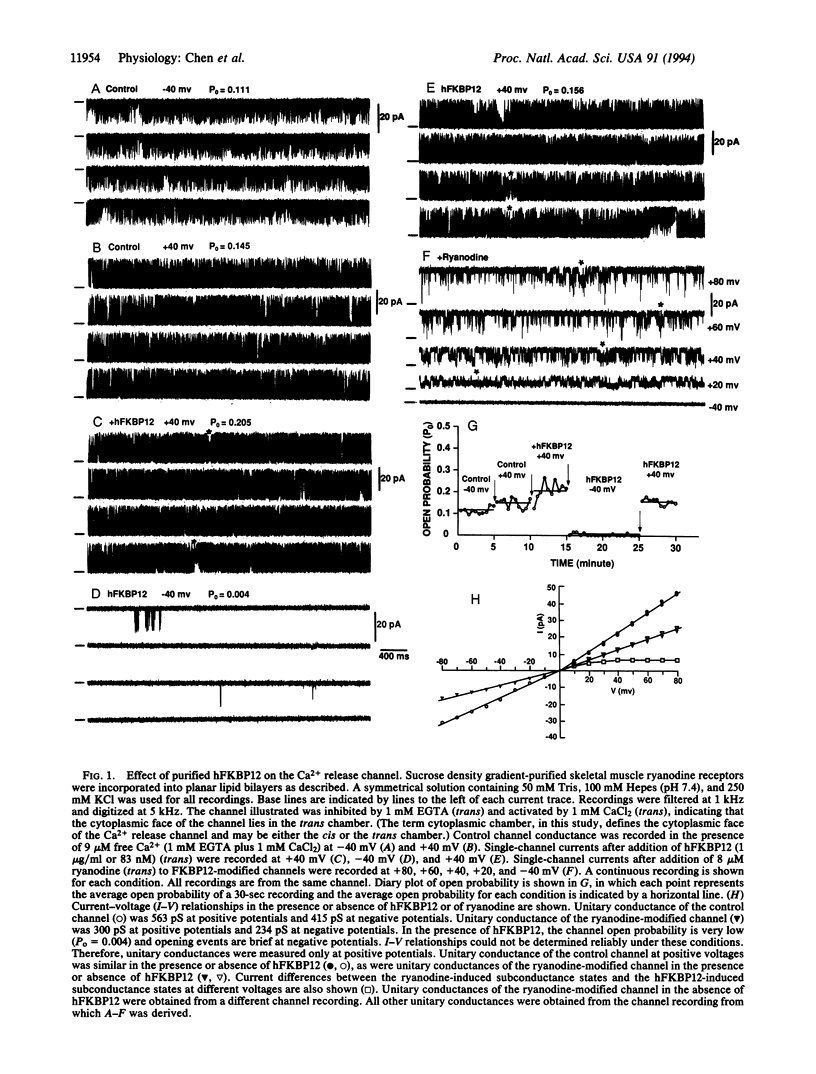
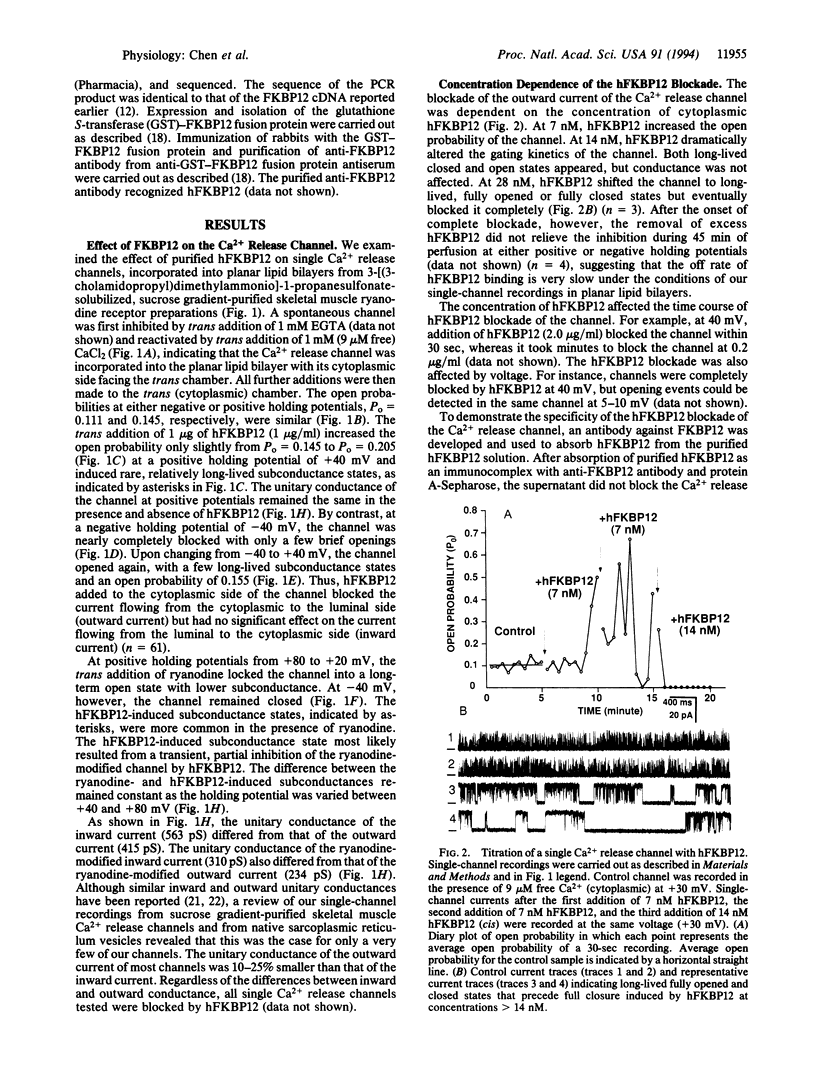
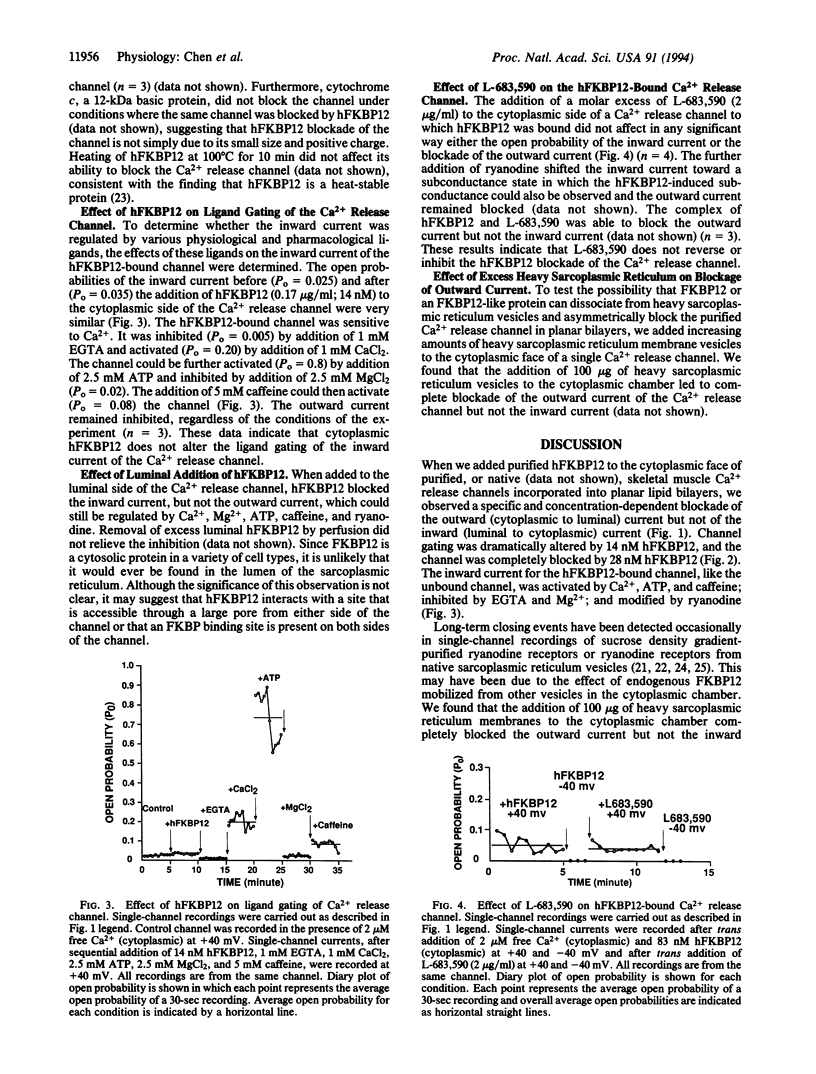
Abstract
A soluble 12-kDa FK506 binding protein (FKBP12), the cellular receptor of the immunosuppressive drug FK506, is tightly associated with the Ca2+ release channel of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum [Jayaraman, T., Brillantes, A. M., Timerman, A. P., Fleischer, S., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Tempst, P. & Marks, A. (1992) J. Biol. Chem. 267, 9474-9477]. We have assessed the role of excess free FKBP12 in the function of single Ca2+ release channels incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. The addition of human recombinant FKBP12 (hFKBP12) to the cytoplasmic face of the Ca2+ release channel blocked the flow of cytoplasmic to luminal current (outward current) in a concentration-dependent manner but had no significant effect on the flow of luminal to cytoplasmic current (inward current). The luminal to cytoplasmic flow of current was modulated by Ca2+, Mg2+, ATP, caffeine, and ryanodine in the presence and absence of FKBP12. An immunosuppressive drug, L-683,590, an analog of FK506, did not block or reverse the asymmetrical hFKBP12 blockade of single Ca2+ release channels in planar lipid bilayers. FKBP12 may play a role in regulation of the flow of ions into the lumen of the sarcoplasmic reticulum through the Ca2+ release channel.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bierer B. E., Mattila P. S., Standaert R. F., Herzenberg L. A., Burakoff S. J., Crabtree G., Schreiber S. L. Two distinct signal transmission pathways in T lymphocytes are inhibited by complexes formed between an immunophilin and either FK506 or rapamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9231–9235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. P., Knudson C. M., Imagawa T., Leung A. T., Sutko J. L., Kahl S. D., Raab C. R., Madson L. Identification and characterization of the high affinity [3H]ryanodine receptor of the junctional sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ release channel. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6460–6463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell K. P., MacLennan D. H. Purification and characterization of the 53,000-dalton glycoprotein from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 10;256(9):4626–4632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. R., Vaughan D. M., Airey J. A., Coronado R., MacLennan D. H. Functional expression of cDNA encoding the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum in COS-1 cells. