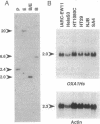
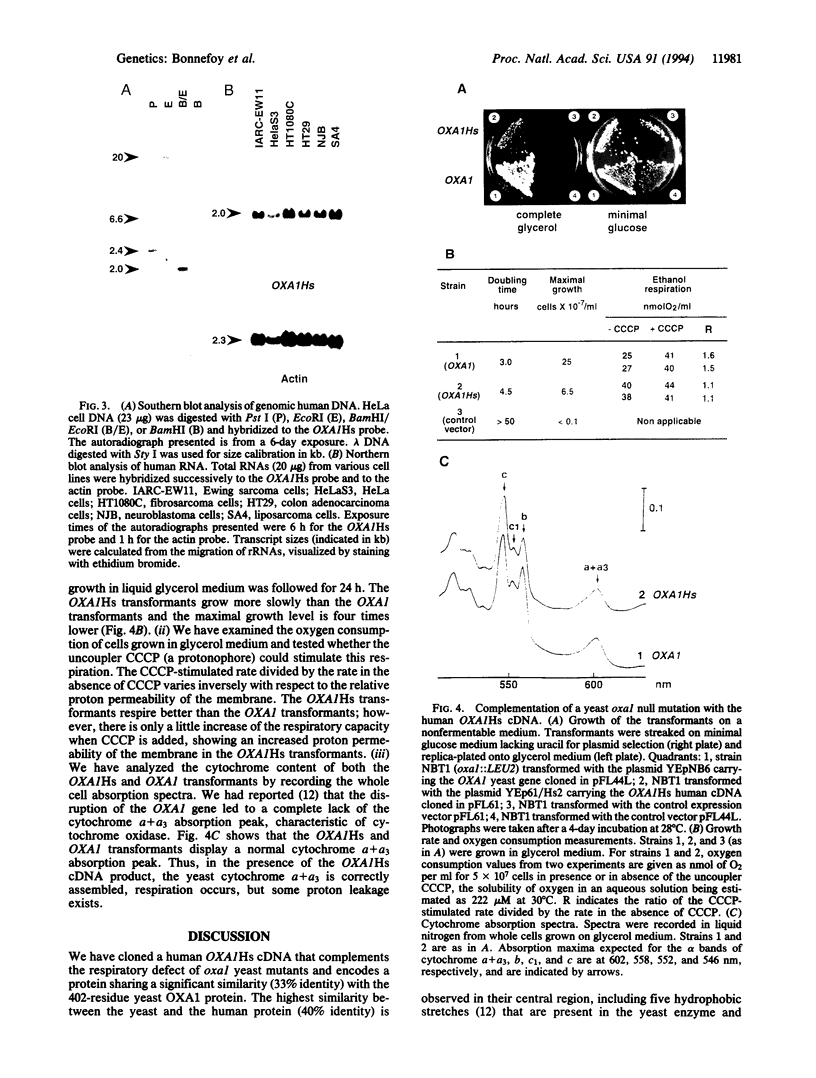
Abstract
The yeast nuclear gene OXA1 is essential for cytochrome oxidase assembly, so that a null mutation in the OXA1 gene leads to complete respiratory deficiency. We have cloned by genetic selection a human OXA1 (OXA1Hs) cDNA that complements the respiratory defect of yeast oxa1 mutants. The deduced sequence of the human protein shares 33% identity with the yeast OXA1 protein. The OXA1Hs cDNA corresponds to a single and relatively highly expressed gene. Oxygen consumption measurements and cytochrome absorption spectra show that replacement of the yeast protein with the human homolog leads to the correct assembly of cytochrome oxidase, suggesting that the proteins play essentially the same role in both organisms.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Attardi G., Schatz G. Biogenesis of mitochondria. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:289–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnefoy N., Chalvet F., Hamel P., Slonimski P. P., Dujardin G. OXA1, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae nuclear gene whose sequence is conserved from prokaryotes to eukaryotes controls cytochrome oxidase biogenesis. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jun 3;239(2):201–212. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet I., Dujardin G., Poyton R. O., Slonimski P. P. Two group I mitochondrial introns in the cob-box and coxI genes require the same MRS1/PET157 nuclear gene product for splicing. Curr Genet. 1990 Aug;18(2):117–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00312599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet I., Dujardin G., Slonimski P. P. ABC1, a novel yeast nuclear gene has a dual function in mitochondria: it suppresses a cytochrome b mRNA translation defect and is essential for the electron transfer in the bc 1 complex. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2023–2031. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07732.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A. Structure and function of cytochrome c oxidase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:569–596. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen D. C., Yang B. C., Kuo T. T. One-step transformation of yeast in stationary phase. Curr Genet. 1992 Jan;21(1):83–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00318659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claisse M. L., Péré-Aubert G. A., Clavilier L. P., Slonimski P. P. Méthode d'estimation de la concentration des cytochromes dans les cellules entières de levure. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Nov;16(3):430–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMauro S., Bonilla E., Lombes A., Shanske S., Minetti C., Moraes C. T. Mitochondrial encephalomyopathies. Neurol Clin. 1990 Aug;8(3):483–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errington J., Appleby L., Daniel R. A., Goodfellow H., Partridge S. R., Yudkin M. D. Structure and function of the spoIIIJ gene of Bacillus subtilis: a vegetatively expressed gene that is essential for sigma G activity at an intermediate stage of sporulation. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Dec;138(12):2609–2618. