechanism for NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3301–3310. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K., Park S., Kanno T., Franzoso G., Siebenlist U. Mutual regulation of the transcriptional activator NF-kappa B and its inhibitor, I kappa B-alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2532–2536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiao P. J., Miyamoto S., Verma I. M. Autoregulation of I kappa B alpha activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):28–32. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordle S. R., Donald R., Read M. A., Hawiger J. Lipopolysaccharide induces phosphorylation of MAD3 and activation of c-Rel and related NF-kappa B proteins in human monocytic THP-1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11803–11810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromlish J. A., Roeder R. G. Human transcription factor IIIC (TFIIIC). Purification, polypeptide structure, and the involvement of thiol groups in specific DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18100–18109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djaballah H., Harness J. A., Savory P. J., Rivett A. J. Use of serine-protease inhibitors as probes for the different proteolytic activities of the rat liver multicatalytic proteinase complex. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 15;209(2):629–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. Generation of p50 subunit of NF-kappa B by processing of p105 through an ATP-dependent pathway. Nature. 1991 Dec 5;354(6352):395–398. doi: 10.1038/354395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. J., Koizumi S., Kondoh A., Mariano J. M., Mavrothalassitis G., Bhat N. K., Papas T. S. Human ETS1 oncoprotein. Purification, isoforms, -SH modification, and DNA sequence-specific binding. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17957–17965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Hemmi K., Powers J. C. Reaction of serine proteases with substituted isocoumarins: discovery of 3,4-dichloroisocoumarin, a new general mechanism based serine protease inhibitor. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 9;24(8):1831–1841. doi: 10.1021/bi00329a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskill S., Beg A. A., Tompkins S. M., Morris J. S., Yurochko A. D., Sampson-Johannes A., Mondal K., Ralph P., Baldwin A. S., Jr Characterization of an immediate-early gene induced in adherent monocytes that encodes I kappa B-like activity. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1281–1289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90022-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel T., Machleidt T., Alkalay I., Krönke M., Ben-Neriah Y., Baeuerle P. A. Rapid proteolysis of I kappa B-alpha is necessary for activation of transcription factor NF-kappa B. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):182–185. doi: 10.1038/365182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bail O., Schmidt-Ullrich R., Israël A. Promoter analysis of the gene encoding the I kappa B-alpha/MAD3 inhibitor of NF-kappa B: positive regulation by members of the rel/NF-kappa B family. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5043–5049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06197.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machleidt T., Wiegmann K., Henkel T., Schütze S., Baeuerle P., Krönke M. Sphingomyelinase activates proteolytic I kappa B-alpha degradation in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):13760–13765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews J. R., Wakasugi N., Virelizier J. L., Yodoi J., Hay R. T. Thioredoxin regulates the DNA binding activity of NF-kappa B by reduction of a disulphide bond involving cysteine 62. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):3821–3830. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Hay R. T., Goodbourn S. Proteolytic degradation of MAD3 (I kappa B alpha) and enhanced processing of the NF-kappa B precursor p105 are obligatory steps in the activation of NF-kappa B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 11;21(22):5059–5066. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.22.5059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto S., Chiao P. J., Verma I. M. Enhanced I kappa B alpha degradation is responsible for constitutive NF-kappa B activity in mature murine B-cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3276–3282. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Michaud C. Pituitary multicatalytic proteinase complex. Specificity of components and aspects of proteolytic activity. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9270–9278. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palombella V. J., Rando O. J., Goldberg A. L., Maniatis T. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is required for processing the NF-kappa B1 precursor protein and the activation of NF-kappa B. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):773–785. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90482-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusbridge N. M., Beynon R. J. 3,4-Dichloroisocoumarin, a serine protease inhibitor, inactivates glycogen phosphorylase b. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 30;268(1):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80991-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. L., Fujita T., Liou H. C., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. The p65 subunit of NF-kappa B regulates I kappa B by two distinct mechanisms. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1266–1276. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Mizel S. B. In vitro activation and nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B catalyzed by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2424–2430. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. C., Ganchi P. A., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. NF-kappa B controls expression of inhibitor I kappa B alpha: evidence for an inducible autoregulatory pathway. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1912–1915. doi: 10.1126/science.8096091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun S. C., Ganchi P. A., Béraud C., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. Autoregulation of the NF-kappa B transactivator RelA (p65) by multiple cytoplasmic inhibitors containing ankyrin motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Feb 15;91(4):1346–1350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.4.1346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thévenin C., Kim S. J., Rieckmann P., Fujiki H., Norcross M. A., Sporn M. B., Fauci A. S., Kehrl J. H. Induction of nuclear factor-kappa B and the human immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat by okadaic acid, a specific inhibitor of phosphatases 1 and 2A. New Biol. 1990 Sep;2(9):793–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledano M. B., Leonard W. J. Modulation of transcription factor NF-kappa B binding activity by oxidation-reduction in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4328–4332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martin R., Vanhove B., Cheng Q., Hofer E., Csizmadia V., Winkler H., Bach F. H. Cytokine-inducible expression in endothelial cells of an I kappa B alpha-like gene is regulated by NF kappa B. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2773–2779. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]