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 13;32(14):3743–3753. doi: 10.1021/bi00065a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. R., Zhang L., MacLennan D. H. Antibodies as probes for Ca2+ activation sites in the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13414–13421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. R., Zhang L., MacLennan D. H. Characterization of a Ca2+ binding and regulatory site in the Ca2+ release channel (ryanodine receptor) of rabbit skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23318–23326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont F. J., Staruch M. J., Koprak S. L., Siekierka J. J., Lin C. S., Harrison R., Sewell T., Kindt V. M., Beattie T. R., Wyvratt M. The immunosuppressive and toxic effects of FK-506 are mechanistically related: pharmacology of a novel antagonist of FK-506 and rapamycin. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):751–760. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Inui M. Biochemistry and biophysics of excitation-contraction coupling. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1989;18:333–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.18.060189.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inui M., Saito A., Fleischer S. Purification of the ryanodine receptor and identity with feet structures of junctional terminal cisternae of sarcoplasmic reticulum from fast skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1740–1747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman T., Brillantes A. M., Timerman A. P., Fleischer S., Erdjument-Bromage H., Tempst P., Marks A. R. FK506 binding protein associated with the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor). J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9474–9477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai F. A., Erickson H., Block B. A., Meissner G. Evidence for a junctional feet-ryanodine receptor complex from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 13;143(2):704–709. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91411-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Brandl C. J., Korczak B., Green N. M. Amino-acid sequence of a Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):696–700. doi: 10.1038/316696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrleitner M., Timerman A. P., Wiederrecht G., Fleischer S. The calcium release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum is modulated by FK-506 binding protein: effect of FKBP-12 on single channel activity of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor. Cell Calcium. 1994 Feb;15(2):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(94)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mészáros L. G., Bak J., Chu A. Cyclic ADP-ribose as an endogenous regulator of the non-skeletal type ryanodine receptor Ca2+ channel. Nature. 