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-12-2609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudinsky O., Bousquet I., Wallis M. G., Slonimski P. P., Dujardin G. The NAM1/MTF2 nuclear gene product is selectively required for the stability and/or processing of mitochondrial transcripts of the atp6 and of the mosaic, cox1 and cytb genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Sep;240(3):419–427. doi: 10.1007/BF00280396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert C. J., Labouesse M., Dujardin G., Slonimski P. P. The NAM2 proteins from S. cerevisiae and S. douglasii are mitochondrial leucyl-tRNA synthetases, and are involved in mRNA splicing. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):473–483. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02835.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labouesse M., Dujardin G., Slonimski P. P. The yeast nuclear gene NAM2 is essential for mitochondrial DNA integrity and can cure a mitochondrial RNA-maturase deficiency. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck C. 'DNA Strider': a 'C' program for the fast analysis of DNA and protein sequences on the Apple Macintosh family of computers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1829–1836. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen J. E., Ko C., Kloeckner-Gruissem B., Poyton R. O. Nuclear functions required for cytochrome c oxidase biogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Characterization of mutants in 34 complementation groups. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 5;261(25):11872–11879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merle P., Kadenbach B. Kinetic and structural differences between cytochrome c oxidases from beef liver and heart. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jun 15;125(1):239–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minet M., Dufour M. E., Lacroute F. Complementation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae auxotrophic mutants by Arabidopsis thaliana cDNAs. Plant J. 1992 May;2(3):417–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.1992.00417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N., Yoshikawa H. Genes and their organization in the replication origin region of the bacterial chromosome. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(5):629–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Gietz R. D. High efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells using single stranded nucleic acids as a carrier. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00340712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taanman J. W., Capaldi R. A. Purification of yeast cytochrome c oxidase with a subunit composition resembling the mammalian enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22481–22485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. W., Puustinen A., Alben J. O., Gennis R. B., Wikström M. Substitution of asparagine for aspartate-135 in subunit I of the cytochrome bo ubiquinol oxidase of Escherichia coli eliminates proton-pumping activity. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 12;32(40):10923–10928. doi: 10.1021/bi00091a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Dieckmann C. L. PET genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Sep;54(3):211–225. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.3.211-225.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterston R., Martin C., Craxton M., Huynh C., Coulson A., Hillier L., Durbin R., Green P., Shownkeen R., Halloran N. A survey of expressed genes in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat Genet. 1992 May;1(2):114–123. doi: 10.1038/ng0592-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]