Abstract
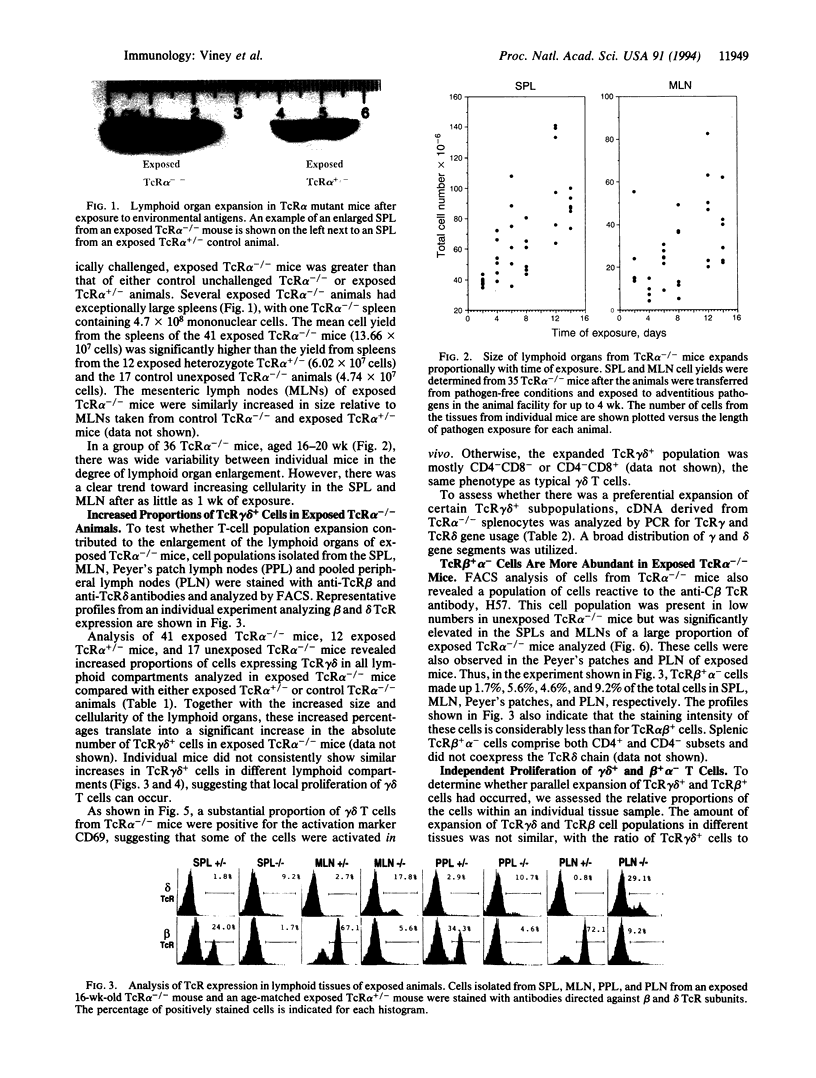
In mice and humans, T cells are characterized on the basis of T-cell receptor (TcR) expression and divided into the major TcR alpha beta + and minor TcR gamma delta + populations. TcR alpha beta + cells are considered to be the primary regulators of the immune response, whereas the function of TcR gamma delta + cells is unclear. Mice congenitally deficient in TcR alpha beta-expressing cells provide an ideal model for analyzing the independent in vivo function of TcR gamma delta + cells in the absence of TcR alpha beta + cells. Here we report that lymphoid organs in TcR alpha mutant mice undergo substantial enlargement after being challenged by environmental antigens. This organ expansion can be attributed in part to increases in the relative proportions and absolute numbers of TcR gamma delta + cells, but an expansion of the recently described TcR beta + alpha - population also has a role. The expansion of the TcR gamma delta + population is polyclonal, as evidenced by the usage of multiple gamma and delta variable chain segments. Furthermore, a substantial proportion of the cells appears to be activated and these activated cells express surface activation markers. The results clearly demonstrate that TcR gamma delta + cells proliferate independently in response to a broad spectrum of challenges. Moreover, since the expansion of the lymphoid tissues and the TcR gamma delta + cell population is excessive relative to that seen in wild-type animals, one role of TcR alpha beta + cells is directly or indirectly to limit the responses of the other lymphoid components.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. P., Havran W. L. The immunobiology of T cells with invariant gamma delta antigen receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:679–705. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.003335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arstila T. P., Toivanen P., Lassila O. Helper activity of CD4+ alpha beta T cells is required for the avian gamma delta T cell response. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Aug;23(8):2034–2037. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Born W., Hall L., Dallas A., Boymel J., Shinnick T., Young D., Brennan P., O'Brien R. Recognition of a peptide antigen by heat shock--reactive gamma delta T lymphocytes. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):67–69. doi: 10.1126/science.1695022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone A., Harbeck R., Dallas A., Nemazee D., Finkel T., O'Brien R., Kubo R., Born W. Alpha beta T-lymphocyte depleted mice, a model for gamma delta T-lymphocyte functional studies. Immunol Rev. 1991 Apr;120:35–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassell D., Forman J. Two roles for CD4 cells in the control of the generation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):3–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobbold S. P., Qin S., Leong L. Y., Martin G., Waldmann H. Reprogramming the immune system for peripheral tolerance with CD4 and CD8 monoclonal antibodies. Immunol Rev. 1992 Oct;129:165–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1992.tb01423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove D., Gray D., Dierich A., Kaufman J., Lemeur M., Benoist C., Mathis D. Mice lacking MHC class II molecules. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):1051–1066. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90448-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson P. O., Hansson J., Widegren B., Dohlsten M., Sjögren H. O., Hedlund G. In vivo induction of gamma/delta T cells with highly potent and selective anti-tumor cytotoxicity. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Nov;21(11):2797–2802. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayolle C., Deriaud E., Leclerc C. In vivo induction of cytotoxic T cell response by a free synthetic peptide requires CD4+ T cell help. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4069–4073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groettrup M., Baron A., Griffiths G., Palacios R., von Boehmer H. T cell receptor (TCR) beta chain homodimers on the surface of immature but not mature alpha, gamma, delta chain deficient T cell lines. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2735–2745. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05339.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grusby M. J., Johnson R. S., Papaioannou V. E., Glimcher L. H. Depletion of CD4+ T cells in major histocompatibility complex class II-deficient mice. Science. 1991 Sep 20;253(5026):1417–1420. doi: 10.1126/science.1910207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerder S., Matzinger P. A fail-safe mechanism for maintaining self-tolerance. J Exp Med. 1992 Aug 1;176(2):553–564. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.2.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromatsu K., Yoshikai Y., Matsuzaki G., Ohga S., Muramori K., Matsumoto K., Bluestone J. A., Nomoto K. A protective role of gamma/delta T cells in primary infection with Listeria monocytogenes in mice. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):49–56. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa Y., Shimizu H., Yoshida M., Takaya M., Arimori S. T cells bearing gamma/delta T cell receptor and their expression of activation antigen in peripheral blood from patients with Sjögren's syndrome. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1991 Nov-Dec;9(6):603–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itohara S., Farr A. G., Lafaille J. J., Bonneville M., Takagaki Y., Haas W., Tonegawa S. Homing of a gamma delta thymocyte subset with homogeneous T-cell receptors to mucosal epithelia. Nature. 1990 Feb 22;343(6260):754–757. doi: 10.1038/343754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janis E. M., Kaufmann S. H., Schwartz R. H., Pardoll D. M. Activation of gamma delta T cells in the primary immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science. 1989 May 12;244(4905):713–716. doi: 10.1126/science.2524098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen-Kragh J., Quayle A. J., Skålhegg B. S., Sioud M., Førre O. Selective activation of resting human gamma delta T lymphocytes by interleukin-2. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Sep;23(9):2092–2099. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyes S., Carew E., Carding S. R., Janeway C. A., Jr, Hayday A. Diversity in T-cell receptor gamma gene usage in intestinal epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5527–5531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombaerts P., Arnoldi J., Russ F., Tonegawa S., Kaufmann S. H. Different roles of alpha beta and gamma delta T cells in immunity against an intracellular bacterial pathogen. Nature. 1993 Sep 2;365(6441):53–56. doi: 10.1038/365053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombaerts P., Clarke A. R., Rudnicki M. A., Iacomini J., Itohara S., Lafaille J. J., Wang L., Ichikawa Y., Jaenisch R., Hooper M. L. Mutations in T-cell antigen receptor genes alpha and beta block thymocyte development at different stages. Nature. 1992 Nov 19;360(6401):225–231. doi: 10.1038/360225a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombaerts P., Mizoguchi E., Grusby M. J., Glimcher L. H., Bhan A. K., Tonegawa S. Spontaneous development of inflammatory bowel disease in T cell receptor mutant mice. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):274–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80069-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. L., Happ M. P., Dallas A., Palmer E., Kubo R., Born W. K. Stimulation of a major subset of lymphocytes expressing T cell receptor gamma delta by an antigen derived from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philpott K. L., Viney J. L., Kay G., Rastan S., Gardiner E. M., Chae S., Hayday A. C., Owen M. J. Lymphoid development in mice congenitally lacking T cell receptor alpha beta-expressing cells. Science. 1992 Jun 5;256(5062):1448–1452. doi: 10.1126/science.1604321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahemtulla A., Fung-Leung W. P., Schilham M. W., Kündig T. M., Sambhara S. R., Narendran A., Arabian A., Wakeham A., Paige C. J., Zinkernagel R. M. Normal development and function of CD8+ cells but markedly decreased helper cell activity in mice lacking CD4. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):180–184. doi: 10.1038/353180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajasekar R., Sim G. K., Augustin A. Self heat shock and gamma delta T-cell reactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1767–1771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H. The structure, function, and molecular genetics of the gamma/delta T cell receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:175–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorle H., Holtschke T., Hünig T., Schimpl A., Horak I. Development and function of T cells in mice rendered interleukin-2 deficient by gene targeting. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):621–624. doi: 10.1038/352621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeen M. J., Ziegler H. K. Intercellular interactions and cytokine responsiveness of peritoneal alpha/beta and gamma/delta T cells from Listeria-infected mice: synergistic effects of interleukin 1 and 7 on gamma/delta T cells. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):985–996. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidovic D., Dembic Z. Qa-1 restricted gamma delta T cells can help B cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;173:239–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen L., Roberts S. J., Viney J. L., Wong F. S., Mallick C., Findly R. C., Peng Q., Craft J. E., Owen M. J., Hayday A. C. Immunoglobulin synthesis and generalized autoimmunity in mice congenitally deficient in alpha beta(+) T cells. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):654–658. doi: 10.1038/369654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