1993 Jul 1;364(6432):76–79. doi: 10.1038/364076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penner R., Neher E., Takeshima H., Nishimura S., Numa S. Functional expression of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):217–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81532-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J. J., Hung S. H., Poe M., Lin C. S., Sigal N. H. A cytosolic binding protein for the immunosuppressant FK506 has peptidyl-prolyl isomerase activity but is distinct from cyclophilin. Nature. 1989 Oct 26;341(6244):755–757. doi: 10.1038/341755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J. J., Wiederrecht G., Greulich H., Boulton D., Hung S. H., Cryan J., Hodges P. J., Sigal N. H. The cytosolic-binding protein for the immunosuppressant FK-506 is both a ubiquitous and highly conserved peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21011–21015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal N. H., Dumont F. J. Cyclosporin A, FK-506, and rapamycin: pharmacologic probes of lymphocyte signal transduction. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:519–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Coronado R., Meissner G. Single channel measurements of the calcium release channel from skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. Activation by Ca2+ and ATP and modulation by Mg2+. J Gen Physiol. 1986 Nov;88(5):573–588. doi: 10.1085/jgp.88.5.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standaert R. F., Galat A., Verdine G. L., Schreiber S. L. Molecular cloning and overexpression of the human FK506-binding protein FKBP. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):671–674. doi: 10.1038/346671a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timerman A. P., Ogunbumni E., Freund E., Wiederrecht G., Marks A. R., Fleischer S. The calcium release channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum is modulated by FK-506-binding protein. Dissociation and reconstitution of FKBP-12 to the calcium release channel of skeletal muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):22992–22999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdivia H. H., Hogan K., Coronado R. Altered binding site for Ca2+ in the ryanodine receptor of human malignant hyperthermia. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 1):C237–C245. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.2.C237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdivia H. H., Valdivia C., Ma J., Coronado R. Direct binding of verapamil to the ryanodine receptor channel of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biophys J. 1990 Aug;58(2):471–481. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82392-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Hung S., Chan H. K., Marcy A., Martin M., Calaycay J., Boulton D., Sigal N., Kincaid R. L., Siekierka J. J. Characterization of high molecular weight FK-506 binding activities reveals a novel FK-506-binding protein as well as a protein complex. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21753–21760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


