Abstract
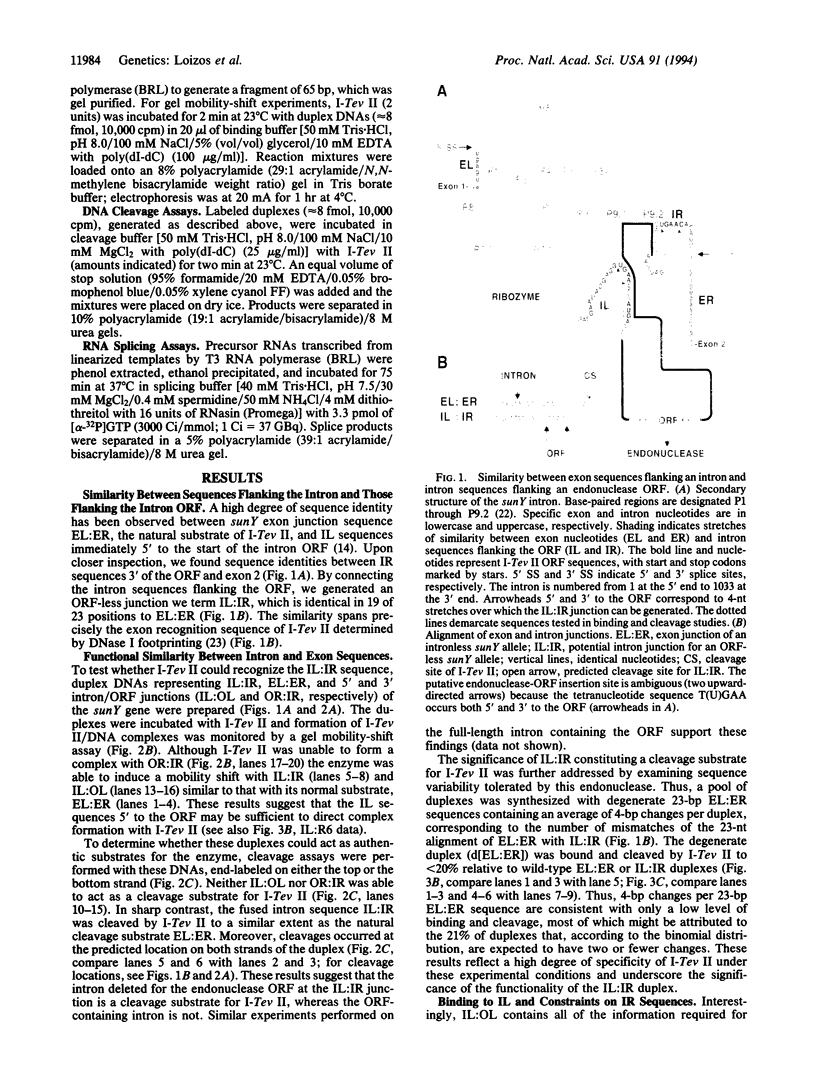
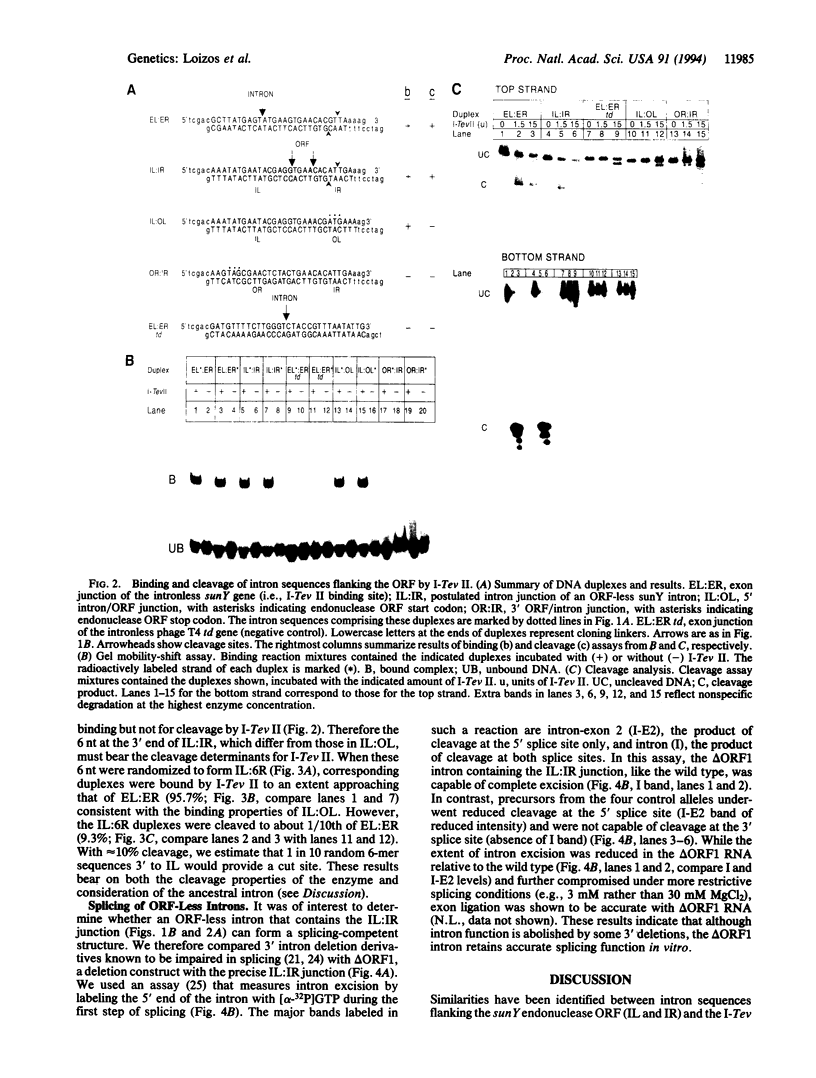
Mobile group I introns are hypothesized to have arisen after invasion by endonuclease-encoding open reading frames (ORFs), which mediate their mobility. Consistent with an endonuclease-ORF invasion event, we report similarity between exon junction sequences (the recognition site for the mobility endonuclease) and intron sequences flanking the endonuclease ORF in the sunY gene of phage T4. Furthermore, we have demonstrated the ability of the intron-encoded endonuclease to recognize and cleave these intron sequences when present in fused form in synthetic constructs. These observations and accompanying splicing data are consistent with models in which the invading endonuclease ORF is provided safe haven within a splicing element. In turn the intron is afforded immunity to the endonuclease product, which imparts mobility to the intron.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belfort M. Phage T4 introns: self-splicing and mobility. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:363–385. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell-Pedersen D., Quirk S., Clyman J., Belfort M. Intron mobility in phage T4 is dependent upon a distinctive class of endonucleases and independent of DNA sequences encoding the intron core: mechanistic and evolutionary implications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3763–3770. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryk M., Belfort M. Spontaneous shuffling of domains between introns of phage T4. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):394–396. doi: 10.1038/346394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. M., Belfort M., Cech T. R., Davies R. W., Schweyen R. J., Shub D. A., Szostak J. W., Tabak H. F. Structural conventions for group I introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7217–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. Conserved sequences and structures of group I introns: building an active site for RNA catalysis--a review. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):259–271. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90492-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colston M. J., Davis E. O. The ins and outs of protein splicing elements. Mol Microbiol. 1994 May;12(3):359–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgaard J. Z., Garrett R. A., Belfort M. A site-specific endonuclease encoded by a typical archaeal intron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5414–5417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Doolittle W. F. Speculations on the early course of evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1271–1275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B. Group I introns as mobile genetic elements: facts and mechanistic speculations--a review. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):91–114. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garriga G., Lambowitz A. M. RNA splicing in neurospora mitochondria: self-splicing of a mitochondrial intron in vitro. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90470-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gott J. M., Zeeh A., Bell-Pedersen D., Ehrenman K., Belfort M., Shub D. A. Genes within genes: independent expression of phage T4 intron open reading frames and the genes in which they reside. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1791–1799. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong H., Kucera R. B., Jack W. E. Characterization of a DNA polymerase from the hyperthermophile archaea Thermococcus litoralis. Vent DNA polymerase, steady state kinetics, thermal stability, processivity, strand displacement, and exonuclease activities. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1965–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambowitz A. M., Belfort M. Introns as mobile genetic elements. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:587–622. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambowitz A. M. Infectious introns. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall P., Davis T. B., Lemieux C. The I-CeuI endonuclease: purification and potential role in the evolution of Chlamydomonas group I introns. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Mar 15;220(3):855–859. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18688.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Jaeger L., Westhof E., Kuras R., Tihy F., Xu M. Q., Shub D. A. Activation of the catalytic core of a group I intron by a remote 3' splice junction. Genes Dev. 1992 Aug;6(8):1373–1385. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.8.1373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Westhof E. Modelling of the three-dimensional architecture of group I catalytic introns based on comparative sequence analysis. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):585–610. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90386-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mota E. M., Collins R. A. Independent evolution of structural and coding regions in a Neurospora mitochondrial intron. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):654–656. doi: 10.1038/332654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman P. S., Butow R. A. Mobile introns and intron-encoded proteins. Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1106–1109. doi: 10.1126/science.2479980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirk S. M., Bell-Pedersen D., Belfort M. Intron mobility in the T-even phages: high frequency inheritance of group I introns promoted by intron open reading frames. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):455–465. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90248-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shub D. A., Goodrich-Blair H. Protein introns: a new home for endonucleases. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90345-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shub D. A., Gott J. M., Xu M. Q., Lang B. F., Michel F., Tomaschewski J., Pedersen-Lane J., Belfort M. Structural conservation among three homologous introns of bacteriophage T4 and the group I introns of eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1151–1155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shub D. A., Xu M. Q., Gott J. M., Zeeh A., Wilson L. D. A family of autocatalytic group I introns in bacteriophage T4. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:193–200. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu M. Q., Shub D. A. The catalytic core of the sunY intron of bacteriophage T4. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):77–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]